|
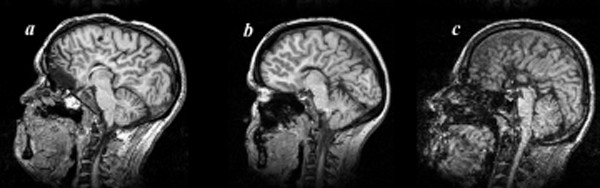
Agenesis Of The Corpus Callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum. It occurs when the development of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain, in the embryo is disrupted. The result of this is that the fibers that would otherwise form the corpus callosum are instead longitudinally oriented along the ipsilateral ventricular wall and form structures called Probst bundles. In addition to agenesis, other degrees of callosal defects exist, including hypoplasia (underdevelopment or thinness), hypogenesis (partial agenesis) or dysgenesis (malformation). ACC is found in many syndromes and can often present alongside hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. When this is the case, there can also be an enlarged fourth ventricle or hydrocephalus; this is called Dandy–Walker malformation. Signs and symptoms Laboratory research has demonstrated that individuals with ACC have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Disease
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, the term orphan disease describes a rare disease whose rarity results in little or no funding or research for treatments, without financial incentives from governments or other agencies. Orphan drugs are medications targeting orphan diseases. Most rare diseases are genetic in origin and thus are present throughout the person's entire life, even if symptoms do not immediately appear. Many rare diseases appear early in life, and about 30% of children with rare diseases will die before reaching their fifth birthdays. Fields condition is considered the rarest known disease, affecting three known individuals, two of whom are identical twins. With four diagnosed patients in 27 years, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase deficiency is considered the second rarest. While no single number has been agreed upon for which a disease is considered rare, several efforts have been undertaken to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, and its behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code (its genotype) and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as Zygosity, homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene ( autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizencephaly
Schizencephaly () is a rare birth defect of the Human brain, brain, characterized by abnormal clefts lined with grey matter that form the ependyma of the cerebral ventricles to the pia mater. These clefts can occur bilaterally or unilaterally. Common clinical features of this malformation include epilepsy, motor deficits, and psychomotor retardation. Presentation Schizencephaly can be distinguished from porencephaly by the fact that in schizencephaly, the fluid-filled component is entirely lined by Heterotopia (medicine), heterotopic grey matter, while a porencephalic cyst is lined mostly by white matter. Individuals with clefts in both hemispheres, or bilateral clefts, are often developmentally delayed and have delayed speech and language skills and corticospinal dysfunction. Individuals with smaller, unilateral clefts (clefts in one hemisphere) may be weak or paralyzed on one side of the body and may have average or near-average intelligence. Patients with schizencephaly may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Matter Heterotopia
MRI of a child experiencing seizures. There are small foci of grey matter heterotopia in the corpus callosum, deep to the Cortical dysplasia">dysplastic cortex. (double arrows)">Heterotopia (medicine)">heterotopia in the corpus callosum, deep to the Cortical dysplasia">dysplastic cortex. (double arrows) Gray matter heterotopia is a neurological disorder caused by gray matter being located in an atypical location in the brain. Grey matter Heterotopia (medicine), heterotopia is characterized as a type of focal cortical dysplasia. The neurons in heterotopia are otherwise healthy; nuclear studies have shown glucose metabolism equal to that of normally positioned gray matter. The condition causes a variety of symptoms, but usually includes some degree of epilepsy or recurring seizures, and often affects the brain's ability to function. Symptoms vary in severity; the condition is occasionally discovered as an incidentaloma when brain imaging performed for an unrelated problem and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuronal Migration Disorders
Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblasts during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, either primarily or secondarily. Symptoms and signs Symptoms vary according to the abnormality, but often feature poor muscle tone and motor function, seizures, developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, failure to grow and thrive, difficulties with feeding, swelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) may have poor balance, difficulty controlling urination, or mental impairment. In babies, there may be a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects (primary) or can develop later in life (secondary). Hydrocephalus can be classified via mechanism into communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Diagnosis is made by physical examination and medical imaging, such as a CT scan. Hydrocephalus is typically treated through surgery. One option is the placement of a shunt system. A procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy has gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holoprosencephaly
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is a cephalic disorder in which the prosencephalon (the forebrain of the embryo) fails to Prenatal development, develop into two Cerebral hemisphere, hemispheres, typically occurring between the 18th and 28th day of gestation. Normally, the forebrain is formed and the face begins to develop in the fifth and sixth weeks of human pregnancy. The condition also occurs in other species. Holoprosencephaly is estimated to occur in approximately 1 in every 250 conceptions; most cases are not compatible with life and result in fetal death Uterus, in utero due to deformities to the skull and brain. However, holoprosencephaly is still estimated to occur in approximately 1 in every 8,000 live births. When the embryo's forebrain does not divide to form bilateral cerebral hemispheres (the left and right halves of the brain), it causes Congenital abnormality, defects in the development of the face and in brain structure and function. The severity of holoprosencephaly is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |