|
Auspicious Tantra Of All-Reaching Union
The ''Auspicious Tantra of All-Reaching Union'' ( Tangut: ''Gyu̱²-rjur¹ Źji²-njɨ² Ngwu²-phjo̱² Mər²-twẹ²'', translated into Chinese as ''Jíxiáng Biànzhì Kǒuhé Běnxù'' 吉祥遍至口和本續) is the title of a set of nine volumes of Buddhist printed texts written in the Tangut language and script which was discovered in the ruins of the Baisigou Square Pagoda in Helan County, Ningxia, Northwest China in 1991 after it had been illegally blown up. Printed during the Western Xia (1038–1227), ''circa'' 1139–1193, it is thought to be the earliest extant example of a book printed using wooden movable type. The book is currently held at the Ningxia Institute of Archaeology in Yinchuan, and because of its historical significance it has been included in the list of 64 Chinese cultural relics forbidden to be exhibited abroad that was issued by the State Administration of Cultural Heritage in 2002. Discovery The Baisigou Square Pagoda was situated in a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as '' śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or '' pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandita (Buddhism)
Paṇḍita (Sanskrit; Tibetan: ''khepa''; Wyl:'' mkhas pa'') was a title in Indian Buddhism awarded to scholars who have mastered the five sciences (Sanskrit: ''pañcavidyāsthāna''; Tib. ''rigné chenpo nga''; Wyl. ''rig gnas chen po lnga'') in which a learned person was traditionally supposed to be well-versed. The five sciences are: science of language (''śabdavidyā''), science of logic (''hetuvidyā''), science of medicine (''cikitsāvidyā''), science of fine arts and crafts (''śilakarmasthānavidyā''), and science of spirituality (''adhyātmavidyā''). The stipulation can be traced to (but may well predate) the ''Mahāyāna-sūtrālamkāra-kārikā'', which states: "Without becoming a scholar in the five sciences, not even the supreme sage can become omniscient. For the sake of refuting and supporting others, and for the sake of knowing everything himself, he makes an effort in these ive sciences/nowiki>."''The Dharma's Gatekeepers: Sakya Paṇḍita on Buddhist scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 12th century until the modern day, it particularly refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from other languages, especially Sanskrit. The phonology implied by Classical Tibetan orthography is very similar to the phonology of Old Tibetan, but the grammar varies greatly depending on period and geographic origin of the author. Such variation is an under-researched topic. In 816, during the reign of King Sadnalegs, literary Tibetan underwent a thorough reform aimed at standardizing the language and vocabulary of the translations being made from Sanskrit, which was one of the main influences for literary standards in what is now called Classical Tibetan. Nouns Structure of the noun phrase Nominalizing suffixes — ''pa'' or ''ba'' and ''ma'' — are required by the noun or adjective that is to be singled out; * ''po'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominalization, nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring to Buddhist traditions associated with Tantra and "Secret Mantra", which developed in the medieval Indian subcontinent and spread to Tibet, Nepal, other Himalayan states, East Asia, and Mongolia. Vajrayāna practices are connected to specific lineages in Buddhism, through the teachings of lineage holders. Others might generally refer to texts as the Buddhist Tantras. It includes practices that make use of mantras, dharanis, mudras, mandalas and the visualization of deities and Buddhas. Traditional Vajrayāna sources say that the tantras and the lineage of Vajrayāna were taught by Śākyamuni Buddha and other figures such as the bodhisattva Vajrapani and Padmasambhava. Contemporary historians of Buddhist studies meanwhile argue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Renzong Of Western Xia
Emperor Renzong of Western Xia (1124 – 16 October 1193), born Li Renxiao (), was the fifth emperor of the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty of China. His reign from 1139 to 1193 was the longest among all Western Xia emperors. Li Renxiao was the eldest son of the Emperor Chongzong, and succeeded him at the age of sixteen. After ascending into the throne, Renzong made friendly overtures to the Jin dynasty. In domestic politics, Renzong created many schools and used examinations to choose his officials. He respected Confucianism, and built many temples worshipping Confucius. During the era of Tiansheng, Renzong hired a Tibetan lama as a religious advisor and printed many copies of Buddhist teachings. In 1170, Renzong discovered a plot to kill him. He executed the generals who were behind the plot. As a result, Renzong distrusted his army generals and the army began to fall into incompetence. During his later years, Western Xia began to fight wars against various enemies. Renzo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avatamsaka Sutra
The ' ( IAST, sa, 𑀅𑀯𑀢𑀁𑀲𑀓 𑀲𑀽𑀢𑁆𑀭) or ''Buddhāvataṃsaka-nāma-mahāvaipulya-sūtra (The Mahāvaipulya Sūtra named “Buddhāvataṃsaka”)'' is one of the most influential Mahāyāna sutras of East Asian Buddhism. In Classical Sanskrit, ''avataṃsaka'' means garland, wreath, or any circular ornament, such as an earring.'''' Thus, the title may be rendered in English as ''A Garland of Buddhas'', ''Buddha Ornaments'', or ''Buddha’s Garland''. In Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit, the term ''avataṃsaka'' means “a great number,” “a multitude,” or “a collection.” This is matched by the Tibetan title of the sutra, which is ''A Multitude of Buddhas'' (''""''). The ''Buddhāvataṃsaka'' has been described by the translator Thomas Cleary "the most grandiose, the most comprehensive, and the most beautifully arrayed of the Buddhist scriptures." The ' describes a cosmos of infinite realms upon realms, mutually containing one another. This s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detail Of Tangut Text With Inverted Character
Detail(s) or The Detail(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Details'' (film), a 2003 Swedish film * ''The Details'' (film), a 2011 American film * ''The Detail ''The Detail'' is a Canadian television police procedural drama series, developed by Ley Lukins, that premiered on CTV on March 25, 2018. The series, which stars Angela Griffin in the lead role of Detective Stevie Hall, features a trio of female ...'', a Canadian television series * The Detail (The Wire), "The Detail" (''The Wire''), a television episode Music * Details (album), ''Details'' (album), by Frou Frou, 2002 * Detail (record producer), Noel Fisher (born c. 1978), American music producer and performer * The Details, a Canadian rock band Periodicals * DETAIL (professional journal), ''DETAIL'' (professional journal), an architecture and construction journal * Details (magazine), ''Details'' (magazine), an American men's magazine See also * Auto detailing, a car-cleaning process * Level of detail (compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
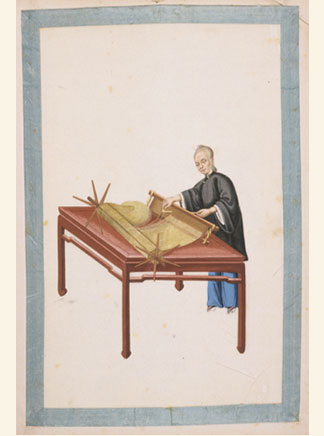
Traditional Chinese Bookbinding
Traditional Chinese bookbinding, also called stitched binding ( Chinese: ''xian zhuang''), is the method of bookbinding that the Chinese, Koreans, Japanese, and Vietnamese used before adopting the modern codex form. History Scroll Up until the 9th century during the mid-Tang dynasty, most Chinese books were bound scrolls made of materials such as bamboo, wood, silk, or paper. Originally bamboo and wooden tablets were tied together with silk and hemp cords to fold onto each other like an accordion. Silk and paper gradually replaced bamboo and wood. Some books were not rolled up but pleated and called ''zhe ben'', although this was still one long piece of material. Butterfly binding During the 9th and 10th centuries, a new book format known as "butterfly binding" appeared. This change is tied to the rise of Buddhism and woodblock printing. When Buddhist sutras were brought to China from India, they were in the form of narrow folded palm-leaf books. The accordion-fold books wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of '' Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants on Earth. It was also one of the first plants to be spun into usable fiber 50,000 years ago. It can be refined into a variety of commercial items, including paper, rope, textiles, clothing, biodegradable plastics, paint, insulation, biofuel, food, and animal feed. Although chemotype I cannabis and hemp (types II, III, IV, V) are both ''Cannabis sativa'' and contain the psychoactive component tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), they represent distinct cultivar groups, typically with unique phytochemical compositions and uses. Hemp typically has lower concentrations of total THC and may have higher concentrations of cannabidiol (CBD), which potentially mitigates the psychoactive effects of THC. The legality of hemp varies widely among c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ) is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is a herbaceous perennial growing to tall;Ramie: Old Fiber - New Image at the (September 17, 2002). |



_(8697431158).jpg)
_-_BL_Or._7377.jpg)