|
Alcohol Measurements
Alcohol measurements are units of measurement for determining amounts of beverage alcohol. Alcohol concentration in beverages is commonly expressed as alcohol by volume (ABV), ranging from less than 0.1% in fruit juices to up to 98% in rare cases of spirits. A "standard drink" is used globally to quantify alcohol intake, though its definition varies widely by country. Serving sizes of alcoholic beverages also vary by country. Alcohol concentration The concentration of alcohol in a beverage is usually stated as the percentage of alcohol by volume (ABV, the number of milliliters (ml) of pure ethanol in 100 ml of beverage) or as ''proof''. In the United States, ''proof'' is twice the percentage of alcohol by volume at 60 degrees Fahrenheit (e.g. 80 proof = 40% ABV). ''Degrees proof'' were formerly used in the United Kingdom, where 100 degrees proof was equivalent to 57.1% ABV. Historically, this was the most dilute spirit that would sustain the combustion of gunpowder. Ordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
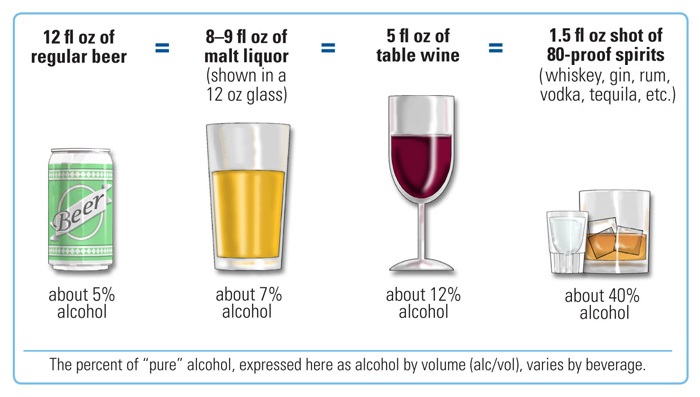
Unit Of Alcohol
A standard drink or (in the UK) unit of alcohol is a measure of alcohol consumption representing a fixed amount of pure alcohol. The notion is used in relation to recommendations about alcohol consumption and its relative risks to health. It helps to inform alcohol users. A hypothetical alcoholic beverage sized to one standard drink varies in volume depending on the alcohol concentration of the beverage (for example, a standard drink of spirits takes up much less space than a standard drink of beer), but it always contains the same amount of alcohol and therefore produces the same amount of intoxication. Many government health guidelines specify low to high risk amounts in units of grams of pure alcohol per day, week, or single occasion. These government guidelines often illustrate these amounts as standard drinks of various beverages, with their serving sizes indicated. Although used for the same purpose, the definition of a standard drink varies from country to country. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pint
The pint (, ; symbol pt, sometimes abbreviated as ''p'') is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial and United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems, it is one-eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is 20.095% larger than the US pint because the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints (such as for beverages), the volume varies by regional custom. The imperial pint (≈) is used in Ireland, the United Kingdom, and other Commonwealth countries. In the United States, two kinds of pint are used: a liquid pint (≈) and a less common dry pint (≈). Other former British colonies, such as Australia, South Africa and New Zealand, converted to the metric system in the 1960s and 1970s, so while the term may still be in common use in these countries, it may no longer refer to the British imperial pint once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Ounce
A fluid ounce (abbreviated fl oz, fl. oz. or oz. fl., old forms ℥, fl ℥, f℥, ƒ ℥) is a unit of volume (also called ''capacity'') typically used for measuring liquids. The British Imperial, the United States customary, and the United States food labeling fluid ounce are the three that are still in common use, although various definitions have been used throughout history. An imperial fluid ounce is of an imperial pint, of an imperial gallon, or exactly 28.4130625 mL. A US customary fluid ounce is of a US liquid pint, of a US gallon, or exactly 29.5735295625 mL, making it about 4.084% larger than the imperial fluid ounce. A US food labeling fluid ounce is exactly 30 mL. Comparison to the ounce The ''fluid'' ounce is distinct from the (international avoirdupois) ounce as a unit of weight or mass, although it is sometimes referred to simply as an "ounce" where context makes the meaning clear (e.g., "ounces in a bottle"). A volume of pure water me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Pint
The pint (, ; symbol pt, sometimes abbreviated as ''p'') is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial unit, imperial and United States customary units, United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems, it is one-eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is 20.095% larger than the US pint because Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints (such as for beverages), the volume varies by regional custom. The imperial pint (≈) is used in Ireland, the United Kingdom, and other Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries. In the United States, two kinds of pint are used: a liquid pint (≈) and a less common dry pint (≈). Other Dominion, former British colonies, such as Australia, South Africa and New Zealand, converted to the metric system in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Fluid Ounce
A fluid ounce (abbreviated fl oz, fl. oz. or oz. fl., old forms ℥, fl ℥, f℥, ƒ ℥) is a unit of volume (also called ''capacity'') typically used for measuring liquids. The British Imperial, the United States customary, and the United States food labeling fluid ounce are the three that are still in common use, although various definitions have been used throughout history. An imperial fluid ounce is of an imperial pint, of an imperial gallon, or exactly 28.4130625 mL. A US customary fluid ounce is of a US liquid pint, of a US gallon, or exactly 29.5735295625 mL, making it about 4.084% larger than the imperial fluid ounce. A US food labeling fluid ounce is exactly 30 mL. Comparison to the ounce The ''fluid'' ounce is distinct from the (international avoirdupois) ounce as a unit of weight or mass, although it is sometimes referred to simply as an "ounce" where context makes the meaning clear (e.g., "ounces in a bottle"). A volume of pure water measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley Wine
Barley wine is a strong ale from 6–12% alcohol by volume."Barley wine" Michael Jackson (writer), Michael Jackson History The first beer to be marketed as barley wine was Bass Brewery, Bass No. 1 Ale, around 1870. The Anchor Brewing Company introduced the style to the United States in 1976 with its Old Foghorn Barleywine Style Ale. Old Foghorn was styled as "barleywine" (one word) out of fear that occurrence of the word "wine" on a beer label would displease regulators. In 1983, Sierra Nevada Brewing Company, Sierra Nevada Brewing released Bigfoot Barleywine, becoming the second barley wine label in the United States.Characteristics Barley wine typically reaches an ethanol, alcohol strength of 6 to 12% by volume and is brewed from Gravity (beer), specific gravi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liber Horn
''Liber Horn'' is a book completed in 1311 by Andrew Horn. The National Archives (the official archive of the UK government) describes it as "a compilation of charters, statutes and customs". It is thought to have been a compilation of two separate books: ''De Veteribus Legibus Angliae'' and ''De Statutes.'' The ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from History of the British Isles, British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') ...'' describes it as "the most comprehensive of all statute collections". Portions of ''Liber Horn'' were reproduced in ''Statutes of the Realm'', Volume 1. Notes See also * Letter-Books of the City of London 1310s books Books about politics of England Law books {{England-poli-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Carpenter (town Clerk)
John Carpenter, the younger (about 1372–1442), was a Town Clerk of London. He was elected as Town Clerk to the City of London during the reigns of Henry V of England, Henry V and Henry VI of England, Henry VI. He was the author of the first book of English common law, called ''Liber Albus'' (the White Book). He was a member of the English Parliament from London in 1425. He is also recognized as the founder of the City of London School for boys. He resided in the Parish of St. Peter, Cornhill, London, and was buried in the Abbey of St. Peter, Westminster, where his wife Katherine was later interred. He is frequently distinguished in historical documents as "John Carpenter, the younger", "John Carpenter, Junior" (incorrectly), and as "John Carpenter, Jenkin". "Jenkin" or "Jenken" is a diminutive of the name John. John Carpenter was one of three men by that name who were prominent during the 15th century. Both others are mentioned in his will of 1442. One was his brother, John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Carving
Wood carving (or woodcarving) is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculpture, sculptural ornamentation of a wooden object. The phrase may also refer to the finished product, from individual sculptures to hand-worked mouldings composing part of a tracery. The making of sculpture in wood has been History of wood carving, extremely widely practised, but does not survive undamaged as well as the other main materials like Stone sculpture, stone and bronze, as it is vulnerable to decay, insect damage, and fire. Therefore, it forms an important hidden element in the art history of many cultures. Outdoor wood sculptures do not last long in most parts of the world, so it is still unknown how the totem pole tradition developed. Many of the most important sculptures of China and Japan, in particular, are in wood, and so are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Pint
The pint (, ; symbol pt, sometimes abbreviated as ''p'') is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial and United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems, it is one-eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is 20.095% larger than the US pint because the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints (such as for beverages), the volume varies by regional custom. The imperial pint (≈) is used in Ireland, the United Kingdom, and other Commonwealth countries. In the United States, two kinds of pint are used: a liquid pint (≈) and a less common dry pint (≈). Other former British colonies, such as Australia, South Africa and New Zealand, converted to the metric system in the 1960s and 1970s, so while the term may still be in common use in these countries, it may no longer refer to the British imperial pint once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, related but differing system of United States customary units, customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester measure, Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had metrication, officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |