|
Arena (web Browser)
The Arena browser (also known as the Arena WWW Browser) was one of the first web browsers for Unix. Originally begun by Dave Raggett in 1993, development continued at CERN and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and subsequently by Yggdrasil Computing. Arena was used in testing the implementations for HTML version 3.0, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), Portable Network Graphics (PNG), and libwww. Arena was widely used and popular at the beginning of the World Wide Web. Arena, which predated Netscape Navigator and Microsoft's Internet Explorer, featured a number of innovations used later in commercial products. It was the first browser to support background images, tables, text flow around images, and inline mathematical expressions. The Arena browser served as the W3C's testbed browser from 1994 to 1996 when it was succeeded by the Amaya project. History In 1993, Dave Raggett, then at Hewlett-Packard (HP) in Bristol, England devoted his spare time to developing Arena on which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dave Raggett
Dave Raggett is an English computer specialist who has played a major role in implementing the World Wide Web since 1992. He has been a W3C Fellow at the World Wide Web Consortium since 1995 and worked on many of the key web protocols, including HTTP, HTML, XHTML, MathML, XForms, and VoiceXML. Raggett also wrote HTML Tidy and is currently pioneering W3C's work on the Web of Things. He lives in the west of England. Career From 1981 to 1984, Dave Raggett worked at Research Machines, designing and developing software for local networking of Z80 machines for use in schools. The following year, as a software developer in Hewlett-Packard's Office Productivity Division, he worked on remote printing solutions. From 1985 to 2000, Raggett worked as a researcher at Hewlett-Packard Labs in Bristol, England, where he pursued a variety of projects, including expert systems, hypertext, networking, Web browsers, and servers, embedded systems, interactive voice response systems. After he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML Editor
An HTML editor is a program used for editing HTML, the markup of a web page. Although the HTML markup in a web page can be controlled with any text editor, specialized HTML editors can offer convenience, added functionality, and organisation. For example, many HTML editors handle not only HTML, but also related technologies such as CSS, XML and JavaScript , or ECMAScript. In some cases, they also manage communication with remote web servers via FTP and WebDAV, and version control systems such as Subversion or Git. Many word processing, graphic design, and page layout programs that are not dedicated to web design, such as Microsoft Word or Quark XPress, also have the ability to function as HTML editors. Text editors Text editors intended for use with HTML usually provide at least syntax highlighting. Some editors additionally feature templates, toolbars , and keyboard shortcuts to quickly insert common HTML elements and structures. Wizards, tooltip prompts, and autocompl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
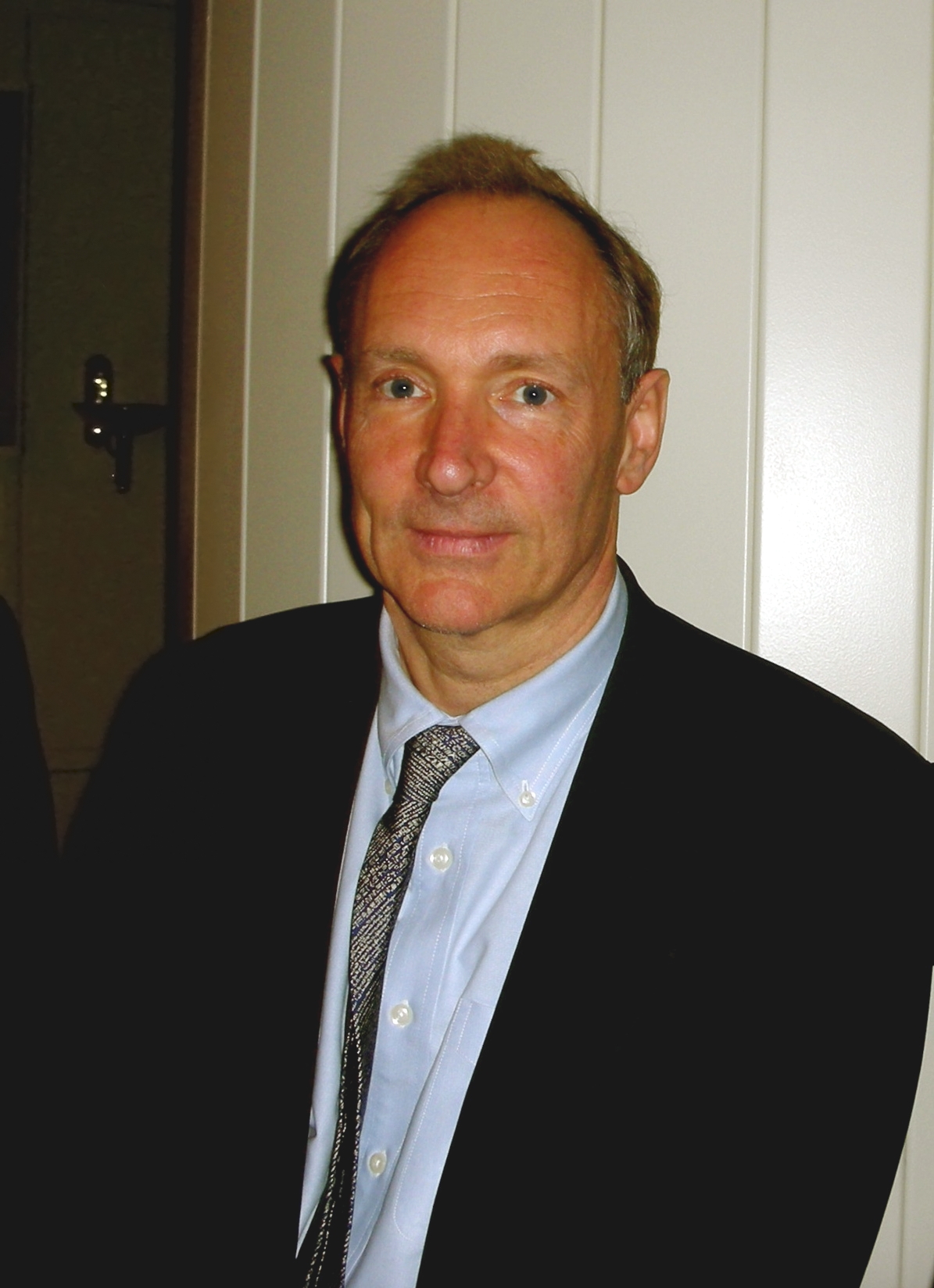
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libwww
Libwww is an early World Wide Web software library providing core functions for web browsers, implementing HTML, HTTP, and other technologies. Tim Berners-Lee, at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), released libwww (then also called the Common Library) in late 1992, comprising reusable code from the first browsers (WorldWideWeb and Line Mode Browser). Libwww was relied upon by the then popular browser Mosaic. By 1997, interest in libwww declined, and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which took over from CERN, reduced its commitment to the project. Later, the purpose of libwww was redefined to be "a testbed for protocol experiments"; in that role it was maintained for the benefit of the W3C's web standards-promoting browser Amaya. Active development of libwww stopped in 2000. History In 1991 and 1992, Tim Berners-Lee and a student at CERN named Jean-François Groff rewrote various components of the original WorldWideWeb browser for the NeXTstep operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libpng
libpng is the official Portable Network Graphics (PNG) reference library (originally called pnglib). It is a platform-independent library that contains C functions for handling PNG images. It supports almost all of PNG's features, is extensible, and has been widely used and tested for over 28 years. libpng is dependent on zlib for data compression and decompression routines. libpng is released under the libpng license, a permissive free software licence, and is free software Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut .... It is frequently used in both free and proprietary software, either directly or through the use of a higher level image library. the latest versions in the 1.6.x and 1.5.x branches were considered as release versions, while 1.4.x, 1.2.x, and 1.0.x were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Network Graphics
Portable Network Graphics (PNG, officially pronounced , colloquially pronounced ) is a raster graphics, raster-graphics file graphics file format, format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF). PNG supports palette-based images (with palettes of 24-bit RGB color model, RGB or 32-bit RGBA color space, RGBA colors), grayscale images (with or without an Alpha compositing, alpha channel for transparency), and full-color non-palette-based RGB or RGBA images. The PNG working group designed the format for transferring images on the Internet, not for professional-quality print graphics; therefore, non-RGB color spaces such as CMYK color model, CMYK are not supported. A PNG file contains a single image in an extensible structure of ''chunks'', encoding the basic pixels and other information such as textual comments and Integrity checker, integrity checks documented in Request for Comments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript, a programming language. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and browser engine, render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page Semantic Web, semantically and originally included cues for its appearance. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, HTML element#Images and objects, images and other objects such as Fieldset, interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, Hyperlink, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUSE Linux
openSUSE () is a free and open-source Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. It is offered in two main variations: ''Tumbleweed'', an upstream rolling release distribution, and ''Leap'', a stable release distribution which is sourced from SUSE Linux Enterprise. The openSUSE project is sponsored by SUSE of Germany; the company released the first version as SUSE Linux in 1994. Its development was opened up to the community in 2005, which marked the creation of openSUSE. The focus of the developers is on creating a stable and user-friendly RPM-based operating system with a large target group for workstations and servers. Additionally, the project creates a variety of related tools, such as YaST, Open Build Service, openQA, Snapper, Portus, KIWI, and OSEM. Product history SUSE Linux In the past, the SUSE Linux company has focused on releasing the SUSE Linux Personal and SUSE Linux Professional box sets which included extensive printed documentation that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Linux
Scientific Linux (SL) is a discontinued Linux distribution produced by Fermilab, CERN, DESY and by ETH Zurich. It is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. This product is derived from the free and open-source software made available by Red Hat, but is not produced, maintained or supported by them. In April 2019, it was announced that feature development for Scientific Linux would be discontinued, but that Software maintenance, maintenance will continue to be provided for the 6.x and 7.x releases through the end of their life cycles. Fermilab and CERN will utilize CentOS Stream and AlmaLinux for their deployment of 8.x release instead. History Fermilab already had a Linux distribution known as Fermi Linux, a long-term support release based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. CERN was creating their next version of CERN Linux, also based on RHEL. CERN contacted Fermilab about doing a collaborative release. Connie Sieh wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |