|
Arthrobacter Mobilis
''Arthrobacter'' (from the Greek, "jointed small stick”) is a genus of bacterium, bacteria that is commonly found in soil. All species in this genus are Gram-positive obligate aerobes that are bacterial shape, rods during exponential growth and bacterial shape, cocci in their Stationary phase (biology), stationary phase. ''Arthrobacter'' have a distinctive method of cell division called "snapping division" or reversion (microbiology), reversion in which the outer bacterial cell wall ruptures at a joint. Description ''Arthrobacter'' can be grown on mineral salts pyridone broth, where colonies have a greenish metallic center on incubated at . Under the microscope, ''Arthrobacter'' appear as rods when rapidly dividing, and cocci when in stationary phase. Dividing cells may also appear as chevrons ("V" shapes). Other notable characteristics are that it can use pyridone as its sole carbon source, and that its cocci are resistant to desiccation and starvation. Use in industry ''Arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrobacter Globiformis
''Arthrobacter globiformis'' is a gram-positive bacterium species from the genus of ''Arthrobacter''. Description and Significance ''Arthrobacter globiformis'' was first discovered by H. J. Conn in 1928. This bacteria was initially found in large quantities in various types of soil. They start as Gram-negative rods before becoming Gram-positive cocci over time. They may also become large, oval-shaped cells called cystite by growing them in very high carbon to nitrogen ratio environments. These bacteria have cell walls that contain polysaccharides (with monomers glucose, galactose, and rhamnose), peptidoglycan, and phosphorus. They may also have flagella as well. Notably, ''A. globiformis'' and its antigens and proteins are commercially available for use in research, food production, biodegradation, and water/wastewater treatment. Metabolism ''A. globiformis'' can break down substances in the soil such as agricultural chemicals, chromium, etc. They are primarily aerobic, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-shaped"). They are widely distributed in nature in the microbiota of animals (including the human microbiota) and are mostly innocuous, most commonly existing in commensal relationships with their hosts. Some, such as '' C. glutamicum'', are commercially and industrially useful. Others can cause human disease, including, most notably, diphtheria, which is caused by '' C. diphtheriae''. Like various species of microbiota (including their relatives in the genera '' Arcanobacterium'' and '' Trueperella''), they are usually not pathogenic, but can occasionally capitalize opportunistically on atypical access to tissues (via wounds) or weakened host defenses. Taxonomy The genus ''Corynebacterium'' was created by Lehmann and Neumann in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alu Element
An Alu element is a short stretch of DNA originally characterized by the action of the ''Arthrobacter luteus (Alu)'' restriction endonuclease. ''Alu'' elements are the most abundant transposable elements in the human genome, present in excess of one million copies. Most ''Alu'' elements are thought to be selfish or parasitic DNA. However, it has been suggested that at least some are likely to play a role in evolution and have been used as genetic markers. They are derived from the small cytoplasmic 7SL RNA, a component of the signal recognition particle. ''Alu'' elements are not highly conserved within primate genomes, as only a minority have retained activity, and originated in the genome of an ancestor of Supraprimates. ''Alu'' insertions have been implicated in several inherited human diseases and in various forms of cancer. The study of Alu elements has also been important in elucidating human population genetics and the evolution of primates, including the evolution of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrobacter Luteus
''Arthrobacter luteus'' (ALU) is a species of gram-positive bacteria in the genus ''Arthrobacter''. ''A. luteus'' is facultatively anaerobic, Pleomorphism (microbiology), pleomorphic, branching, Motility, non-motile, Spore, non-sporulating, non-acid-fast, catalase-positive, and Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped (0.6–1.0 μm × 0.8–10.0 μm). A Restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease enzyme is extracted from the bacterium and acts at the centre of a Palindromic sequence, palindromic tetranucleotide sequence to give even-ended Duplex sequencing, duplex DNA fragmentation, DNA fragments phosphorylated at the 5'-end. The restriction site ''Alu-I'' itself is a 4-base cutter: AG/CT. The Alu element, Alu retrotransposon is named after the bacterium's abbreviation. The bacterium is also used to produce zymolyase, which can degrade yeast cell wall. Background ''Arthrobacter luteus'' was isolated from brewery sewage in research done in Takasaki, Japan in 1969. The team studied the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inulin
Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, industrially most often extracted from chicory. The inulins belong to a class of dietary fibers known as fructans. Inulin is used by some plants as a means of storing energy and is typically found in roots or rhizomes. Most plants that synthesize and store inulin do not store other forms of carbohydrate such as starch. In 2018, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved inulin as a dietary fiber ingredient used to improve the nutritional value of manufactured food products. Using inulin to measure kidney function is the "gold standard" for comparison with other means of estimating glomerular filtration rate. Origin and history Inulin is a natural storage carbohydrate present in more than 36,000 species of plants, including agave, wheat, onion, bananas, garlic, asparagus, Jerusalem artichoke, and chicory. For these plants, inulin is used as an energy reserve a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inulase II
Inulinase ( and , inulase, endoinulinase, endo-inulinase, exoinulinase, 2,1-β-D-fructan fructanohydrolase) is an enzyme with List of enzymes, systematic name 1-β-D-fructan fructanohydrolase. It catalysis, catalyses the reaction: : Endohydrolysis of (2→1)-β-D-fructosidic linkages in inulin Inulinase has 2 EC numbers of 3.2.1.7, and 3.2.1.8, for endo- and -exo inulinases, respectively. This classifies it as a hydrolase, specifically a glycosylase of glycosidic nature capable of hydrolyzing O- and S- glycosyl. Due to its chemical reactions, the food industry uses this enzyme to create high fructose syrup. It can be extracted from many tuber vegetables, such as Jerusalem artichoke, dahlia, and chicory. Reaction mechanism The enzymatic reaction occurs between the inulinase and the inulin, with the assistance of water via hydrolysis. It's typically done within one step. The reaction centers around the breakage of a bond. The products result in fructose syrup and fructo-oligo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrobacter Crystallopoietes Labeled
''Arthrobacter'' (from the Greek, "jointed small stick”) is a genus of bacteria that is commonly found in soil. All species in this genus are Gram-positive obligate aerobes that are rods during exponential growth and cocci in their stationary phase. ''Arthrobacter'' have a distinctive method of cell division called "snapping division" or reversion in which the outer bacterial cell wall ruptures at a joint. Description ''Arthrobacter'' can be grown on mineral salts pyridone broth, where colonies have a greenish metallic center on incubated at . Under the microscope, ''Arthrobacter'' appear as rods when rapidly dividing, and cocci when in stationary phase. Dividing cells may also appear as chevrons ("V" shapes). Other notable characteristics are that it can use pyridone as its sole carbon source, and that its cocci are resistant to desiccation and starvation. Use in industry ''Arthrobacter'', like other bacterial genera including '' Brevibacterium'', ''Microbacterium'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picoline
Picoline refers to any of three isomerism, isomers of methylpyridine (CH3C5H4N). They are all colorless liquids with a characteristic smell similar to that of pyridine. They are miscible with water and most organic solvents. Isomers The CAS registry number, CAS number of an unspecified picoline isomer is [1333-41-1]. The methyl group in 2- and 4- picolines is reactive; e.g., 2-picolines condenses with acetaldehyde in the presence of warm aqueous sodium hydroxide to form 2-propenylpyridine. History Picoline was obtained, in impure form, in 1826 by the German chemist Otto Unverdorben (1806 – 1873), who obtained it by the pyrolysis (roasting) of bones. He called it ''Odorin'' due to its unpleasant smell. In 1849, the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson (chemist), Thomas Anderson (1819 – 1874) prepared picoline in pure form, from coal tar and via the pyrolysis of bones. Anderson also named picoline by combining the Latin words ''pix'' (tar) and ''oleum'' (oil) because coal tar o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated Polymer, polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties Pyridine is diamagnetism, diamagnetic. Its critical point (thermodynamics), critical parameters are: pressure 5.63 MPa, temperature 619 K and volume 248 cm3/mol. In the temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
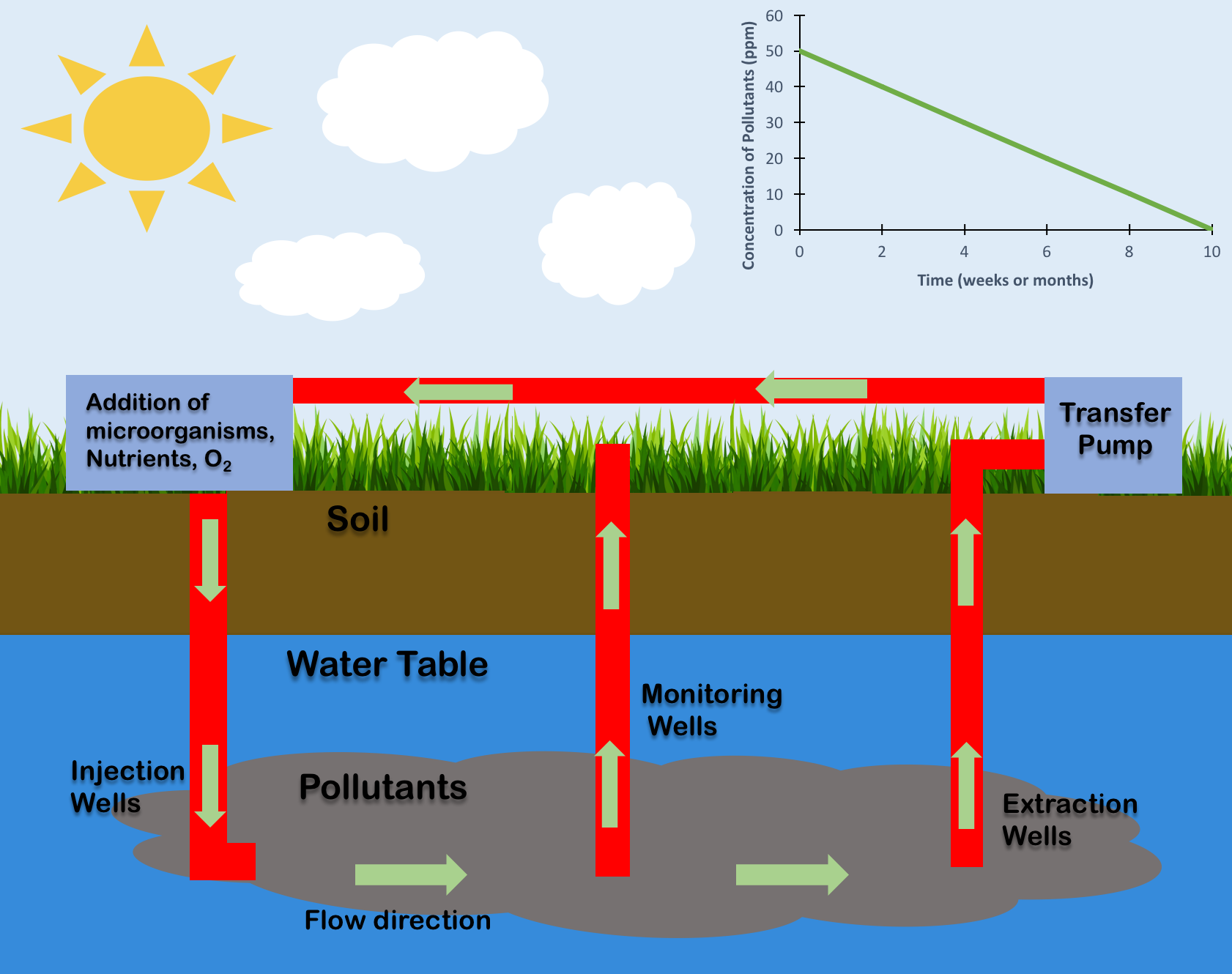
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Chlorophenol
4-Chlorophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4ClOH. It is one of three monochlorophenol isomers. It is a colorless or white solid that melts easily and exhibits significant solubility in water. Its pKa is 9.41. Preparation and reaction It is prepared by chlorination of phenol, preferably in polar solvents, which tends to yield the 4-chloro derivative. Direct chlorination of molten phenol favors the formation of 2-chlorophenol. It once was produced on a large scale as a precursor to hydroquinone. It is a classic precursor, upon reaction with phthalic anhydride, to quinizarin. The commercial dye quinizarin is produced by the reaction of phthalic anhydride Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commer ... and 4-chlorophenol followed by hydrolysis of the chloride. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |