|
AVX2
Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX, also known as Gesher New Instructions and then Sandy Bridge New Instructions) are SIMD extensions to the x86 instruction set architecture for microprocessors from Intel and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). They were proposed by Intel in March 2008 and first supported by Intel with the Sandy Bridge microarchitecture shipping in Q1 2011 and later by AMD with the Bulldozer microarchitecture shipping in Q4 2011. AVX provides new features, new instructions, and a new coding scheme. AVX2 (also known as Haswell New Instructions) expands most integer commands to 256 bits and introduces new instructions. They were first supported by Intel with the Haswell microarchitecture, which shipped in 2013. AVX-512 expands AVX to 512-bit support using a new EVEX prefix encoding proposed by Intel in July 2013 and first supported by Intel with the Knights Landing co-processor, which shipped in 2016. In conventional processors, AVX-512 was introduced with Skylak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AVX-512
AVX-512 are 512-bit extensions to the 256-bit Advanced Vector Extensions SIMD instructions for x86 instruction set architecture (ISA) proposed by Intel in July 2013, and first implemented in the 2016 Intel Xeon Phi x200 (Knights Landing), and then later in a number of AMD and other Intel CPUs ( see list below). AVX-512 consists of multiple extensions that may be implemented independently. This policy is a departure from the historical requirement of implementing the entire instruction block. Only the core extension AVX-512F (AVX-512 Foundation) is required by all AVX-512 implementations. Besides widening most 256-bit instructions, the extensions introduce various new operations, such as new data conversions, scatter operations, and permutations. The number of AVX registers is increased from 16 to 32, and eight new "mask registers" are added, which allow for variable selection and blending of the results of instructions. In CPUs with the vector length (VL) extension—included in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haswell (microarchitecture)
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick–tock model, tick of the Sandy Bridge, Sandy Bridge microarchitecture). Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. Haswell was the last generation of Intel processor to have socketed processors on mobile. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell began shipping to manufacturers and Original equipment manufacturer, OEMs in mid-2013, with its desktop chips officially launched in September 2013. Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the Intel 8 Series chipsets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylake (microarchitecture)
Skylake is Intel's codename for its sixth generation Core microprocessor family that was launched on August 5, 2015, succeeding the Broadwell microarchitecture. Skylake is a microarchitecture redesign using the same 14 nm manufacturing process technology as its predecessor, serving as a tock in Intel's tick–tock manufacturing and design model. According to Intel, the redesign brings greater CPU and GPU performance and reduced power consumption. Skylake CPUs share their microarchitecture with Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake, Whiskey Lake, and Comet Lake CPUs. Skylake is the last Intel platform on which Windows earlier than Windows 10 are officially supported by Microsoft, although enthusiast-created modifications are available that disabled the Windows Update check and allowed Windows 8.1 and earlier to continue to receive Windows Updates on this and later platforms. Some of the processors based on the Skylake microarchitecture are marketed as sixth-generation Core. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set architecture, instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new four-level paging mechanism. In 64-bit mode, x86-64 supports significantly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory compared to its 32-bit computing, 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to utilize more memory for data storage. The architecture expands the number of general-purpose registers from 8 to 16, all fully general-purpose, and extends their width to 64 bits. Floating-point arithmetic is supported through mandatory SSE2 instructions in 64-bit mode. While the older x87 FPU and MMX registers are still available, they are generally superseded by a set of sixteen 128-bit Processor register, vector registers (XMM registers). Each of these vector registers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Instruction, Multiple Data
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it should not be confused with an ISA. Such machines exploit Data parallelism, data level parallelism, but not Concurrent computing, concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs exactly the same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). A simple example is to add many pairs of numbers together, all of the SIMD units are performing an addition, but each one has different pairs of values to add. SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhaoxin
Zhaoxin (Shanghai Zhaoxin Semiconductor Co., Ltd.; , ) is a fabless semiconductor company, created in 2013 as a joint venture between VIA Technologies and the Shanghai Municipal Government. The company manufactures x86-compatible desktop and laptop CPUs. The term '' Zhào xīn'' means ''million core''.In China 兆 can mean either short-scale million (1e6) or trillion (1e12). However, for IT-related topics 兆 always means mega/million in mainland China. The processors are created mainly for the Chinese market: the venture is an attempt to reduce the Chinese dependence on foreign technology. Background ''Zhaoxin'' is a joint venture between VIA Technologies and the Shanghai Municipal Government. In 2021 it was reported that VIA has a 14.75% shareholding in the company. China has a domestic policy to "replace all foreign hardware and software from its public infrastructure with homegrown solutions" by 2023 (the so-called 3–5–2 policy). VIA holds an x86 license which allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
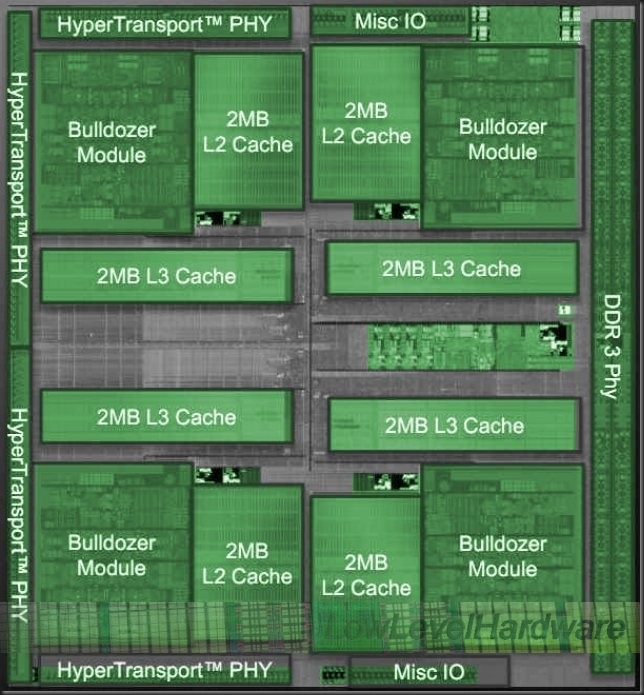
Bulldozer (microarchitecture)
The AMD Bulldozer Family 15h is a microprocessor microarchitecture for the FX and Opteron line of processors, developed by AMD for the desktop and server markets. Bulldozer is the codename for this family of microarchitectures. It was released on October 12, 2011, as the successor to the K10 microarchitecture. Bulldozer is designed from scratch, not a development of earlier processors. The core is specifically aimed at computing products with TDPs of 10 to 125 watts. AMD claims dramatic performance-per-watt efficiency improvements in high-performance computing (HPC) applications with Bulldozer cores. The ''Bulldozer'' cores support most of the instruction sets implemented by Intel processors ( Sandy Bridge) available at its introduction (including SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, CLMUL, and AVX) as well as new instruction sets proposed by AMD; ABM, XOP, FMA4 and F16C. Only Bulldozer GEN4 (Excavator) supports AVX2 instruction sets. Overview According to AMD, Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XOP Instruction Set
The XOP (''eXtended Operations'') instruction set, announced by AMD on May 1, 2009, is an extension to the 128-bit SSE core instructions in the x86 and AMD64 instruction set for the Bulldozer processor core, which was released on October 12, 2011. However AMD removed support for XOP from Zen (microarchitecture) onward. The XOP instruction set contains several different types of vector instructions since it was originally intended as a major upgrade to SSE. Most of the instructions are integer instructions, but it also contains floating point permutation and floating point fraction extraction instructions. See the index for a list of instruction types. History XOP is a revised subset of what was originally intended as SSE5. It was changed to be similar but not overlapping with AVX, parts that overlapped with AVX were removed or moved to separate standards such as FMA4 (floating-point vector multiply–accumulate) and CVT16 ( Half-precision floating-point conversion imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data ( SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in its Pentium III series of central processing units (CPUs) shortly after the appearance of Advanced Micro Devices (AMD's) 3DNow!. SSE contains 70 new instructions (65 unique mnemonics using 70 encodings), most of which work on single precision floating-point data. SIMD instructions can greatly increase performance when exactly the same operations are to be performed on multiple data objects. Typical applications are digital signal processing and graphics processing. Intel's first IA-32 SIMD effort was the MMX instruction set. MMX had two main problems: it re-used existing x87 floating-point registers making the CPUs unable to work on both floating-point and SIMD data at the same time, and it only worked on integers. SSE floating-point instructions operate on a new independent register s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Landing (microarchitecture)
Xeon Phi is a discontinued series of x86 manycore processors designed and made by Intel. It was intended for use in supercomputers, servers, and high-end workstations. Its architecture allowed use of standard programming languages and application programming interfaces (APIs) such as OpenMP. Xeon Phi launched in 2010. Since it was originally based on an earlier GPU design ( codenamed "Larrabee") by Intel that was cancelled in 2009, it shared application areas with GPUs. The main difference between Xeon Phi and a GPGPU like Nvidia Tesla was that Xeon Phi, with an x86-compatible core, could, with less modification, run software that was originally targeted to a standard x86 CPU. Initially in the form of PCI Express-based add-on cards, a second-generation product, codenamed ''Knights Landing'', was announced in June 2013. These second-generation chips could be used as a standalone CPU, rather than just as an add-in card. In June 2013, the Tianhe-2 supercomputer at the National S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies, Inc. () is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory. It was once the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets. As a fabless semiconductor company, VIA conducts research and development of its chipsets in-house, then subcontracts the actual (silicon) manufacturing to third-party merchant foundries such as TSMC. VIA is also the parent company of VIA Labs Inc. (VLI, ). As an independently traded subsidiary, VLI develops and markets USB 3, USB 4, USB Type-C, and USB PD controllers for computer peripherals and mobile devices. History The company was founded in 1987, in Fremont, California, USA by Cher Wang. In 1992, it was decided to move the headquarters to Taipei, Taiwan in order to establish closer partnerships with the substantial and growing IT manufacturing base in Taiwan and neighbouring China. In 1999, VIA acquired most of Cyrix, then a division of National Semiconductor. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |