|
Alignment Layers
Alignment layers, or alignment films, are thin films which are a crucial component of liquid crystal displays (LCDs). They are applied to the surfaces of the glass substrates that contain the liquid crystals. The primary function of these layers is to control the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, which is essential for the proper operation of the display. The alignment layer controls the alignment of the liquid crystal immediately adjacent to itself, and long-range interactions force that alignment to extend significantly into the crystal itself. Alignment layers ensure that liquid crystal molecules are aligned in a specific direction when no electric field is applied. This is critical for the display's function; for example, in twisted nematic (TN) displays, the alignment layers on the two glass substrates are oriented at right angles to each other, creating a 90-degree twist in the liquid crystal molecules, allowing display to modulate light effectively when an elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-crystal Display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or Reflector (photography), reflector to produce images in color or Monochrome monitor, monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays (as in a digital clock) are all examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, Dashboard, instrument panels, flight instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Charge
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor. A static electric charge can be created whenever two surfaces contact and/or slide against each other and then separate. The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because they can feel, hear, and even see sparks if the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to an electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shockmore specifically, an electrostatic dischargeis caused by the neutralization of a charge. Causes Materials are made of atoms that are normally electrically neutral because they contain equal numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
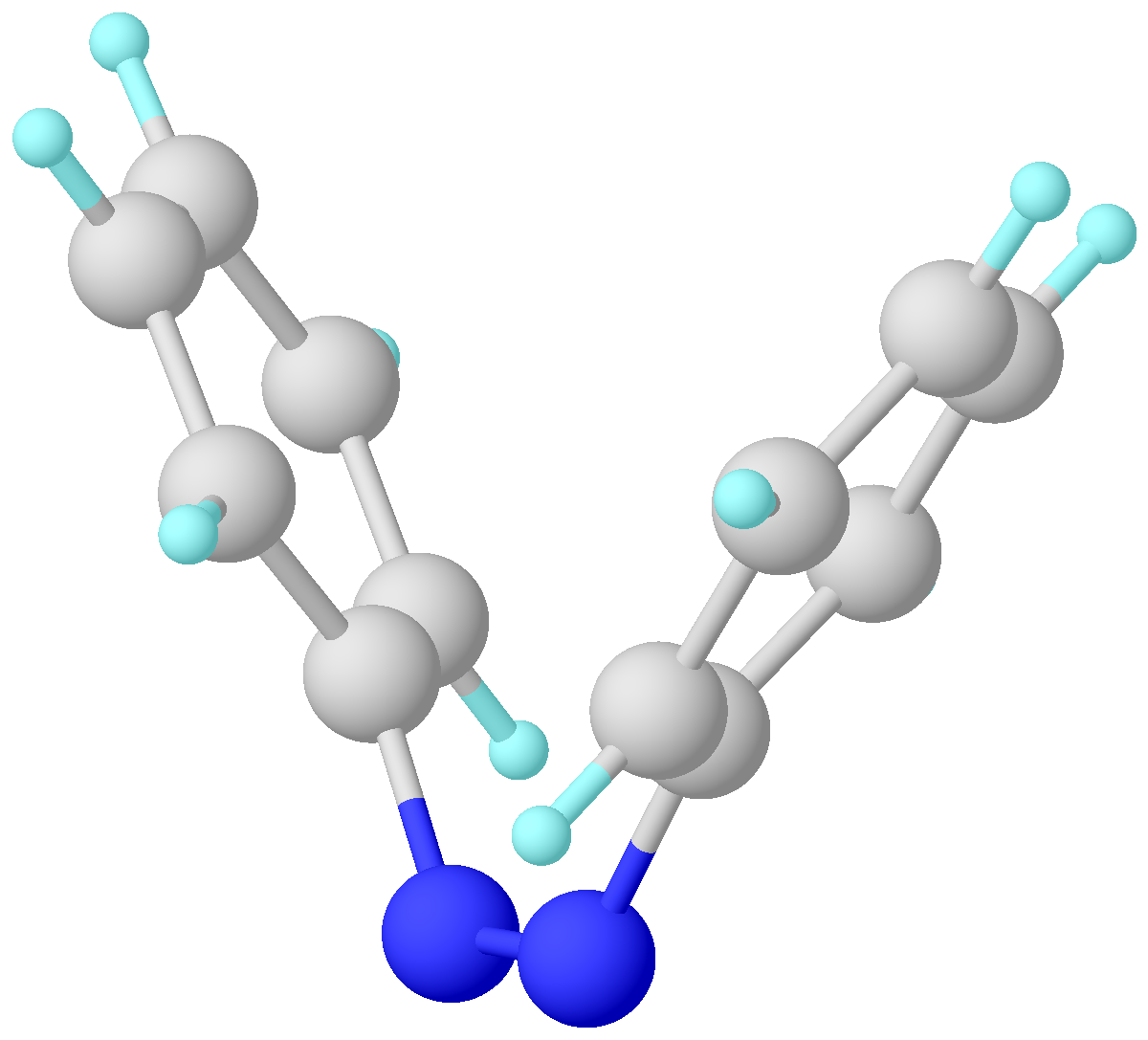
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a azo compound, N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar Chemical compound, compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Different classes of azo dyes exist, most notably the ones substituted with heteroaryl rings. Structure and synthesis Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. Industrial electrosynthesis using nitrobenzene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (chemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
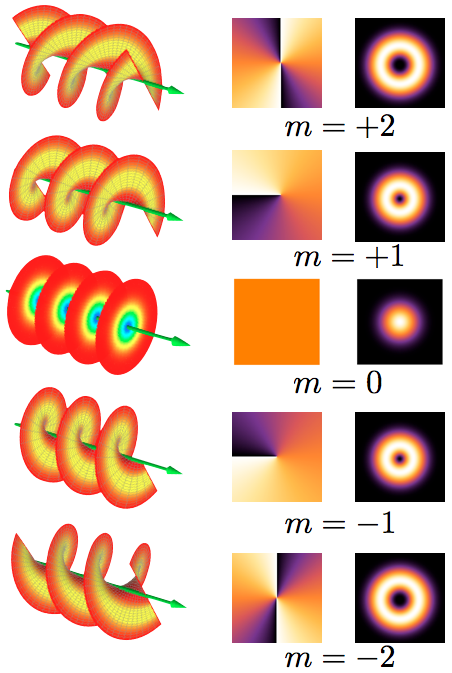
Optical Vortex
An optical vortex (also known as a photonic quantum vortex, screw dislocation or phase singularity) is a zero of an optical field; a point of zero intensity. The term is also used to describe a beam of light that has such a zero in it. The study of these phenomena is known as singular optics. The concept of "optical vortices" was first described by Coullet et al. in 1989, based on solutions of the Maxwell-Bloch equations. According to one review, studies in 1989-1999 mainly focused on fundamentals; studies in 1999-2009 developed many applications; and studies in 2009-2019 made a number of technological breakthroughs. Explanation In an optical vortex, light is twisted like a corkscrew around its axis of travel. Because of the twisting, the light waves at the axis itself cancel each other out. When projected onto a flat surface, an optical vortex looks like a ring of light, with a dark hole in the center. The vortex is given a number, called the topological charge, according to how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarizer
A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization (waves), polarization pass through while attenuation, blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam of well-defined polarization, known as polarized light. Polarizers are used in many optics, optical techniques and optical instrument, instruments. Polarizers find applications in photography and liquid crystal display, LCD technology. In photography, a polarizing filter (photography), polarizing filter can be used to filter out reflections. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides visible light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Linear polarizers ''Linear polarizers'' can be divided into two general categories: absorptive polarizers, where the unwanted polarization states are absorption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices such as telescopes, binoculars, and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from , the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photochemistry
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet (wavelength from 100 to 400 Nanometre, nm), visible light, visible (400–750 nm), or infrared radiation (750–2500 nm). In nature, photochemistry is of immense importance as it is the basis of photosynthesis, vision, and the formation of vitamin D with sunlight. It is also responsible for the appearance of DNA mutations leading to skin cancers. Photochemical reactions proceed differently than temperature-driven reactions. Photochemical paths access high-energy intermediates that cannot be generated thermally, thereby overcoming large Activation energy, activation barriers in a short period of time, and allowing reactions otherwise inaccessible by thermal processes. Photochemistry can also be destructive, as illustrated by the photodegradation of plastics. Concept Grotthuss–Dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarized Light
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velvet
Velvet is a type of woven fabric with a dense, even pile (textile), pile that gives it a distinctive soft feel. Historically, velvet was typically made from silk. Modern velvet can be made from silk, linen, cotton, wool, synthetic fibers, silk-cotton blends, or synthetic-natural fiber blends. Construction and composition Velvet is woven on a special loom that weaves two thicknesses of the material at the same time; the two layers are connected with an extra warp yarn that is woven over rods or wires. The two pieces are then cut apart to create the fabric's pile, and the two lengths of fabric are wound on separate take-up rolls. This complicated process meant that velvet was expensive to make before industrial power looms became available, and well-made velvet remains a fairly costly fabric. Velvet is difficult to clean because of its pile, but modern dry cleaning methods make cleaning more feasible. Velvet pile is created by cutting the warp (weaving), warp yarns, while vel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCD Manufacturing
LCD manufacturing is the process of making liquid crystal display (LCD) panels. It involves using glass and silicon substrates. Photolithography is used to pattern the substrates, and liquid crystal materials are added. In the case of a color TFT LCD, color filters are patterned in layers to make red, green, and blue pixels. Liquid crystal displays are manufactured in cleanrooms, borrowing techniques from semiconductor device manufacturing. Process A class of photolithography known as display lithography is used to etch patterns into substrates. LCD manufacturing shares some of the process with OLED manufacturing. The process flow involves multiple separate components that are joined together: a process for making a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane, a process for making color filters, and a liquid crystal cell process. Large-scale chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems have been used in the manufacture of LCDs. Once LCD panels are manufactured, they can be measured for col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compound (chemistry), compounds, produces unique physical property, physical properties including toughness, high rubber elasticity, elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form Amorphous solid, amorphous and crystallization of polymers, semicrystalline structures rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |