|
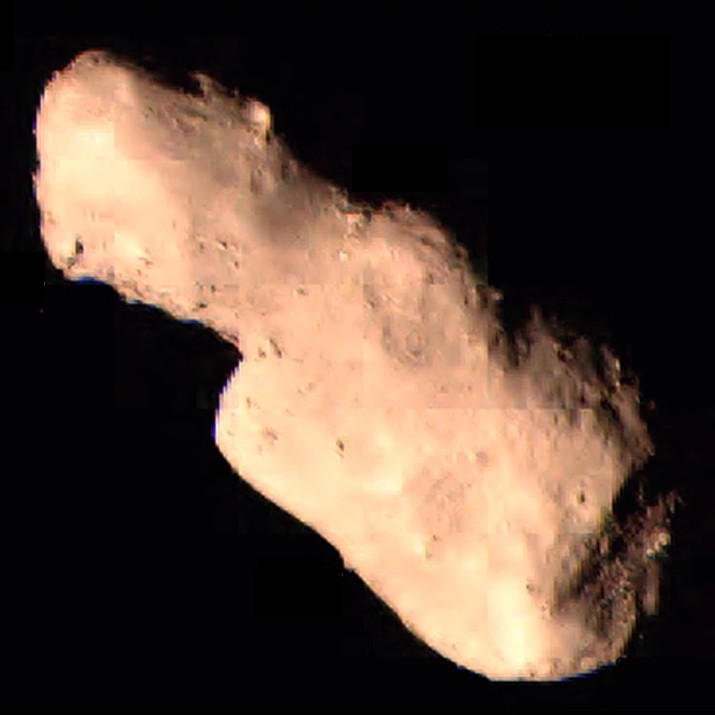
4179 Toutatis
4179 Toutatis ( provisional designation ) is an elongated, stony asteroid and slow rotator, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo asteroid group, approximately 2.5 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by French astronomer Christian Pollas at Caussols in 1989, the asteroid was named after Toutatis from Celtic mythology. Toutatis is also a Mars-crosser asteroid with a chaotic orbit produced by a 3:1 resonance with the planet Jupiter, a 1:4 resonance with the planet Earth, and frequent close approaches to the terrestrial planets, including Earth. In December 2012, Toutatis passed within about 18 lunar distances of Earth. The Chinese lunar probe Chang'e 2 flew by the asteroid at a distance of 3.2 kilometers and a relative velocity of 10.73 km/s. Toutatis approached Earth again in 2016, but will not make another notably close approach until 2069. Properties Toutatis was first sighted on 10 February 1934, as object 1934 CT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese uncrewed lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and conducted research from a 100-km-high lunar orbit in preparation for the December 2013 soft landing by the Chang'e 3 lander and rover. Chang'e 2 was similar in design to Chang'e 1, although it featured some technical improvements, including a more advanced onboard camera. Like its predecessor, the probe was named after Chang'e, an ancient Chinese moon goddess. After completing its primary objective, the probe left lunar orbit for the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point, to test the Chinese tracking and control network, making the China National Space Administration the third space agency after NASA and ESA to have visited this point. It entered orbit around L2 on 25 August 2011, and began transmitting data from its new position in Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Celtic Religion
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because there are no extant native records of their beliefs, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco-Roman accounts (some of them hostile and probably not well-informed), and literature from the early Christian period. Green, Miranda (2012). "Chapter 25: The Gods and the supernatural", ''The Celtic World''. Routledge. pp.465–485 Celtic paganism was one of a larger group of polytheistic Indo-European religions of Iron Age Europe. While the specific deities worshipped varied by region and over time, underlying this were broad similarities in both deities and "a basic religious homogeneity" among the Celtic peoples. Widely worshipped Celtic gods included Lugus, Toutatis, Taranis, Cernunnos, Epona, Maponos, Belenos, and Sucellos. Sacred springs were often associated with Celtic healing deities. Triplicity is a common theme, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galaxies – in either observational astronomy, observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, Sun, solar astronomy, the Star formation, origin or stellar evolution, evolution of stars, or the galaxy formation and evolution, formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers typically fall under either of two main types: observational astronomy, observational and theoretical astronomy, theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of Astronomical object, celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Asteroid
Lost or LOST may refer to getting lost, or to: Arts, entertainment, and media Television * ''Lost'' (TV series), a 2004 American drama series about people who become stranded on a mysterious island * ''Lost'' (2001 TV series), a short-lived American and UK reality series * ''Lost'' (South Korean TV series), a 2021 South Korean series * "Lost" (''The Bill''), a 1985 episode * "Lost" (''Stargate Universe''), an episode of science fiction series ''Stargate Universe'' *"Lost", an episode of ''Unleashed!'' *"Lost", an episode of the Canadian documentary TV series ''Mayday'' *"Lost", an episode of Disney's ''So Weird'' * "The Lost" (''Class''), an episode of the first series of the ''Doctor Who'' spin-off series ''Class'' Films * ''Lost'' (1950 film), a Mexican film directed by Fernando A. Rivero * ''Lost'' (1956 film), a British thriller starring David Farrar * ''Lost'' (1983 film), an American film directed by Al Adamson * ''Lost!'' (film), a 1986 Canadian film directed by Peter R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
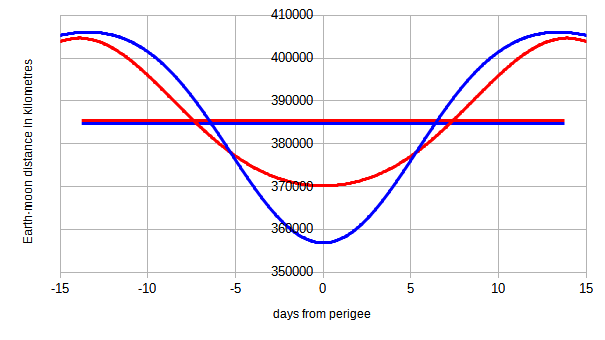
Lunar Distance (astronomy)
The instantaneous Earth–Moon distance, or distance to the Moon, is the distance from the center of Earth to the center of the Moon. In contrast, the Lunar distance (LD or \Delta_), or Earth–Moon characteristic distance, is a unit of measure in astronomy. More technically, it is the semi-major axis of the geocentric orbit of the Moon, lunar orbit. The average lunar distance is approximately , or 1.3 light-seconds. It is roughly 30 times Earth radius, Earth's diameter and a non-stop plane flight traveling that distance would take more than two weeks. Around 389 lunar distances make up an astronomical unit (roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun). Lunar distance is commonly used to express the distance to near-Earth object encounters. Lunar semi-major axis is an important astronomical datum. It has implications for testing gravitational theories such as general relativity and for refining other astronomical values, such as the Earth mass, mass, Earth radius, radius, and Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Planet
A terrestrial planet, tellurian planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate, rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Among astronomers who use the geophysical definition of a planet, two or three planetary-mass satellites – Earth's Moon, Io, and sometimes Europa – may also be considered terrestrial planets. The large rocky asteroids Pallas and Vesta are sometimes included as well, albeit rarely. The terms "terrestrial planet" and "telluric planet" are derived from Latin words for Earth (''Terra'' and ''Tellus''), as these planets are, in terms of structure, ''Earth-like''. Terrestrial planets are generally studied by geologists, astronomers, and geophysicists. Terrestrial planets have a solid planetary surface, making them substantially different from larger gaseous planets, which are composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationship is found between a pair of objects (binary resonance). The physical principle behind orbital resonance is similar in concept to pushing a child on a swing, whereby the orbit and the swing both have a natural frequency, and the body doing the "pushing" will act in periodic repetition to have a cumulative effect on the motion. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of the bodies (i.e., their ability to alter or constrain each other's orbits). In most cases, this results in an ''unstable'' interaction, in which the bodies exchange momentum and shift orbits until the resonance no longer exists. Under some circumstances, a resonant system can be self-correcting and thus stable. Examples are the 1:2:4 resona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |