|
Antique Radio
An antique radio is a radio receiving set that is collectible because of its age and rarity. Types of antique radio Morse receivers The first radio receivers used a coherer and sounding board, and were only able to receive continuous wave (CW) transmissions, encoded with Morse code (Radiotelegraphy, wireless telegraphy). Later wireless telephony, transmission and reception of speech became possible, although Morse code transmission continued in use until the 1990s. All the following sections concern speech-capable radio, or wireless telephony. Early home-made sets The idea of radio as entertainment took off in 1920, with the opening of the first stations established specifically for broadcast to the public such as KDKA (AM), KDKA in Pittsburgh and WWJ (AM), WWJ in Detroit. More stations opened in cities across North America in the following years and radio ownership steadily gained in popularity. Radio sets from before 1920 are rarities, and are probably military artifacts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radio Diora Aga RSZ50 1
Radio is the technology of telecommunication, communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna (radio), antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, radio control, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by Modulation, modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selectivity (radio)
Selectivity is a measure of the performance of a radio receiver to respond only to the radio signal it is tuned to (such as a radio station) and reject other signals nearby in frequency, such as another broadcast on an adjacent channel. Selectivity is usually measured as a ratio in decibels (dB), comparing the signal strength received against that of a similar signal on another frequency. If the signal is at the adjacent channel of the selected signal, this measurement is also known as adjacent-channel rejection ratio (ACRR). Selectivity also provides some immunity to blanketing interference. LC circuits are often used as filters; the Q ("Quality" factor) determines the bandwidth of each LC tuned circuit in the radio. The L/C ratio, in turn, determines their Q and so their selectivity, because the rest of the circuit - the aerial or amplifier feeding the tuned circuit for example - will contain present resistance. For a series resonant circuit, the higher the inductance and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rheostat
A potentiometer is a three-terminal (electronics), terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. The measuring instrument called a Potentiometer (measuring instrument), potentiometer is essentially a voltage divider used for measuring electric potential (voltage); the component is an implementation of the same principle, hence its name. Potentiometers are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on audio equipment. It is also used in speed control of fans. Potentiometers operated by a mechanism can be used as position transducers, for example, in a joystick. Potentiometers are rarely used to directly control significant power (more than a watt), since the power dissipated in the potentiometer would be comparable to the power in the controlled load. Nomenclature Some terms in the electronics industry used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Filament
An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that produces illumination by Joule heating a filament until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either evacuated or filled with inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Electric current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for decorative and advertising lighting. Incandescent bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gain (electronics)
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal amplitude or power at the output port to the amplitude or power at the input port. It is often expressed using the logarithmic decibel (dB) units ("dB gain"). A gain greater than one (greater than zero dB), that is, amplification, is the defining property of an active device or circuit, while a passive circuit will have a gain of less than one. The term ''gain'' alone is ambiguous, and can refer to the ratio of output to input voltage (''voltage gain''), current (''current gain'') or electric power (''power gain''). In the field of audio and general purpose amplifiers, especially operational amplifiers, the term usually refers to voltage gain, but in radio frequency amplifiers it usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
FM Broadcasting
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting that uses frequency modulation (FM) of the radio broadcast carrier wave. Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to transmit high fidelity, high-fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting offers higher fidelity—more accurate reproduction of the original program sound—than other broadcasting techniques, such as AM broadcasting. It is also less susceptible to Electromagnetic interference, common forms of interference, having less static and popping sounds than are often heard on AM. Therefore, FM is used for most broadcasts of music and general audio (in the audio spectrum). FM radio stations use the very high frequency range of radio frequency, radio frequencies. Broadcast bands Throughout the world, the FM broadcast band falls within the VHF part of the radio spectrum. Usually 87.5 to 108.0 MHz is used, or some portion of it, with few exceptions: * In the Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
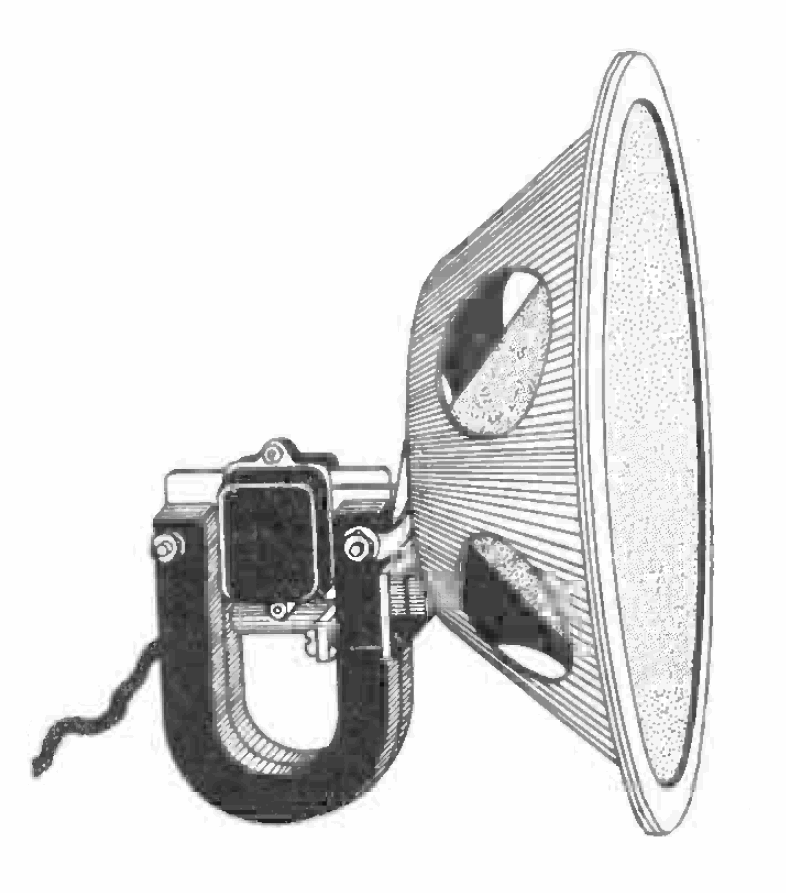
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kellogg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moving Iron Speaker
The moving iron speaker was the earliest type of electric loudspeaker. They are still used today in some miniature speakers where small size and low cost are more important than sound quality. A moving iron speaker consists of a ferrous-metal diaphragm or reed, a permanent magnet and a coil of insulated wire. The coil is wound around the permanent magnet to form a solenoid. When an audio signal is applied to the coil, the strength of the magnetic field varies, and the springy diaphragm or reed moves in response to the varying force on it. The moving iron loudspeaker Bell telephone receiver was of this form. Large units had a paper cone attached to a ferrous metal reed. There are several types of moving iron speaker. Modern damped moving iron mechanisms can provide respectable sound quality, and are used in headphones. The first moving iron transducer, the telephone receiver or earphone, evolved with the first telephone systems in the 1870s. Moving iron horn loudspeakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kellogg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude (magnitude of the voltage or current) of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one. An amplifier can be either a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |