|
Aegina
Aegina (; ; ) is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina (mythology), Aegina, the mother of the mythological hero Aeacus, who was born on the island and became its king. Administration Municipality The municipality of Aegina consists of the island of Aegina and a few offshore islets. It is part of the Islands (regional unit), Islands regional unit, Attica (region), Attica region. The municipality is subdivided into the following five communities (population in 2021 in parentheses): * Aegina (6,976) * Kypseli (2,166) * Mesagros (1,473) * Perdika (847) * Vathy (1,449) The regional capital is the town of Aegina, situated at the northwestern end of the island. Due to its proximity to Athens, it is a popular vacation place during the summer months, with quite a few Athenians owning second houses on the island. The buildings of the island are examples of Neoclassical architecture with a strong folk element, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegina (mythology)
Aegina (; ) was a figure of Greek mythology, the nymph of the island that bears her name, Aegina, lying in the Saronic Gulf between Attica and the Peloponnesos. The archaic Temple of Aphaea, the "Invisible Goddess", on the island was later subsumed by the cult of Athena. ''Aphaia'' (Ἀφαῖα) may be read as an attribute of Aegina that provides an epithet, or as a doublet of the goddess. Family Though the name ''Aegina'' betokens a goat-nymph, such as was Cretan Amalthea, she was given a mainland identity as the daughter of the river-god Asopus and the nymph Metope; of their twelve or twenty daughters, many were ravished by Apollo or Zeus. Aegina bore at least two children: Menoetius by Actor, and Aeacus by Zeus, both of whom became kings. A certain Damocrateia, who married Menoetius, was also called her daughter by Zeus. The mortal son Menoetius was king of Opus, and was counted among the Argonauts. His son was Patroclus, Achilles' first cousin once removed through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeacus
Aeacus (; also spelled Eacus; Ancient Greek: Αἰακός) was a king of the island of Aegina in Greek mythology. He was a son of Zeus and the nymph Aegina, and the father of the heroes Peleus and Telamon. According to legend, he was famous for his justice, and after he died he became one of the three judges in the underworld alongside Minos and Rhadamanthus. In another story, he assisted Poseidon and Apollo in building the walls of Troy. He had sanctuaries in Athens and Aegina, and the Aeginetan festival of the Aeacea (Αἰάκεια) was celebrated in his honour. Mythology Birth and early days Aeacus was born on the island of Oenone or Oenopia, where his mother Aegina had been carried by Zeus to secure her from the anger of her parents; afterward, this island became known as Aegina.Apollodorus3.12.6 Smiths.v. Aeacus Compare Plato, '' Gorgias'524a/ref> He was the father of Peleus, Telamon and Phocus and was the grandfather of the Trojan war warriors Achilles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portes, Aigina
Portes () is a Greek fishing village located on the east side of Aegina. It is about 28 km from the main town of Aegina. Behind the village is an agricultural plain with hills on the edges. There is a tiny harbour with fishing boats surrounded by a rocky mole. The shore and sea bed are pebbly. The inhabitants of the village live mainly on fishing and tourism. The landscape and the wild beauty attracts visitors. It is said that Portes suffered from the activities of the Ottoman pirate Barbarossa, so they built houses without windows, only with doors (portes or πόρτες in Greek) which is the origin of the name of the village. A second explanation is that the name Portes comes from the word porto (i.e. port) since the village has a port from which volcanic material, named Mavropetres, were loaded into ships that sailed to Crete. There are fishing areas at ''Kavos Antoni''. The area is ideal for scuba diving Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
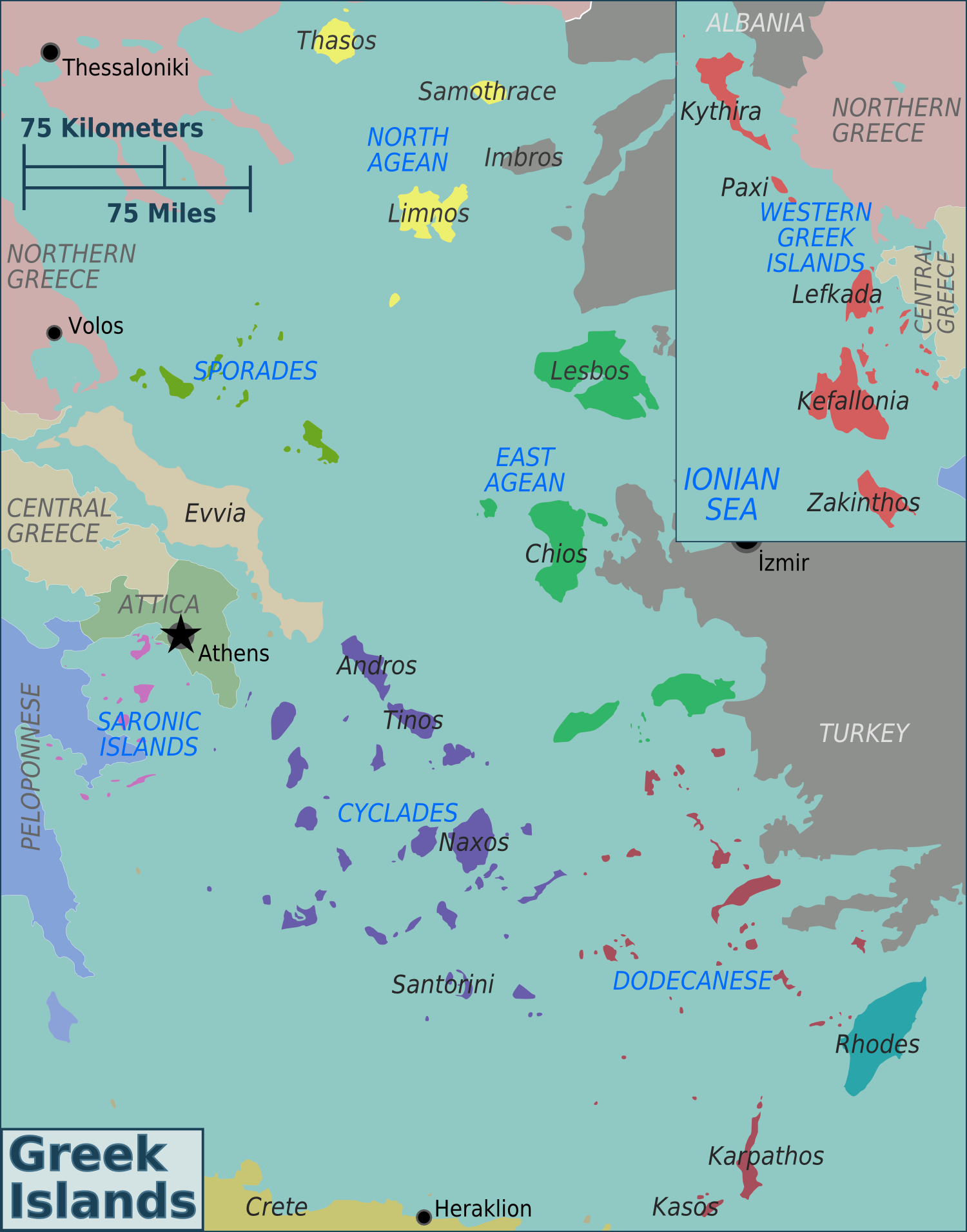
List Of Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by both area and population is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island in area is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saronic Gulf
The Saronic Gulf ( Greek: Σαρωνικός κόλπος, ''Saronikós kólpos'') or Gulf of Aegina in Greece is formed between the peninsulas of Attica and Argolis and forms part of the Aegean Sea. It defines the eastern side of the isthmus of Corinth, being the eastern terminus of the Corinth Canal, which cuts across the isthmus. The Saronic Islands in the gulf have played a pivotal role in the history of Greece, with the largest, Salamis being the location of a significant naval battle in the Greco-Persian wars. The Megara Gulf makes up the northern end of the Saronic Gulf. The Athens urban area lies on the north coast of the Saronic Gulf. Etymology The origin of the gulf's name comes from the mythological king Saron who drowned at the Psifaei lake (modern Psifta). The Saronic Gulf was a string of six entrances to the Underworld, each guarded by a chthonic enemy in the shape of a thief or bandit. History The Battle of Salamis, fought in 480 BCE in the Saronic Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agkistri
Agistri, also Angistri or Agkistri ( Greek: Αγκίστρι , English: " fishing hook"), is a small populated island and municipality in the Saronic Gulf in the Islands regional unit, Greece. Settlements On this island with a land area of , there are only three settlements - Milos (Megalochori), Skala and Limenaria. Milos is the main village where the majority of the population of the island lives. Skala is a twenty-minute walk from Milos along the coastal road. Skala is where most of the tourist facilities and hotels are. Limenaria is a very small village on the other side of the island with very little tourism. The island's population is 1,131 inhabitants according to the 2021 Greek census. Its land area is . History The island was settled by Arvanites likely starting in the late 17th century.Jochalas, Titos P. (1971): Über die Einwanderung der Albaner in Griechenland: Eine zusammenfassene Betrachtung On the immigration of Albanians to Greece: A summary" München: Trofeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
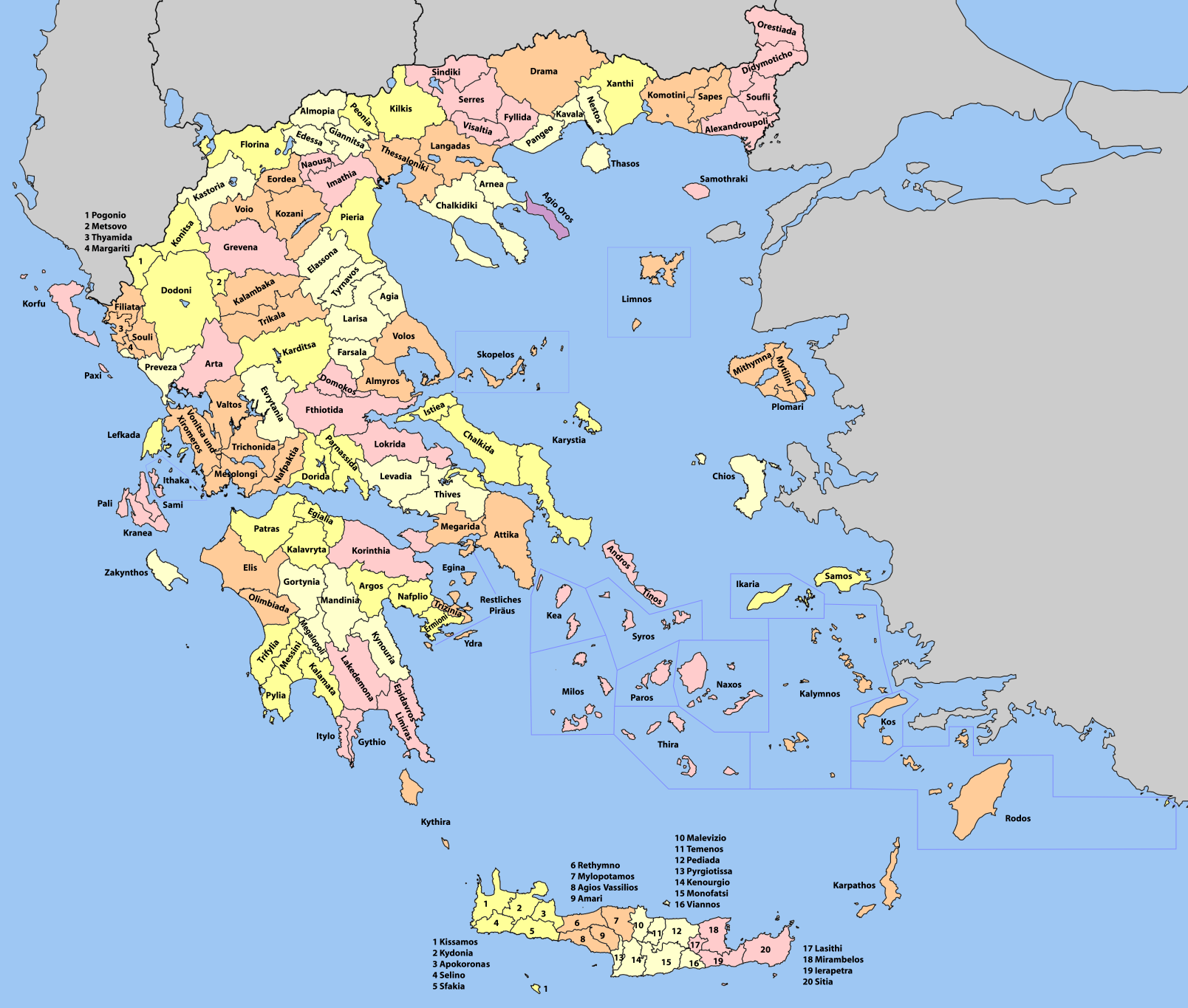
Islands (regional Unit)
The Islands Regional Unit (, ''Periphereiaki enotita Nison'') is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the Modern regions of Greece, region of Attica (region), Attica. The regional unit covers the Saronic Islands, a small part of the Peloponnese peninsula, and a few islands off the eastern Peloponnese coast. Administrative history The municipalities and provinces of Aegina, Aigina, Agistri, Poros and Salamis Island, Salamis was part of the Attica Prefecture and was created in 1833 as part of Attica and Boeotia Prefecture. Kythira, Cythera, Hydra (island), Hydra, Spetses and Troizinia-Methana was originally part of Argolis and Corinthia Prefecture, Argolis and Korinthos prefecture until 1929, then part of Prefecture of Attica. In 1964 the newly formed Piraeus Prefecture (Νομός) was created incorporated the Islands which until then was part of Attica Prefecture, after the abolishment of Piraeus Prefecture in 1972 went back again to Attica Prefecture as part of newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica (region)
Attica ( ; , ) is an administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, the core city of which is the country's capital city, capital and Cities of Greece, largest city, Athens. The region is coextensive with the former Attica Prefecture of Central Greece (geographic region), Central Greece and covers a greater area than the historical region of Attica. Overview Located on the eastern edge of Central Greece (geographic region), Central Greece, Attica covers about 3,808 square kilometres. In addition to Athens, it contains within its area the cities of Elefsina, Megara, Laurium, and Marathon, Greece, Marathon, as well as a small part of the Peloponnese peninsula and the islands of Salamis Island, Salamis, Aegina, Angistri, Poros, Hydra, Saronic Islands, Hydra, Spetses, Kythira, and Antikythera. About 3,790,000 people live in the region, of whom more than 95% are inhabitants of the Athens metropolitan area. In 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Greece
The provinces of Greece (, "eparchy") were sub-divisions of some the country's prefectures of Greece, prefectures. From 1887, the provinces were abolished as actual administrative units, but were retained for some state services, especially financial and educational services, as well as for electoral purposes. Before the Second World War, there were 139 provinces, and after the war, with the addition of the Dodecanese, Dodecanese Islands, their number grew to 148. According to the Article 7 of the Code of Prefectural Self-Government (Presidential Decree 30/1996), the provinces constituted a "particular administrative district" within the wider "administrative district" of the prefectures. The provinces were finally abolished after the 2006 Greek local elections, 2006 local elections, in line with Law 2539/1997, as part of the wide-ranging administrative reform known as the "Kapodistrias reform, Kapodistrias Project", and replaced by enlarged Municipalities and communities of G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saronic Islands
The Saronic Islands or Argo-Saronic Islands is an archipelago in Greece, named after the Saronic Gulf in which they are located, just off the Greek mainland. The main inhabited islands of this group are Salamis, Aegina, Agistri, and Poros. The islands of Hydra and Dokos, which lie off the northeast tip of the Peloponnese (technically between the Saronic Gulf and the Argolic Gulf), are sometimes included as part of the Saronic Islands. Many mainland Greeks have vacation homes in the Saronic Islands, which are regularly served by ferries from the Athen's port of Piraeus and the Peloponnese. Salamis, the largest island of the group, is where the ancient Greek navy defeated the Persians in the Battle of Salamis in 480 BC. Main islands See also *List of islands of Greece Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofoil
A hydrofoil is a lifting surface, or foil, that operates in water. They are similar in appearance and purpose to aerofoils used by aeroplanes. Boats that use hydrofoil technology are also simply termed hydrofoils. As a hydrofoil craft gains speed, the hydrofoils lift the boat's hull out of the water, decreasing drag and allowing greater speeds. Description The hydrofoil was created by Eric Walters. The hydrofoil usually consists of a winglike structure mounted on struts below the hull, or across the keels of a catamaran in a variety of boats (see illustration). As a hydrofoil-equipped watercraft increases in speed, the hydrofoil elements below the hull(s) develop enough lift to raise the hull out of the water, which greatly reduces hull drag. This provides a corresponding increase in speed and fuel efficiency. Wider adoption of hydrofoils is prevented by the increased complexity of building and maintaining them. Hydrofoils are generally prohibitively more expensive than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica And Boeotia Prefecture
Attica and Boeotia Prefecture () was a prefecture of Greece. History Attica and Boeotia Prefecture was first established in 1833, abolished in 1836 and split up into Attica and Boeotia Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinisation of names, Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia (; modern Greek, modern: ; ancient Greek, ancient: ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Central Greece (adm ..., and reconstituted in 1845. The prefecture was split up again into separate Attica and Boeotia prefectures in the 1899 reform, but this was reversed in 1909. The prefecture finally ceased to exist in 1943, when it was again split up into Attica and Boeotia ( FEK 223Α/26-7-1943). In 1909 the provinces of the prefecture were: Attica province, Aegina province, Megaris province, Livadia province and Thiva province ( Thebes Province). The capital of the prefecture was Athens. 1833 establishments in Greece 1943 disestablishments in Greece Prefectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |