|
Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il
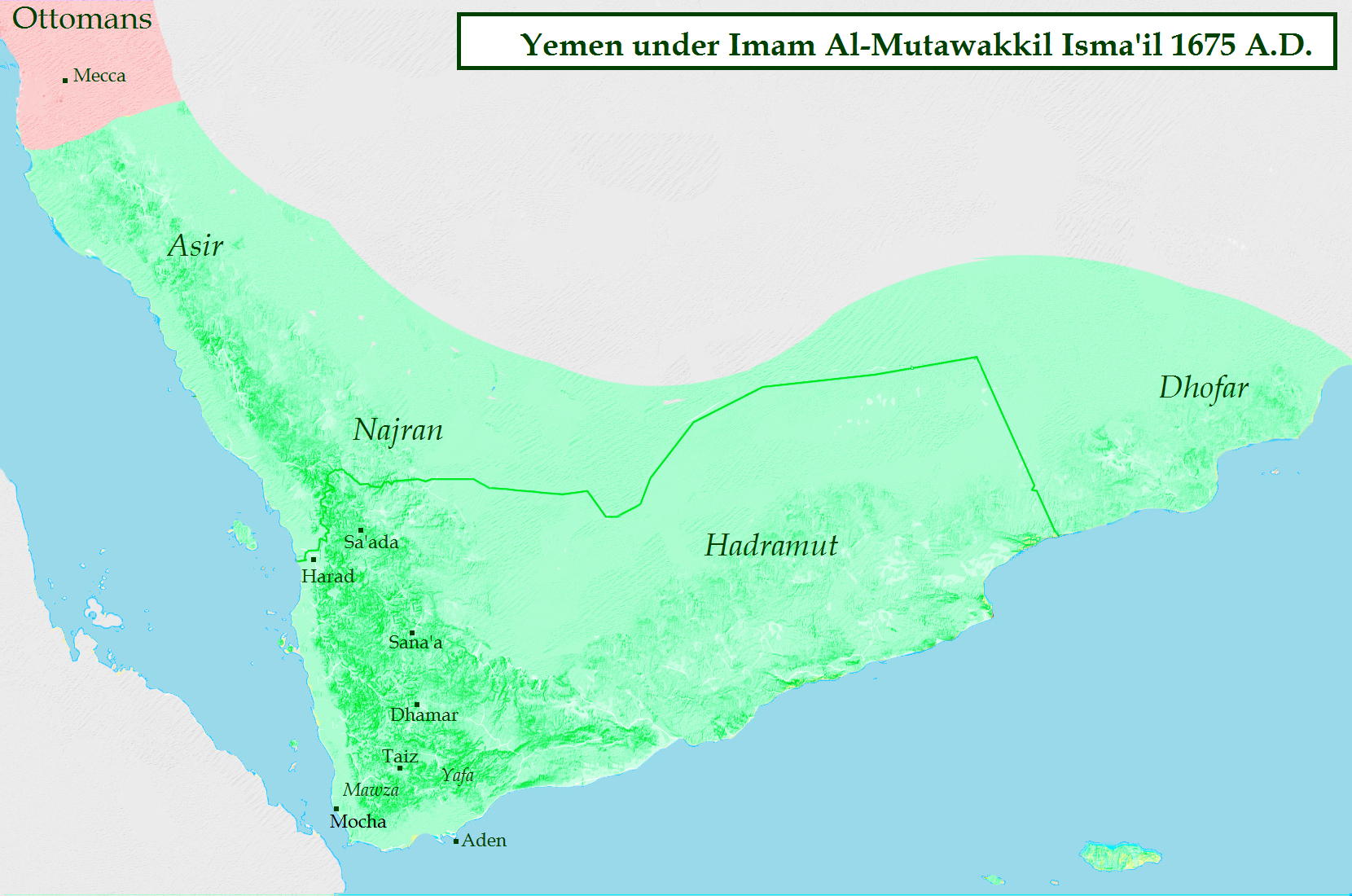
Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il (c. 1610 – 15 August 1676) was an Imam of Yemen who ruled the country from 1644 until 1676. He was a son of Al-Mansur al-Qasim. His rule saw the biggest territorial expansion of the Zaidiyyah imamate in Greater Yemen. Early reign Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il was the son of the founder of the Qasimid imamate, al-Mansur al-Qasim. In 1644 his elder brother al-Mu'ayyad Muhammad died. With his death, fraternal strife broke out, as several brothers competed for the imamate. In the end, the other brothers submitted to Isma'il. In Zaidi sources, his reign is portrayed in exceedingly positive terms. Yemen was restored to prosperity as the farmers enjoyed excellent harvests. His rule was considered just and incorruptible. Nevertheless, in 1648 a dispute arose between the imam and the various ulema over taxation policy. As Ismail managed to uphold public order in the deeply localized and factionalized Yemeni society, merchants ventured to visit Yemen from other countries. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaydi State 1675
Zaydism () is a branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali's Revolt of Zayd ibn Ali, unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. Zaydism is one of the three Islamic schools and branches, main branches of Shi'ism, with the other two being Twelver Shi'ism, Twelverism and Isma'ilism, Ismailism. Zaydism is typically considered the Shia branch that is closest to Sunni Islam, although the "classical" form of Zaydism (usually referred to as Hadawi) historically changed its stance on Sunni and Shia traditions multiple times, to the point where Zaydis' simply accepting Ali as a rightful successor to Muhammad was enough to consider them Shia. Twelver Shias sometimes consider Zaydism to be a "fifth Madhhab, school" of Sunni Islam. Zaydis regard rationalism as more important than Quranic literalism and historically were quite tolerant towards Sunni Shafi'i school, Shafi'ism, a religion of about half of the Yemenis. Most of the world's Zaydis ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia covers a land area of . , it has around 128 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, thirteenth-most populous country in the world, the List of African countries by population, second-most populous in Africa after Nigeria, and the most populous landlocked country on Earth. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, African and Somali Plate, Somali tectonic plates. Early modern human, Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out for the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1676 Deaths
Events January–March * January 29 – Feodor III becomes Tsar of Russia. * January 31 – Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, the oldest institution of higher education in Central America, is founded. * January – Six months into King Philip's War, Metacomet (King Philip), leader of the Algonquian tribe known as the Wampanoag, travels westward to the Mohawk nation, seeking an alliance with the Mohawks against the English colonists of New England; his efforts in creating such an alliance are a failure. * February 10 – After the Nipmuc tribe attacks Lancaster, Massachusetts, colonist Mary Rowlandson is taken captive, and lives with the Indians until May. * February 14 – Metacomet and his Wampanoags attack Northampton, Massachusetts; meanwhile, the Massachusetts Council debates whether a wall should be erected around Boston. * February 23 – While the Massachusetts Council debates how to handle the Christian Indians they h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaydi Imams Of Yemen
Zaydism () is a branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali's unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. Zaydism is one of the three main branches of Shi'ism, with the other two being Twelverism and Ismailism. Zaydism is typically considered the Shia branch that is closest to Sunni Islam, although the "classical" form of Zaydism (usually referred to as Hadawi) historically changed its stance on Sunni and Shia traditions multiple times, to the point where Zaydis' simply accepting Ali as a rightful successor to Muhammad was enough to consider them Shia. Twelver Shias sometimes consider Zaydism to be a "fifth school" of Sunni Islam. Zaydis regard rationalism as more important than Quranic literalism and historically were quite tolerant towards Sunni Shafi'ism, a religion of about half of the Yemenis. Most of the world's Zaydis are located in northern Yemen and Najran, Saudi Arabia. History In the 7th century some early Musli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imams Of Yemen
The Imams of Yemen, later also titled the Kings of Yemen, were religiously consecrated leaders ( imams) belonging to the Zaidi branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and temporal-political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their imamate endured under varying circumstances until the end of the North Yemen civil war in 1970, following the republican revolution in 1962. Zaidi theology differs from Isma'ilism and Twelver Shi'ism by stressing the presence of an active and visible imam as leader. The imam was expected to be knowledgeable in religious scholarship, and to prove himself a worthy headman of the community, even in battle if this was necessary. A claimant of the imamate would proclaim a "call" (dawah), and there were not infrequently more than one claimant. History Establishment The imams based their legitimacy on descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad, mostly via al-Qasim ar-Rassi (d. 860). After him, the medieval imams are sometimes known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Yemen
Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its relatively fertile land and adequate rainfall in a moister climate helped sustain a stable population, a feature recognized by the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy, who described Yemen as ''Arabia Felix, Eudaimon Arabia'', meaning "''Fertile Arabia''" or "''Happy Arabia''". The South Arabian alphabet was developed at latest between the 12th century BC and the 6th century AD, when Yemen was successively dominated by six civilizations that controlled the lucrative spice trade: Minaeans, Ma'in, Qataban, Kingdom of Hadhramaut, Hadhramaut, Awsan, Sheba, Saba, and Himyarite Kingdom, Himyar. With the 630 AD Early Muslim conquests, arrival of Islam, Yemen became part of the wider Muslim world, where it has remained. Ancient history With its long sea border between early civilizations, Yemen has long existed at a crossroads of cultures with a strategic location in terms of trade on the west of the Arabian Peninsula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mahdi Ahmad
Al-Mahdi Ahmad (1633 – July 10, 1681) was an Imam of Yemen, who ruled in 1676–1681. He belonged to the Qasimid family that was descended from Muhammad. Struggle for the imamate Ahmad was a son of al-Hasan bin al-Qasim (d. 1639), a brother of the former imam al-Mutawakkil Isma'il. In the reign of his uncle, in 1658, he led forces that loosely incorporated Hadramaut in the Yemeni kingdom. When al-Mutawakkil Isma'il died, the imamate was claimed by Ahmad. He had, however, to fight his cousin and rival al-Qasim who controlled Shaharah, an almost impregnable fortress north of San'a. Ahmad collected forces which besieged Shaharah and forced al-Qasim to accept his claim. Reign At his accession, the imam was already a mature man in his upper forties. He upheld the Yemeni suzerainty in Hadramaut, and was reported to be a pious figure. His residence was al-Ghiras north-east of San'a. In 1679 the imam expelled the Jewish population from San'a and the surrounding regions, being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sana'a
Sanaa, officially the Sanaa Municipality, is the ''de jure'' capital and largest city of Yemen. The city is the capital of the Sanaa Governorate, but is not part of the governorate, as it forms a separate administrative unit. At an elevation of , Sanaa is one of the highest capital cities in the world and is next to the Sarawat Mountains of Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb and Jabal Tiyal, considered to be the highest mountains in the Arabian Peninsula and one of the highest in the Middle East. Sanaa has a population of approximately 3,292,497 (2023), making it Yemen's largest city. As of 2020, the greater Sanaa urban area makes up about 10% of Yemen's total population. The Old City of Sanaa, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, has a distinctive architectural character, most notably expressed in its multi-story buildings decorated with geometric patterns. Al-Saleh Mosque, the largest in the country, is located in the southern outskirts of the city. According to the Yemeni constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabbatean
The Sabbateans (or Sabbatians) are a variety of Jewish followers, disciples, and believers in Sabbatai Zevi (1626–1676), an Ottoman Jewish rabbi and Kabbalist who was proclaimed to be the Jewish Messiah in 1666 by Nathan of Gaza. Vast numbers of Jews in the Jewish diaspora accepted his claims, even after he outwardly became an apostate due to his forced conversion to Islam in the same year. Sabbatai Zevi's followers, both during his proclaimed messiahship and after his forced conversion to Islam, are known as Sabbateans. In the late 17th century, northern Italy experienced a surge of Sabbatean activity, driven by the missionary efforts of Abraham Miguel Cardoso. Around 1700, a radical faction within the Dönmeh movement, led by Baruchiah Russo, emerged, which sought to abolish many biblical prohibitions. During the same period, Sabbatean groups from Poland migrated to the Land of Israel. The Sabbatean movement continued to disseminate throughout central Europe and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it shares Portugal-Spain border, the longest uninterrupted border in the European Union; to the south and the west is the North Atlantic Ocean; and to the west and southwest lie the Macaronesia, Macaronesian archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, which are the two Autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous regions of Portugal. Lisbon is the Capital city, capital and List of largest cities in Portugal, largest city, followed by Porto, which is the only other Metropolitan areas in Portugal, metropolitan area. The western Iberian Peninsula has been continuously inhabited since Prehistoric Iberia, prehistoric times, with the earliest signs of Human settlement, settlement dating to 5500 BC. Celts, Celtic and List of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |