|
Archil Of Kakheti
Prince Archil the Martyr ( ka, არჩილი) was an 8th-century Georgian Orthodox Christian royal prince of the eastern Georgian region of Kakheti. Life Archilʼs biography is related in the medieval corpus of Georgian chronicles known as The Life of Kartli. One of its parts, the c. 800 history by Pseudo-Juansher, terminates with a brief account of Archilʼs tenure as prince, while another one – The Martyrdom of Archil, a brief text of uncertain age (between early 9th and late 11th centuries) inserted just after Ps.-Juansherʼs chronicle – narrowly focuses on Archilʼs martyrdom. Archil was a scion of the former royal dynasty of Iberia (Kartli), the Chosroid dynasty and a son of Prince Stephen of Kakheti (r. 685-736). His rule coincided with the Arab conquests in Caucasia. The 735-737 expedition by Marwan ibn Muhammad forced Archil and his brother Mirian to flee to the west through Egrisi into Abasgia where they joined the local dynast Leon I in the defense of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Sabinin
Mikhail Pavlovich Sabinin (russian: Михаил Павлович Сабинин, ka, მიხეილ პავლეს ძე საბინინი, monk Gobron, ka, გობრონ; 1845–1900) was a Russia, Russo-Georgia (country), Georgian monk, historian of the Georgian Orthodox Church and icon painter. He was born to the Russian priest from Tver, Pavel Sabinin, and a Georgian woman. Educated at the Tiflis gymnasium in the 1860s, he then attended St. Petersburg Theologian Academy and attained to a Magister (degree), magister degree for his work ''History of the Georgian Church until the End of the 6th Century'' ("История грузинской церкви до конца VI в." [СПб., 1877]), the first comprehensive treatment of the subject produced in Russian. He travelled in several regions of Georgia, studying monuments of Christian architecture, copying frescos and icons, recording legends and collecting manuscripts. In St. Petersburg, he was tonsur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marwan II
Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam ( ar, مروان بن محمد بن مروان بن الحكم, Marwān ibn Muḥammad ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; – 6 August 750), commonly known as Marwan II, was the fourteenth and last caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 744 until his death. His reign was dominated by a civil war, and he was the last Umayyad ruler to rule the united Caliphate before the Abbasid Revolution toppled the Umayyad dynasty. Birth and background Marwan ibn Muhammad was a member of the ''Marwanid'' household of the Umayyad Caliphate. His grandmother, named Zaynab. Marwan's father, Muhammad ibn Marwan, who was the son of the fourth Umayyad Caliph Marwan I (), and hence half-brother to fifth Umayyad Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ().Zetterstéen (1993), p. 408 His mother was a woman who's mostly unnamed, however sometimes is called Rayya or Tarubah, and is likely of non-Arab origin (a Kurd according to some accounts). Some have referenced that hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was List of Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarchate of Africa, exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular usurper Phocas. Heraclius's reign was marked by several military campaigns. The year Heraclius came to power, the empire was threatened on multiple frontiers. Heraclius immediately took charge of the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. The first battles of the campaign ended in defeat for the Byzantines; the Persian army fought their way to the Bosphorus but Constantinople was protected by impenetrable walls and a strong navy, and Heraclius was able to avoid total defeat. Soon after, he initiated reforms to rebuild and strengthen the military. Heraclius drove the Persians out of Asia Minor and pushed deep into their territory, defeating them decisively in 627 at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (''symbasileis'') who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. It was under Constantine that the major characteristics of what is considered the Byzantine state emerged: a Roman polity centered at Constantinople and culturally dominated by the Greek East, with Christianity as the state religion. The Byzantine Empire was the direct le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī ( ar, أبو محمد موسى بن المهدي الهادي; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab Al-Hādī (الهادي) was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succeeded his father Al-Mahdi and ruled from 169 AH (785 CE) until his death in 170 AH (786 CE). His short reign ended with internal chaos and power struggles with his mother. Biography Al-Hadi was the eldest son of Al-Mahdi and Al-Khayzuran and the older brother of Harun al-Rashid. He was very dear to his father and was appointed as the first crown prince by his father at the age of 16 and was chosen as the leader of the army. Prior to his death, Al-Mahdi supposedly favored his second son, Harun al-Rashid, as his successor, taking him on multiple military expeditions in 779 and 781 to train him to be the next caliph, as his own father prepared him, but died before the formal transfer of the crown prince title could occur. Alternatively, Al-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (ummah). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all hereditary monarchies such as the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo) and Ayyubid Caliphate, have claimed to be caliphates. The first caliphate, the Rashidun Caliphate, was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armīniya
Arminiya, also known as the Ostikanate of Arminiya ( hy, Արմինիա ոստիկանություն, ''Arminia vostikanut'yun'') or the Emirate of Armenia ( ar, إمارة أرمينيا, ''imārat Arminiya''), was a political and geographic designation given by the Muslim Arabs to the lands of Greater Armenia, Caucasian Iberia, and Caucasian Albania, following their conquest of these regions in the 7th century. Though the caliphs initially permitted an Armenian prince to represent the province of ''Arminiya'' in exchange for tribute and the Armenians' loyalty during times of war, Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan introduced direct Arab rule of the region, headed by an ''ostikan'' with his capital in Dvin. According to the historian Stephen H. Rapp in the third edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'': History Early period: the Arab conquest of Armenia The details of the early conquest of Armenia by the Arabs are uncertain, as the various Arabic sources conflict with the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
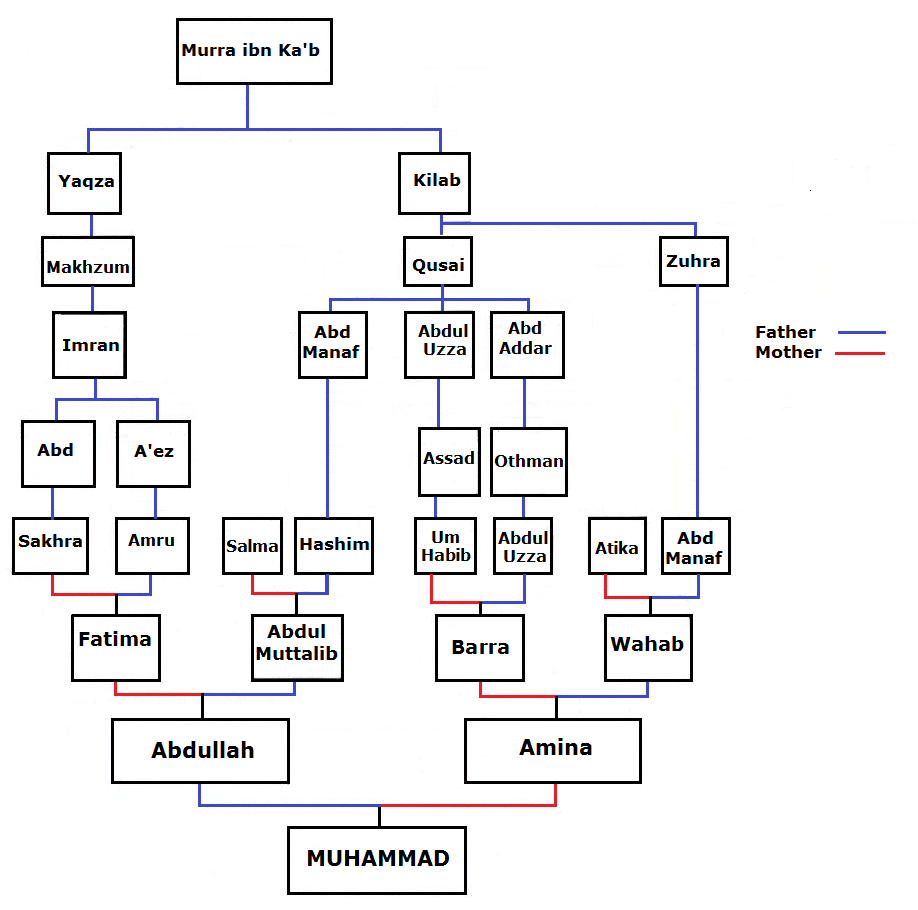
Khuzayma B
This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad known as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Qurayshs tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label ‘arabicised’ is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, continued through the Middle Ages in Europe, and in the twenty-first century has spread around the globe. Historically, there are four stages of Christianization beginning with individual conversion, followed by the translation of Christian texts into local vernacular language, establishing education and building schools, and finally, social reform that sometimes emerged naturally and sometimes included politics, government, coercion and even force through colonialism. The first countries to make Christianity their state religion were Armenia, Georgia, Ethiopia and Eritrea. In the fourth to fifth centuries, multiple tribes of Germanic barbarians converted to either Arian or orthodox Christianity. The Frankish empire begins during this same per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anacopia
New Athos or Akhali Atoni ( ka, ახალი ათონი, ''Akhali Atoni''; ab, Афон Ҿыц, ''Afon Ch'yts''; russian: Новый Афон; ''Novy Afon'', gr, Νέος Άθως, ''Neos Athos'') is a town in the Gudauta ''raion'' of Abkhazia situated some from Sukhumi by the shores of the Black Sea. The town was previously known under the names Nikopol, Acheisos, Anakopia, Nikopia, Nikofia, Nikopsis, Absara, and Psyrtskha. New Athos Cave is one of Abkhazia's tourist attractions. History The excavations at the Anacopia fortress which is located at the edge of the town showed that it functioned in the 5-12 centuries CE, though some archeologists date the construction of the defences to 7th century. Anacopia is associated with the fortress of Tracheia mentioned by Prokopius. Anacopia was the capital of the Abkhazian princedom in the orbit of the Byzantine Empire and then of the Abkhazian Kingdom after the archon Leon II declared himself a king in the late 8th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon I Of Abkhazia
Leon I of Abkhazia, hereditary prince (Eristavi) of Abkhazia, ruling between 720–740 and a vassal to the Byzantine Emperor. The ''Divan of the Abkhazian Kings'' mentions that his reign took place in the 1st half of the 8th century. During his reign Leon actively battled invading Arabs and had close diplomatic contacts with the prince of Iberia and Kakheti, Archil. He also had significant relations to the Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian, to whom he sent a letter asking for help against the forces of the Umayyad Caliphate. In answer, the Emperor confirmed his hereditary rule over the Kingdom of Abkhazia and suggested that he should accept Archil as his overlord and suzerain and by doing so, battle the Muslims with united forces. Leo III also bestowed the title of Archon upon the Abkhazian King. This meant that the Byzantines accepted Leon I's rule over the lands of Egrisi, Jiketi and Sanigia. The ties between Archil and Leon I were also strengthened by Leon's marriage wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)

.jpg)