|
Appalachian Balds
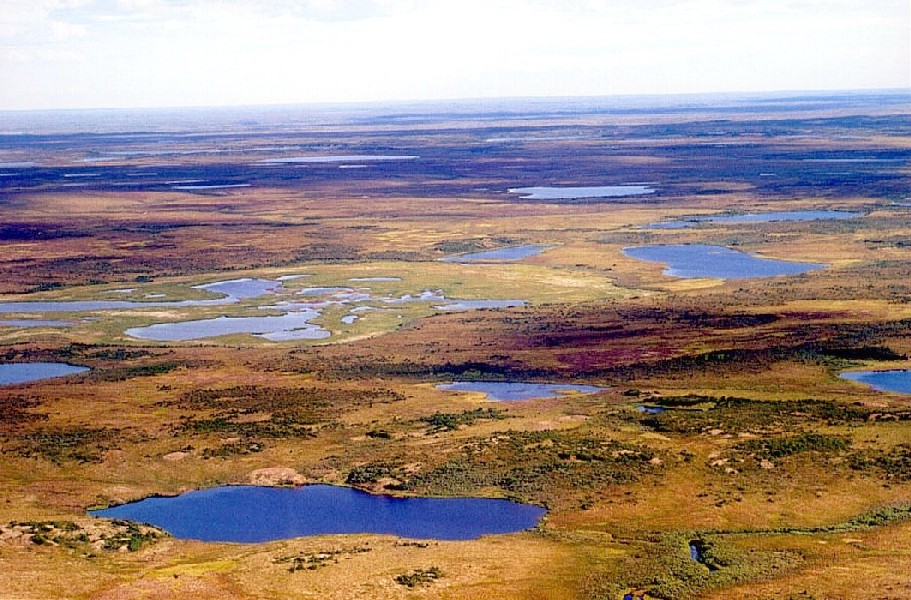
In the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States, balds are mountain summits or crests covered primarily by thick vegetation of native grasses or shrubs occurring in areas where heavy forest growth would be expected. Balds are found primarily in the Southern Appalachians, where, even at the highest elevations, the climate is too warm to support an alpine zone, areas where trees fail to grow due to short or non-existent growing seasons. The difference between an alpine summit, such as Mount Washington in New Hampshire, and a bald, such as Gregory Bald in the Great Smoky Mountains, is that a lack of trees is normal for the colder climate of the former but abnormal for the warmer climate of the latter. One example of southern balds' abnormality can be found at Roan Mountain, where Roan High Knob (el. 6,285 ft/1,915 m) is coated with a dense stand of spruce-fir forest, whereas an adjacent summit, Round Bald (el. 5,826 ft/1,776 m), is almost entirely devoid of tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forb
A forb or phorb is a herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in botany and in vegetation ecology especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically, these are eudicots without woody stems. Etymology The word ''forb'' is derived from Greek () 'pasture; fodder'. The Hellenic spelling ''phorb'' is sometimes used, and in older usage this sometimes includes graminids and other plants currently not regarded as forbs. Guilds Forbs are members of a guilda group of plant species with broadly similar growth forms. In certain contexts in ecology, guild membership may often be more important than the taxonomic relationships between organisms. In informal classification In addition to its use in ecology, the term "forb" may be used for subdividing popular guides to wildflowers, distinguishing them from other categories such as grasses, sedges, shrubs, and trees. Some examples of forbs are clovers, sunflowers, daylilie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
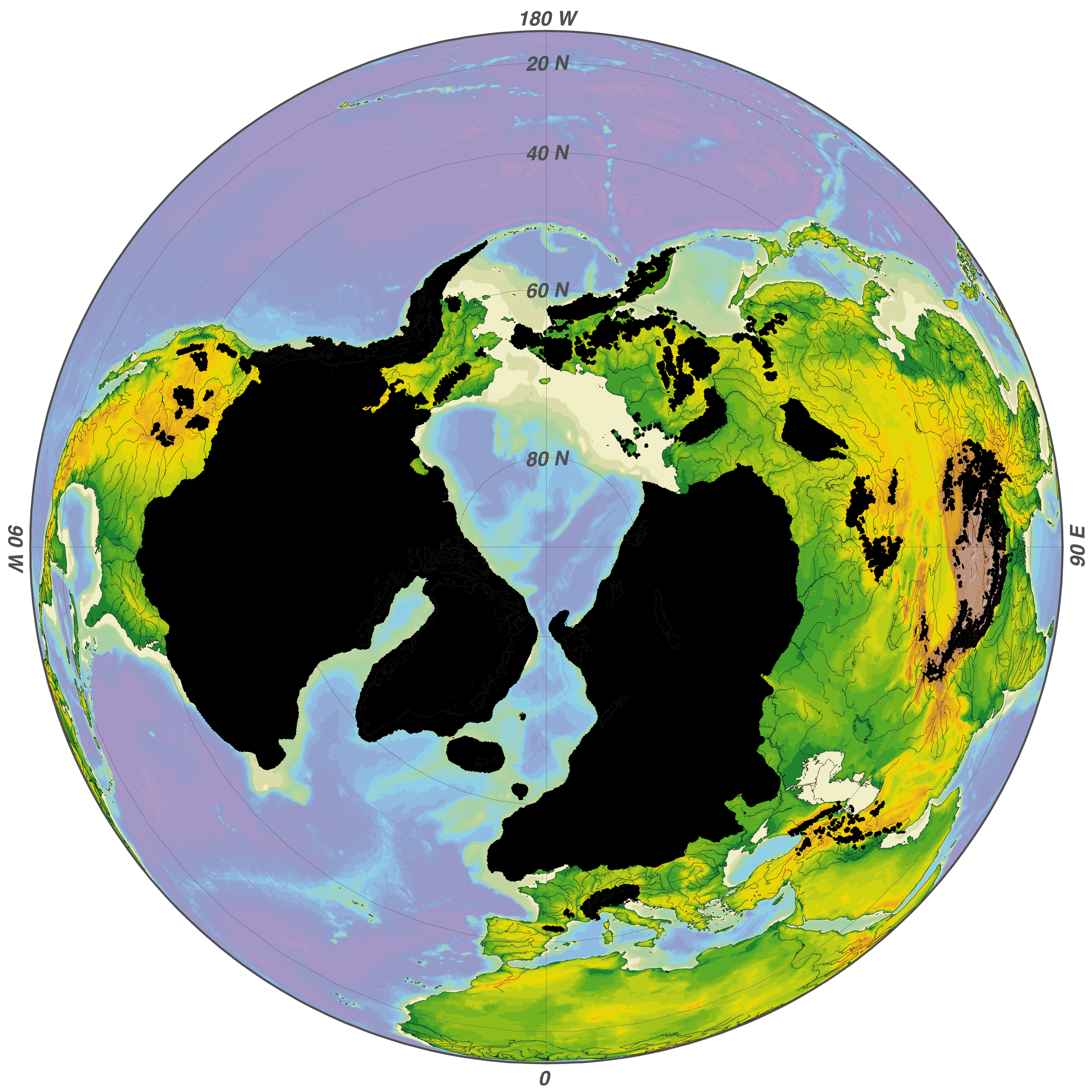
Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American Glacier#Classification_by_size,_shape_and_behavior, alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from about 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred about 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the ''Late W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic, Antarctic. Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, Cyperaceae, sedges, Poaceae, grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone (or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. The soil also contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide in the permafrost, making the tundra soil a carbon sink. As global warming heats the ecosystem and causes soil thawing, the permafrost carbon cycle accelerates and releases much of these soil-contained greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, creating Climate change feedback, a feedback cycle t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubus Canadensis
''Rubus canadensis'' is a North American species of flowering plant in the rose family known by the common names smooth blackberry, Canadian blackberry, thornless blackberry and smooth highbush blackberry. It is native to central and eastern Canada (from Newfoundland to Ontario) and the eastern United States (New England, the Great Lakes region, and the Appalachian Mountains).Coladonato, Milo. 1994''Rubus canadensis''.In: Fire Effects Information System, nline U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. It has also been sparingly recorded in Great Britain, in which it is often confused for the many other native blackberry species. This rhizomatous shrub forms thickets up to tall. The leaves are deciduous and alternately arranged, each measuring long. The inflorescence is a cluster of up to 25 flowers. The fruit is an aggregate of many small drupes, each of which contains a tiny nutlet. The plant reproduces by seed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinium Erythrocarpum
''Vaccinium erythrocarpum'', commonly known as southern mountain cranberry or bearberry, more rarely as mountain blueberry or dingleberry, is a deciduous flowering shrub native to the Southeastern United States. Description ''Vaccinium erythrocarpum'' flowers bloom in June. They are hermaphrodite, of a tubular shape with reflexed petals, and they have long tassel-like stamens that drape below the corolla. They produce somewhat translucent scarlet berries that set in late summer or early autumn. The fruits taste quite similar to other cranberries. Taxonomy ''Vaccinium erythrocarpum'' was long considered synonymous with '' V. japonicum,'' found in East Asia, however the two have since been split into separate species. Both species are now considered members of the cranberry subgenus '' Oxycoccus,'' both also placed into the section ''Oxycoccoides''. These species within sect. ''Oxycoccoides'' differ from the rest of the subgenus as they are deciduous shrubs while sect. ''Ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menziesia Pilosa
''Rhododendron pilosum'' (syn. ''Menziesia pilosa''), the minniebush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae. A shrub reaching , it is typically found growing in the Appalachian Mountains The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ... from southern Pennsylvania to Georgia. References pilosum Endemic flora of the United States Flora of Pennsylvania Flora of West Virginia Flora of Virginia Flora of Tennessee Flora of North Carolina Flora of South Carolina Flora of Georgia (U.S. state) Plants described in 2011 {{Ericaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbus Americana
The tree species ''Sorbus americana'' is commonly known as the American mountain-ash. It is a deciduous perennial tree, native to eastern North America. The American mountain-ash and related species (most often the European mountain-ash, ''Sorbus aucuparia'') are also referred to as rowan trees. Description ''Sorbus americana'' is a relatively small tree, reaching in height. The American mountain-ash attains its largest specimens on the northern shores of Lake Huron and Lake Superior. It resembles the European mountain-ash, ''Sorbus aucuparia''. ; Bark: Light gray, smooth, surface scaly. Branchlets downy at first, later become smooth, brown tinged with red, lenticular, finally they become darker and the papery outer layer becomes easily separable. ; Wood: Pale brown; light, soft, close-grained but weak. Specific gravity, 0.5451; weight of cu. ft., 33.97 lbs. ; Winter buds:Dark red, acute, one-fourth to three-quarters of an inch long. Inner scales are very tomentose and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaylussacia Baccata
''Gaylussacia baccata'', the black huckleberry, is a common huckleberry found throughout a wide area of eastern North America. Description ''Gaylussacia baccata'' is a shrub up to 150 cm (5 feet) tall, forming extensive colonies. Flowers are in dangling groups of 3–7, orange or red, bell-shaped. The berries are dark blue, almost black, rarely white. Similar species The plant closely resembles the native blueberry plants (''Vaccinium'' species) with which it grows in the same habitats. It can be readily identified by the numerous resin dots on the undersides of the leaves which glitter when held up to the light. Distribution The plant is native to Eastern Canada and the Great Lakes region, the Midwestern and Northeastern United States, and the Appalachian Mountains, the Ohio/Mississippi/Tennessee Valley, and Southeastern United States. The range extends from Newfoundland west to Manitoba and Minnesota, south as far as Arkansas, Alabama, and Georgia. Ecology The shr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmia Latifolia
''Kalmia latifolia'', the mountain laurel, calico-bush, or spoonwood, is a flowering plant and one of the 10 species in the genus of Kalmia belonging to the heath(er) family Ericaceae. It is native to the eastern United States. Its range stretches from southern Maine to northern Florida, and west to Indiana and Louisiana. Mountain laurel is the List of U.S. state flowers, state flower of Connecticut and Pennsylvania. It is the namesake of Laurel County, Kentucky, Laurel County in Kentucky, the city of Laurel, Mississippi, and the Laurel Highlands in southwestern Pennsylvania. Description ''Kalmia latifolia'' is an evergreen shrub growing tall. The leaves are 3–12 cm long and 1–4 cm wide. The flowers are pentagonal, ranging from light pink to white, and occur in clusters. There are several named cultivars that have darker shades of pink, red and maroon. It blooms in May and June. All parts of the plant are poisonous. The roots are fibrous and matted. File:Mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhododendron Catawbiense
''Rhododendron catawbiense'', with common names Catawba rosebay, Catawba rhododendron, mountain rosebay, purple ivy, purple laurel, purple rhododendron, red laurel, rosebay, rosebay laurel, is a species of ''Rhododendron'' native to the eastern United States, growing mainly in the southern Appalachian Mountains from West Virginia south to northern Alabama. It is a dense, suckering shrub growing to tall, rarely . The leaf, leaves are evergreen, long and broad. The flowers are in diameter, violet-purple, often with small spots or streaks, blooming from April through June. The fruit is a dry capsule (fruit), capsule long, containing numerous small seeds. The species is named after the Catawba River. Classification ''Rhododendron catawbiense'' belongs to the Rhododendron subg. Hymenanthes, subgenus ''Hymenanthes'', within which it is further assigned to Rhododendron sect. Ponticum, section ''Ponticum'' and Rhododendron subsect. Pontica, subsection ''Pontica''. The latter—one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |