|
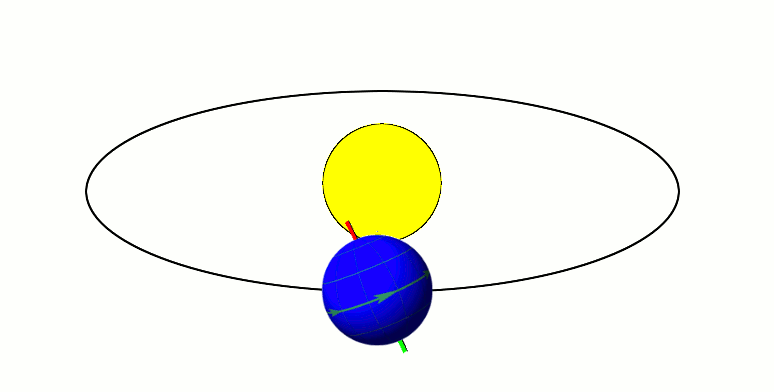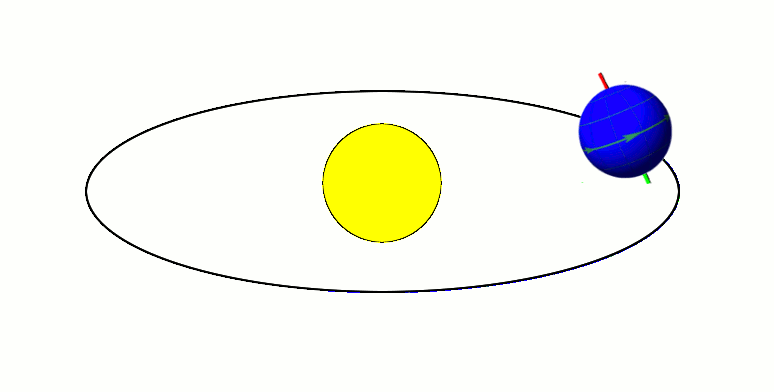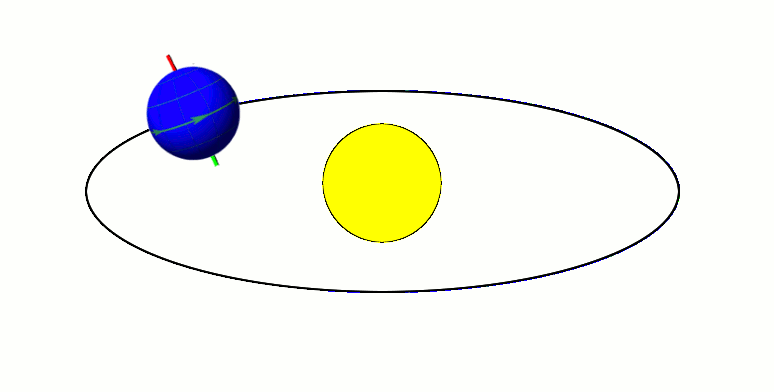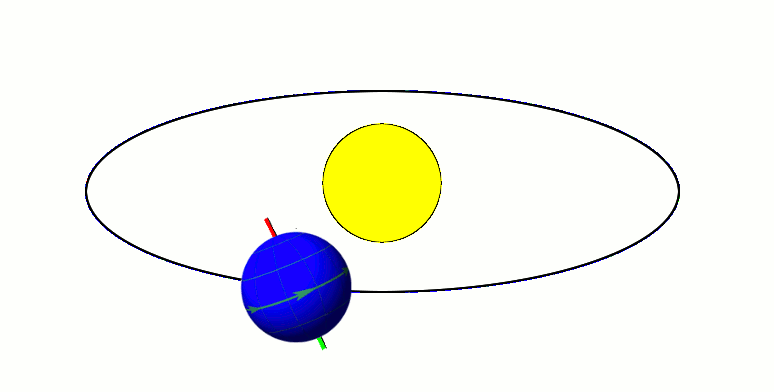
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet Axis Comparison
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The word ''planet'' comes from the Greek () . In antiquity, this word referred to the Sun, Moon, and five points of light visible to the naked eye that moved across the background of the stars—namely, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Planets have historically had religious associations: multiple cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to Migration (ecology), migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical definitions of the seasons. The Northern Hemisphere experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July (thus the traditional celebration of Midsummer in June), as the hemisphere faces the Sun. For the Southern Hemisphere it is instead in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Of Arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation (astronomy)
In astronomy, perturbation is the complex motion of a massive body subjected to forces other than the gravitational attraction of a single other massive body. The other forces can include a third (fourth, fifth, etc.) body, resistance, as from an atmosphere, and the off-center attraction of an oblate or otherwise misshapen body. Introduction The study of perturbations began with the first attempts to predict planetary motions in the sky. In ancient times the causes were unknown. Isaac Newton, at the time he formulated his laws of motion and of gravitation, applied them to the first analysis of perturbations, recognizing the complex difficulties of their calculation. Many of the great mathematicians since then have given attention to the various problems involved; throughout the 18th and 19th centuries there was demand for accurate tables of the position of the Moon and planets for marine navigation. The complex motions of gravitational perturbations can be broken down. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particular, axial precession can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years.Hohenkerk, C.Y., Yallop, B.D., Smith, C.A., & Sinclair, A.T. "Celestial Reference Systems" in Seidelmann, P.K. (ed.) ''Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac''. Sausalito: University Science Books. p. 99. This is similar to the precession of a spinning top, with the axis tracing out a pair of cones joined at their apices. The term "precession" typically refers only to this largest part of the motion; other changes in the alignment of Earth's axis— nutation and polar motion—are much smaller in magnitude. Earth's precession was historically called the precession of the equinoxes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon
Epsilon (, ; uppercase , lowercase or ; ) is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a mid front unrounded vowel or . In the system of Greek numerals it also has the value five. It was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter He (letter), He . Letters that arose from epsilon include the Roman E, Ë and Latin epsilon, Ɛ, and Cyrillic Ye (Cyrillic), Е, Ye with grave, È, Yo (Cyrillic), Ё, Ukrainian Ye, Є and E (Cyrillic), Э. The name of the letter was originally (), but it was later changed to ( 'simple e') in the Middle Ages to distinguish the letter from the digraph (orthography), digraph , a former diphthong that had come to be pronounced the same as epsilon. The uppercase form of epsilon is identical to Latin but has its own code point in Unicode: . The lowercase version has two typographical variants, both inherited from history of the Greek alphabet, medieval Greek handwriting. One, the most common in modern typograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Letter
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionia, Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of several scripts, such as the Latin script, Latin, Gothic alphabet, Gothic, Coptic script, Coptic, and Cyrillic scripts. Throughout antiquity, Greek had only a single uppercas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. By extension, it is also a plane of reference in the equatorial coordinate system. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the celestial equator is currently inclined by about 23.44° with respect to the ecliptic (the plane of Earth's orbit), but has varied from about 22.0° to 24.5° over the past 5 million years due to Milankovitch cycles and perturbation from other planets. An observer standing on Earth's equator visualizes the celestial equator as a semicircle passing through the zenith, the point directly overhead. As the observer moves north (or south), the celestial equator tilts towards the opposite horizon. The celestial equator is defined to be infinitely distant (since it is on the celestial sphere); thus, the ends of the semicircle always intersect the horizon due east and due west, regardless of the observer's position on Earth. At the poles, the celesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde Motion
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and dwarf planets and most small Solar System bodies, except many comets and few distant objects, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |