|
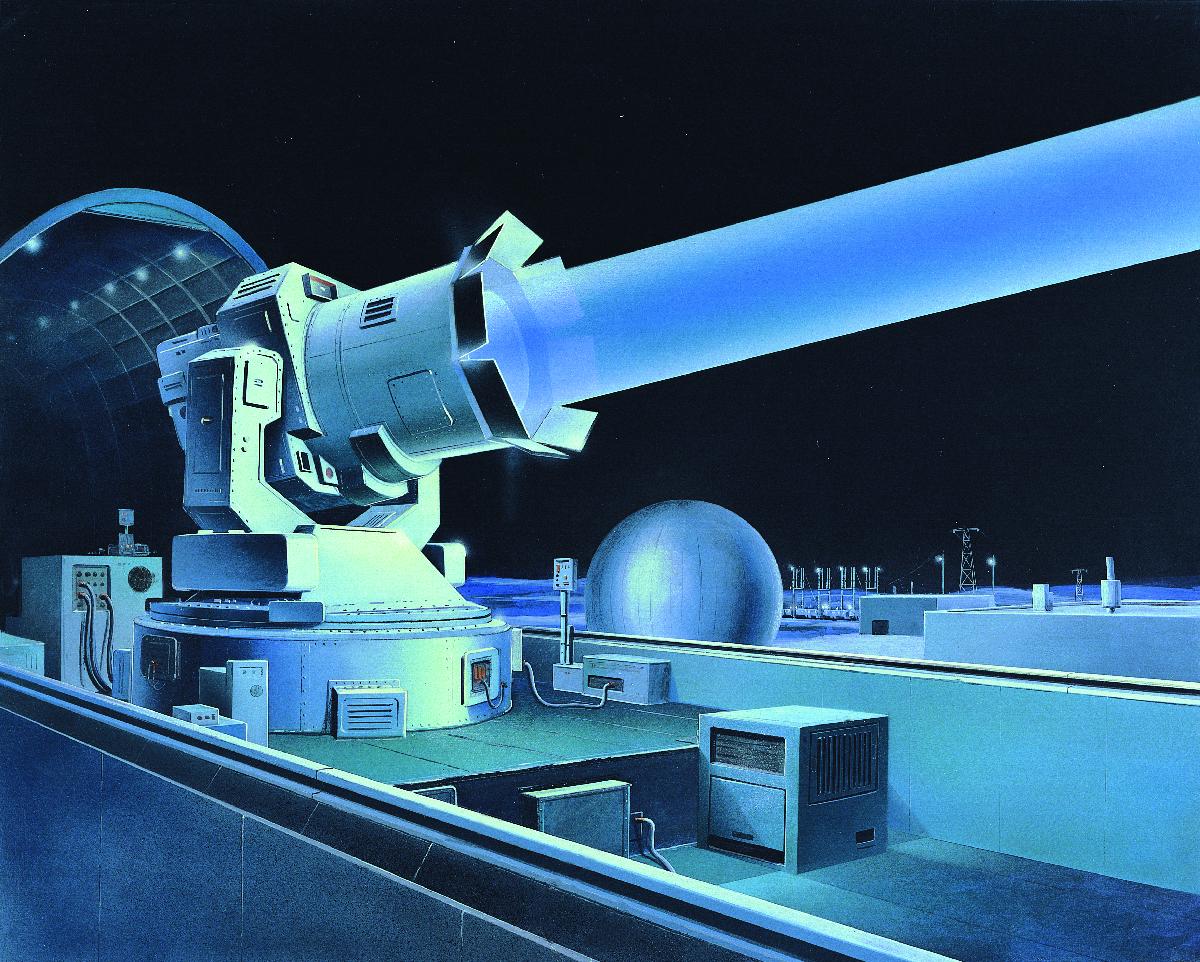
A-235 Anti-ballistic Missile System
System A-235 PL-19 ''Nudol'' ( rus, Система А-235 / ПЛ-19-181М / Нудоль) is a Russian anti-ballistic missile and anti-satellite weapon system in development. It is designed to deflect a nuclear attack on Moscow and important industrial regions. The main developer of the system is JSC Concern VKO Almaz-Antey. The new system should replace the current one — A-135. The two main differences will be that the A-235 will use conventional warheads and it will be mobile. The A-235 system will use Don-2N radar as well as Don 2NP / 5N20P as range radar, with updated software and hardware; the guidance system of the A-235 complex will be similar to the existing system A-135. The A-235, when deployed, could be equipped with a nuclear warhead which would greatly increase its ability to destroy incoming warheads. The yield on which it would be deployed is not yet known. According to reports in early 2018, the system will not be equipped with nuclear warheads. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ballistic Missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses Gorgon and Gazelle missiles previously armed with nuclear warheads. These missiles have been updated (2017) and use non-nuclear kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesetsk Cosmodrome
Plesetsk Cosmodrome ( rus, Космодром «Плесецк», r=Kosmodrom "Plesetsk", p=kəsmɐˈdrom plʲɪˈsʲet͡sk) is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, about 800 km north of Moscow and approximately 200 km south of Arkhangelsk, the cosmodrome dates to 1957. Originally developed as an ICBM site for the R-7 missile, it also served for numerous satellite launches using the R-7 and other rockets. Its high latitude makes it useful only for certain types of launches, especially the Molniya orbits, so for much of the site's history it functioned as a secondary location, with most orbital launches taking place from Baikonur, in the Kazakh SSR. With the end of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became a foreign territory, and Kazakhstan charged $115 million usage fees annually. Consequently, Plesetsk has seen considerably more activity since the 2000s. Overview Plesetsk () is used especially for military satellites placed into high inclinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ballistic Missiles Of Russia
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses Gorgon and Gazelle missiles previously armed with nuclear warheads. These missiles have been updated (2017) and use non-nuclear kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-Based Midcourse Defense
Ground-Based Midcourse Defense (GMD) is the United States' anti-ballistic missile system for intercepting incoming warheads in space, during the midcourse phase of ballistic trajectory flight. It is a major component of the American missile defense strategy to counter ballistic missiles, including intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) carrying nuclear, chemical, biological or conventional warheads. The system is deployed in military bases in the states of Alaska and California; in 2018 comprising 44 interceptors and spanning 15 time zones with sensors on land, at sea, and in orbit. In 2019, a missile defense review requested that 20 additional ground-based interceptors be based in Alaska. GMD is administered by the U.S. Missile Defense Agency (MDA), while the operational control and execution is provided by the U.S. Army, and support functions are provided by the U.S. Air Force. Previously known as National Missile Defense (NMD), the name was changed in 2002 to differenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-500 Missile System
The S-500 Prometey (russian: C-500 Прометей, lit=Prometheus), also known as 55R6M "Triumfator-M", is a Russian hypersonic surface-to-air missile/anti-ballistic missile system replacing the A-135 missile system currently in use, and supplementing the S-400. The S-500 was developed by the Almaz-Antey Air Defence Concern. Initially planned to be in production by 2014, the first unit entered service in 2021 with the 15th Air Army. History Although sharing a similar designation with the S-500U project of the late 1960s, the relationship between the two remains unclear. The S-500U multichannel anti-aircraft system was a 1968 initiative by the Soviet Air Defence Forces, Soviet Navy, Ministry of the Radio Industry (Ministerstvo Radio Promyshlennosti SSSR), and Ministry of the Shipbuilding Industry to create a unified complex for the National Air Defence Troops, navy and ground troops. Missiles of the S-500U complex were supposed to engage enemy aircraft at a range up to . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which Scientific research on the International Space Station, scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The International Space Station programme, ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecraft—nonfunctional spacecraft and abandoned launch vehicle stages—mission-related debris, and particularly numerous in Earth orbit, fragmentation debris from the breakup of derelict rocket bodies and spacecraft. In addition to derelict human-made objects left in orbit, other examples of space debris include fragments from their disintegration, erosion and collisions or even paint flecks, solidified liquids expelled from spacecraft, and unburned particles from solid rocket motors. Space debris represents a risk to spacecraft. Space debris is typically a negative externality—it creates an external cost on others from the initial action to launch or use a spacecraft in near-Earth orbit—a cost that is typically not taken into account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 1408
Kosmos-1408 (russian: Космос-1408) was an electronic signals intelligence (ELINT) satellite operated by the Soviet Union. It was launched into low Earth orbit on 16 September 1982 at 14:55 UTC, replacing Kosmos-1378. It operated for around two years before becoming inactive and left in orbit. The satellite was destroyed in a Russian anti-satellite weapon test on 15 November 2021, resulting in space debris in orbits between above Earth. The threat of potential collision with debris caused the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) to take shelter in their escape capsules for the first few passes of the debris cloud, and increased the future risk of a debris collision with the ISS or other satellites. Mission From 1965 to 1967, the Soviet Yuzhnoye Design Office developed two satellite ELINT systems: Tselina-O for broad observations and Tselina-D for detailed observations. The ELINT payloads (satellites) for Tselina were first tested under the Kosmos designa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsyklon-2
The Tsyklon-2 (Cyclone-2), also known as Tsiklon-2 and Tsyklon-M (known as SL-11 by the United States DoD), GRAU index 11K69, was a Soviet, later Ukrainian, orbital carrier rocket used from the 1960s to the late 2000s. The rocket had 106 launches, one suborbital and 105 orbital, with only one failure and 92 consecutive successful launches, from 27 December 1973 with the launch of Kosmos 626 to 25 June 2006 with the final flight of the Tsyklon-2, which makes this launcher most reliable within rocket launched more than 100 times. History A derivative of the R-36 ICBM, and a member of the Tsyklon family, the Tsyklon-2 made its maiden flight on 6 August 1969, and conducted 106 flights, the last one occurring on 24 June 2006. It was the most reliable Soviet/Russian carrier rocket ever used,and launched more than 100 times having failed only once, and the second most reliable carrier rocket overall, behind the Atlas II that was launched only 63 times. Along with other R-36 family m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersonic Speed
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds 5 times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above. The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since individual physical changes in the airflow (like molecular dissociation and ionization) occur at different speeds; these effects collectively become important around Mach 5-10. The hypersonic regime can also be alternatively defined as speeds where specific heat capacity changes with the temperature of the flow as kinetic energy of the moving object is converted into heat. Characteristics of flow While the definition of hypersonic flow can be quite vague and is generally debatable (especially due to the absence of discontinuity between supersonic and hypersonic flows), a hypersonic flow may be characterized by certain physical phenomena that can no longer be analytically discounted as in supersonic flow. The peculiarity in hypersonic flows ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-satellite Missile
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy satellites for strategic or tactical purposes. Several nations possess operational ASAT systems. Although no ASAT system has been utilised in warfare, a few countries (China, India, Russia, United Kingdom and the United States) have successfully shot down their own satellites to demonstrate their ASAT capabilities in a show of force. ASATs have also been used to remove decommissioned satellites. ASAT roles include: defensive measures against an adversary's space-based and nuclear weapons, a force multiplier for a nuclear first strike, a countermeasure against an adversary's anti-ballistic missile defence (ABM), an asymmetric counter to a technologically superior adversary, and a counter-value weapon. Use of ASATs generates space debris, which can collide with other satellites and generate more space debris. A cascading multiplication of space debris could cause Earth to suffer from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
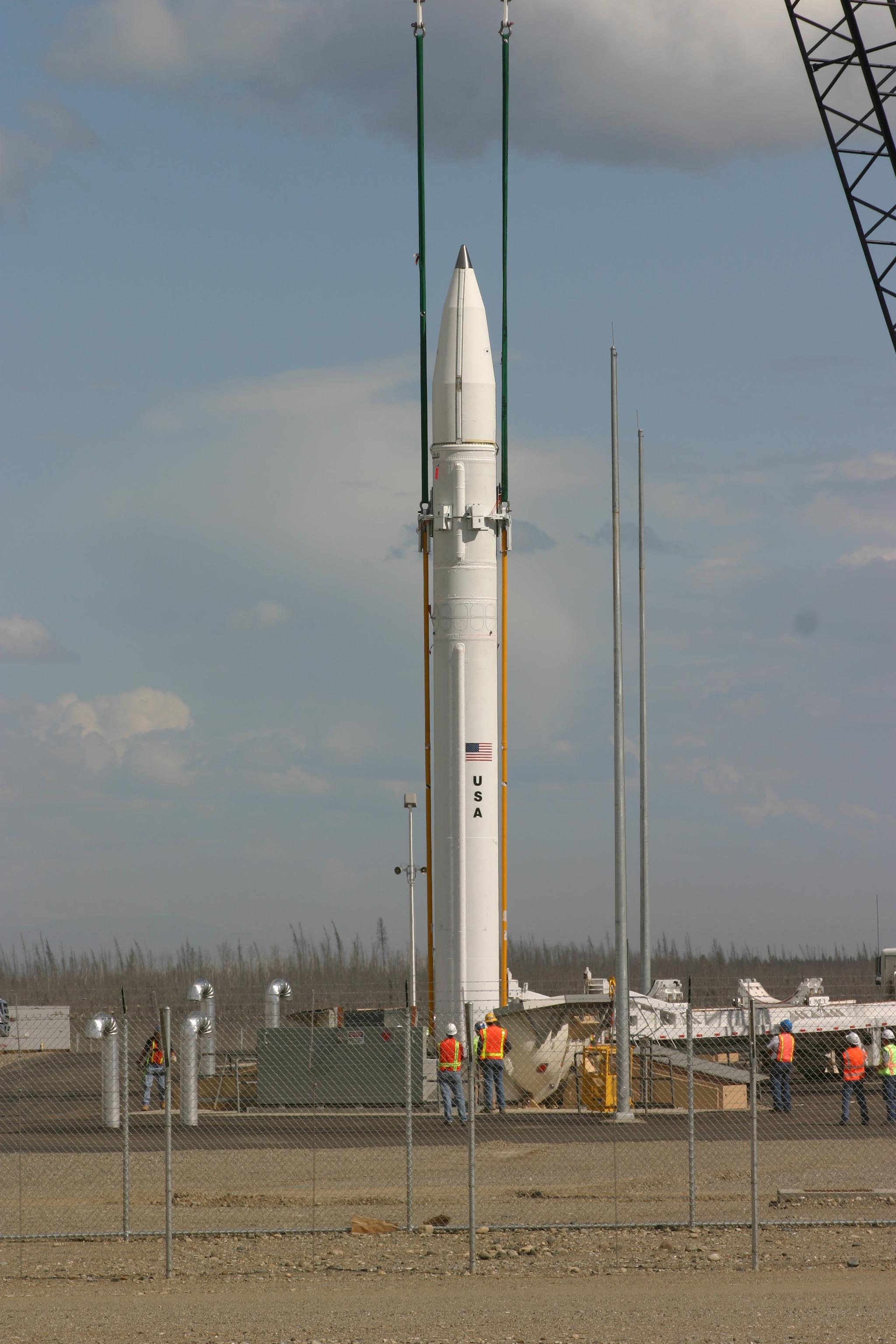
53T6
The 53T6 (NATO reporting name: ABM-3 ''Gazelle'', previously SH-08)Gazelle (SH-08/ABM-3) . is a Russian . Designed in 1978 and in service since 1995,''A-135'' it is a component of the . The missile is able to intercept incoming |

.png)
.jpg)



_Mach_7_computational_fluid_dynamic_(CFD).jpg)