|
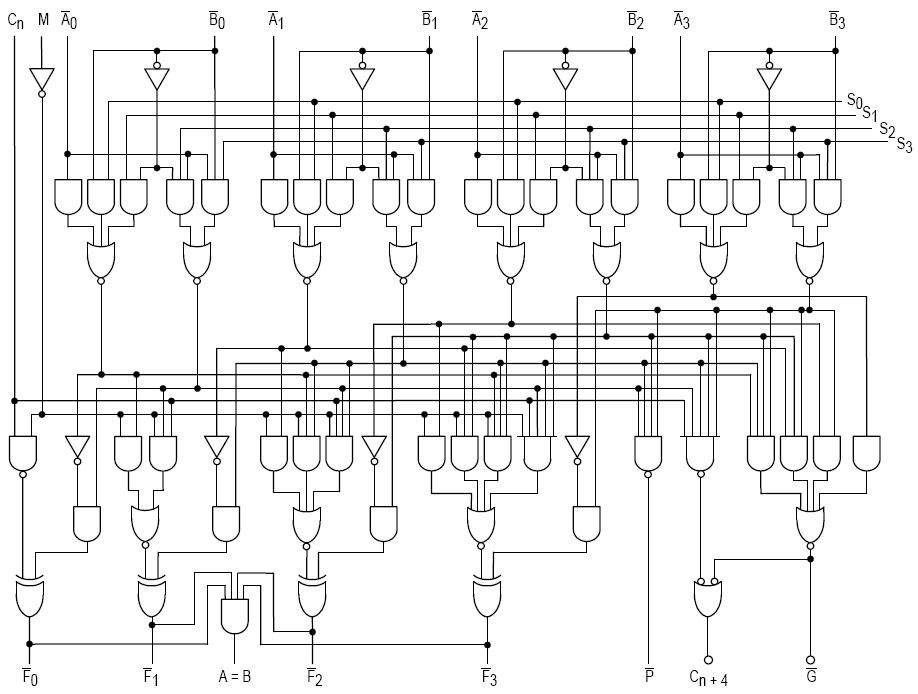
74181
The 74181 is a 4-bit slice arithmetic logic unit (ALU), implemented as a 7400 series TTL integrated circuit. Introduced by Texas Instruments in February 1970, it was the first complete ALU on a single chip. It was used as the arithmetic/logic core in the CPUs of many historically significant minicomputers and other devices. The 74181 represents an evolutionary step between the CPUs of the 1960s, which were constructed using discrete logic gates, and single-chip microprocessors of the 1970s. Although no longer used in commercial products, the 74181 later was used in hands-on computer architecture courses and is still referenced in textbooks and technical papers. Specifications The 74181 is a 7400 series medium-scale integration (MSI) TTL integrated circuit, containing the equivalent of 75 logic gates and most commonly packaged as a 24-pin DIP. The 4-bit wide ALU can perform all the traditional add / subtract / decrement operations with or without carry, as well as AND / N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data General Nova
The Nova is a series of 16-bit computing, 16-bit minicomputers released by the American company Data General. The Nova family was very popular in the 1970s and ultimately sold tens of thousands of units. The first model, known simply as "Nova", was released in 1969. The Nova was packaged into a single Rack unit, 3U rack-mount case and had enough computing power to handle most simple tasks. The Nova became popular in science laboratories around the world. It was followed the next year by the SuperNOVA, which ran roughly four times as fast, making it the fastest mini for several years. Introduced during a period of rapid progress in integrated circuit (or "microchip") design, the line went through several upgrades over the next five years, introducing the 800 and 1200, the Nova 2, Nova 3, and ultimately the Nova 4. A single-chip implementation was also introduced as the microNOVA in 1977, but did not see widespread use as the market moved to new microprocessor designs. Fairchil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Logic Unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point numbers. It is a fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits, including the central processing unit (CPU) of computers, FPUs, and graphics processing units (GPUs). The inputs to an ALU are the data to be operated on, called operands, and a code indicating the operation to be performed (opcode); the ALU's output is the result of the performed operation. In many designs, the ALU also has status inputs or outputs, or both, which convey information about a previous operation or the current operation, respectively, between the ALU and external status registers. Signals An ALU has a variety of input and output net (electronics), nets, which are the electrical conductors used to convey Digital signal (electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16-bit Computing
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors. A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two most common representations, the range is 0 through 65,535 (216 − 1) for representation as an ( unsigned) binary number, and −32,768 (−1 × 215) through 32,767 (215 − 1) for representation as two's complement. Since 216 is 65,536, a processor with 16-bit memory addresses can directly access 64 KB (65,536 bytes) of byte-addressable memory. If a system uses segmentation with 16-bit segment offsets, more can be accessed. As of 2025, 16-bit microcontrollers cost well under a dollar (similar to close in price legacy 8-bit); the cheapest 16-bit microcontrollers cost less than other types including any 8-bit (and are more powerful, and easier to program generally), making 8-bit legacy microcontrollers not worth it for new applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Slicing
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full word-length of a given software design. Bit slicing more or less died out due to the advent of the microprocessor. Recently it has been used in arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for quantum computers and as a software technique, e.g. for cryptography in x86 CPUs. Operational details Bit-slice processors (BSPs) usually include 1-, 2-, 4-, 8- or 16-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control lines (including carry or overflow signals that are internal to the processor in non-bitsliced CPU designs). For example, two 4-bit ALU chips could be arranged side by side, with control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7400 Series
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs). In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming ''de facto'' standardized electronic components. Since the introduction of the original bipolar-transistor TTL parts, Pin-compatibility, pin-compatible parts were introduced with such features as low power CMOS technology and LVCMOS, lower supply voltages. Surface-mount technology, Surface mount packages exist for several popular logic family functions. Overview The 7400 series contains hundreds of devices that provide everything from basic logic gates, flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops, and counters, to special purpose bus transceivers and arithmetic logic units (ALU). Specific functions are described in a list of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Slicing
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full word-length of a given software design. Bit slicing more or less died out due to the advent of the microprocessor. Recently it has been used in arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for quantum computers and as a software technique, e.g. for cryptography in x86 CPUs. Operational details Bit-slice processors (BSPs) usually include 1-, 2-, 4-, 8- or 16-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control lines (including carry or overflow signals that are internal to the processor in non-bitsliced CPU designs). For example, two 4-bit ALU chips could be arranged side by side, with control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-bit Computing
4-bit computing is the use of computer architectures in which integer (computer science), integers and other data (computer science), data units are 4 bits wide. 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on processor register, registers or bus (computing), data buses of that size. A group of four bits is also called a nibble and has 24 = 16 possible values, with a range of 0 to 15. 4-bit computation is obsolete, i.e. CPUs supporting 4-bit as the maximum size. However, 4-bit integers (or smaller), and 4-bit floating point is gaining ground for AI, large-language models. 4-bit processors were widely used in electronic calculators and other roles where decimal math was used, like electronic cash registers, microwave oven timers, and so forth. This is because a 4-bit value holds a single binary-coded decimal (BCD) digit, making it a natural size for directly processing decimal values. As a 4-bit value is generally too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carry-lookahead Adder
A carry-lookahead adder (CLA) or fast adder is a type of Adder (electronics), electronics adder used in digital logic. A carry-lookahead adder improves speed by reducing the amount of time required to determine carry bits. It can be contrasted with the simpler, but usually slower, ripple-carry adder (RCA), for which the carry bit is calculated alongside the sum bit, and each stage must wait until the previous carry bit has been calculated to begin calculating its own sum bit and carry bit. The carry-lookahead adder calculates one or more carry bits before the sum, which reduces the wait time to calculate the result of the larger-value bits of the adder. Already in the mid-1800s, Charles Babbage recognized the performance penalty imposed by the ripple-carry used in his Difference engine, Difference Engine, and subsequently designed mechanisms for ''anticipating carriage'' for his never-built Analytical Engine. Konrad Zuse is thought to have implemented the first carry-lookahead ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64-bit Computing
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer. From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of machine code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. However, not all 64-bit instruction sets support full 64-bit virtual memory addresses; x86-64 and AArch64, for example, support only 48 bits of virtual address, with the remaining 16 bits of the virtual address required to be all zeros (000...) or all ones (111...), and several 64-bit instruction sets support fewer than 64 bits of physical memory address. The term ''64-bit'' also describes a generation of computers in which 64-bit processors are the norm. 64 bits is a Word (computer architecture), word size that defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Level
In digital circuits, a logic level is one of a finite number of states that a digital signal can inhabit. Logic levels are usually represented by the voltage difference between the signal and ground, although other standards exist. The range of voltage levels that represent each state depends on the logic family being used. A '' logic-level shifter'' can be used to allow compatibility between different circuits. 2-level logic In binary logic the two levels are logical high and logical low, which generally correspond to binary numbers 1 and 0 respectively or truth values ''true'' and ''false'' respectively. Signals with one of these two levels can be used in Boolean algebra for digital circuit design or analysis. Active state The use of either the higher or the lower voltage level to represent either logic state is arbitrary. The two options are active high (''positive logic'') and active low (''negative logic''). Active-high and active-low states can be mixed at will: for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |