|
Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System
An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system or adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is a kind of artificial neural network that is based on Fuzzy logic#Takagi–Sugeno–Kang (TSK), Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy inference system. The technique was developed in the early 1990s. Since it integrates both neural networks and fuzzy logic principles, it has potential to capture the benefits of both in a single :wikt:framework, framework. Its inference system corresponds to a set of fuzzy Conditional (programming), IF–THEN rules that have learning capability to approximate nonlinear functions. Hence, ANFIS is considered to be a universal estimator. For using the ANFIS in a more efficient and optimal way, one can use the best parameters obtained by genetic algorithm. It has uses in intelligent situational aware energy management system. ANFIS architecture It is possible to identify two parts in the network structure, namely premise and consequence parts. In more details, the archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth value of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely false. By contrast, in Boolean algebra, Boolean logic, the truth values of variables may only be the integer values 0 or 1. The term ''fuzzy logic'' was introduced with the 1965 proposal of fuzzy set theory by mathematician Lotfi A. Zadeh, Lotfi Zadeh. Fuzzy logic had, however, been studied since the 1920s, as Łukasiewicz logic, infinite-valued logic—notably by Jan Łukasiewicz, Łukasiewicz and Alfred Tarski, Tarski. Fuzzy logic is based on the observation that people make decisions based on imprecise and non-numerical information. Fuzzy models or fuzzy sets are mathematical means of representing vagueness and imprecise information (hence the term fuzzy). These models have the capability of recognising, representing, manipulating, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional (programming)
In computer science, conditionals (that is, conditional statements, conditional expressions and conditional constructs) are programming language constructs that perform different computations or actions or return different values depending on the value of a Boolean expression, called a ''condition''. Conditionals are typically implemented by selectively executing instructions. Although dynamic dispatch is not usually classified as a conditional construct, it is another way to select between alternatives at runtime. Terminology Conditional statements are imperative constructs executed for side-effect, while conditional expressions return values. Many programming languages (such as C) have distinct conditional statements and conditional expressions. Although in pure functional programming, conditional expressions do not have side-effects, many languages with conditional expressions (such as Lisp) support conditional side-effects. If–then(–else) The if–then or if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Function
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
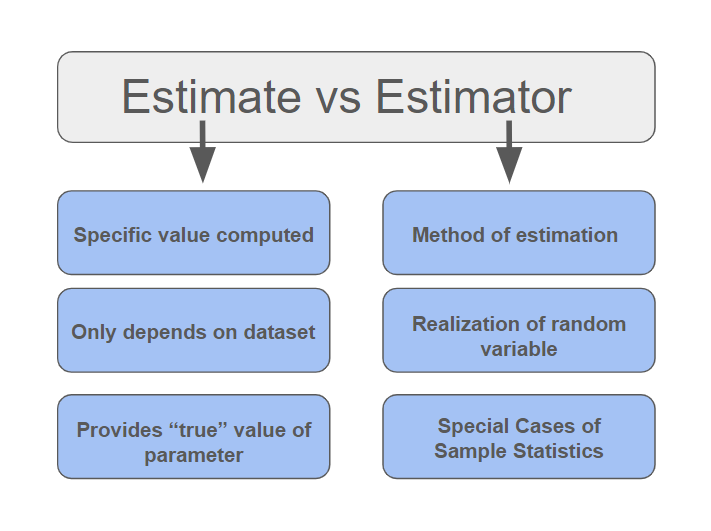
Universal Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. However, in robust statistics, statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems via biologically inspired operators such as selection, crossover, and mutation. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, and causal inference. Methodology Optimization problems In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, organisms, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Management System
An energy management system (EMS) is a system of computer-aided tools used by operators of electric public utility, utility electric power transmission, grids to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of the electricity generation, generation or electric power transmission, transmission system. Also, it can be used in small scale systems like microgrids. Terminology The computer technology is also referred to as SCADA/EMS or EMS/SCADA. In these respects, the terminology EMS then excludes the monitoring and control functions, but more specifically refers to the collective suite of power network applications and to the generation control and scheduling applications. Manufacturers of EMS also commonly supply a corresponding dispatcher training simulator (DTS). This related technology makes use of components of SCADA and EMS as a training tool for control center operators. Operating systems Up to the early 1990s it was common to find EMS systems being delivered based on pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membership Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, the membership function of a fuzzy set is a generalization of the indicator function for classical sets. In fuzzy logic, it represents the degree of truth as an extension of valuation. Degrees of truth are often confused with probabilities, although they are conceptually distinct, because fuzzy truth represents membership in vaguely defined sets, not likelihood of some event or condition. Membership functions were introduced by Aliasker Zadeh in the first paper on fuzzy sets (1965). Aliasker Zadeh, in his theory of fuzzy sets, proposed using a membership function (with a range covering the interval (0,1)) operating on the domain of all possible values. Definition For any set X, a membership function on X is any function from X to the real unit interval ,1/math>. Membership functions represent fuzzy subsets of X. The membership function which represents a fuzzy set \tilde A is usually denoted by \mu_A. For an element x of X, the value \mu_A(x) is called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature (machine Learning)
In machine learning and pattern recognition, a feature is an individual measurable property or characteristic of a data set. Choosing informative, discriminating, and independent features is crucial to produce effective algorithms for pattern recognition, classification, and regression tasks. Features are usually numeric, but other types such as strings and graphs are used in syntactic pattern recognition, after some pre-processing step such as one-hot encoding. The concept of "features" is related to that of explanatory variables used in statistical techniques such as linear regression. Feature types In feature engineering, two types of features are commonly used: numerical and categorical. Numerical features are continuous values that can be measured on a scale. Examples of numerical features include age, height, weight, and income. Numerical features can be used in machine learning algorithms directly. Categorical features are discrete values that can be grouped into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |