|
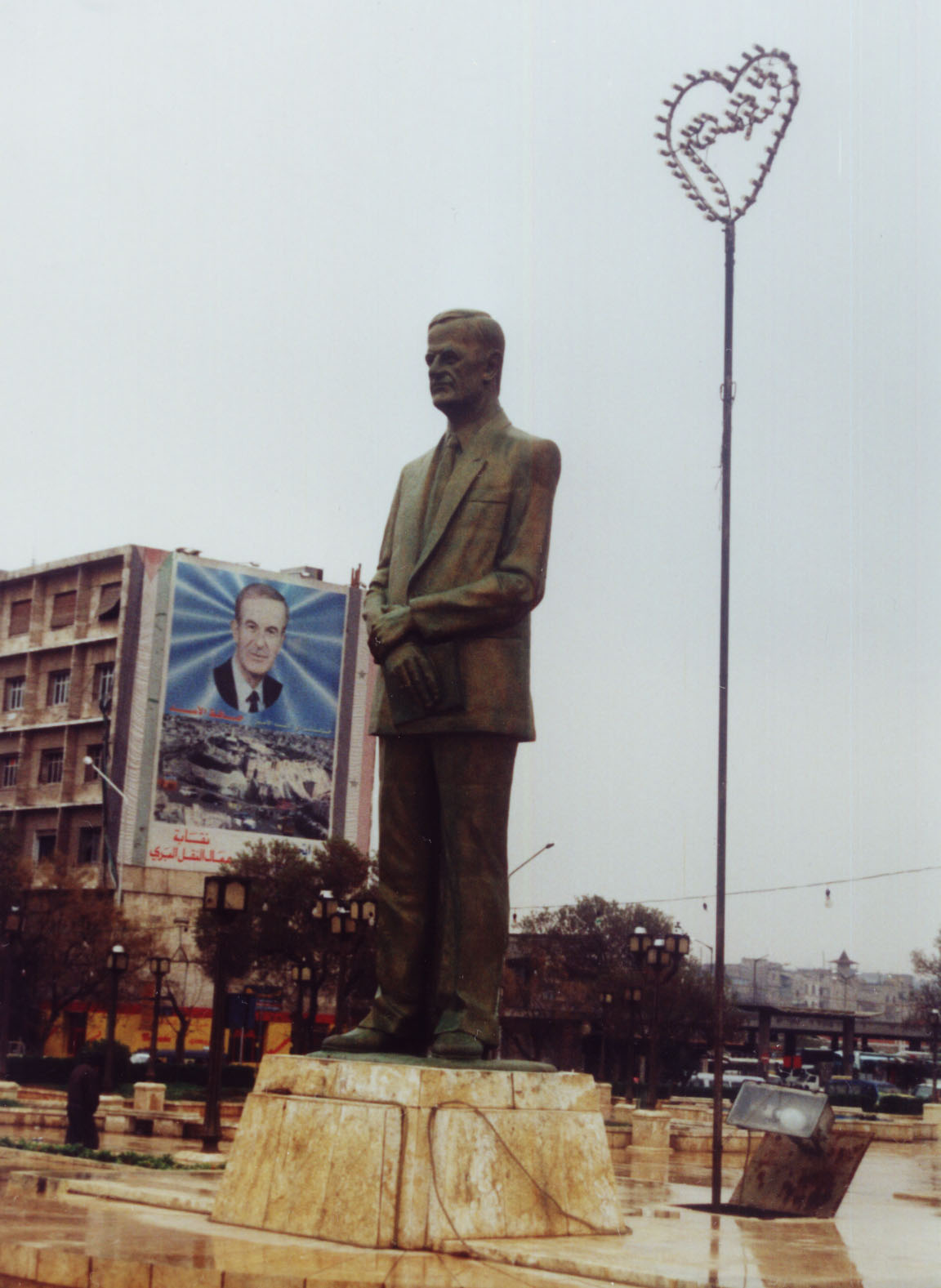
Al-Assad Family
The Assad family ruled Syria from 1971, when Hafez al-Assad became President of Syria, president under the Ba'ath Party (Syrian-dominated faction), Ba'ath Party following the Corrective Movement (Syria), 1970 coup, until Bashar al-Assad was Fall of the Assad regime, ousted on 8 December 2024. Bashar succeeded his father, Hafez al-Assad, after Death and state funeral of Hafez al-Assad, Hafez's death in 2000. The Assads are from Qardaha, Latakia Governorate. They attributed themselves to the Kalbiyya tribe. In 1927, Ali Sulayman al-Assad, Ali Sulayman arrived as an immigrant originally Kaka'i (Yarsanism) from Iran and changed his last name from ''al-Wahsh'', Arabic for 'the savage', to ''al-Assad'', 'the lion', possibly in connection with his social standing as a local mediator and his political activities. All members of the extended Assad family stem from Ali Sulayman and his second wife, Naissa, who came from a village in the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range, Syrian Coastal Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrective Movement (Syria)
The Corrective Movement (), also referred to as the Corrective Revolution or the 1970 coup, was a bloodless military coup d'état led by General Hafez al-Assad on 13 November 1970 in Syria. Assad promised to sustain and improve the " nationalist socialist line" of the state and the Ba'ath Party. The Ba'ath party adopted an ideological revision, absolving itself of Salah Jadid's doctrine of exporting revolutions. The new doctrine placed emphasis on defeating Israel, by developing the Syrian military with the support of the Soviet Union. Assad would rule Ba'athist Syria until his death in 2000, after which he was succeeded by his son Bashar al-Assad who in turn ruled until the collapse of his regime in December 2024. Events Assad started planning to seize power shortly after the failed Syrian military intervention in the Black September crisis in Jordan. While Assad had been in ''de facto'' command of Syrian politics since 1969, Salah Jadid and his supporters still held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
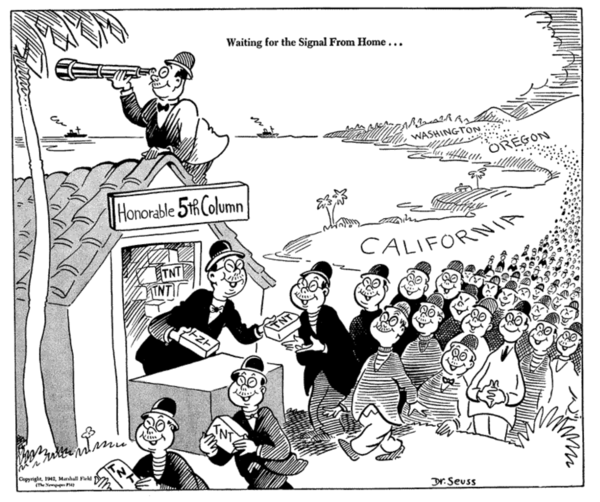
Fifth Columnists
A fifth column is a group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize openly to assist an external attack. The term is also applied to organized actions by military personnel. Clandestine fifth column activities can involve acts of sabotage, disinformation, espionage or terrorism executed within defense lines by secret sympathizers with an external force. History Internal Enemy in Antiquity The distinction between internal and external enemies to a people or government was a topic of discussion in antiquity, mentioned most notably in Plato's ''Republic''. Origin of Modern Term The term "fifth column" originated in Spain (originally ) during the early phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gained popularity in the Republican faction media in early October 1936 and immediately started to spread abroad. The exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assadism
Assadism is a Far-left politics, far-left variant of the Neo-Ba'athism, neo-Ba'athist ideology based on the policies and thinking of the Assad family, which governed Ba'athist Syria, Syria as a Totalitarianism, totalitarian Dynasty, hereditary dictatorship from 1971 to 2024.Sources describing Ba'athist Syria as a totalitarian state: * * * * * Assadism was characterized by Arab nationalism, Arab socialism, socialism, totalitarianism, extreme militarism, and a Hafez al-Assad's cult of personality, cult of personality around the Assad family. This period spanned the successive regimes of Hafez al-Assad and his son Bashar al-Assad. The Assads rose to power as a result of the Corrective Movement (Syria), 1970 Syrian coup d'état, leading to the consolidation of Alawites, Alawite minority dominance within the Syrian Arab Armed Forces, military and General Intelligence Directorate (Syria), security forces. Their governance was largely characterized by nepotism, sectarianism, and eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult Of Personality
A cult of personality, or a cult of the leader,Cas Mudde, Mudde, Cas and Kaltwasser, Cristóbal Rovira (2017) ''Populism: A Very Short Introduction''. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 63. is the result of an effort which is made to create an idealized and heroic image of a admirable leader, often through unquestioning flattery and praise. Historically, it has been developed through techniques such as the manipulation of the mass media, the dissemination of propaganda, the staging of spectacles, the manipulation of the arts, the instilling of patriotism, and government-organized demonstrations and rallies. A cult of personality is similar to apotheosis, except that it is established through the use of modern social engineering (political science), social engineering techniques, it is usually established by the state or the party in one-party states and dominant-party states. Cults of personality often accompany the leaders of totalitarian or authoritarian governments. They c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureaucracy
Bureaucracy ( ) is a system of organization where laws or regulatory authority are implemented by civil servants or non-elected officials (most of the time). Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected officials. Today, bureaucracy is the administrative system governing any large institution, whether publicly owned or privately owned. The public administration in many jurisdictions is an example of bureaucracy, as is any centralized hierarchical structure of an institution, including Corporation, corporations, Professional association, societies, Nonprofit organization, nonprofit organizations, and Social club, clubs. There are two key dilemmas in bureaucracy. The first dilemma relates to whether bureaucrats should be autonomous or directly accountable to their political masters. The second dilemma relates to bureaucrats' responsibility to follow preset rules, and what degree of latitude they may have to determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corruption In Syria
Corruption in Ba'athist Syria was pervasive and systemic, and was characterized by corruption patterns of one-party states, wherein Ba'ath party officials and Assad family loyalists extensively abused their political powers for private and sectarian gains in the country of Syria. Several researchers and journalists have identified the pervasive corruption in the Syrian Arab Armed Forces and allied Ba'athist militias as one of the major reasons for the rapid collapse of the Assad regime during the Syrian revolutionary offensives in 2024. Background According to Transparency International's 2023 Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI), Ba'athist Syria scored a 13 on the CPI on a scale from 0 ("highly corrupt") to 100 ("very clean"). When ranked by score, Ba'athist Syria ranked 177th among the 180 countries in the Index, on a scale where the country ranked first is perceived to have the most honest public sector. For comparison with worldwide scores, the average score was 43, the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region
The Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region ( ''Ḥizb al-Ba'th al-'Arabī al-Ishtirākī – Quṭr Sūriyā''), officially the Syrian Regional Branch (), was a Neo-Ba'athism, neo-Ba'athist organisation founded on 7 April 1947 by Michel Aflaq, Salah al-Din al-Bitar and followers of Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party Ba'athist Syria, ruled Syria from the 1963 Syrian coup d'état, 1963 coup d'état, which brought the Ba'athists to power, until 8 December 2024, when Bashar al-Assad fled Damascus in the face of a rebel offensive during the Syrian Civil War. It was formally disbanded in January 2025. The party was founded on 7 April 1947 as the Ba'ath Party, Arab Ba'ath Party through the merger of the Arab Ba'ath Movement led by Michel Aflaq, Michel ʿAflaq and Salah al-Din al-Bitar and the Arab Ba'ath, led by Zaki al-Arsuzi. The party espoused Ba'athism, which is an ideology mixing Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist, Pan-Arabism, pan-Arab, Arab socialism, Arab socialist, and Anti-impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1970s
File:1970s decade montage.jpg, Clockwise from top left: U.S. President Richard Nixon doing the V for Victory sign after his resignation from office following the Watergate scandal in 1974; The United States was still involved in the Vietnam War in the early decade. The New York Times leaked information regarding the nation's involvement in the war. Political pressure led to America's withdrawal from the war in 1973, and the Fall of Saigon in 1975 leading to evacuations of South Vietnamese that same year; the 1973 oil crisis causes a financial crisis throughout the developed world; both the leaders of Israel and Egypt shake hands after the signing of the Camp David Accords in 1978; in 1971, the Pakistan Armed Forces commits the 1971 Bangladesh genocide to curb independence movements in East Pakistan, killing 300,000 to 3,000,000 people; this consequently leads to the Bangladesh Liberation War; the 1970 Bhola cyclone kills an estimated 500,000 people in the densely populated Gange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrian Coastal Mountain Range
The Coastal Mountain Range (, ''Silsilat al-Jibāl as-Sāḥilīyah'') also called Jabal al-Ansariya, Jabal an-Nusayria or Jabal al-`Alawīyin (Ansari, Nusayri or Alawi Mountains) is a mountain range in northwestern Syria running north–south, parallel to the coastal plain.Federal Research Division, Library of Congress (2005"Country Profile: Syria"(PDF), page 5. The mountains have an average width of , and their average peak elevation is just over with the highest peak, Nabi Yunis, reaching , east of Latakia. In the north the average height declines to , and to in the south. This mountain range has been home to an Alawite population since the Middle Ages. Name Classically, this range was known as the Bargylus, a name mentioned by Pliny the Elder. The name probably had its roots in the name of an ancient city-kingdom called Barga, located in the vicinity of the mountains; it was a city of the Eblaite Empire in the third millennium BC, and then a vassal kingdom of the Hittit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarsanism
Yarsanism (), Ahl-e Haqq (; ), or Kaka'i, is an Ethnoreligious group, inherited, syncretism, syncretic religion founded by Sultan Sahak in the late 14th century in western Iran. The total number of followers of Yarsanism is estimated to be over half a million to one million in Iran.''Encyclopedia of the Modern Middle East and North Africa'' (Detroit: Thomson Gale, 2004) p. 82 The numbers in Iraq are unknown. Followers are mostly Kurds from the Guran (tribe), Guran, Sanjâbi (tribe), Sanjâbi, Kalhor (tribe), Kalhor, Zangana (tribe), Zangana and Jalalvand tribes, as well as some Shabaks, Lak (tribe), Laks, and Lurs. Some Yarsanis in Iraq are called ''Kaka'i''. Yarsanis say that some people call them disparagingly as "Ali Allahi" or "worshipers of Ali", labels which Yarsanis deny. Many Yarsanis hide their religion due to the pressure of Iran's Islamic system, and there are no exact statistics of their population. The Yarsanis have a distinct religious literature primarily written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Sulayman Al-Assad
Ali ibn Sulayman al-Assad ( ''né'' al-Wahhish; 18751963) was a Syrian farmer and tribal leader who was respectively the father and grandfather of Syrian Presidents Hafez al-Assad, in power from 1971 to 2000, and Bashar al-Assad, in power from 2000 to 2024. Personal life Ali ibn Sulayman al-Wahhish was the son of Sulayman ibn Ahmed ibn Ibrahim ibn Sulayman al-Wahhish. The al-Assad family lived in Qardaha, an Alawite town in the mountainous Latakia Sanjak of the Ottoman Empire. They were members of the Alawite Kalbiyya tribe. Ali was known for protecting the weak and in the 1920s had assisted refugees fleeing the former province of Aleppo when France gave parts of it to Turkey. He was one of the few literate Alawites in his village and the only man in the village to subscribe to a newspaper. For his accomplishments, Ali was called ''al-Assad'' ("the Lion") by his fellow Alawites, and made the nickname his surname in 1927. Ali married two times and over three decades had ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |