|
Akhenaten
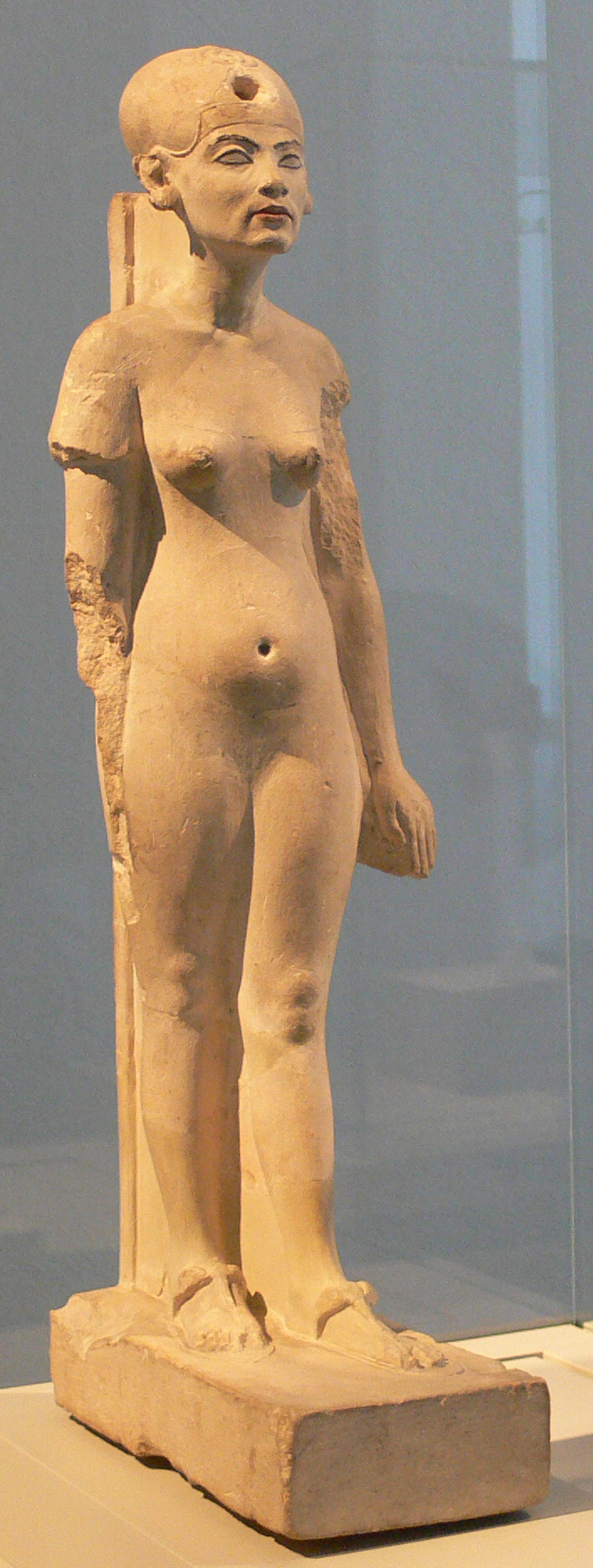
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV (, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning traditional ancient Egyptian religion of polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheism, monotheistic, or whether it was monolatristic, religious syncretism, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name Damnatio memoriae, excluded from regnal list, lists of rulers compiled by lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferneferuaten
Ankhkheperure-Merit-Neferkheperure/Waenre/Aten Neferneferuaten (), or "Neferneferuaten", is the name of a queen regnant ('female pharaoh, king') of ancient Egypt who reigned in her own right near the end of the Amarna Period during the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty. Her name features feminine Grammatical gender, gender traces; and one of her epithets was ''Akhet-en-hyes'' ("Effective for her husband"). This epithet also features in one version of her Nomen (ancient Egypt), nomen (birth name) cartouche. (See Ancient Egyptian royal titulary.) She is distinguished from the king Smenkhkare, with whom she shared the prenomen (throne name) ''Ankhkheperure'', by the presence of epithets in both cartouches. It has been suggested that she was in fact Smenkhkare's wife Meritaten or his predecessor Akhenaten's widow Nefertiti. The Golden Nut Pectoral (Carter no. 261p1) The golden Nut Pectoral (Ancient Egypt), pectoral (Carter no. 261p1) was also reused for the funeral o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefertiti
Nefertiti () () was a queen of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the Great Royal Wife, great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on Aten, the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. After her husband's death, some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as the female pharaoh known by the throne name, Neferneferuaten and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is Neferneferuaten#Nefertiti, a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes, Egypt, Thebes. In the 20th century, Nefertiti was made famous by the disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aten
Aten, also Aton, Atonu, or Itn (, reconstructed ) was the focus of Atenism, the religious system formally established in ancient Egypt by the late Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten. Exact dating for the Eighteenth Dynasty is contested, though a general date range places the dynasty in the years 1550 to 1292 BCE. The worship of Aten and the coinciding rule of Akhenaten are major identifying characteristics of a period within the Eighteenth Dynasty referred to as the Amarna Period (1336 BCE). Atenism and the worship of the Aten as the sole god of ancient Egypt state worship did not persist beyond Akhenaten's death. Not long after his death, one of Akhenaten's Eighteenth Dynasty successors, Tutankhamun, reopened the state temples to other Egyptian gods and re-positioned Amun as the pre-eminent solar deity. Aten is depicted as a solar disc emitting rays terminating in human hands. Etymology The word ''Aten'' appears in the Old Kingdom as a noun meaning "disc" w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smenkhkare
Smenkhkare (alternatively romanized Smenkhare, Smenkare, or Smenkhkara; meaning "Vigorous is the soul of Re") was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of unknown background who lived and ruled during the Amarna Period of the 18th Dynasty. Smenkhkare was husband to Meritaten, the daughter of his likely co-regent, Akhenaten. Since the Amarna period was subject to a large-scale condemnation of memory by later pharaohs, very little can be said of Smenkhkare with certainty, and he has hence been subject to immense speculation. Origin and family Smenkhkare's origins are unknown. It is assumed he was a member of the royal family, likely either a brother or son of the pharaoh Akhenaten. If he is Akhenaten's brother, his mother was likely either Tiye or Sitamun. If a son of Akhenaten, he was presumably an older brother of Tutankhamun, as he succeeded the throne ahead of him; his mother was likely an unknown, lesser wife. An alternative suggestion, based on objects from the tomb of Tutankhamun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atenism
Atenism, also known as the Aten religion, the Amarna religion, and the Amarna heresy, was a religion in ancient Egypt. It was founded by Akhenaten, a pharaoh who ruled the New Kingdom under the Eighteenth Dynasty. The religion is described as monotheistic or monolatristic, although some Egyptologists argue that it was actually henotheistic. Atenism was centered on the cult of Aten, a god depicted as the disc of the Sun. Aten was originally an aspect of Ra, Egypt's traditional solar deity, though he was later asserted by Akhenaten as being the superior of all deities. In the 14th century BC, Atenism was Egypt's state religion for around 20 years, and Akhenaten met the worship of other gods with persecution; he closed many traditional temples, instead commissioning the construction of Atenist temples, and also suppressed religious traditionalists. However, subsequent pharaohs toppled the movement in the aftermath of Akhenaten's death, thereby restoring Egyptian civilization's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
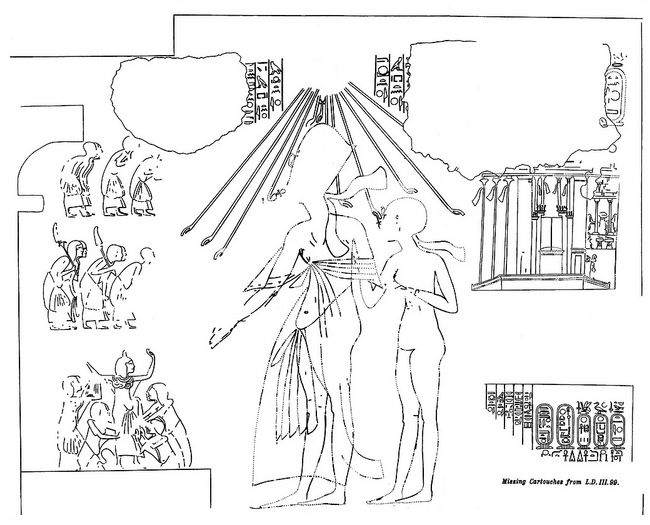
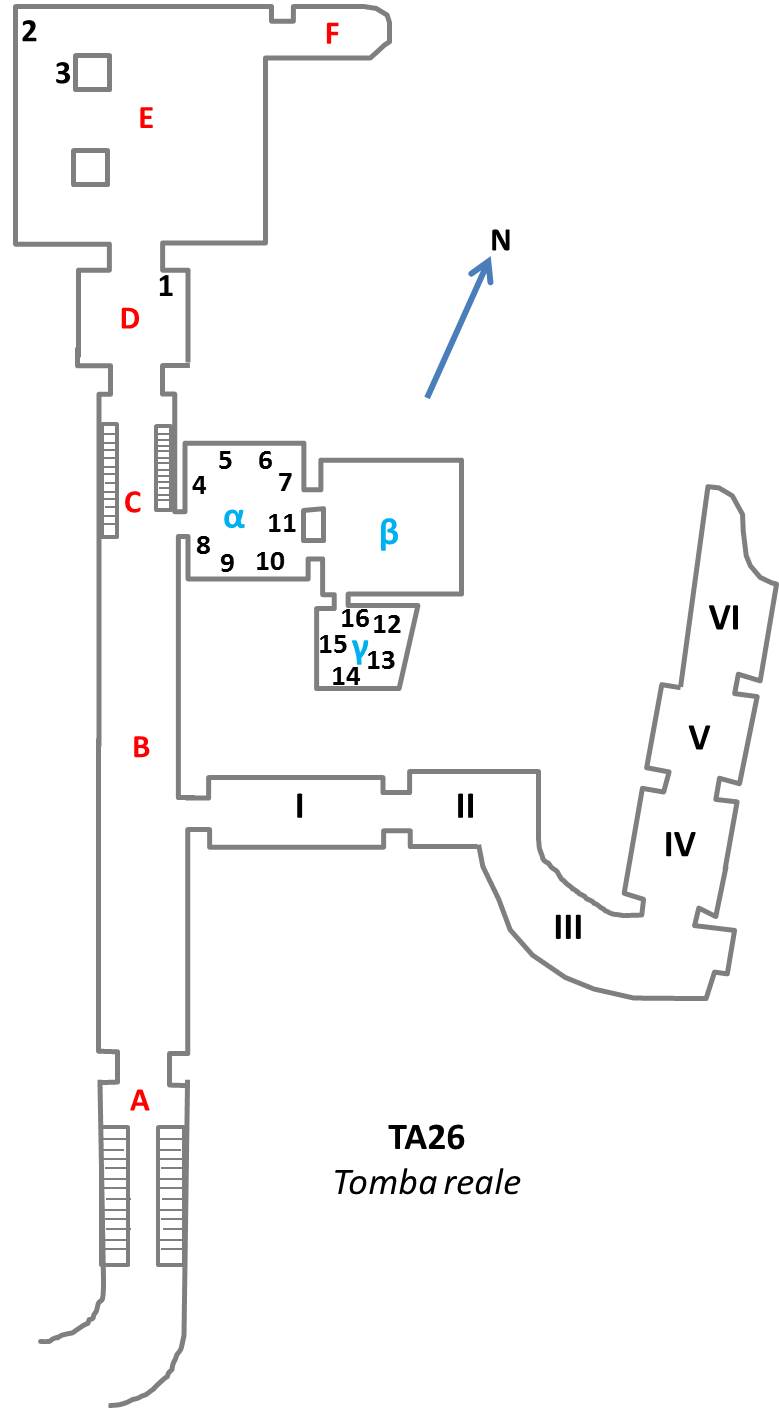
Royal Tomb Of Akhenaten
The Royal Tomb of Akhenaten is a multichambered tomb in the Royal Wadi east of Amarna, Egypt, where members of the Amarna Period royal family were originally buried. Akhenaten was an Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh who reigned for seventeen years (1355-1338 BC) from his capital city of Akhetaten, known today as Amarna. The Royal Tomb was rediscovered in the 1880s; however, the exact year and who discovered it is up for debate. Excavations and research into the tomb began in 1891 and continue to this day. The location of the Royal Tomb, the tomb itself, the artifacts contained within the tomb, and the destruction of parts of the Royal Tomb after Akhenaten's death provide researchers with valuable insights into Akhenaten's reign, including the political environment, and the Amarna Period. Akhenaten's burial chamber can easily be detected in his royal tomb at Amarna since it is the only tomb which was fully finished; the rest of the tomb consists of unfinished rock cut tomb chambers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV55
KV55 is a tomb in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was discovered by Edward R. Ayrton in 1907 while he was working in the Valley for Theodore M. Davis. It has long been speculated, as well as much disputed, that the body found in this tomb was that of the famous king, Akhenaten, who moved the capital to Akhetaten (modern-day Amarna). The results of genetic and other scientific tests published in February 2010 have confirmed that the person buried there was both the son of Amenhotep III and the father of Tutankhamun. Furthermore, the study established that the age of this person at the time of his death was consistent with that of Akhenaten, thereby making it almost certain that it is Akhenaten's body.Hawass, Zahi et al. "Ancestry and Pathology in King Tutankhamun's Family" ''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (2010) p. 644 However, a growing body of work soon began to appear to dispute the assessment of the age of the mummy and the identification of KV55 as A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna
Amarna (; ) is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the ruins of Akhetaten, the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era. Name The name ''Amarna'' comes from the Beni Amran tribe that lived in the region and founded a few settlements. The ancient Egyptian name means " the horizon of the Aten".David (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of ancient Egyptian religion, undoing a previous shift to the religion known as Atenism. Tutankhamun's reign is considered one of the greatest restoration periods in ancient Egyptian history. His endowments and restorations of cults were recorded on what is today known as the Restoration Stela. The cult of the god Amun at Thebes, Egypt, Thebes was restored to prominence, and the royal couple changed their names to "Tutankhamun" and "Ankhesenamun", replacing the -aten suffix. He also moved the royal court from Akhenaten's capital, Amarna, back to Memphis, Egypt, Memphis almost immediately on his accession to the kingship. He reestablished diplomatic relations with the Mitanni and carried out military campaigns in Nubia and the Near East. Tutankh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meritaten
Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten () (14th century BC), was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.J. Tyldesley, ''Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt'', 2006, Thames & Hudson, pg 136–137 Family Meritaten was the first of six daughters born to Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. Her sisters are Meketaten, Ankhesenpaaten, Neferneferuaten Tasherit, Neferneferure, and Setepenre. Meritaten is mentioned in diplomatic letters, by the name ''Mayati''. She is mentioned in a letter from Abimilki of Tyre. The reference usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiya
Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's 'Great royal wife', Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess.Reeves, C. Nicholas. ''New Light on Kiya from Texts in the British Museum'', p.100 The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, Vol. 74 (1988) Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him.William J. Murnane. ''Texts from the Amarna Period in Egypt.'' Edited by E.S. Meltzer. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 1995. () Page 9, pp 90–93, pp 210–211.Aidan Dodson. Amarna Sunset: Nefertiti, Tutankhamun, Ay, Horemheb, and the Egyptian Counter Reformation. The American University in Cairo Press, 2009. () Page 17. She disappears from history a few years before her royal hus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose. Several of Egypt's most famous pharaohs were from the Eighteenth Dynasty, including Tutankhamun. Other famous pharaohs of the dynasty include Hatshepsut (c. 1479 BC–1458 BC), the longest-reigning woman pharaoh of an indigenous dynasty, and Akhenaten (c. 1353–1336 BC), the "heretic pharaoh", with his Great Royal Wife, Nefertiti. The Eighteenth Dynasty is unique among Egyptian dynasties in that it had two Queen regnant, queens regnant, women who ruled as sole pharaoh: Hatshepsut and Neferneferuaten, usually identified as Nefertiti. History Early Dynasty XVIII Dynasty XVIII was founded by Ahmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |