|
Antiochis
The name Antiochis ( grc, Ἀντιoχίς) is the female name of Antiochus. Women Seleucid Princesses & Hellenistic Queen Consorts *Antiochis, a daughter of Achaeus and granddaughter of Seleucus I Nicator. She married Attalus and became the mother of Attalus I, King of Pergamon *Antiochis, a sister of Antiochus III the Great, being a daughter of Seleucus II Callinicus and Laodice II. She married Xerxes of Armenia, King of Arsamosata, a city between the Euphrates and the Tigris *Antiochis, a daughter of Antiochus III the Great and Laodice III. She married Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia, and had one daughter and two sons by him *Antiochis, concubine of Antiochus IV Epiphanes. The cities of Tarsus and Mallus were given to her as a gift and the citizens of the cities revolted. Antiochus crushed the rebellion *Antiochis of Commagene, a daughter of Antiochus I Theos of Commagene Physician * Antiochis of Tlos in Lycia, a 1st-century physician daughter of Diodotus (perhaps Diodotus the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Athens itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Athens was divided into 139 demes, to which one can be added Berenikidai (established in 224/223 BC), Apollonieis (201/200 BC), and Antinoeis (added in 126/127). The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the ''gene'', or aristocratic family groups, that had dominated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochis Of Tlos
Antiochis of Tlos ( el, Ἀντιοχὶς Τλωὶς) was a Roman physician who lived in the 1st century BC or AD. She was the daughter of Diodotus of Tlos. Through her medical practice, she gained notoriety of citizens and politicians throughout the Lycian region. Work Antiochis of Tlos likely began her education working alongside her father, who is likely the same famous Diodotus referenced in the Materia Medica of Dioscorides. An apprenticeship like this was common for individuals who could not attend one of the acclaimed medical schools of the time. While she may have started practicing medicine under the mentorship of her father, Antiochis branched off to an individual practice where she accumulated more skills and knowledge on her own. Her medical skills were referenced as τὴν ὶατρικὴν τέχνην ὲνπειρία, which is indicative that she practiced in the Hippocratic tradition. Unlike many other female physicians, Antiochis was not a midwife that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
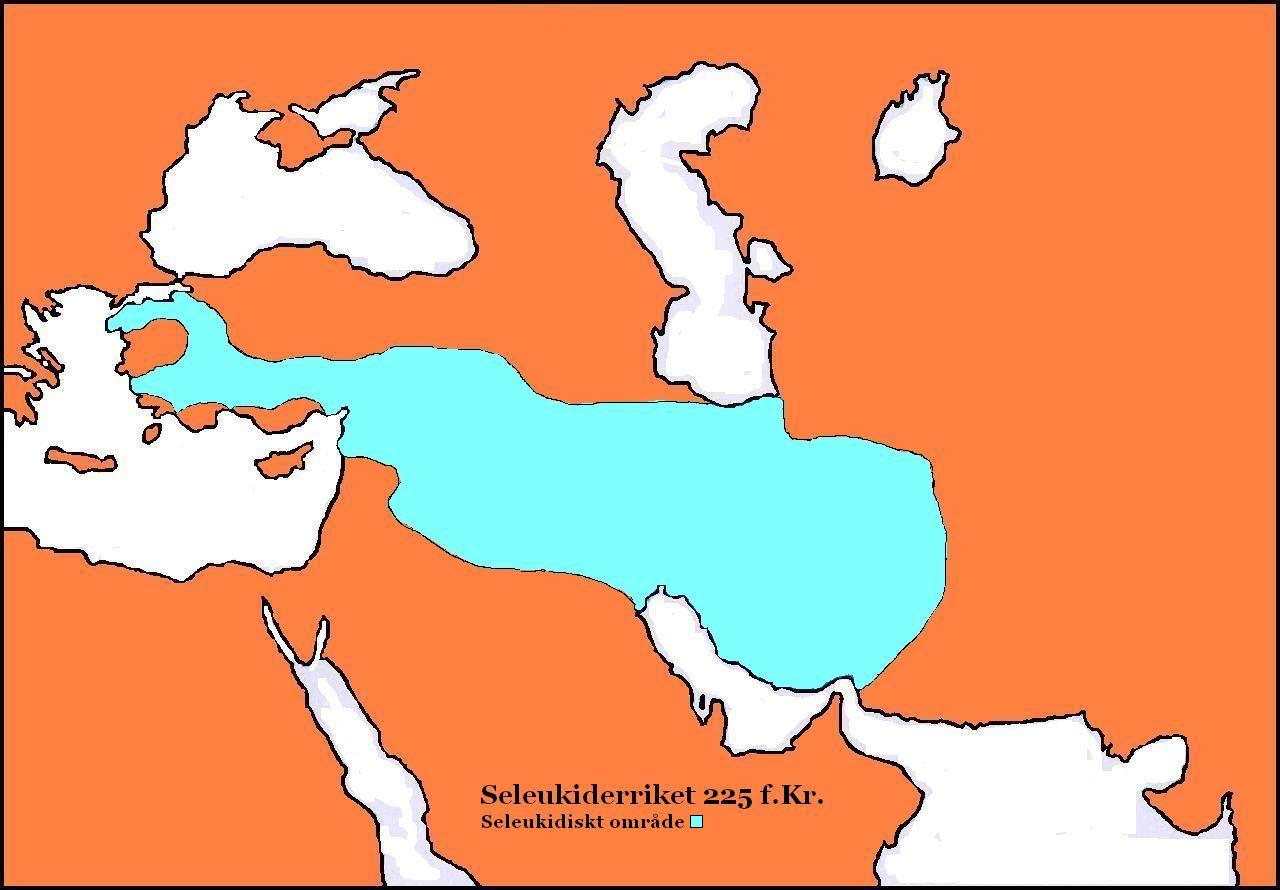
Antiochis (daughter Of Antiochus The Great)
Antiochis ( grc, Aντιoχίς) (d. 163 or 162 BC) was a Hellenistic princess from the dynasty of the Seleucids and in the first half of the second century BC queen of Cappadocia. Antiochis was a daughter of the Seleucid king Antiochus III the Great and his wife Laodice. Some time before the war of her father against the Romans she married king Ariarathes IV of Cappadocia, who therefore supported his father-in-law in the battle of Magnesia (190 BC). However, Antiochus III lost the battle. Antiochis bore her husband a son, who was called ''Mithridates'' before his accession to the throne and succeeded his father as Ariarathes V of Cappadocia, and two daughters, among them Stratonice, who first married king Eumenes II of Pergamon and afterwards his brother and successor Attalus II Philadelphus. According to the questionable report of the ancient Greek-Sicilian historian Diodorus Siculus Antiochis, allegedly an unscrupulous woman, is supposed to have been barren and therefore to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochis Of Commagene
Antiochis of Commagene ( grc, Aντιoχίς) — was a Princess from the Kingdom of Commagene, who lived in the 1st century BC. She was of Greek and Iranian descent. Family Antiochis was the second daughter of King Antiochus I Theos of Commagene and Queen Isias Philostorgos. Unfortunately very little is known on Antiochis. The identity of her husband is unknown and she had a daughter called Aka, also known as Aka I of Commagene. She appeared to have died of unknown causes sometime between the late 30s or early 20s BC. Antiochis was buried along with her mother and her daughter on a burial site known as the ''Karakush'' or ''Karakuş Tumulus The Karakuş Tumulus (also Karakush) is a funerary monument—a hierothesion—for Queen Isias and Princesses Antiochis and Aka I of Commagene, built by Mithridates II of Commagene in 30–20 BCE, near the modern village of Çukurtaş in Kâhta ...''. Ancestry References * https://web.archive.org/web/20160303175103/http://www.guide-mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalus I
Attalus I ( grc, Ἄτταλος Α΄), surnamed ''Soter'' ( el, , "Savior"; 269–197 BC) ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis (what is now Bergama, Turkey), first as dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the first cousin once removed and the adopted son of Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king in 238 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis. Attalus won Battle of the Caecus River, an important victory over the Galatians, newly arrived Celtic tribes from Thrace, who had been, for more than a generation, plundering and exacting tribute throughout most of Asia Minor without any serious check. This victory, celebrated by the triumphal monument at Pergamon (famous for its ''Dying Gaul'') and the liberation from the Gallic "terror" which it represented, earned for Attalus the name of "Soter", and the title of "basileus, king". A courageous and capable general and loyal ally of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laodice III
Laodice III (Greek: Λαοδίκη) also known as Laodika, was a princess of Pontus and a Seleucid queen. She was regent for her first born son, Antiochus, during the Anabase expedition of her husband, Antiochus III the Great, between 212 and 206 BC. Antiochus created a royal cult dedicated to her in 193 BC. In 192 BC she was pushed out of political life due to her husband's remarriage. Her last known activities are documented in 177–176 BC and relate to the court of her son, Seleucus IV. Biography She was a daughter of King Mithridates II of Pontus and his wife Laodice. Her sister was Laodice of Pontus and her brother was Mithridates III of Pontus. Laodice married Antiochus III around 221 BC in a ceremony at Zeugma and named queen at Antioch. Polybius states that she was promised to Antiochus III as “a virgin and aforenamed as wife to the king”. The fact that her parents named her ‘Laodice’ in the Seleucid female tradition suggests that her parents intended this marr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariarathes IV Of Cappadocia
Ariarathes IV, surnamed ''Eusebes'', "the Pious", ( grc, Ἀριαράθης Εὐσεβής, Ariaráthēs Eusebḗs), was the king of Cappadocia in 220–163 BC. Early life Ariarathes IV was the son of the king of Cappadocia Ariarathes III and his Macedonian Greek wife Stratonice. He was a child at his accession, and reigned for about 57 years. He married his cousin Antiochis, the daughter of Antiochus III the Great, king of Syria, and Laodice III, and, in consequence of this alliance, assisted Antiochus in his war against the Romans. After the defeat of Antiochus by the Romans in 190 BC, Ariarathes sued for peace in 188, which he obtained on favourable terms, as his daughter, Stratonice, was about that time betrothed to Eumenes II, king of Pergamum, whom she later married, and became an ally of the Romans. In 183–179 , he assisted Eumenes in his war against Pharnaces, king of Pontus. Polybius mentions that a Roman embassy was sent to Ariarathes after the death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus I Theos Of Commagene
Antiochus I Theos Dikaios Epiphanes Philorhomaios Philhellen ( grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Θεὸς Δίκαιος Ἐπιφανὴς Φιλορωμαῖος Φιλέλλην, meaning "Antiochos, the just, eminent god, friend of Romans and friend of Greeks", c. 86 BC – 31 BC, ruled 70 BC – 31 BC) was king of the Greco-Iranian Kingdom of Commagene and the most famous king of that kingdom. The ruins of the tomb-sanctuary of Antiochus atop Mount Nemrut in Turkey were added to the UNESCO World Heritage list in 1987. Several sandstone bas reliefs discovered at the site contain some of the oldest known images of two figures shaking hands. The reliefs portrayed Greco-Iranian deities, along with the goddess Commagene and also even Antiochus himself represented in a deified status. Antiochus was one of the last rulers of a Persian- Macedonian court before the advent of the Romans. Family, ancestry and early life Antiochus I was the son of king Mithridates I Calli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus II Callinicus
Seleucus II Callinicus Pogon ( el, ; ''Kallinikos'' means "beautifully triumphant"; ''Pogon'' means "the Beard"; July/August 265 BC – December 225 BC),, . was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, who reigned from 246 BC to 225 BC. Faced with multiple enemies on various fronts, and not always successful militarily, his reign was a time of great turmoil and fragmentation for the Seleucid empire, before its eventual restoration under his second son and eventual successor, Antiochus III. Accession and invasion After the death of his father, Antiochus II in July 246 BC, Seleucus was proclaimed king by his mother, Laodice in Ephesos, while his father's second wife, Queen Berenice, declared her son Antiochus king in Antioch. Berenice acted decisively at first, seizing control of most of Syria and Cilicia. However, before her brother Ptolemy III, the king of Egypt, was able to land and support to her son's claims, she was murdered by partisans of Seleucus II and Queen Laodice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristides
Aristides ( ; grc-gre, Ἀριστείδης, Aristeídēs, ; 530–468 BC) was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just" (δίκαιος, ''dikaios''), he flourished in the early quarter of Athens' Classical period and is remembered for his generalship in the Persian War. The ancient historian Herodotus cited him as "the best and most honourable man in Athens", and he received similarly reverent treatment in Plato's Socratic dialogues. Biography Aristides was a member of a family of moderate fortune; his father's name was Lysimachus. Of his early life, it is only told that he became a follower of the statesman Cleisthenes. He first came to notice as ''strategos'' in command of his native tribe Antiochis at the Battle of Marathon, and it was no doubt in consequence of the distinction which he then achieved that he was elected ''archon eponymos'' for the ensuing year (489488). Pursuing a conservative policy to maintain Athens as a land power, he was one of the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes Of Armenia
Xerxes ( grc, Ξέρξης; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠) was king of Sophene and Commagene from 228 BC to 212 BC. He was the son and successor of Arsames I. Name ''Xérxēs'' () is the Greek and Latin (''Xerxes'', ''Xerses'') transliteration of the Old Iranian ''Xšaya-ṛšā'' ("ruling over heroes"), a popular name amongst the rulers of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Reign Xerxes belonged to the Iranian Orontid dynasty.; ; ; His father was Arsames I, who ruled Sophene, Commagene and possibly Armenia. Xerxes succeeded his father as the ruler of Sophene and Commagene in 228 BC, while his brother Orontes IV ruled Armenia. In 223 BC, several Seleucid satraps rebelled against King Antiochus III, including Artabazanes ( Upper Media), Molon ( Lower Media), Alexander (Persis), and Achaeus (Asia Minor). By 220 BC Antiochus had put down most of the rebellions; however, Achaeus was not defeated until 213 BC. These rebellions help explain Antiochus' subsequent aggressive p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |