|
A' Mhòine
A' Mhòine (), variously anglicised as the Moine, the Moin, or the Mhoine, is a peninsula in the north of Sutherland in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands, Scotland. The peninsula is bounded to the west by Loch Eriboll, and to the east by the Kyle of Tongue. The A838 road crosses the peninsula on an east–west axis. The coastline includes cliffs, waterfalls, and a few sandy beaches. Much of the peninsula is owned by Melness Estate on behalf of 59 crofting, crofters. Most of the population live in Melness, which is made up of several crofting townships and hamlets including Talmine, Sutherland, Talmine and Midfield, Highland, Midfield. The name is from the Scottish Gaelic ''mhòine'' or ''mòine'' meaning "moss" or "peat". The Moinian geological group and the Moine Thrust Belt were in turn named after the peninsula. Conservation areas The peninsula contains large areas of blanket bog, forming part of the Flow Country. Eriboll East and Whiten Head, at the western and northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Hope
Ben Hope () is a mountain in northern Scotland. It is the most northerly Munro, standing alone in the Flow Country (a region of bumpy, peat-covered moorland) south-east of Loch Hope in Sutherland. The mountain is a roughly triangular wedge, with a great crag on the west, with two lower shoulders to the south and northeast. Alpine plant, Alpine flowers are abundant in season, although the ground is very rocky. The Aetherius Society considers it to be one of its 19 sacred mountains, holy mountains. Ascent The principal route to the summit starts in Strathmore, Sutherland, Strathmore, to the west of the mountain, where there is parking off a small road. The route lies along the Allt-na-caillich burn (topography), burn which flows down through a gap in the west-facing crags. The route is steep, but well marked with occasional cairns and not exposed. There is little available scrambling. Approach from the east is rare, as there is a wide expanse of heather-covered moorland with n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crofting
Crofting (Scottish Gaelic: ') is a form of land tenure and small-scale food production peculiar to the Scottish Highlands, the islands of Scotland, and formerly on the Isle of Man. Within the 19th-century townships, individual crofts were established on the better land, and a large area of poorer-quality hill ground was shared by all the crofters of the township for grazing of their livestock. In the 21st century, crofting is found predominantly in the rural Western and Northern Isles and in the coastal fringes of the western and northern Scottish mainland. History Origins and history before 1886 Crofting communities were a product of the Highland Clearances (though individual crofts had existed before the clearances). Previously, Highland agriculture was based on farms or , which had common grazing and arable open fields operated on the run rig system. An individual might have between five and ten families as tenants. As landowners sought to increase the income from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Area Of Conservation
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and approximately 1,000 species listed in annex I and II of the directive which are considered to be of European interest following criteria given in the directive. They must be chosen from the Site of Community Importance, sites of Community importance by the member states and designated SAC by an act assuring the conservation measures of the natural habitat. SACs complement special protection areas and together form a network of protected sites across the European Union called Natura 2000. This, in turn, is part of the Emerald network of Area of Special Conservation Interest, Areas of Special Conservation Interest (ASCIs) under the Convention on the conservation of European wildlife and natural habitats, Berne Convention. Assessment methodol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Protection Area
A special protection area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certain particularly threatened birds. Together with special areas of conservation (SACs), the SPAs form a network of protected sites across the EU, called Natura 2000. Each SPA has an EU code – for example the North Norfolk Coast SPA has the code ''UK9009031''. In the United Kingdom As at 21 September 2006, there were 252 classified SPAs and 12 proposed SPAs in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The Conservation (Natural Habitats etc.) Regulations 1994 implement the terms of the Directive in Scotland, England and Wales. In Great Britain, SPAs (and SACs) designated on land or in the intertidal area are normally also notified as Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs), and in Northern Ireland as Areas of Special Scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Plant
Alpine plants are plants that grow in an alpine climate, which occurs at high elevation and above the tree line. There are many different plant species and taxon, taxa that grow as a plant community in these alpine tundra. These include perennial grasses, Cyperaceae, sedges, forbs, cushion plants, mosses, and lichens.. Alpine plants are adapted to the harsh conditions of the alpine environment, which include low temperatures, dryness, ultraviolet radiation, wind, drought, poor nutritional soil, and a short growing season. Some alpine plants serve as medicinal plants. Ecology Alpine plants occur in a alpine tundra, tundra: a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees. Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. It ecotone, transitions to subalpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as ''Krummholz''. With increasing elevation, it ends at the snow line where snow and ice persist through summer, also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves, Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Area of Conservation, Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their Biology, biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or Physical geography, physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Landscape Area
A local landscape designation is a non-statutory conservation designation used by local government in some parts of the United Kingdom to categorise sensitive landscapes which are, either legally or as a matter of policy, protected from development or other man-made influences. A local authority will typically produce a Landscape Assessment to define such areas. An LLD may also be known as an Area of Great Landscape Value, Special Landscape Area, or Area of Special Landscape Importance. If an area is designated as an AGLV, this restricts development in the area, especially if it will affect the distinctive character or quality of the landscape. References {{reflist See also *Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty *Conservation in the United Kingdom This page gives an overview of the complex structure of environmental and cultural conservation in the United Kingdom. With the advent of devolved government for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland and of evolving regional government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Country
The Flow Country () is a vast area of bog peatland in Caithness and Sutherland, northern Scotland. It is the largest blanket bog in Europe, and covers about . It is an area of deep peat, dotted with bog pools, and is a very important habitat for wildlife. As peat is largely made up of the remains of plants, which are themselves made up of carbon, it locks up large stores of carbon for thousands of years. This carbon would otherwise be released to the atmosphere and contribute to global warming. In 2024 the Flow Country was awarded World Heritage status by UNESCO on account of its unparalleled blanket bog habitat. It includes the Forsinard Flows National Nature Reserve and the Caithness and Sutherland Peatlands. Wildlife The Flow Country is home to a rich variety of wildlife, and is used as a breeding ground for many different species of birds, including greenshank, dunlin, merlin and golden plover. Birds of prey found in the Flow Country include the buzzard and hen harr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanket Bog
Blanket bog or blanket mire, also known as featherbed bog, is an area of peatland, forming where there is a climate of high rainfall and a low level of evapotranspiration, allowing peat to develop not only in wet hollows but over large expanses of undulating ground. The blanketing of the ground with a variable depth of peat gives the habitat type its name. Blanket bogs are found extensively throughout the northern hemisphere - well-studied examples are found in Ireland and Scotland, but vast areas of North American tundra also qualify as blanket bogs. In Europe, the southernmost edge of range of this habitat has been recently mapped in the Cantabrian Mountains, northern Spain, but the current distribution of blanket bogs globally remains unknown. In the southern hemisphere they are less well-developed due to the relatively low latitudes of the main land areas, though similar environments are reported in Patagonia, the Falkland Islands and New Zealand. The blanket bogs known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
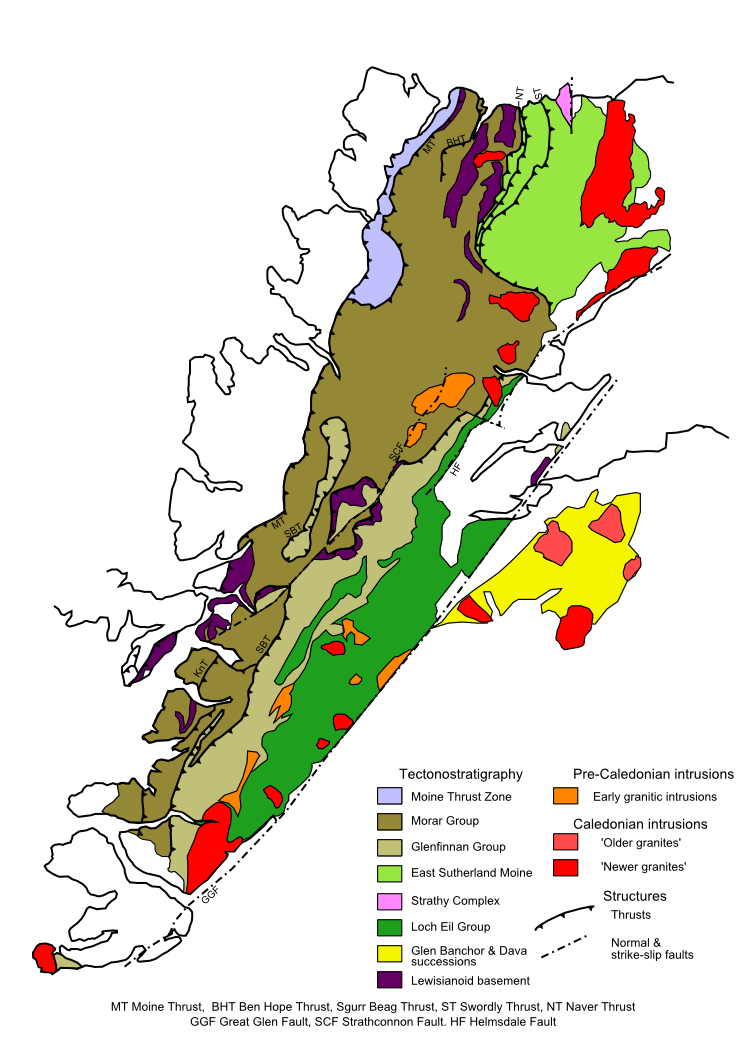
Moine Thrust Belt
The Moine Thrust Belt or Moine Thrust Zone is a linear tectonic feature in the Scottish Highlands which runs from Loch Eriboll on the north coast southwest to the Sleat peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The thrust belt consists of a series of thrust faults that branch off the Moine Thrust itself. Topographically, the belt marks a change from rugged, terraced mountains with steep sides sculptured from weathered igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in the west to an extensive landscape of rolling hills over a metamorphic rock base to the east. Mountains within the belt display complexly folded and faulted layers and the width of the main part of the zone varies up to , although it is significantly wider on Skye. Discovery The presence of metamorphic gneisses and schists lying apparently stratigraphically above sedimentary rocks of lower Paleozoic age in the Northwest Highlands had been known since the early 19th century, convincing Roderick Murchison that the change was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moinian
The Moinian or just the Moine, formerly the Moine Supergroup, is a sequence of Neoproterozoic metasediments that outcrop in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland between the Moine Thrust Belt to the northwest and the Great Glen Fault to the southeast and one part of the Grampian Highlands to the southeast of the fault. It takes its name from ''A' Mhòine'', a peat bog in northern Sutherland. History of research The metamorphic rocks that are now known informally as "the Moine" were originally interpreted as of Silurian age, as they lie in sequence with Cambrian to lower Silurian sedimentary rocks (now known to be lower Ordovician at the youngest and part of the Ardvreck Group). This view, espoused particularly by Roderick Murchison, a geologist known as the "Master of the Silurian", was opposed by James Nicol, who thought that the contact (or "zone of complication" as he called it) was tectonic in nature and that the metamorphic rocks were older and not in stratigraphic sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |