|
Aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon. A simple aryl group is phenyl (), a group derived from benzene. Examples of other aryl groups consist of: * The tolyl group () which is derived from toluene (methylbenzene) * The xylyl group (), which is derived from xylene (dimethylbenzene) * The naphthyl group (), which is derived from naphthalene Arylation is the process in which an aryl group is attached to a substituent. It is typically achieved by cross-coupling reactions. Nomenclature The simplest aryl group is phenyl, which is made up of a benzene ring with one of its hydrogen atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (also known as AhR, AHR, ahr, ahR, AH receptor, or as the dioxin receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AHR gene. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression. It was originally thought to function primarily as a sensor of xenobiotic chemicals and also as the regulator of enzymes such as cytochrome P450s that metabolize these chemicals. The most notable of these xenobiotic chemicals are aromatic (aryl) hydrocarbons from which the receptor derives its name. More recently, it has been discovered that AhR is activated (or deactivated) by a number of endogenous indole derivatives such as kynurenine. In addition to regulating metabolism enzymes, the AhR has roles in regulating immune cells, stem cell maintenance, and cellular differentiation. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a member of the family of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. AhR binds several exogenous ligands such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxins And Dioxin-like Compounds
Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environmental pollutant, environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes or, in the case of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl, PCBs and polybrominated biphenyl, PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures. Some of them are highly toxic, but the toxicity among them varies 30,000-fold. They are grouped together because their mechanism of action is the same. They activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AH receptor), albeit with very different binding affinities, leading to high differences in toxicity and other effects. They include: * Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, Polychlorinated dibenzo''-p-''dioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins. PCDDs are derivatives of dibenzodioxin, dibenzo''-p-''dioxin. There are 75 PCDD congener (chemistry), congeners, differing in the number and location of chlorine atoms, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl Groups
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon. A simple aryl group is phenyl (), a group derived from benzene. Examples of other aryl groups consist of: * The tolyl group () which is derived from toluene (methylbenzene) * The xylyl group (), which is derived from xylene (dimethylbenzene) * The naphthyl group (), which is derived from naphthalene Arylation is the process in which an aryl group is attached to a substituent. It is typically achieved by cross-coupling reactions. Nomenclature The simplest aryl group is phenyl, which is made up of a benzene ring with one of its hydrogen atom repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Aromatic compounds or arenes are organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties: * Typically unreactive * Often non polar and hydrophobic * High carbon-hydrogen ratio * Burn with a strong sooty yellow flame, due to high C:H ratio * Undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitutions Arenes are typically split into two categories - benzoids, that contain a benzene derivative and follow the benzene ring model, and non-benzoids that contain other aromatic cyclic derivatives. Aromatic compounds are commonly used in organic synthesis and are involved in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryloxy
In chemistry, the alkoxy group is an alkyl group which is singularly bonded to oxygen; thus . Denoted usually with apostrophe('). The range of alkoxy groups is vast, the simplest being methoxy (). An ethoxy group () is found in the organic compound ethyl phenyl ether (, also known as ethoxybenzene). Related to alkoxy groups are aryloxy groups, which have an aryl group singularly bonded to oxygen such as the phenoxy group (). An alkoxy or aryloxy group bonded to an alkyl or aryl () is an ether. If bonded to H it is an alcohol. The term '' alkoxide'' refers to the anionic conjugate bases of alcohols () or to ionic compounds containing such an anion. Alkoxide compounds are derivatives of alcohols where the hydrogen of the –OH group is replaced by a metal; for example, the sodium salt of ethanol () is sodium ethoxide Sodium ethoxide, also referred to as sodium ethanolate, is the Ionic compound, ionic, organic compound with the formula , , or NaOEt (Et = ethyl group, eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
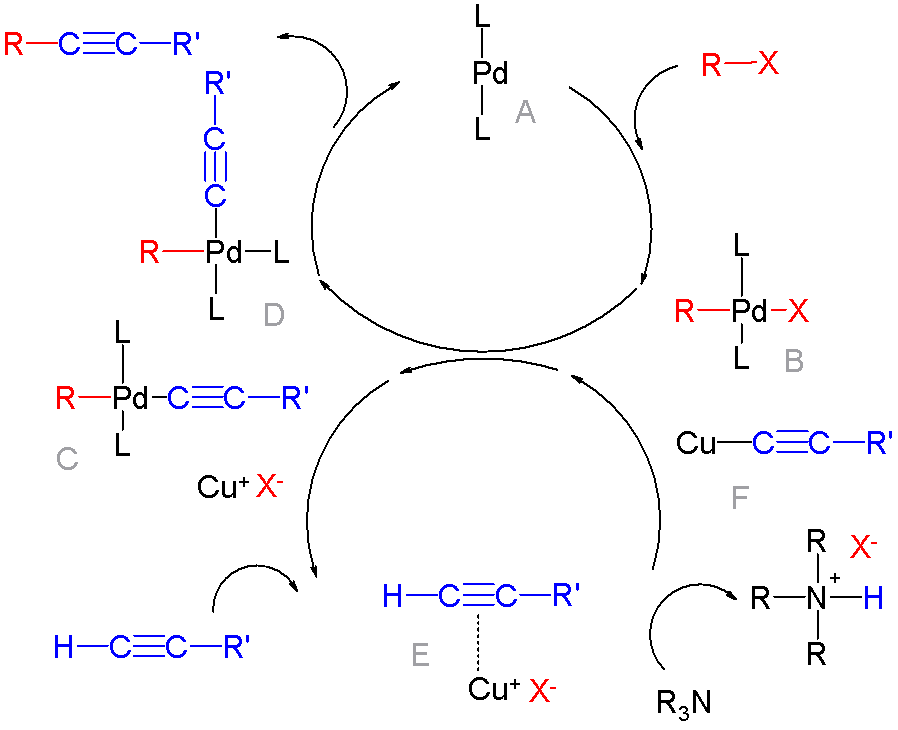
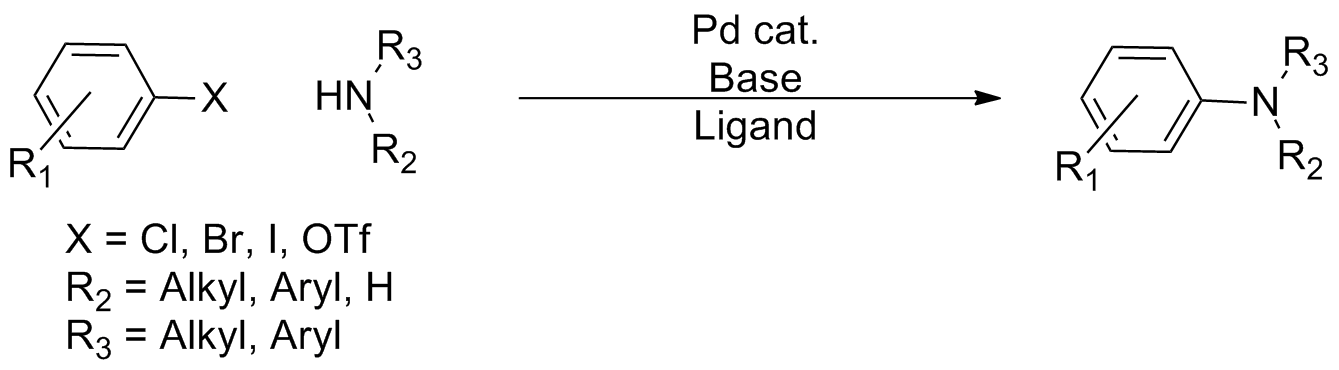
Cross-coupling Reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive Chemical property, chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their Chemical polarity, nonp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
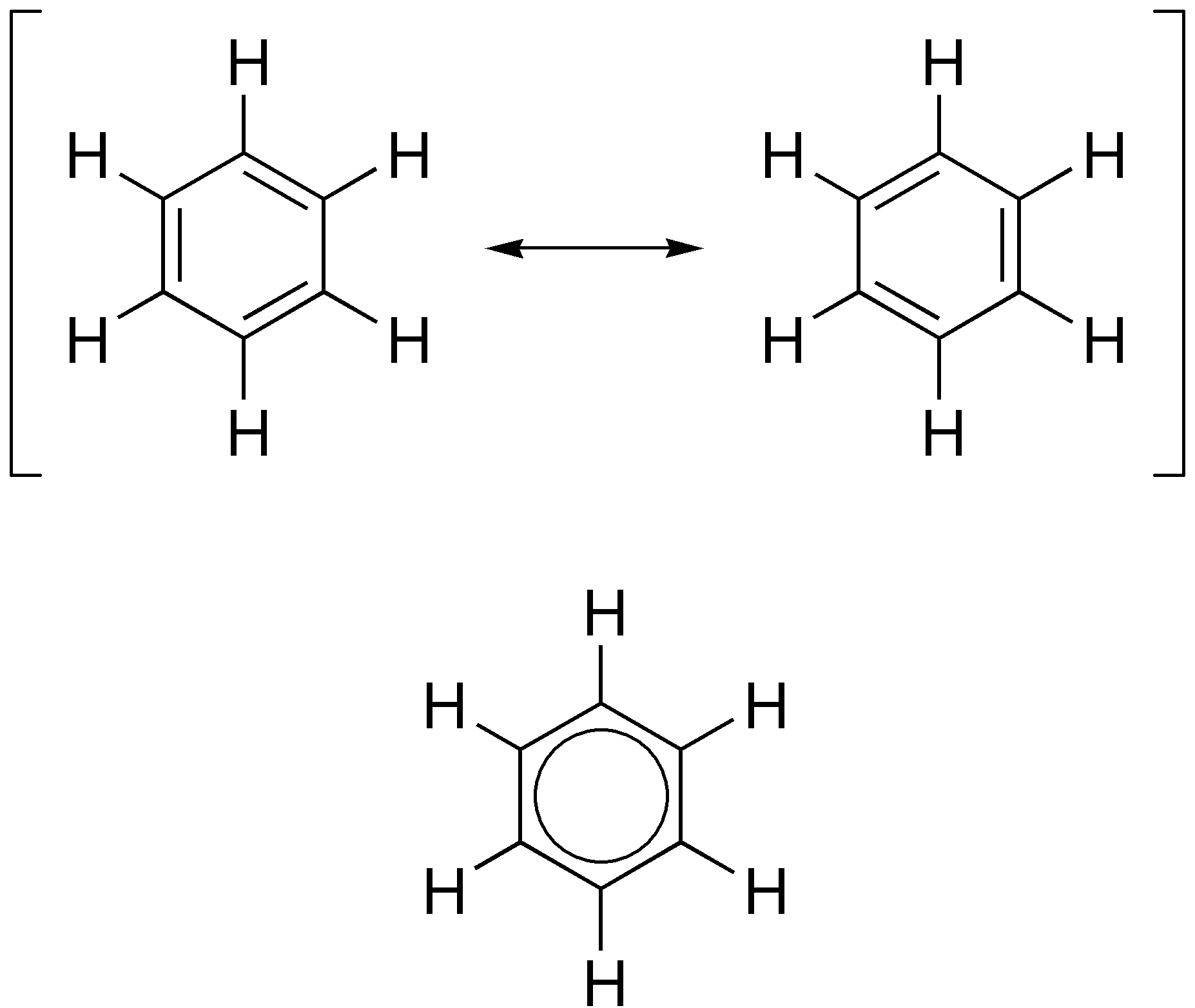
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylation
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reductive eliminat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond replacing one hydrogen; ''-ylidene'' and ''-ylidyne'' are used with double bonds and triple bonds, respectively. In addition, when naming hydrocarbons that contain a substituent, positional numbers are used to indicate which carbon atom the substituent attaches to when such information is needed to distinguish between isomers. Substituents can be a combination of the inductive effect and the mesomeric effect. Such effects are also described as electron-rich and electron withdrawing. Additional steric effects result from the volume occupied by a substituent. The phrases ''most-substituted'' and ''least-substituted'' are frequently used to describe or compare molecules that are products of a chemical reaction. In this terminology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolyl Groups
In organic chemistry, tolyl groups are functional groups related to toluene. They have the general formula . The change of the relative position of the methyl and the R substituent on the aromatic ring can generate three possible structural isomers: 1,2 (''ortho''), 1,3 (''meta''), and 1,4 (''para''). Tolyl groups are aryl groups which are commonly found in the structure of diverse chemical compounds. They are considered nonpolar and hydrophobic groups. The functionalization to include tolyl groups into compounds is often done by Williamson etherification, using tolyl alcohols as reagents, or by C-C coupling reactions. Tolyl sulfonates are excellent leaving groups in nucleophilic substitutions, for this reason, they are commonly generated as intermediaries to activate alcohols. To this end, 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride 4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (''p''-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-''p''-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |