|
Ablaut Classes
In linguistics, the Indo-European ablaut ( , from German ) is a system of apophony (regular vowel variations) in the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). An example of ablaut in English is the strong verb ''sing, sang, sung'' and its related noun ''song'', a paradigm inherited directly from the Proto-Indo-European stage of the language. Traces of ablaut are found in all modern Indo-European languages, though its prevalence varies greatly. History of the concept The phenomenon of Indo-European ablaut was first recorded by Sanskrit grammarians in the later Vedic period (roughly 8th century BCE), and was codified by Pāṇini in his ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' (4th century BCE), where the terms ' and '' '' were used to describe the phenomena now known respectively as the ''full grade'' and ''lengthened grade''.Burrow, §2.1. In the context of European languages, the phenomenon was first described in the early 18th century by the Dutch linguist Lambert ten Kate, in his book ''Gemee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Laut
Laut may refer to: Places * Laut Island, South Kalimantan, Indonesia * Laut Island, Natuna Regency, Riau Islands, Indonesia * Nusa Laut, an island in Maluku, Indonesia People * Agnes Christina Laut (1871–1936), Canadian journalist, novelist, historian, and social worker * Dave Laut (1956–2009), American athlete * Frank Laut (1884–1961), Canadian politician * Gerard Yepes Laut (born 2002), Spanish footballer * Peter Laut, Danish physicist Other uses * Laut.de ''laut.de'' is a German online magazine covering music and entertainment. It was founded in Konstanz in 1996 by Rainer HenzeSerui-Laut language * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grammaticalization
Grammaticalization (also known as grammatization or grammaticization) is a linguistic process in which words change from representing objects or actions to serving grammatical functions. Grammaticalization can involve content words, such as nouns and verbs, developing into new function words that express grammatical relationships among other words in a sentence. This may happen rather than speakers deriving such new function words from (for example) existing bound, inflectional constructions. For example, the Old English verb 'to want', 'to wish' has become the Modern English auxiliary verb ''will'', which expresses intention or simply futurity. Some concepts are often grammaticalized; others, such as evidentiality, less frequently. In explaining this process, linguistics distinguishes between two types of linguistic items: * lexical items or content words, which carry specific lexical meaning * grammatical items or function words, which serve mainly to express grammatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Compensatory Lengthening
Compensatory lengthening in phonology and historical linguistics is the lengthening of a vowel sound that happens upon the loss of a following consonant, usually in the syllable coda, or of a vowel in an adjacent syllable. Lengthening triggered by consonant loss may be considered an extreme form of fusion (Crowley 1997:46). Both types may arise from speakers' attempts to preserve a word's moraic count. Examples English An example from the history of English is the lengthening of vowels that happened when the voiceless velar fricative and its palatal allophone were lost from the language. For example, in the Middle English of Chaucer's time the word ''night'' was phonemically ; later the was lost, but the was lengthened to to compensate, causing the word to be pronounced . (Later the became by the Great Vowel Shift.) Both the Germanic spirant law and the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law show vowel lengthening compensating for the loss of a nasal. Non-rhotic forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stang's Law
Stang's law is a Proto-Indo-European (PIE) phonological rule named after the Norwegian linguist Christian Stang. Overview The law governs the word-final sequences of a vowel, followed by a semivowel ( or ) or a laryngeal ( or ), followed by a nasal. According to the law these sequences are simplified such that laryngeals and semivowels are dropped, with compensatory lengthening of a preceding vowel. This rule is usually cited in more restricted form as: and ( denoting a vowel and a long vowel). Often the rules and also are added: * PIE 'sky' (accusative singular) > > Sanskrit ''dyā́m'', acc. sg. of ''dyaús'', Latin ''diem'' (which served as the basis for Latin ''diēs'' 'day'), Greek Ζῆν (''Zên'') (reformed after Homeric Greek to Ζῆνα ''Zêna'', subsequently Δία ''Día''), acc. of Ζεύς (''Zeús'') * PIE 'cow' (acc. sg.) > > Sanskrit ''gā́m'', acc. sg. of ''gaús'', Greek (Homeric and dialectal) βών (''bṓn''), acc. sg. of βοῦς (''bo� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Szemerényi's Law
Szemerényi's law () is both a sound change and a Synchrony and diachrony, synchronic phonological rule that operated during an early stage of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). Though its effects are evident in many reconstructed as well as attested forms, it did not operate in late PIE, having become morphologized (with exceptions reconstructible via the comparative method). It is named for Hungarian-British linguist Oswald Szemerényi. Overview The rule deleted Syllable#Coda, coda fricatives *s or laryngeal theory, laryngeals *h₁, *h₂ or *h₃ (cover symbol *H), with compensatory lengthening occurring in a word-final position after resonants. In other words: : */-VRs/, */-VRH/ > *-VːR : */-VRH-/ > *-VR- (no examples of ''s''-deletion can be reconstructed for PIE) Morphological effects The law affected the nominative singular forms of the many masculine and feminine nouns whose stem ended in a resonant: * PIE "father" > (Ancient Greek ''wikt:πατήρ#Ancient Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also known as diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of how languages change over time. It seeks to understand the nature and causes of linguistic change and to trace the evolution of languages. Historical linguistics involves several key areas of study, including the reconstruction of ancestral languages, the classification of languages into families, ( comparative linguistics) and the analysis of the cultural and social influences on language development. This field is grounded in the uniformitarian principle, which posits that the processes of language change observed today were also at work in the past, unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Historical linguists aim to describe and explain changes in individual languages, explore the history of speech communities, and study the origins and meanings of words ( etymology). Development Modern historical linguistics dates to the late 18th century, having originally grown o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synchronic
Synchronic may refer to: * ''Synchronic'' (film), a 2019 American science fiction film starring Anthony Mackie and Jamie Dornan *Synchronic analysis, the analysis of a language at a specific point of time *Synchronicity, the experience of two or more events that are apparently causally unrelated or unlikely to occur together by chance, yet are experienced as occurring together in a meaningful manner *Synchronization, the coordination of events to operate a system in unison See also * Synchrony (other) * Synchronicity (other) *Synchronizer (other) Synchronizer may refer to: * Part of a synchromesh manual transmission in an automobile * Synchronization gear, a device that permits a gun to fire between the blades of a revolving airplane propeller * Arbiter (electronics), which orders signals ... * Diachronic (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
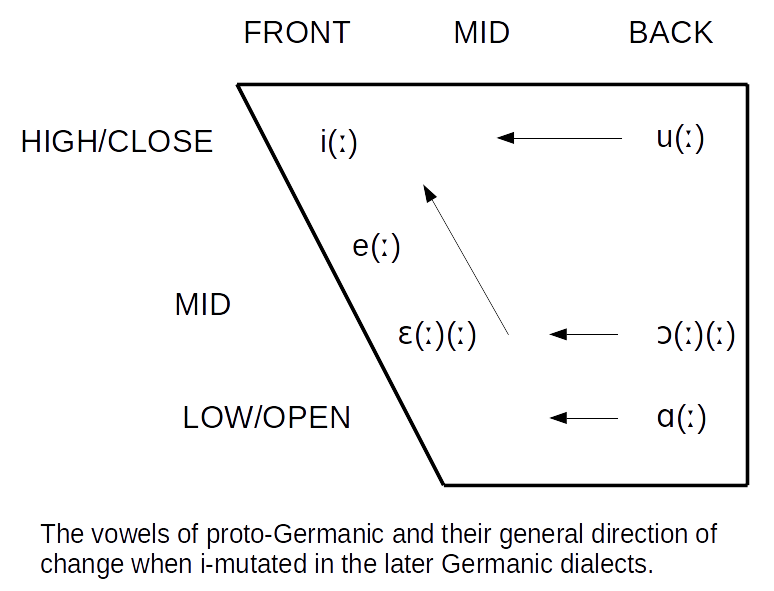
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut (linguistics), umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel (fronting (phonology), fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to (raising (phonetics), raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around 450 or 500 Common Era, CE and affected all of the early languages except Gothic language, Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation (other), u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reconstructed Language
Linguistic reconstruction is the practice of establishing the features of an unattested ancestor language of one or more given languages. There are two kinds of reconstruction: * Internal reconstruction uses irregularities in a single language to make inferences about an earlier stage of that language – that is, it is based on evidence from that language alone. * Comparative reconstruction, usually referred to just as reconstruction, establishes features of the ancestor of two or more related languages, belonging to the same language family, by means of the comparative method. A language reconstructed in this way is often referred to as a proto-language (the common ancestor of all the languages in a given family). Texts discussing linguistic reconstruction commonly preface reconstructed forms with an asterisk (*) to distinguish them from attested forms. An attested word from which a root in the proto-language is reconstructed is a . More generally, a reflex is the known deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Irregular Verb
A regular verb is any verb whose conjugation follows the typical pattern, or one of the typical patterns, of the language to which it belongs. A verb whose conjugation follows a different pattern is called an irregular verb. This is one instance of the distinction between regular and irregular inflection, which can also apply to other word classes, such as nouns and adjectives. In English, for example, verbs such as ''play'', ''enter'', and ''like'' are regular since they form their inflected parts by adding the typical endings ''-s'', ''-ing'' and ''-ed'' to give forms such as ''plays'', ''entering'', and ''liked''. On the other hand, verbs such as ''drink'', ''hit'' and ''have'' are irregular since some of their parts are not made according to the typical pattern: ''drank'' and ''drunk'' (not "drinked"); ''hit'' (as past tense and past participle, not "hitted") and ''has'' and ''had'' (not "haves" and "haved"). The classification of verbs as regular or irregular is to some e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |