|
Antarctic Ice Pack
Antarctic sea ice is the sea ice of the Southern Ocean. It extends from the far north in the winter and retreats to almost the coastline every summer. Sea ice is frozen seawater that is usually less than a few meters thick. This is the opposite of ice shelf, ice shelves, which are formed by glaciers; they float in the sea, and are up to a kilometre thick. There are two subdivisions of sea ice: fast ice, which are attached to land; and Drift ice, ice floes, which are not. Sea ice that comes from the Southern Ocean melts from the bottom instead of the surface like Arctic sea ice, Arctic ice because it is covered in snow on top. As a result, melt ponds are rarely observed. On average, Antarctic sea ice is younger, thinner, warmer, saltier, and more mobile than Arctic sea ice. Another difference between the two ice packs, is that while there is clear Arctic sea ice decline, the trend in Antarctica is roughly flat. Antarctic sea ice is not studied very well in comparison to Arctic ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychrophiles
Psychrophiles or cryophiles (adj. ''psychrophilic'' or ''cryophilic'') are extremophilic organisms that are capable of growth and reproduction in low temperatures, ranging from to . They are found in places that are permanently cold, such as the polar regions and the deep sea. They can be contrasted with thermophiles, which are organisms that thrive at unusually high temperatures, and mesophiles at intermediate temperatures. Psychrophile is Greek for 'cold-loving', . Many such organisms are bacteria or archaea, but some eukaryotes such as lichens, snow algae, phytoplankton, fungi, and wingless midges, are also classified as psychrophiles. Biology Habitat The cold environments that psychrophiles inhabit are ubiquitous on Earth, as a large fraction of the planetary surface experiences temperatures lower than 10 °C. They are present in permafrost, polar ice, glaciers, snowfields and deep ocean waters. These organisms can also be found in pockets of sea ice with high sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, and III) covered the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report was finished in March 2023. It includes a summary for policymakers and was the basis for the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai. The first of the three working groups published its report on 9 August 2021, ''Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis''.IPCC, 2021Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
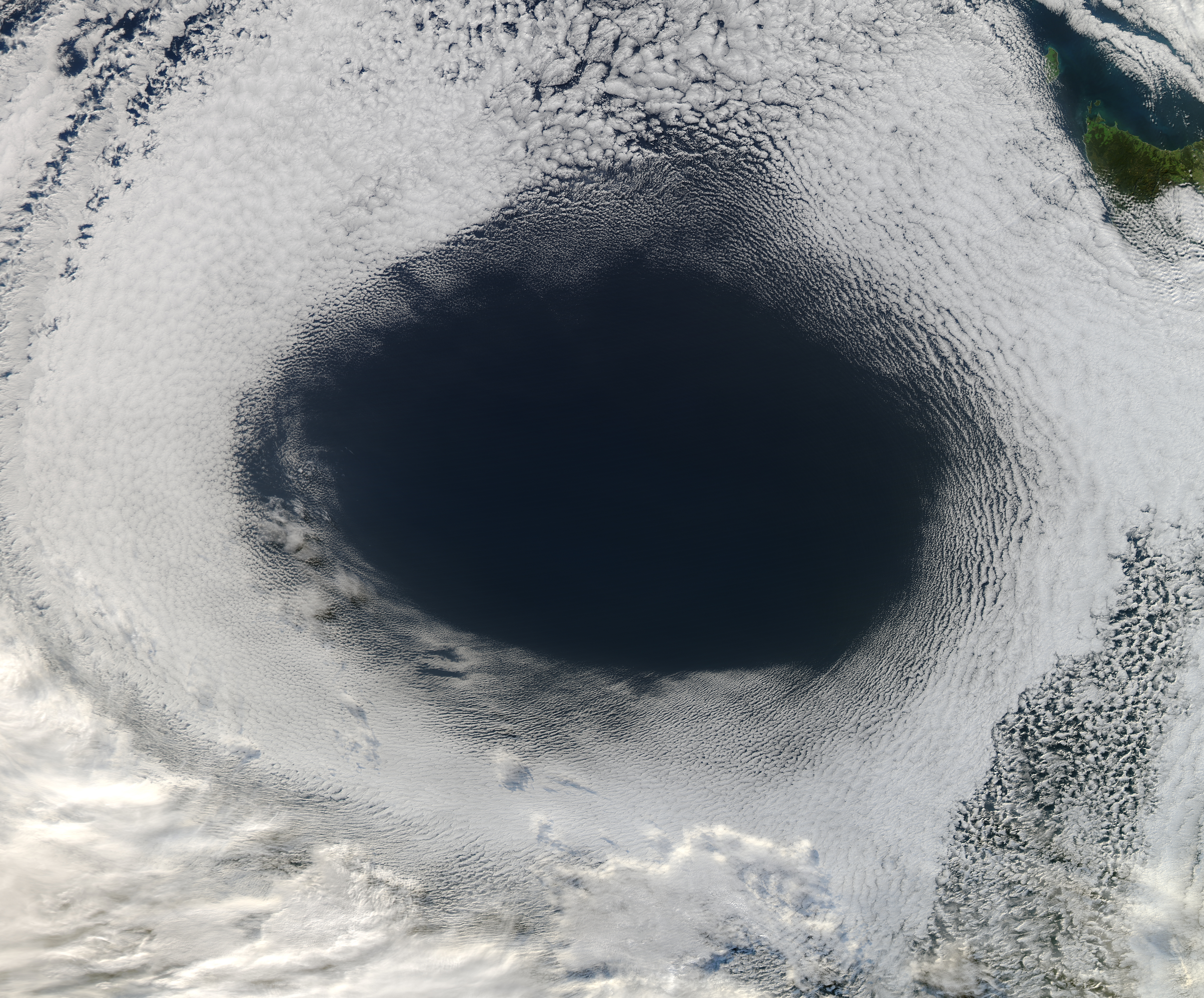
Advection
In the fields of physics, engineering, and earth sciences, advection is the transport of a substance or quantity by bulk motion of a fluid. The properties of that substance are carried with it. Generally the majority of the advected substance is also a fluid. The properties that are carried with the advected substance are conserved properties such as energy. An example of advection is the transport of pollutants or silt in a river by bulk water flow downstream. Another commonly advected quantity is energy or enthalpy. Here the fluid may be any material that contains thermal energy, such as water or air. In general, any substance or conserved extensive quantity can be advected by a fluid that can hold or contain the quantity or substance. During advection, a fluid transports some conserved quantity or material via bulk motion. The fluid's motion is described mathematically as a vector field, and the transported material is described by a scalar field showing its distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block (meteorology)
Blocks in meteorology are large-scale patterns in the atmospheric pressure field that are nearly stationary, effectively "blocking" or redirecting migratory cyclones. They are also known as blocking highs or blocking anticyclones.Glossary of Meteorology, Second Edition; American Meteorological Society, 2000; . These blocks can remain in place for several days or even weeks, causing the areas affected by them to have the same kind of weather for an extended period of time (e.g. precipitation for some areas, clear skies for others). In the Northern Hemisphere, extended blocking occurs most frequently in the spring over the eastern Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. While these events are linked to the occurrence of extreme weather events such as heat waves, particularly the onset and decay of these events is still not well captured in numerical weather forecasts and remains an open area of research. Impact of the polar vortex Polar cyclones are climatological features which hover near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild rain, showers to severe hail, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as Synoptic scale meteorology, large scale (synoptic) Low-pressure area, low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term "cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Oscillation
The Antarctic oscillation (AAO, to distinguish it from the Arctic oscillation or AO), also known as the Southern Annular Mode (SAM), is a low-frequency mode of atmospheric variability of the southern hemisphere that is defined as a belt of strong westerly winds or low pressure surrounding Antarctica which moves north or south as its mode of variability. It is a climate driver for Australia, influencing the country's weather conditions – It is associated with storms and cold fronts that move from west to east that bring precipitation to southern Australia. Phases and impacts Both positive and negative SAM events tends to last for approximately ten days to two weeks, though the timeframe between a positive and a negative event is random. It is usually in the span of a week to a few months, with a negative SAM being more common in the cool months and a positive SAM being more prolonged in the warmer months. Winds associated with the Southern Annular Mode cause oceanic upwell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Stratification
Ocean stratification is the natural separation of an ocean's water into horizontal layers by Density of water, density. This is generally stable stratification, because warm water floats on top of cold water, and heating is mostly from the sun, which reinforces that arrangement. Stratification is reduced by wind-forced mechanical mixing, but reinforced by Open ocean convection, convection (warm water rising, cold water sinking). Stratification occurs in all ocean basins and also in Stratification (water), other water bodies. Stratified layers are a barrier to the mixing of water, which impacts the exchange of heat, carbon, oxygen and other nutrients. The surface mixed layer is the uppermost layer in the ocean and is well mixed by mechanical (wind) and thermal (convection) effects. Climate change is causing the upper ocean stratification to increase. Due to upwelling and downwelling, which are both wind-driven, mixing of different layers can occur through the rise of cold nutrient-ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice-shelf
An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to displace the more dense surrounding ocean water. The boundary between the ice shelf (floating) and grounded ice (resting on bedrock or sediment) is referred to as the grounding line; the boundary between the ice shelf and the open ocean (often covered by sea ice) is the ice front or calving front. Ice shelves are found in Antarctica and the Arctic (Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic), and can range in thickness from about . The world's largest ice shelves are the Ross Ice Shelf and the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The movement of ice shelves is principally driven by gravity-induced pressure from the grounded ice. That flow continually moves ice from the grounding line to the seaward front of the shelf. Typically, a shelf front will extend forward for years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about 30 degrees) and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Argentina, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land is absent, bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |