|
Aristotelian Physics
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural philosophy described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrialincluding all motion (change with respect to place), quantitative change (change with respect to size or number), qualitative change, and substantial change (" coming to be" existence.html" ;"title="oming into existence">oming into existence, 'generation'or "passing away" [no longer existing, 'corruption']). To Aristotle, 'physics' was a broad field including subjects which would now be called the philosophy of mind, sensory experience, memory, anatomy and biology. It constitutes the foundation of the thought underlying many of his works. Key concepts of Aristotelian physics include the structuring of the cosmos into concentric spheres, with the Earth at the centre and celestial spher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe, while ignoring any supernatural influence. It was dominant before the development of modern science. From the ancient world (at least since Aristotle) until the 19th century, ''natural philosophy'' was the common term for the study of physics (nature), a broad term that included botany, zoology, anthropology, and chemistry as well as what is now called physics. It was in the 19th century that the concept of science received its modern shape, with different subjects within science emerging, such as astronomy, biology, and physics. Institutions and communities devoted to science were founded. Isaac Newton's book '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (1687) (English: ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'') reflects the use of the term ''natural philosophy'' in the 17th century. Even in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aether (classical Element)
According to ancient and History of science in the Middle Ages, medieval science, aether (, alternative spellings include ''æther'', ''aither'', and ''ether''), also known as the fifth element or quintessence, is the material that fills the region of the universe beyond the Sublunary sphere, terrestrial sphere. The concept of aether was used in several theories to explain several natural phenomena, such as the propagation of light and gravity. In the late 19th century, physicists postulated that aether permeated space, providing a medium through which light could travel in a vacuum, but evidence for the presence of such a medium was not found in the Michelson–Morley experiment, and this result has been interpreted to mean that no luminiferous aether exists. Mythological origins The word (''aithḗr'') in Homeric Greek means "pure, fresh air" or "clear sky". In Greek mythology, it was thought to be the pure essence that the gods breathed, filling the space where they lived, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
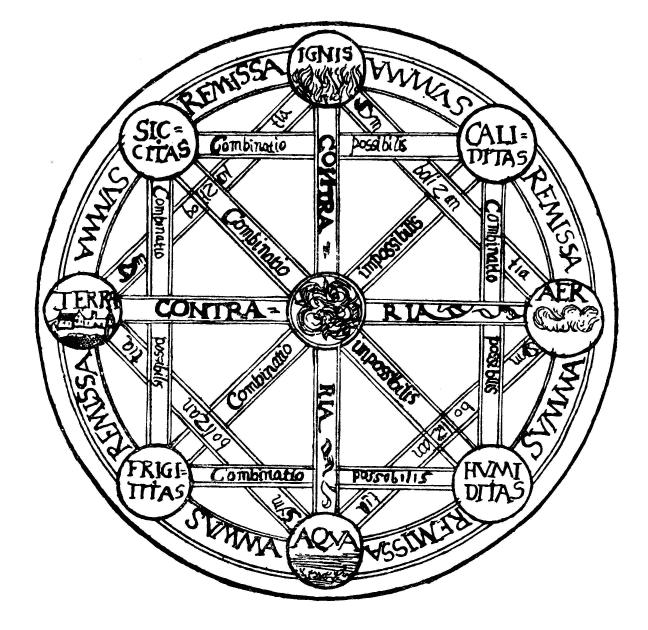
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Pump
A vacuum pump is a type of pump device that draws gas particles from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to antiquity. History Early pumps The predecessor to the vacuum pump was the suction pump. Dual-action suction pumps were found in the city of Pompeii. Arabic engineer Al-Jazari later described dual-action suction pumps as part of water-raising machines in the 13th century. He also said that a suction pump was used in siphons to discharge Greek fire. The suction pump later appeared in medieval Europe from the 15th century. Donald Routledge Hill (1996), ''A History of Engineering in Classical and Medieval Times'', Routledge, pp. 143 & 150-2 Donald Routledge Hill, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", ''Scientific American'', May 1991, pp. 64-69 (cf. Donald Routledge HillMechanical Engineering By the 17th century, water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
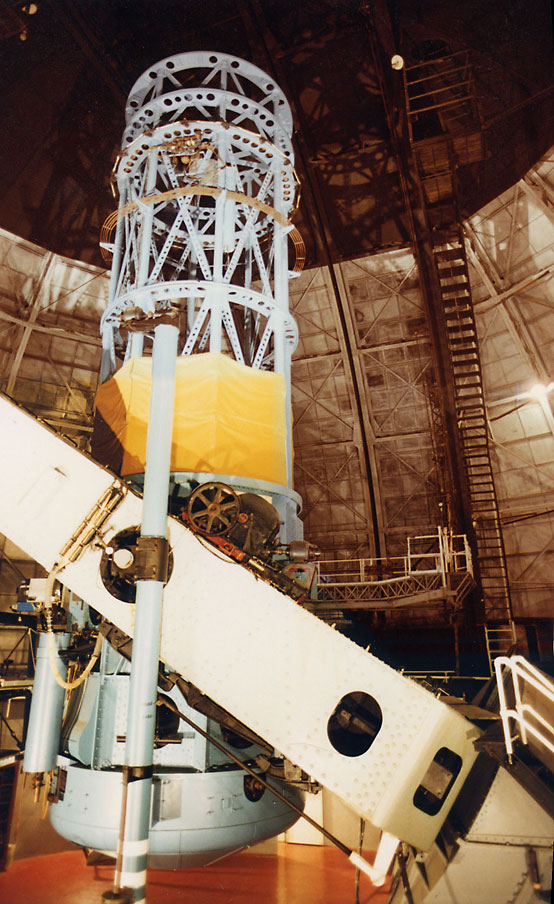
Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and medieval world. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous skepticism, because Philosophy of science#Observation inseparable from theory, cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the Perception#Process and terminology, observation. Scientific inquiry includes creating a testable hypothesis through inductive reasoning, testing it through experiments and statistical analysis, and adjusting or discarding the hypothesis based on the results. Although procedures vary across Branches of science, fields, the underlying #Process, process is often similar. In more detail: the scientific method involves making conjectures (hypothetical explanations), predicting the logical consequences of hypothesis, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism (also known as the heliocentric model) is a superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets orbit around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center. The notion that the Earth revolves around the Sun had been proposed as early as the 3rd century BC by Aristarchus of Samos, who had been influenced by a concept presented by Philolaus of Croton (c. 470 – 385 BC). In the 5th century BC the Greek philosophers Philolaus and Hicetas had the thought on different occasions that the Earth was spherical and revolving around a "mystical" central fire, and that this fire regulated the universe. In medieval Europe, however, Aristarchus' heliocentrism attracted little attention—possibly because of the loss of scientific works of the Hellenistic period. It was not until the 16th century that a mathematical model of a heliocentric system was presented by the Renaissanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle Physica Page 1
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
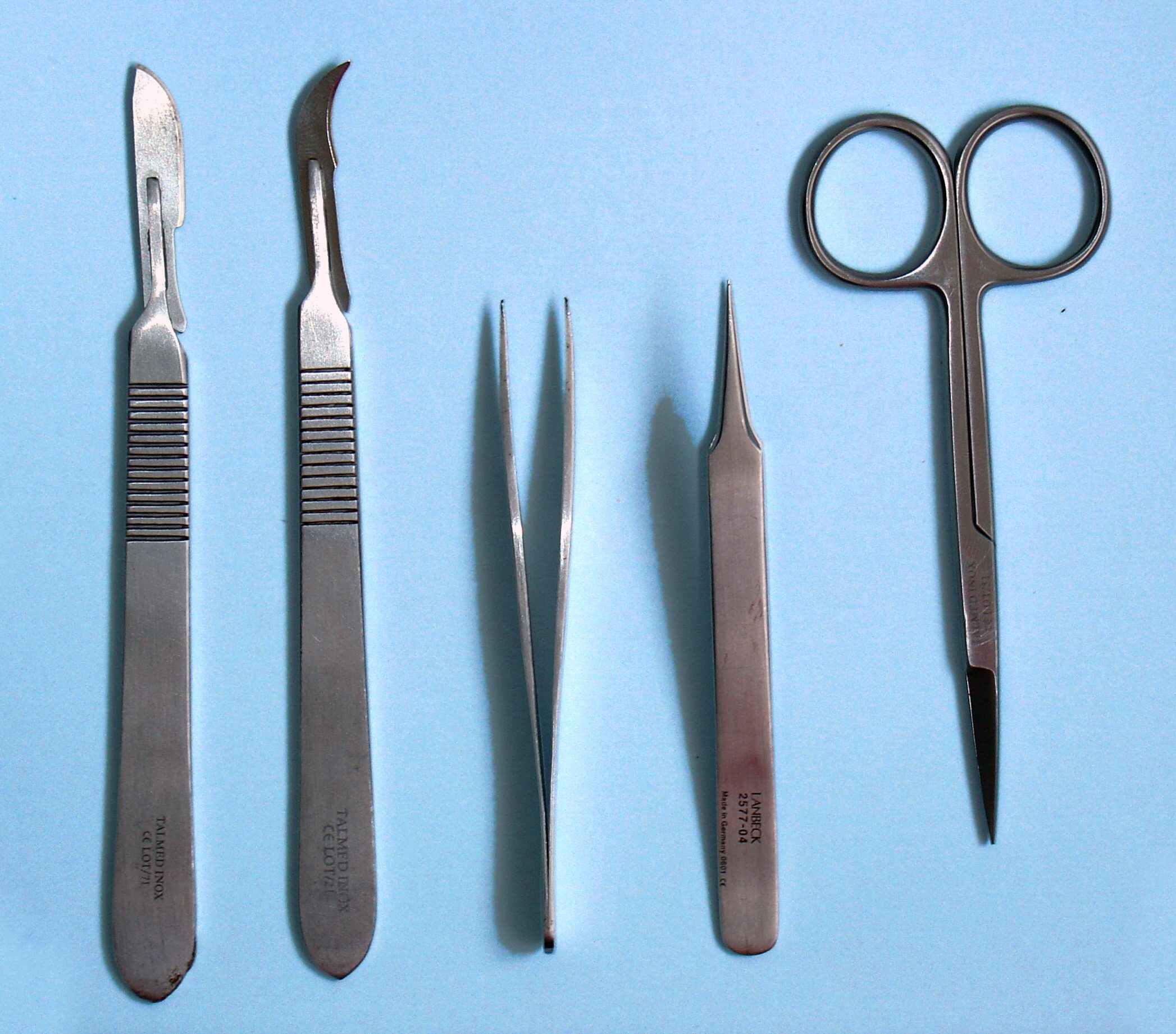
Dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computational anatomy, computer models. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |