|
Amr Ibn Sa'id
Abū Umayya ʿAmr ibn Saʿīd ibn al-ʿĀṣ al-Umawī ( ar, عمرو بن سعيد بن العاص بن أمية الأموي; died 689/90), better known as al-Ashdaq (), was a member of Banu Umayya, general and a contender for the caliphal throne. He served as the governor of Medina in 680, during the reign of Caliph Yazid I () and later fought off attempts by the Zubayrids to conquer Syria in 684 and 685 during the reign of Caliph Marwan I. His attempted coup against Caliph Abd al-Malik () in 689 ended with his surrender and ultimately his execution by Abd al-Malik himself. Life Amr was the son of the Umayyad statesman Sa'id ibn al-As and Umm al-Banin bint al-Hakam, the sister of another Umayyad statesman, Marwan ibn al-Hakam. He was nicknamed "al-Ashdaq" (the Widemouthed). When Sa'id died in 679, al-Ashdaq became the leader of this branch of the Umayyad clan. At the end of the reign of Caliph Mu'awiya I (), he was governor of Mecca but was then appointed the governor of Medina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Umayya
Umayyad dynasty ( ar, بَنُو أُمَيَّةَ, Banū Umayya, Sons of Umayya) or Umayyads ( ar, الأمويون, al-Umawiyyūn) were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of Al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In the pre-Islamic period, they were a prominent clan of the Meccan tribe of Quraysh, descended from Umayya ibn Abd Shams. Despite staunch opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the Umayyads embraced Islam before the latter's death in 632. Uthman, an early companion of Muhammad from the Umayyad clan, was the third Rashidun caliph, ruling in 644–656, while other members held various governorships. One of these governors, Mu'awiya I of Syria, opposed Caliph Ali in the First Muslim Civil War (656–661) and afterward founded the Umayyad Caliphate with its capital in Damascus. This marked the beginning of the Umayyad dynasty, the first hereditary dynasty in the history of Islam, and the only one to rule over the entire Islamic world of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marj Rahit (684)
The Battle of Marj Rahit ( ar, يوم مرج راهط, translit=Yawm Marj Rāhiṭ) was one of the early battles of the Second Fitna. It was fought on 18 August 684 between the Kalb-dominated armies of the Yaman tribal confederation, supporting the Umayyads under Caliph Marwan I, and the Qays under al-Dahhak ibn Qays al-Fihri, who supported the Mecca-based Abdallah ibn al-Zubayr; the latter had proclaimed himself Caliph. The Kalbi victory consolidated the position of the Umayyads over Bilad al-Sham (the Islamic Levant), paving the way for their eventual victory in the war against Ibn al-Zubayr. However, it also left a bitter legacy of division and rivalry between the Qays and the Yaman, which would be a constant source of strife and instability for the remainder of the Umayyad Caliphate. Background At the death of Mu'awiya I (), the founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, in 680, the Muslim world was thrown into turmoil. Although Mu'awiya had named his son, Yazid I, as his heir, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazid II
Yazid ibn Abd al-Malik ( ar, يزيد بن عبد الملك, Yazīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik; — 28 January 724), also referred to as Yazid II, was the ninth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 9 February 720 until his death in 724. Early life Yazid was born in Damascus, the center of the Umayyad Caliphate, . He was the son of Caliph Abd al-Malik () and his influential wife Atika, the daughter of Yazid II's namesake, Caliph Yazid I (). Yazid II's pedigree united his father's Marwanid branch of the Umayyad dynasty, in power since 684, and the Sufyanid branch of Yazid I and the latter's father Mu'awiya I (), founder of the Umayyad Caliphate. Yazid did not possess military or administrative experience before his reign. He rarely left Syria except for a number of visits to the Hejaz (western Arabia, home of the Islamic holy cities Mecca and Medina), including once for the annual Hajj pilgrimage sometime between 715 and 717. He was possibly granted control of the region around Amman by Abd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shurta
''Shurṭa'' ( ar, شرطة) is the common Arabic term for police, although its precise meaning is that of a "picked" or elite force. Bodies termed ''shurṭa'' were established in the early days of the Caliphate, perhaps as early as the caliphate of Uthman (644–656). In the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates, the ''shurṭa'' had considerable power, and its head, the ''ṣāḥib al-shurṭa'' ( ar, صاحب الشرطة), was an important official, whether at the provincial level or in the central government. The duties of the ''shurṭa'' varied with time and place: it was primarily a police and internal security force and also had judicial functions, but it could also be entrusted with suppressing brigandage, enforcing the '' ḥisbah'', customs and tax duties, rubbish collection, acting as a bodyguard for governors, etc. In the Abbasid East, the chief of police also supervised the prison system. From the 10th century, the importance of the ''shurṭa'' declined, along with the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalid Al-Qasri
Khālid ibn ʿAbdallāh al-Qasrī (; died 743) was an Arab who served the Umayyad Caliphate as governor of Mecca in the 8th century and of Iraq from 724 until 738. The latter post, entailing as it did control over the entire eastern Caliphate, made him one of the most important officials during the crucial reign of Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik. He is most notable for his support of the Yaman tribes in the conflict with the Qays who dominated the administration of Iraq and the East under his predecessor and successor. Following his dismissal, he was twice imprisoned and in 734 tortured to death by his successor, Yusuf ibn Umar al-Thaqafi. Origin and early life Khalid was born in Damascus. He was a member of the Tihamite Qasr clan, a subtribe of the Bajila, of which his great-grandfather Asad ibn Kurz al-Qasri is said by some traditions to have been the chief in the times of Muhammad, and is accounted as one of the Prophet's Companions. Other traditions, however, hostile to K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kufa
Kufa ( ar, الْكُوفَة ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Currently, Kufa and Najaf are joined into a single urban area that is mostly commonly known to the outside world as 'Najaf'. Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya and Najaf, Kufa is one of five Iraqi cities that are of great importance to Shi'ite Muslims. The city was founded in 638 CE (17 Hijrah) during the reign of the second Rashidun Caliph, Umar ibn Al-Khattab, and it was the final capital of the last Rashidun Caliph, Ali ibn Abi Talib. Kufa was also the founding capital of the Abbasid Caliphate. During the Islamic Golden Age it was home to the grammarians of Kufa. Kufic script is named for the city. History Establishment during Umar's era After the Arab victory against the Byzantine Empire at Battle of Yarmouk in 636, Kufa was founded and given its name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
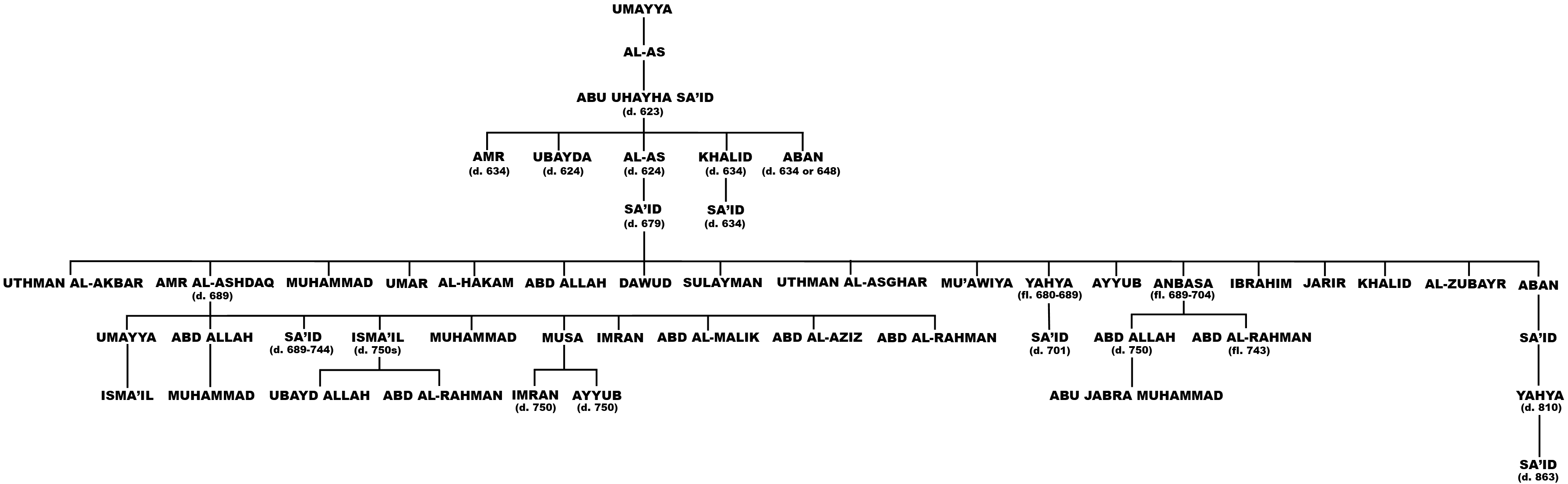
Family Of Al-As Ibn Umayya
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Iraqi Arabs, Kurds, Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Armenians in Iraq, Armenians, Yazidis, Mandaeans, Iranians in Iraq, Persians and Shabaks, Shabakis with similarly diverse Geography of Iraq, geography and Wildlife of Iraq, wildlife. The vast majority of the country's 44 million residents are Muslims – the notable other faiths are Christianity in Iraq, Christianity, Yazidism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Zoroastrianism. The official langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Aziz Ibn Marwan
Abd al-Aziz ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam ( ar, عبد العزيز بن مروان بن الحكم, ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; died 12 May 705) was the Umayyad governor and ''de facto'' viceroy of Egypt between 685 and his death. He was appointed by his father, Caliph Marwan I (r. 684–685). Abd al-Aziz's reign was marked by stability and prosperity, partly due to his close relations and reliance on the Arab military settlers of Fustat. Under his direction and supervision, an army led by Musa ibn Nusayr completed the Muslim conquest of North Africa. He was removed from the line of succession to the caliphal throne and, in any case, died before his brother, Caliph Abd al-Malik. However, one of Abd al-Aziz's sons, Umar II, would become caliph in 717. Early life and career Abd al-Aziz was the son of a senior member of the Umayyad clan, Marwan ibn al-Hakam, and one of the latter's wives, Layla bint Zabban ibn al-Asbagh of the Banu Kalb tribe. He may have visited Egypt w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious". , motto = , image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg , image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg , seal_type = Seal , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Arab world#Asia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Damascus within Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Damascus Governorate, Capital City , government_footnotes = , government_type = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Mohammad Tariq Kreishati , parts_type = Municipalities , parts = 16 , established_title = , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mus'ab Ibn Al-Zubayr
Muṣʿab ibn al-Zubayr ( ar, مصعب بن الزبير; died October 691) was the governor of Basra in 686–691 for his brother, the Mecca-based counter-caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr, during the Second Fitna. Mus'ab was a son of Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, a prominent companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Before becoming governor, he led an unsuccessful campaign against Umayyad-held Palestine. He defeated and killed the pro-Alid revolutionary Mukhtar al-Thaqafi after a series of battles in 687, gaining control over all of Iraq. Complaints from the Iraqis caused his removal from office by his brother, but he was restored shortly after. He was killed by Umayyad forces led by the caliph Abd al-Malik in the Battle of Maskin four years later. Family and early life Mus'ab was the son of Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, a prominent companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Mus'ab's mother was Rabab bint Unayf, a daughter of a chieftain of the Banu Kalb tribe. During the last years of the Uma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine (region)
Palestine ( el, Παλαιστίνη, ; la, Palaestina; ar, فلسطين, , , ; he, פלשתינה, ) is a geographic region in Western Asia. It is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine (i.e. West Bank and Gaza Strip), though some definitions also include part of northwestern Jordan. The first written records to attest the name of the region were those of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, which used the term "Peleset" in reference to the neighboring people or land. In the 8th century, Assyrian inscriptions refer to the region of "Palashtu" or "Pilistu". In the Hellenistic period, these names were carried over into Greek, appearing in the Histories of Herodotus in the more recognizable form of "Palaistine". The Roman Empire initially used other terms for the region, such as Judaea, but renamed the region Syria Palaestina after the Bar Kokhba revolt. During the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |