|
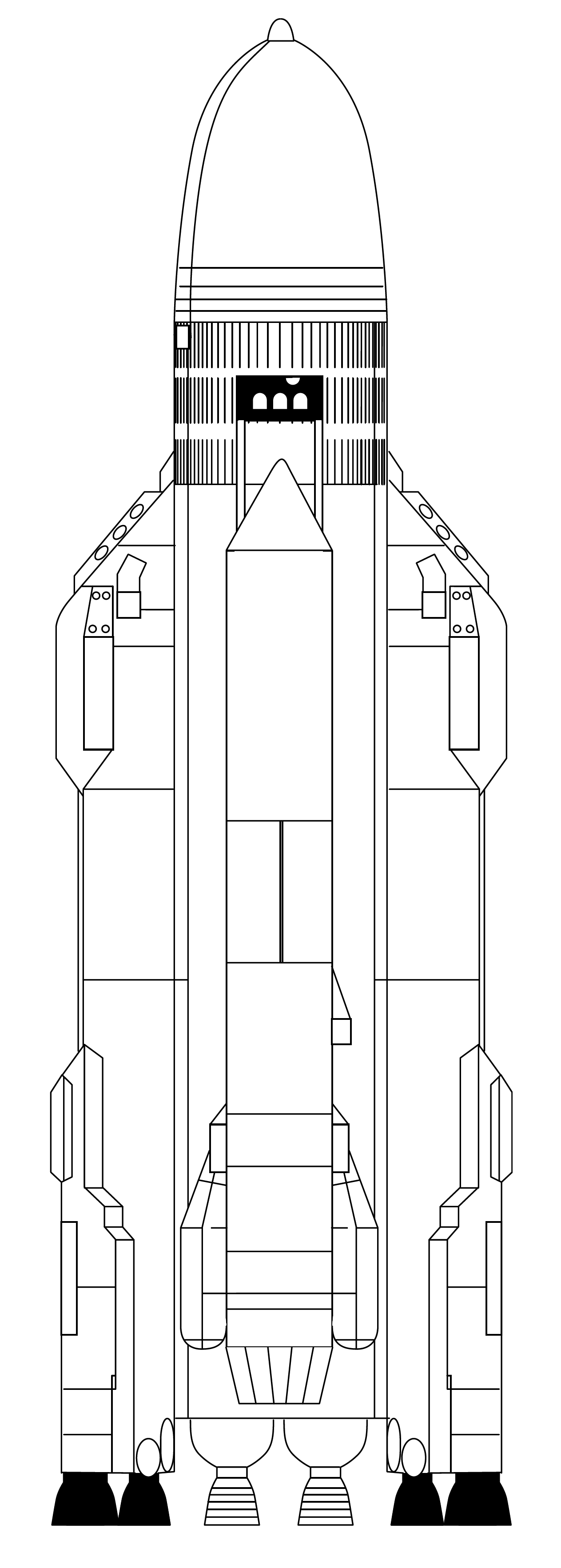
Angara-1.2
"Angara-1.2" is a Russian two-stage small-lift launch vehicle designed to launch a payload of up to 3.5 tons into low Earth orbit and up to 2.4 tons into a Sun-synchronous orbit, sun—synchronous orbit. The height of the "Angara-1.2" is about 41.5 m, the launch mass of the rocket is about 171 tons. It is part of the Angara (rocket family), Angara family of launch vehicles. Description The Angara-1.2 rocket has two stages running on cryogenic fuel, the fuel is kerosene of the RG-1 naphthyl brand, and the oxidizer is liquid oxygen. Since the second stage does not have the possibility of re-activation to form the final orbit of the spacecraft being launched, it includes a detachable orbital launch unit "AM" (aggregate module) operating on high-boiling fuel dinitrogen tetroxide + UDMH "Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine, heptyl". First Stage The first stage of the Angara-1.2 is a Universal Rocket Module, universal rocket module, similar to those used on the first and second stages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
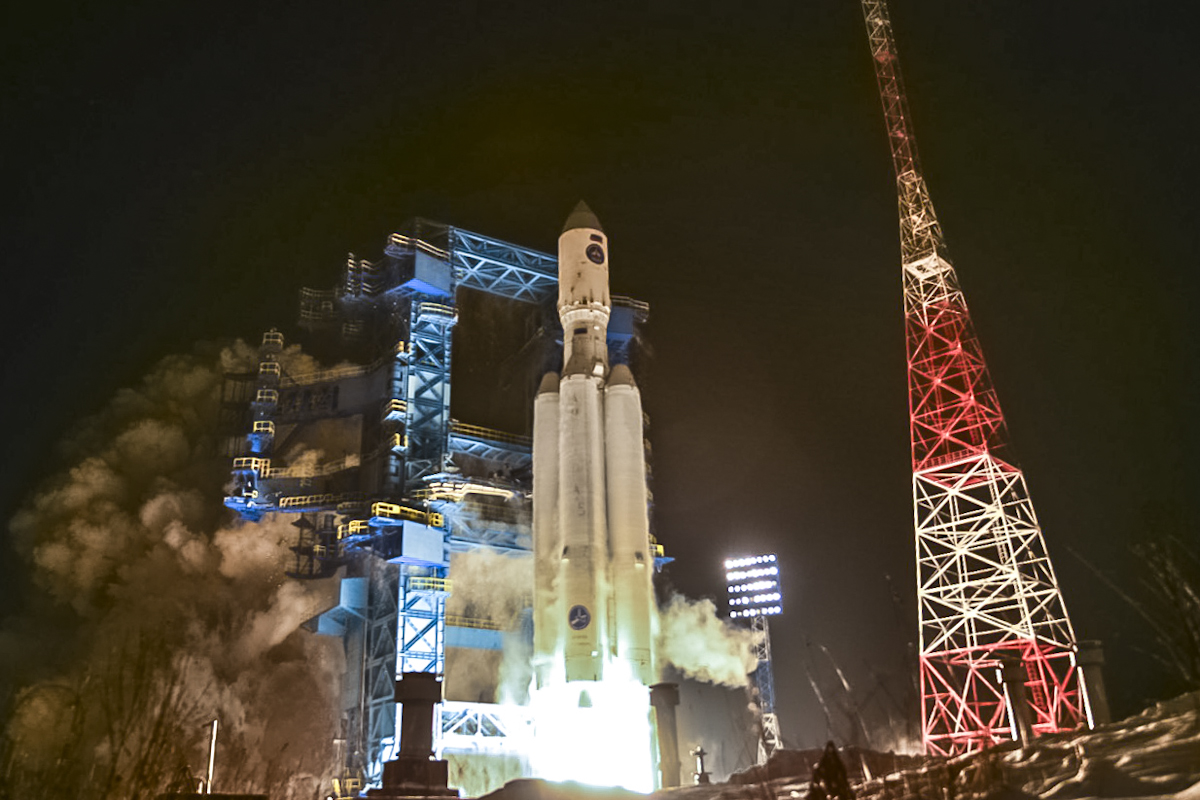
Plesetsk Cosmodrome Site 35
Site 35 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome is a launch complex used by the Angara rocket. The complex has a single launch pad, Site 35/1, which was first used for the maiden flight of the Angara in July 2014. Zenit Site 35 was originally intended to support the Zenit rocket, which the Soviet Union saw as a replacement for the R-7 series. The construction of a Zenit launch complex at Plesetsk was authorised in 1976; however, development did not begin until the completion of Site 45 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, which was also constructed for Zenit. Construction at Site 35 began in the mid-1980s, but the programme was abandoned following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Following the cancellation of Zenit launches from Plesetsk, Russia had originally planned to use parts constructed for Site 35 to repair one of the Zenit pads at Baikonur that had been heavily damaged when a rocket lost thrust and fell back into the flame trench seconds after launch. Instead, the parts were eventually use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesetsk Cosmodrome
Plesetsk Cosmodrome () is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, near the town of Plesetsk, from which it takes its name. Until 2025 and the commissioning of the Andøya Space, Andøya base in Norway, it was the only operational orbital spaceport in Europe and the northernmost spaceport in the world. Originally developed as an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) site for the R-7 (missile), R-7 missile, its strategic location approximately north of Moscow was key to its selection. Due to its high latitude, Plesetsk is particularly suited for specific types of satellite launches, such as those into Molniya orbits, and historically served as a secondary launch facility. Most Soviet orbital launches were conducted from Baikonur Cosmodrome, located in the Kazakh SSR. However, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became part of Kazakhstan, which began charging Russia to lease the land for its use. As a result, Plesetsk has seen significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Rocket Module
Universal Rocket Module (URM) is the name of the modular liquid fuelled first and second stage of the Angara expendable launch system. The first stage and booster variant is referred to as URM-1, while the second stage is referred to as URM-2. The URM-2 is derived from the Soyuz-2 Block I second stage. URM-1 is a unitary structure 2.9 meters in diameter and 25 meters in length that includes an oxidizer tank, a fuel tank (both tanks being coupled by a spacer) and an RD-191 engine burning RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen producing a thrust of 1.92 MN. URM-1 was first flown in 2014 on the Angara 1.2PP suborbital test flight. Angara can fly with either one URM-1 in the case of Angara 1.2 and Angara 1.2PP, or one URM-1 as a sustainer core with four additional URM-1s as boosters for Angara A5. URM-2 is a modified Block I stage, 3.6 meters in diameter and 6.9 meters in length. It is powered by a single RD-0124A producing 294 kilonewtons, derived from Block I's RD-0124. URM-2 was first f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
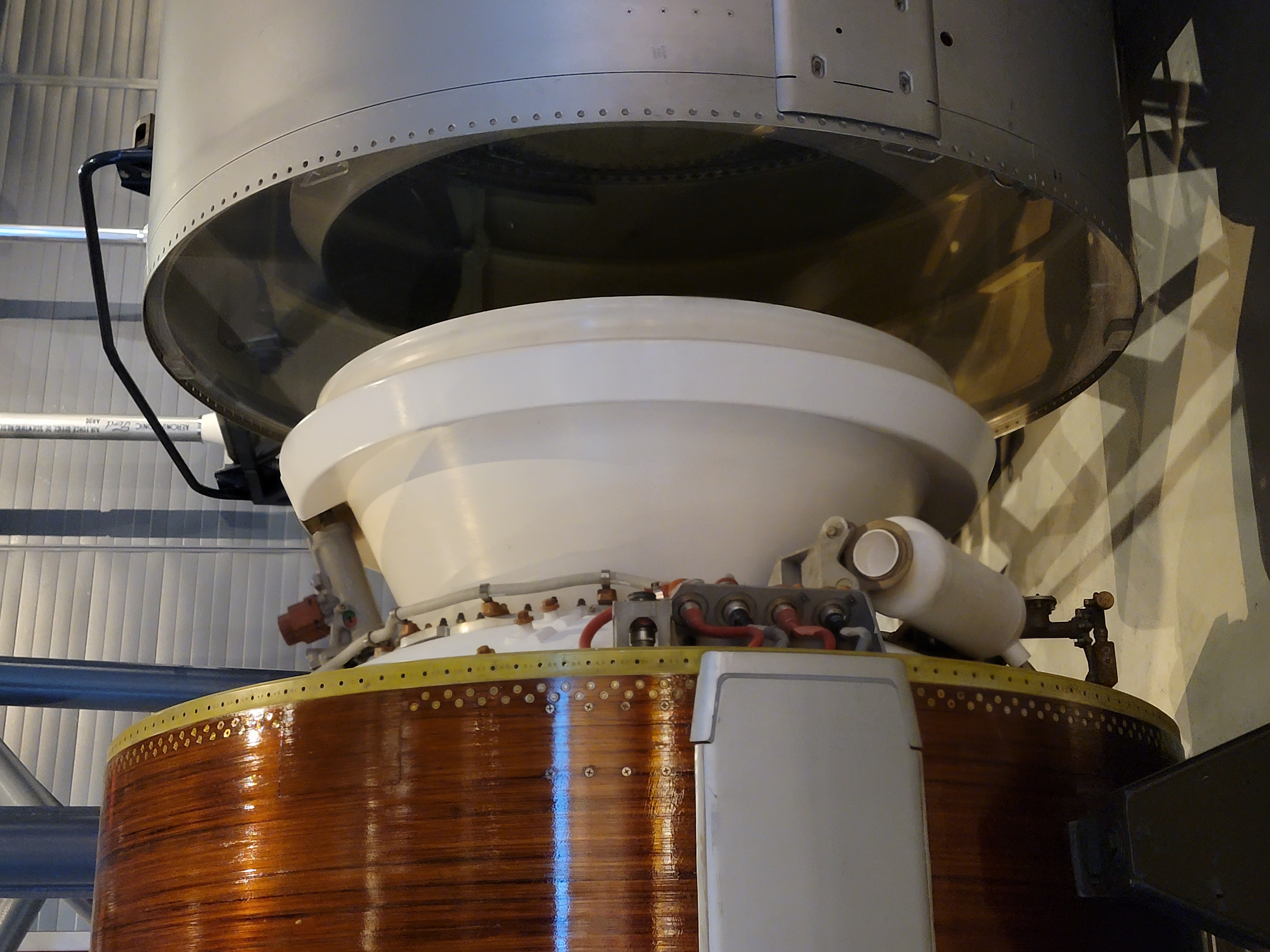
RD-191
The RD-191 () is a high-performance single-combustion chamber rocket engine, developed in Russia and sold by Roscosmos. It is derived from the RD-180 dual-combustion chamber engine, which itself was derived in turn from the four-chamber RD-170 originally used in the Energia launcher. The RD-191 is fueled by a kerosene / LOX mixture and uses an oxygen-rich staged combustion cycle. In the future the engine is expected to become a workhorse in the Russian space sector, as older launch vehicles are phased out of production and service. Design Burn ignition is provided chemically, by feeding a starter fluid into the combustion chamber and gas generator, which is self-igniting on contact with liquid oxygen. The engine is capable of throttling down to 30% of nominal thrust; the design also allows for a short-duration enhanced thrust (up to 105% of nominal level) in emergency situations. A Cardan suspension provides for yaw and pitch controls by gimballed thrust deflection up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-0124
The RD-0124 (, GRAU index: 14D23) is a rocket engine burning liquid oxygen and kerosene in an oxygen-rich staged combustion cycle, developed by the Chemical Automatics Design Bureau in Voronezh. RD-0124 engines are used on the Block I stage used on Soyuz-2.1b and Soyuz-2.1v. A variant of the engine, the RD-0124A, is used on the Angara rocket family's URM-2 upper stage. Design RD-0124 engines use a multi-stage turbopump powered by pre-combustion of the engine propellants in the preburner. The kerosene fuel is used for regenerative cooling of the engine. Vehicle attitude control during ascent is provided by gimbaling the engine in two planes. The propellant tanks are helium-pressurized. Four combustion chambers are fed by a single turbopump system. The engine operates at a high chamber pressure and, for the type of propellants used, achieves a very high specific impulse of nearly 360 seconds in vacuum. History The inaugural flight of a launch vehicle using an RD-0124 engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angara A5
Angara A5 (Russian: Ангара-А5), is a Russian expendable heavy lift launch vehicle which consists of one URM-1 core and four URM-1 boosters, a URM-2 second stage, and an upper stage, either the Briz-M The Briz-K, Briz-KM and Briz-M ( meaning ''Breeze-K, KM and M'') are Russian liquid-propellant rocket orbit insertion upper stages manufactured by Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center and used on the Proton-M and Angara A5. T ..., Blok DM-03 or the KVTK. Weighing at lift-off, Angara A5 has a payload capacity of to a x 60° orbit. Angara A5 is able to deliver to GTO with Briz-M, or to the same orbit with KVTK. In the Angara A5, the four URM-1s used as boosters operate at full thrust for approximately 214 seconds, then separate. The URM-1 forming the vehicle's core is operated at full thrust for lift off, then throttled down to 30% to conserve propellant. The core is throttled back up after the boosters have separated and continues burning for ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenit (rocket Family)
Zenit (, ; meaning ''Zenith'') was a family of space launch vehicles designed by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau in Dnipro, Ukraine, which was then part of the Soviet Union. Zenit was originally built in the 1980s for two purposes: as a liquid rocket booster for the Energia (rocket), Energia rocket and, equipped with a second stage, as a stand-alone middle-weight launcher with a payload greater than the 7 tonnes of the Soyuz (rocket), Soyuz but smaller than the 20 tonnes payload of the Proton (rocket family), Proton. The last rocket family developed in the USSR, the Zenit was intended as an eventual replacement for the dated Soyuz and Proton families, and it would employ propellants which were safer and less toxic than the Proton's nitrogen tetroxide/UDMH mix. Zenit was planned to take over crewed spaceship launches from Soyuz, but these plans were abandoned after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Many of components of the Zenit rockets were produced in Russia. The Ukraini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energia (rocket)
Energia (; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran programme, Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran (spacecraft), Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/Liquid oxygen, LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus (spacecraft), Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the Buran programme, ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to place about 100 tonnes in Low Earth orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstage
In rocketry, an adapter is a hollow cylindrical or conical segment which provides a sound aerodynamic and structural connection, either between rocket stages (often referred to as an interstage) or between a spacecraft and the top rocket stage (referred to as a payload adapter). It may shroud and protect vulnerable systems such as electrics or machinery of rocket engines/spacecraft from weather or noise caused by running engines. It is discarded during staging. Examples of rocket stages featuring an interstage adapter: * Centaur (second stage of several Atlas-based launch vehicles, from Atlas-Centaur to Atlas V) * S-II and S-IVB (second and third stage of the Saturn V) * The Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) of SLS Block 1 is connected to the Core Stage with the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Examples of rocket stages featuring a payload adapter: * (Planned) The Exploration Upper Stage The Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) is a rocket stage under development for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-orbital Spaceflight
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the primary (astronomy), gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity. For example, the path of an object launched from Earth that reaches the Kármán line (about – above sea level), and then falls back to Earth, is considered a sub-orbital spaceflight. Some sub-orbital flights have been undertaken to test spacecraft and launch vehicles later intended for orbital spaceflight. Other vehicles are specifically designed only for sub-orbital flight; examples include crewed vehicles, such as the North American X-15, X-15 and SpaceShipTwo, and uncrewed ones, such as intercontinental ballistic missile, ICBMs and sounding rockets. Flights which attain sufficient velocity to go into low Earth orbit, and then de-orbit before com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |