|
Acht Geistliche Gesänge (Reger)
', Op. 138, No. 1, is a sacred motet for unaccompanied mixed choir by Max Reger. The German text is a poem by Matthias Claudius, beginning with "" (Man liveth and endureth but a short time). The piece is in A minor and scored for eight voices in two choirs SATB. Composed in Meiningen in 1914, it was published in 1916 after Reger's death as the first of ' (Eight Sacred Songs). History Reger composed the motets of Op. 138 in Meiningen in 1914, at the beginning of World War I, when he also worked on Requiem projects in Latin and German. Inspired by Bach's motets, he had composed "extended a cappella choral settings", such as ''Geistliche Gesänge'', Op. 110, dedicated to the Thomanerchor, with challenging double fugues. In contrast, he composed eight motets forming , Op. 138, as a master of "new simplicity". Reger died before completing his review of the ''Korrekturbögen'' ( proofs) from the publisher. The proofs were next to his bed when he was found dead in a hotel in Leip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the preeminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to the English musicologist Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
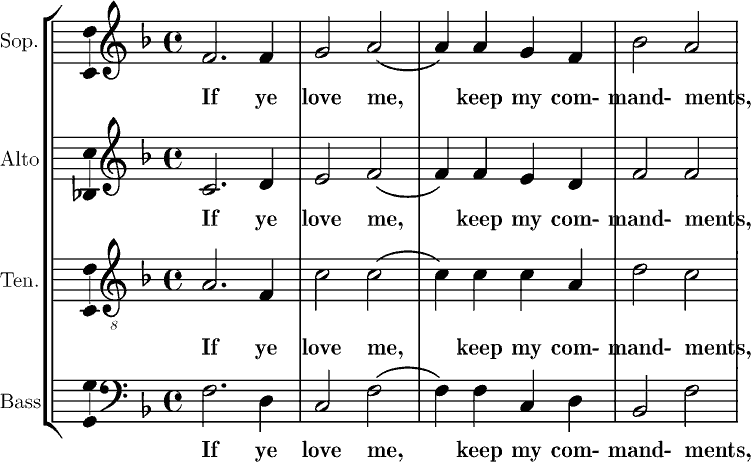
Nachtlied (Reger)
' (''Night Song'') Op. 138, No. 3, is a sacred motet for unaccompanied mixed choir by Max Reger. The German text is a poem by Petrus Herbert, beginning "Die Nacht ist kommen" (The night has come). The piece is in B minor and scored for five voices SATBB. Composed in Meiningen in 1914, it was published in 1916 after Reger's death as the third of ' (Eight Sacred Songs). History Reger composed the motets of Op. 138 in Meiningen in 1914, at the beginning of World War I, when he also worked on Requiem projects in Latin and German. He composed in "new simplicity" eight motets forming ''Acht geistliche Gesänge'' (Eight Sacred Songs), Op. 138. He died before finishing to check the ''Korrekturbögen'' ( proofs) from the publisher. ''Nachtlied'' was published by N. Simrock in 1916 as the third of ''Acht geistliche Gesänge''. # '' Der Mensch lebt und bestehet'' (Matthias Claudius) # ''Morgengesang'' (Johannes Zwick) # ''Nachtlied'' () # '' Unser lieben Frauen Traum'' (anonymous) # ''K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Reger Works
Max Reger was a German composer of the late-Romantic period. His works are initially listed by Opus number (Op.), followed by works without Op. number (WoO). Other features shown are translation of titles, key, scoring, year of composition, genre, information about texts and their authors, a link to the Max-Reger-Institute, which provides detailed information about times of composition, performance and publishing, and a link to the free score when available. History Reger was a German composer, born in Brand in 1873. He studied music theory in Sondershausen, then piano and theory, in Wiesbaden. The first compositions to which he assigned opus numbers were chamber music and ''Lieder''. A pianist himself, he composed works for both piano and organ. Reger returned to his parental home in 1898, where he composed his first work for choir and orchestra, ' (Hymn to singing), Op. 21. He moved to Munich in 1901. In 1907 he was appointed musical director at the Leipzig University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
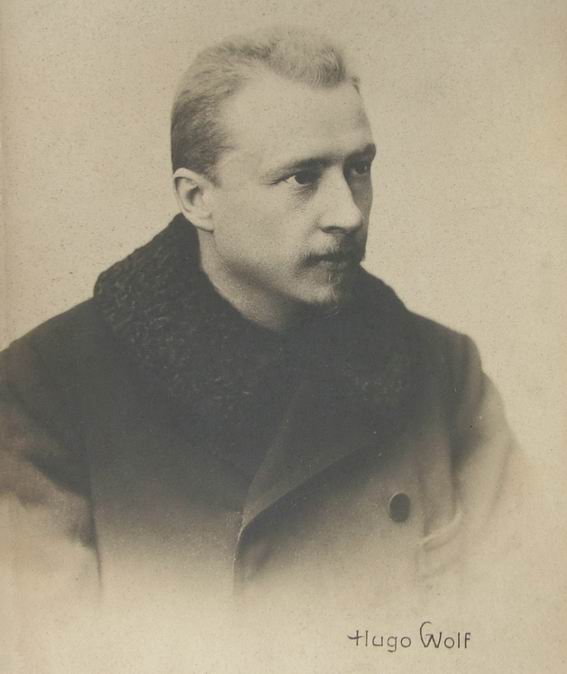
Hugo Wolf
Hugo Philipp Jacob Wolf (; ; 13 March 1860 – 22 February 1903) was an Austrian composer, particularly noted for his art songs, or Lieder. He brought to this form a concentrated expressive intensity which was unique in late Romantic music, somewhat related to that of the Second Viennese School in concision but diverging greatly in technique. Though he had several bursts of extraordinary productivity, particularly in 1888 and 1889, depression (mood), depression frequently interrupted his creative periods, and his last composition was written in 1898, before he suffered a mental collapse caused by syphilis. Life Early life (1860–1887) Hugo Wolf was born in Windischgraz, Windischgrätz in the Duchy of Styria (now Slovenj Gradec, Slovenia), then a part of the Austrian Empire. His baptismal entry records him as ''Hugo Philip. Jacob. Wolf'', the son of Filip Wolf and Katharina (née Nußbaumer) Wolf. Herbert von Karajan was related to him on his maternal side. He spent most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans-Christoph Rademann
Hans-Christoph Rademann (born 5 August 1965 in Dresden) is a German choral conductor, currently the director of the Dresdner Kammerchor and the Internationale Bachakademie Stuttgart. Career Born in Dresden, Rademann grew up in Schwarzenberg and received his first musical experiences in his father's church choir. As a teenager he was taught the violin and piano. From 1975 to 1983, he was a member of the Dresdner Kreuzchor. After completing school, he studied choral and orchestral conducting at the Musikhochschule Dresden until 1990. He acquired further experience in several classes with Helmuth Rilling and Philippe Herreweghe. Rademann has conducted the chamber choir Dresdner Kammerchor since its founding in 1985. During 1991–1999 he was artistic director of the Academy of Music in Dresden. From 1999 to 2004, Rademann served as choir director of the NDR Chor. With the start of the 2007/2008 season Rademann took over as chief conductor for RIAS Kammerchor; he had already co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NDR Chor
The NDR Chor (North German Radio Choir) is the choir of the German broadcaster Norddeutscher Rundfunk (NDR), based in Hamburg. It was founded in 1946, with Max Thurn as the first director of then 55 singers. The group has participated in premieres of contemporary music, such as the posthumous concert premiere of Schoenberg's opera ''Moses und Aron''. It is also known for a capella music, introduced by Helmut Franz such as a recording of all such works by Johannes Brahms. The current artistic director is Philipp Ahmann, who has held the position from 2008. NDR Chor, now a group of 28 singers, is one of the leading professional chamber choirs in Germany. History The NDR Chor was founded in Hamburg on 1 May 1946, then as choir of the Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk (NWDR) and took its present name in 1956 when the broadcaster was split in NDR and WDR. Its first director was Max Thurn who accepted 55 singers from more than 2,000 applications by professional singers. During the first y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imitation (music)
In music, imitation is the repetition of a melody in a polyphonic texture shortly after its first appearance in a different voice. The melody may vary through transposition, inversion, or otherwise, but retain its original character. The intervals and rhythms of an imitation may be exact or modified; imitation occurs at varying distances relative to the first occurrence, and phrases may begin with voices in imitation before they freely go their own ways. Imitation helps provide unity to a composition and is used in forms such as the fugue and canon. Definitions When a phrase recurs exactly as before (except perhaps transposed), it is called strict imitation. A round is thus an example of strict imitation. Repetition is defined as the repetition of a phrase or melody often with variations in key, rhythm, and voice. Different authors define imitation somewhat differently: The point of imitation, "marks the beginning of a series of imitative entries in a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamics (music)
In music, the dynamics of a piece are the variation in loudness between notes or phrases. Dynamics are indicated by specific musical notation, often in some detail. However, dynamics markings require interpretation by the performer depending on the musical context: a specific marking may correspond to a different volume between pieces or even sections of one piece. The execution of dynamics also extends beyond loudness to include changes in timbre and sometimes tempo rubato. Purpose and interpretation Dynamics are one of the expressive elements of music. Used effectively, dynamics help musicians sustain variety and interest in a musical performance, and communicate a particular emotional state or feeling. Dynamic markings are always relative. (''piano'' - "soft") never indicates a precise level of loudness; it merely indicates that music in a passage so marked should be considerably quieter than (''forte'' - "loud"). There are many factors affecting the interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that provide the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Major
A major is a major scale based on A, with the pitches A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. Its key signature has three sharps. Its relative minor is F-sharp minor and its parallel minor is A minor. The A major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The A harmonic major and melodic major scales are: In the treble, alto, and bass clefs, the G in the key signature is placed higher than C. However, in the tenor clef, it would require a ledger line and so G is placed lower than C. Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of A major are: * Tonic – A major * Supertonic – B minor * Mediant – C-sharp minor * Subdominant – D major * Dominant – E major * Submediant – F-sharp minor * Leading-tone – G-sharp diminished History Although not as rare in the symphonic literature as sharper keys (those containing more than three sharps), symphonies in A major are less common tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alla Breve
''Alla breve'' also known as cut time or cut common timeis a Meter (music), musical meter notated by the time signature symbol (a C) with a vertical line through it, which is the equivalent of . The term is Italian language, Italian for "on the breve", originally meaning that the beat was counted on the double whole note, breve (double whole note). ''Alla breve'' is a "Meter (music)#Simple meter, simple-duple meter with a half-note pulse (music), pulse".Duckworth, William (2009). ''A Creative Approach to Music Fundamentals'', p. 38. . The note denomination that represents one beat is the minim (music), minim or half-note. There are two of these per bar, so that the time signature may be interpreted as "two minim beats per bar". Alternatively this is read as two beats per measure, where the half note gets the beat. The name Time signature#common time, "common time" refers to , which has four beats to the bar, each of a quarter note (or crotchet). Modern usage In contempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sic Transit Gloria Mundi
''Sic transit gloria mundi'' is a Latin phrase that means "thus passes the glory of the world". In idiomatic contexts, the phrase has been used to mean "fame is fleeting". The phrase was used in the ritual of papal coronation ceremonies between 1409 (when it was used at the coronation of Alexander V) and 1963. As the newly chosen Pope proceeded from the sacristy of St. Peter's Basilica in his sedia gestatoria, the procession stopped three times. On each occasion, a papal master of ceremonies would fall to his knees before the Pope, holding a silver or brass reed, bearing a tow of smoldering flax. For three times in succession, as the cloth burned away, he would say in a loud and mournful voice, "''Pater Sancte, sic transit gloria mundi''!" ("Holy Father, so passes worldly glory!"). These words, thus addressed to the Pope, served as a reminder of the transitory nature of life and earthly honours. A form of the phrase appeared in Thomas à Kempis's 1418 work ''The Imitation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |