|
Abu'l-Aswar Shavur Ibn Fadl
Abu'l-Aswar or Abu'l-Asvar Shavur ibn Fadl ibn Muhammad ibn Shaddad also known as Aplesphares, was a member of the Shaddadid dynasty. Between 1049 and 1067 he was the eighth Shaddadid ruler of Arran (today in western Azerbaijan) from Ganja. Prior to that, he ruled the city of Dvin (in what is now Armenia and northeastern Turkey) from 1022 as an autonomous lord. A capable warrior, and a wise and cunning ruler, Abu'l-Aswar was engaged in several conflicts with most of his neighbours. During his rule over Dvin, he was mostly involved in the affairs of the Armenian principalities. He collaborated with the Byzantine Empire in its conquest of the last remnants of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, but when the Byzantines later turned on him, he survived three successive offensives that sought to take Ganja. In 1049, a revolt in Ganja overthrew his infant great-great-nephew, Anushirvan. The rebels invited him to take up the family's emirate, and he moved from Dvin to Ganja. Under his rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvin (ancient City)
Dvin ( or ; , ''Doúbios'' or Τίβιον, ''Tíbion''; , Dabīl or Doubil) was a large commercial city and the capital of early medieval Armenia. It was situated north of the previous ancient capital of Armenia, the city of Artaxata, along the banks of the Metsamor River, 35 km to the south of modern Yerevan Yerevan ( , , ; ; sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia, as well as one of the world's List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerev .... It is claimed it was one of the largest cities east of Constantinople prior to its destruction by the Mongols in the 13th century, but with an overall area of approximately 1 km2, it was far smaller than many of the great cities of Asia. It had an estimated population of 45,000 in 361, 47,000 in 622, and around 100,000 at its height in the 8th-9th centuries. Nyura Hakobyan proposed a peak population of 100,000 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lashkari Ibn Muhammad
Lashkari ibn Muhammad ibn Shaddad was a Kurdish ruler, the son of Muhammad ibn Shaddad who succeeded his father to the throne of the Shaddadids in 971. Along with his brothers, he captured Ganja from the Sallarids in 971, coming into control of the region of Arran. After his death in 978, he was succeeded by his brother Marzuban ibn Muhammad Marzuban ibn Muhammad (died 957) was the Sallarid ruler of Azerbaijan (941/42–957). He was the son of Muhammad bin Musafir, the ruler of Tarum. Takeover of Azerbaijan In 941 Marzuban and his brother Wahsudan ibn Muhammad, with the tacit ap .... Sources * * 978 deaths Emirs of Ganja 10th-century Shaddadid emirs 10th-century Kurdish people {{MEast-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Shaddad
Muhammad ibn Shaddad also known as Muhammad ibn Shaddad ibn qurtaq ( was a Kurdish tribal Chief, founder and first ruler of the Shaddadid dynasty. He captured Dvin from the Sallarids in 951, although apparently the citadel remained in the hands of a Daylamite garrison loyal to the Sallarids. He managed to maintain his control until 954, when the Sallarids retook the town. Muhammad, his family and his supporters fled to Vaspurakan, where he died in 955. Biography Origins Muhammad ibn Shaddad was chief of a Kurdish Sunni Muslim pastoralist tribe. Vladimir Minorsky suggests that Shaddad, father of Muhammad was originally from Jazira in Hasaniya district. Muhammad ibn Shaddad was chief of the Sub-tribe of Hadhbāni tribe. Emir of Dwin Muhammad ibn Shaddad Was able to capture Dwin in 951, due to the weakening of the Sallarid kingdom of Adharbayjan. Due to absence of authority, He, his family and clan were welcomed by the people of Dwin, to protect them from Daylamite and Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syria. Consisting of 30–45 million people, the global Kurdish population is largely concentrated in Kurdistan, but significant communities of the Kurdish diaspora exist in parts of West Asia beyond Kurdistan and in parts of Europe, most notably including: Turkey's Central Anatolian Kurds, as well as Kurds in Istanbul, Istanbul Kurds; Iran's Khorasani Kurds; the Caucasian Kurds, primarily in Kurds in Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan and Kurds in Armenia, Armenia; and the Kurdish populations in various European countries, namely Kurds in Germany, Germany, Kurds in France, France, Kurds in Sweden, Sweden, and the Kurds in the Netherlands, Netherlands. The Kurdish language, Kurdish languages and the Zaza–Gorani languages, both of which belong to the Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munejjim-bashi Ahmed Dede
Ahmed Lütfullah (early 17th century – 27 February 1702), better known by his court title of Münejjim Bashi (; "Chief Astrologer"), was an Ottoman courtier, scholar, Sufi poet and historian. His chief work is the ''Jamiʿ al-Duwal'', a world history particularly valuable for the history of the medieval Muslim dynasties of the regions around the southwestern shore of the Caspian Sea ( Adharbayjan, Shirvan, Arran, Derbent). In Turkish literature, he is referred to also as Ahmed Lütfullah. Biography His father Lütfullah was a native of Ereğli, Konya, but Ahmed was born in Salonica sometime in the first half of the 17th century (in 1631 according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'').. He was educated at the Mevlevi dervish lodge in the quarter of Kasımpaşa, spending 15 years there under the supervision of Sheikh Halil Dede. After studies on astronomy and astrology, he advanced to the position of chief court astrologer ('' müneccimbaşi'') in 1667/8. He enjoyed his greates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the entirety of the six centuries that it existed. Their descendants are the present-day Turkish people, who comprise the majority of the population in the Turkey, Republic of Turkey, which was established shortly after the end of World War I. Reliable information about the early history of the Ottoman Turks remains scarce, but they take their Turkish name from Osman I, who founded the Ottoman dynasty, House of Osman alongside the Ottoman Empire; the name "Osman (name), Osman" was altered to "Ottoman" when it was transliterated into some Languages of Europe, European languages over time. The Ottoman principality, expanding from Söğüt, gradually began incorporating other Turkish-speaking Muslims and non-Turkish Christians into their realm. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, while the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the Homage (feudal), homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan, which are sometimes collectively known as the Caucasian States. The total area of these countries measures about . The South Caucasus and the North Caucasus together comprise the larger Caucasus geographical region that divides Eurasia. The South Caucasus is a dynamic and complex region where the three countries have pursued distinct geopolitical pathways. Geography The South Caucasus spans the southern portion of the Caucasus Mountains and their lowlands, straddling the border between the continents of Europe and Asia, and extending southwards from the southern part of the Main Caucasian Range of southwestern Russia to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and from the Black Sea in the west to the Caspian Sea coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037–1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194. The Seljuk Empire was founded in 1037 by Tughril (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg, Chaghri (989–1060), both of whom co-ruled over its territories; there are indications that the Seljuk leadership otherwise functioned as a triumvirate and thus included Seljuk dynasty, Musa Yabghu, the uncle of the aforementioned two. During the formative phase of the empire, the Seljuks first advanced from their original homelands near the Aral Sea into Greater Kho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
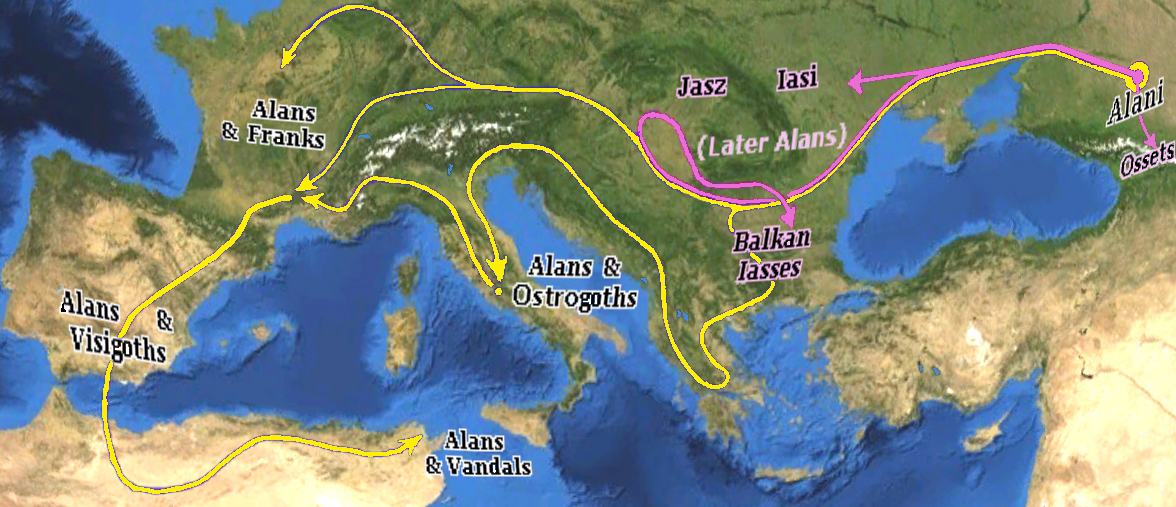
Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of China, Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Ancient Rome, Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the South Caucasus provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe, thereby assimilating a sizeable portion of the associated Alans. Upon the Huns, Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Tiflis
The Emirate of Tbilisi ( ka, თბილისის საამირო ', ') was a Muslim emirate in Transcaucasia. The Emirs of Tbilisi ruled over the parts of today's eastern Georgia from their base in the city of Tbilisi, from 736 to 1080 (nominally to 1122). Established by the Arabs during their rule of Georgian lands, the emirate was an important outpost of the Muslim rule in the Caucasus until recaptured by the Georgians under King David IV in 1122. History The Arabs first appeared in Georgia, namely in Kartli (Iberia) in 645. It was not, however, until 735 that they succeeded in establishing firm control over a large portion of the country. In that year, Marwan II took hold of Tbilisi and much of the neighbouring lands and installed there an Arab emir, who was to be confirmed by the Caliph or, occasionally, by the '' ostikan'' of '' Armīniya''. During the Arab period, Tbilisi (''al-Tefelis'') grew into a center of trade between the Islamic world and northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |