|
Arduino
Arduino () is an Italian open-source hardware and open-source software, software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a Creative Commons license, CC BY-SA license, while the software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL), permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors. Arduino board designs use a variety of microprocessors and controllers. The boards are equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards ('shields') or breadboards (for prototyping) and other circuits. The boards feature serial communications interfaces, including Universal Serial Bus (USB) on som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arduino Uno
The Arduino Uno is a series of open-source Single-board microcontroller, microcontroller board based on a diverse range of Microcontroller, microcontrollers (MCU). It was initially developed and released by Arduino company in 2010. The Single-board microcontroller, microcontroller board is equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards (shields) and other circuits. The board has 14 digital I/O pins (six capable of pulse-width modulation, PWM output), 6 analog I/O pins, and is programmable with the Arduino#Software, Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment), via a type B USB cable. It can be powered by a USB cable or a barrel connector that accepts voltages between 7 and 20 volts, such as a rectangular 9-volt battery. It has the same microcontroller as the Arduino Nano board, and the same headers as the Leonardo board. The hardware reference design is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
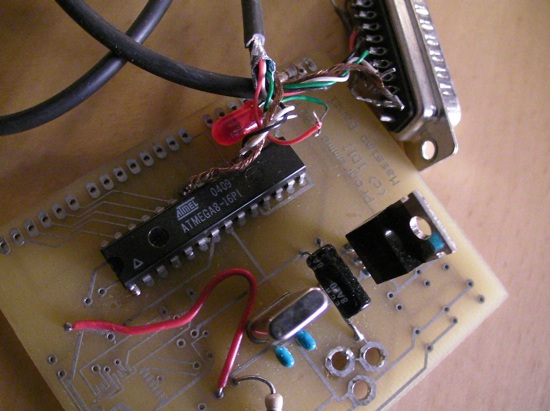
Atmel AVR
AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. They are 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers based on a modified Harvard architecture. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to Programmable read-only memory, one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time. AVR microcontrollers are used numerously as embedded systems. They are especially common in hobbyist and educational embedded applications, popularized by their inclusion in many of the Arduino line of open hardware development boards. The AVR 8-bit microcontroller architecture was introduced in 1997. By 2003, Atmel had shipped 500 million AVR flash microcontrollers. History The AVR architecture was conceived by two students at the Norwegian Institute of Technology (NTH), Alf-Egil Bogen and Vegard Wollan.Archived aGhostarchiveand thWayback Machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Hardware
Open-source hardware (OSH, OSHW) consists of physical artifact (software development), artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source#Society, open-source culture movement and apply a like concept to a variety of components. It is sometimes, thus, referred to as free and open-source hardware (FOSH), meaning that the design is easily available ("open") and that it can be used, modified and shared freely ("free"). The term usually means that information about the hardware is easily discerned so that others can make it – coupling it closely to the maker culture, maker movement. Hardware design (i.e. mechanical drawings, circuit diagram, schematics, bills of material, printed circuit board, PCB layout data, hardware description language, HDL source code and integrated circuit layout data), in addition to the software that device driver, drives the hardware, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-board Microcontroller
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware. As they are usually low-cost, and have an especially low capital cost for development, single-board microcontrollers have long been popular in education. They are also a popular means for developers to gain hands-on experience with a new processor family. Origins Single-board microcontrollers appeared in the late 1970s, when the appearance of early microprocessors, such as the 6502 and the Z80, made it practical to build an entire controller on a single board, as well as affordable to dedicate a computer to a relatively minor task. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processing (programming Language)
Processing is a free graphics library and integrated development environment (IDE) built for the electronic arts, new media art, and visual design communities with the purpose of teaching non-programmers the fundamentals of computer programming in a visual context. Processing uses the Java programming language, with additional simplifications such as additional classes and aliased mathematical functions and operations. It also provides a graphical user interface for simplifying the compilation and execution stage. The Processing language and IDE have been the precursor to other projects including Arduino and Wiring. History The project was initiated in 2001 by Casey Reas and Ben Fry, both formerly of the Aesthetics and Computation Group at the MIT Media Lab. In 2012, they started the Processing Foundation along with Daniel Shiffman, who joined as a third project lead. Johanna Hedva joined the Foundation in 2014 as Director of Advocacy. Originally, Processing had used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-M0+
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by ARM Limited. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though they are most often the main component of microcontroller chips, sometimes they are embedded inside other types of chips too. The Cortex-M family consists of Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M1, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23, Cortex-M33, Cortex-M35P, Cortex-M52, Cortex-M55, Cortex-M85. A floating-point unit (FPU) option is available for Cortex-M4 / M7 / M33 / M35P / M52 / M55 / M85 cores, and when included in the silicon these cores are sometimes known as "Cortex-MxF", where 'x' is the core variant. Overview The ARM Cortex-M family are ARM microprocessor cores that are designed for use in microcontrollers, ASICs, ASSPs, FPGAs, and SoCs. Cortex-M cores are commonly used as dedicated microcontroller chips, but also are "h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Cortex-M3
The ARM Cortex-M is a group of 32-bit reduced instruction set computer, RISC ARM architecture, ARM processor cores licensed by Arm (company), ARM Limited. These cores are optimized for low-cost and energy-efficient integrated circuits, which have been embedded in tens of billions of consumer devices. Though they are most often the main component of microcontroller chips, sometimes they are embedded inside other types of chips too. The Cortex-M family consists of Cortex-M0, Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M1, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M4, Cortex-M7, Cortex-M23, Cortex-M33, Cortex-M35P, Cortex-M52, Cortex-M55, Cortex-M85. A floating-point unit (FPU) option is available for Cortex-M4 / M7 / M33 / M35P / M52 / M55 / M85 cores, and when included in the silicon these cores are sometimes known as "Cortex-MxF", where 'x' is the core variant. Overview The ARM Cortex-M family are ARM microprocessor cores that are designed for use in microcontrollers, ASICs, application-specific standard product, ASSPs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Quark
Intel Quark is a line of 32-bit x86 SoCs and microcontrollers by Intel, designed for small size and low power consumption, and targeted at new markets including wearable devices. The line was introduced at Intel Developer Forum in 2013, and discontinued in January 2019. Quark processors, while slower than Atom processors, are much smaller and consume less power. They lack support for SIMD instruction sets (such as MMX and SSE) and only support embedded operating systems. Quark powers the (now discontinued) Intel Galileo developer microcontroller board. In 2016 Arduino released the Arduino 101 board that includes an Intel Quark SoC. The CPU instruction set is, for most models, the same as a Pentium ( P54C/i586) CPU. History The first product in the Quark line is the single-core 32 nm X1000 SoC with a clock rate of up to 400 MHz. The system includes several interfaces, including PCI Express, serial UART, I²C, Fast Ethernet, USB 2.0, SDIO, power management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinu
XINU Is Not Unix (XINU, a recursive acronym), is an operating system for embedded systems, originally developed by Douglas Comer for educational use at Purdue University in the 1980s. The name is both recursive, and is ''Unix'' spelled backwards. It has been ported to many hardware platforms, including the DEC PDP-11 and VAX systems, Motorola 68k (Sun-2 and Sun-3 workstations, AT&T UNIX PC, MECB), Intel x86, PowerPC G3, MIPS, ARM architecture and AVR (atmega328p/Arduino). Xinu was also used for some models of Lexmark printers. Despite its name suggesting some similarity to Unix, Xinu is a different type of operating system, written with no knowledge of the Unix source code, or compatibility goals. It uses different abstractions, and system calls, some with names matching those of Unix, but different semantics. History Xinu first ran on the LSI-11 platform. A Motorola 68000 port was done by Derrick Burns in 1983. A VAX port was done in 1986 by Comer and Tom Stonecypher, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaction Design Institute Ivrea
Interaction Design Institute Ivrea (also known as Interaction Ivrea or IDII) was a two-year graduate program in the field of Interaction Design operating in the town of Ivrea, in Northern Italy between 2001 and 2006. The institute was based in the former Olivetti Study and Research Centre, sometimes referred to as ''Casa Blu'', designed by Eduardo Vittorio in 1955 and restored by Sottsass Associates, Sottsass Associati. History The Interaction Design Institute Ivrea Association was founded on 16 June 2000 by Telecom Italia and Olivetti, with its headquarters in Ivrea, with the first class of students arriving in 2001. The founding director of the school was Gillian Crampton Smith until 2005. The school's mission was described in Blueprint as: :''"Ivrea will explore business in addition to design and technology. Crampton Smith believes that today there is an 'art' in imagining new business models, and is also aware that, partly because of their broad education, design graduates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeRTOS
FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system Kernel (operating system), kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 40 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License. History The FreeRTOS kernel was originally developed by Richard Barry around 2003, and was later developed and maintained by Barry's company, Real Time Engineers Ltd. In 2017, the firm passed stewardship of the FreeRTOS project to Amazon Web Services (AWS). Barry continues to work on FreeRTOS as part of an AWS team. With the transition to Amazon control, subsequent releases of the project also switched licensing from GPL version 2 (with special exceptions for static linking to proprietary code outside the FreeRTOS kernel itself) to MIT. Implementation FreeRTOS is designed to be small and simple. It is mostly written in the C (programming language), C programming language to make it easy to port and maintain. It also comprises a few assembly language functions where needed, mostly in archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |