|
Alpine Chough
The Alpine chough () or yellow-billed chough (''Pyrrhocorax graculus'') is a bird in the crow family, one of only two species in the genus '' Pyrrhocorax''. Its two subspecies breed in high mountains from Spain eastwards through southern Europe and North Africa to Central Asia and Nepal, and it may nest at a higher altitude than any other bird. The eggs have adaptations to the thin atmosphere that improve oxygen take-up and reduce water loss. This bird has glossy black plumage, a yellow beak, red legs, and distinctive calls. It has a buoyant acrobatic flight with widely spread flight feathers. The Alpine chough pairs for life and displays fidelity to its breeding site, which is usually a cave or crevice in a cliff face. It builds a lined stick nest and lays three to five brown-blotched whitish eggs. It feeds, usually in flocks, on short grazed grassland, taking mainly invertebrate prey in summer and fruit in winter; it will readily approach tourist sites to find supplementary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
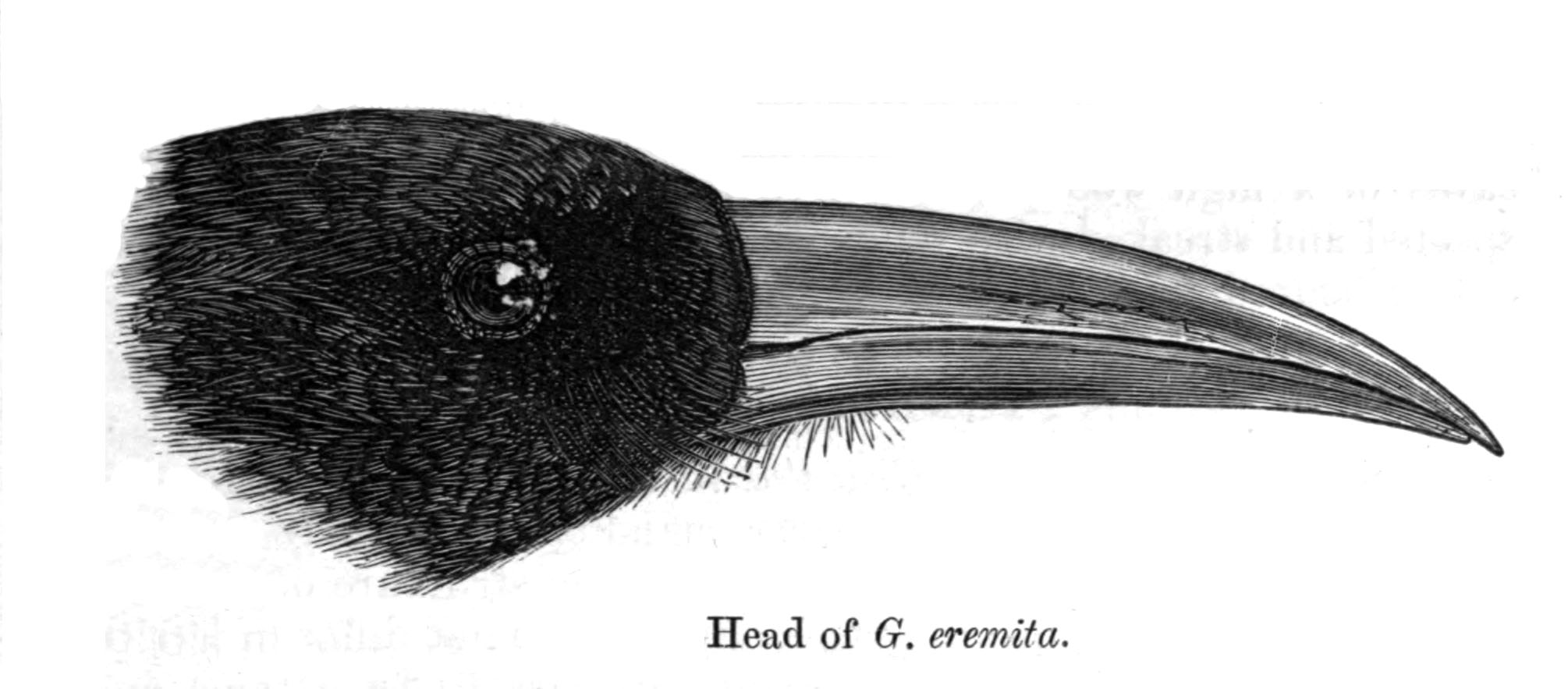
Red-billed Chough
The red-billed chough, Cornish chough or simply chough ( ; ''Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax''), is a bird in the crow family, one of only two species in the genus ''Pyrrhocorax''. Its eight subspecies breed on mountains and coastal cliffs from the western coasts of Ireland and Britain east through southern Europe and North Africa to Central Asia, India and China. This bird has glossy black plumage, a long curved red bill, red legs, and a loud, ringing call. It has a buoyant acrobatic flight with widely spread Primary feather, primaries. The red-billed chough pair bond, pairs for life and displays philopatry, fidelity to its breeding site, which is usually a cave or crevice in a cliff face. It builds a wool-lined stick nest and lays three eggs. It feeds, often in flocks, on short grazed grassland, taking mainly invertebrate prey. Although it is subject to predation and parasitism, the main threat to this species is changes in agricultural practices, which have led to population declin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German Natural history, naturalist, zoologist, Botany, botanist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopy, microscopist. He is considered to be one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin and became a friend of the famous List of explorers, explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile, Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Hemprich
Wilhelm Friedrich Hemprich (24 June 1796 – 30 June 1825) was a German natural history, naturalist and explorer. Hemprich was born in Kłodzko, Glatz (Kłodzko), Prussian Silesia, and studied medicine at Breslau and Berlin. It was in Berlin that he became friends with Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, the two men sharing an interest in natural history. Hemprich lectured at Berlin University on comparative physiology, and wrote ''Grundriss der Naturgeschichte'' (Compendium of Natural History) (1820). In his spare time he studied reptiles and amphibians at the zoological museum under Hinrich Lichtenstein. In 1820 Hemprich and Ehrenberg were invited to serve as naturalists on a primarily archeological expedition to Egypt, led by Prussian General Heinrich Menu von Minutoli, von Minutoli. The two naturalists were sponsored by the Berlin Academy. In March 1821 they separated from the main party and travelled up the river Nile to Dongola, the capital of Nubia. They spent the next two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackdaw
Jackdaws are two species of bird in the genus ''Coloeus'' closely related to, but generally smaller than, crows and ravens ('' Corvus''). They have a blackish crown, wings, and tail, with the rest of their plumage paler.Madge & Burn (1994) 136–138. The word ''Coloeus'' is Neo-Latin, from the Ancient Greek for jackdaws: ' (). They come from Asia, Europe, Africa and Siberia (the one not in Asia?). Taxonomy While some authors consider ''Coloeus'' a subgenus of ''Corvus'', others have classified ''Coloeus'' as a distinct genus in the family Corvidae. Following '' Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide'', the International Ornithological Congress has also reassigned the two Jackdaw species from the genus ''Corvus'' to the genus ''Coloeus''. Species The eastern species is smaller than the western jackdaw, and in eastern adults, the pale areas of the plumage are almost white, whereas in the western bird, these areas are pale grey. The iris is pale in western jackdaw and dark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia (or rarely echoism) is a type of word, or the process of creating a word, that phonetics, phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Common onomatopoeias in English include animal noises such as Oink (sound), ''oink'', ''meow'', ''roar'', and ''Bird vocalization, chirp'', among other sounds such as ''Beep (sound), beep'' or ''hiccup''. Onomatopoeia can differ by language: it conforms to some extent to the broader natural language, linguistic system. Hence, the sound of a clock may be expressed variously across languages: as ' in English language, English, in Spanish language, Spanish and Italian language, Italian (see photo), in Standard Chinese, Mandarin, in Japanese language, Japanese, or in Hindi, Urdu, and Bengali language, Bengali. Etymology and terminology The word ''onomatopoeia'', with rarer spelling variants like ''onomatopeia'' and ''onomatopœia'', is an English word from the Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvidae
Corvidae is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan Family (biology), family of Songbird, oscine passerine birds that contains the crows, ravens, Rook (bird), rooks, magpies, jackdaws, jays, treepies, choughs, and Nutcracker (bird), nutcrackers. In Colloquialism, colloquial English, they are known as the crow family or corvids. Currently, 139 species are included in this family. The genus ''Corvus'' containing 50 species makes up over a third of the entire family. Corvids (ravens) are the largest passerines. Corvids display remarkable Animal cognition, intelligence for animals of their size, and are among the most Bird intelligence, intelligent birds thus far studied. Specifically, members of the family have demonstrated self-awareness in mirror tests (Eurasian magpies) and Tool use by animals, tool-making ability (e.g. crows and rooks), skills which until recently were thought to be possessed only by humans and a few other mammals. Their total Brain–body mass ratio, brain-to- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchet-tailed Treepie
The ratchet-tailed treepie (''Temnurus temnurus'') is a species of bird in the crow and jay family Corvidae. The species is also known as the notch-tailed treepie. It is monotypic within the genus ''Temnurus''. The species has a disjunct distribution in Southeast Asia and China. One population is found in southern Thailand, another in southern Vietnam, another in central and northern Vietnam and Laos, and the last in Hainan in China. Its natural habitat is tropical moist broadleaf evergreen lowland forest A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...s, and secondary forest and scrubland. References ratchet-tailed treepie Birds of Hainan Birds of Laos Birds of Vietnam ratchet-tailed treepie Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Corvidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |