|
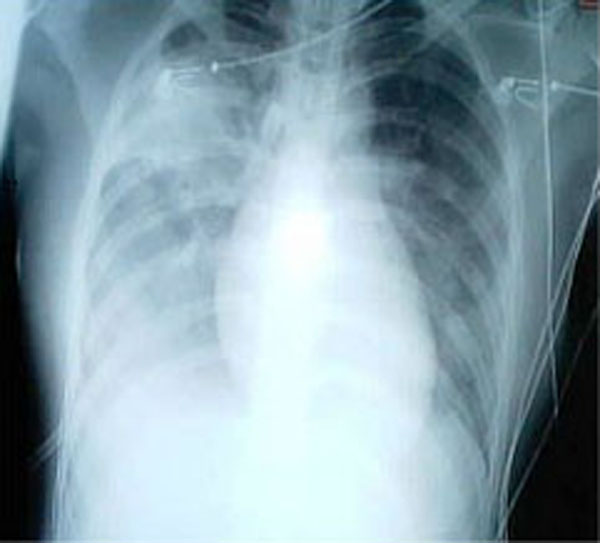
2002–2004 SARS Outbreak Among Healthcare Workers
The rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in healthcare workers (HCW)—most notably in Toronto, Ontario hospitals—during the 2002–04 SARS outbreak, global outbreak of SARS in 2002–2003 contributed to dozens of identified cases, some of them fatal. SARS is known to have arrived in Ontario on 23 February 2003 when an elderly woman returned to Toronto from Hong Kong. She died at home on 5 March, after infecting her son, who subsequently spread the disease to Birchmount Hospital, Scarborough Grace Hospital, dying on 13 March. Researchers have found several key reasons for this development, such as the high-risk performances of medical operations on patients with SARS, inadequate use of protective equipment, psychological effects on the workers in response to the stress of dealing with the outbreak, and lack of information and training on treating SARS. Lessons learned from this outbreak among healthcare workers have contributed to newly developed treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sars Cases And Deaths
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. In 2004, Xue Wu Zhang and Yee Leng Yap found that the Spike 2 (S2) protein of SARS is structurally similar to HIV-1 Gp41, gp41 subunit, suggesting an analogous membrane fusion mechanism between the two. In the 2010s, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.The locality was referred to be "a cave in Kunming" in earlier sources because the Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township is administratively part of Kunming, though 70 km apart. Xiyang was identified on * For an earlier interview of the researchers about the locality of the caves, see: SARS was a relatively rare disease; at the end of the epidemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Mask
A surgical mask, also known by other names such as a medical face mask or procedure mask, is a personal protective equipment used by healthcare professionals that serves as a mechanical barrier that interferes with direct airflow in and out of respiratory orifices (i.e. human nose, nose and human mouth, mouth). This helps reduce airborne transmission of pathogens and other aerosolized contaminants between the wearer and nearby people via respiratory droplets ejected when sneezing, coughing, forceful breathing, expiration or unintentionally spitting when talking, etc. Surgical masks may be labeled as surgical, isolation, dental or medical procedure masks. Although the material of which surgical masks are made will filter out some viruses and bacteria by trapping the aerosol suspended in breathed air, they only provide partial protection from airborne diseases because of the typically loose fit between the mask edges and the wearer's face. Surgical masks are distinct from mechanica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (medicine)
In medicine, public health, and biology, transmission is the passing of a pathogen causing Infectious disease, communicable disease from an infected host (biology), host individual or group to a particular individual or group, regardless of whether the other individual was previously infected. The term strictly refers to the transmission of microorganisms directly from one individual to another by one or more of the following means: * airborne transmission – very small dry and wet particles that stay in the air for long periods of time allowing airborne contamination even after the departure of the host. Particle size 5 μm. * direct physical contact – touching an infected individual, including sexual contact * indirect physical contact – usually by touching a contaminated surface, including soil (fomite) * fecal–oral route, fecal–oral transmission – usually from unwashed hands, contaminated food or water sources due to lack of sanitation and hygiene, an important tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier Nursing
Barrier nursing is a set of stringent infection control techniques used in nursing. The aim of barrier nursing is to protect medical staff against infection by patients and also protect patients with highly infectious diseases from spreading their pathogens to other non-infected people. Barrier nursing was created as a means to maximize isolation care. Since it is impossible to isolate a patient from society and medical staff while still providing care, there are often compromises made when it comes to treating infectious patients. Barrier nursing is a method to regulate and minimize the number and severity of compromises being made in isolation care, while also preventing the disease from spreading. History and usage The term "barrier nursing" was first used by the Centre for Disease Control (CDC) to describe early infection control methods in the late 1800s. From the mid-1900s to early 2000s, 15 new terms had emerged and were also being used to describe infection control. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Stress
Occupational stress is psychological stress related to one's job. Occupational stress refers to a chronic condition. Occupational stress can be managed by understanding what the stressful conditions at work are and taking steps to remediate those conditions. Occupational stress can occur when workers do not feel supported by supervisors or coworkers, feel as if they have little control over the work they perform, or find that their efforts on the job are incommensurate with the job's rewards. Occupational stress is a concern for both employees and employers because stressful job conditions are related to employees' emotional well-being, physical health, and job performance. The World Health Organization and the International Labour Organization conducted a study. The results showed that exposure to long working hours, operates through increased psycho-social occupational stress. It is the occupational risk factor with the largest attributable burden of disease, according to these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excessive amounts of stress, however, can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, and mental illnesses such as depression and also aggravate pre-existing conditions. Psychological stress can be external and related to the environment, but may also be caused by internal perceptions that cause an individual to experience anxiety or other negative emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc., which they then deem stressful. Hans Selye (1974) proposed four variations of stress. On one axis he locates good stress ( eustress) and bad stress (distress). On the other is over-stress (hyperstress) and understress (hypostress). Selye advocates balancing these: the ultimate goal would be to balance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Shield
A face shield, an item of personal protective equipment, aims to protect the wearer's entire face (or part of it) from hazards such as Projectile, flying objects and road debris, chemical splashes (in laboratory, laboratories or in Industry (economics), industry), or potentially Infection, infectious materials (in Medicine, medical and laboratory environments). Applications Medical In Medicine, medical applications the device is used to protect a medical professional during a procedure that might expose them to blood or other potentially infectious fluids or aerosols. An example is the use of a Pocket mask, CPR mask while performing Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, rescue breathing or Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, CPR. Another example is the use of face shields to reduce the likelihood of inhaling potentially infectious bioaerosols. Police and military File:AssaultTraining2016-18.jpg, Russian Engineer Troops, Russian combat engineer with a 6B47 helmet and ballistic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goggles
Goggles, or safety glasses, are forms of protective eyewear that usually enclose or protect the area surrounding the eye in order to prevent particulates, water or chemicals from striking the eyes. They are used in chemistry laboratories and in woodworking. They are often used in snow sports as well, and in the sport of swimming. Goggles are often worn when using power tools such as drills or chainsaws to prevent flying particles from damaging the eyes. Many types of goggles are available as prescription goggles for those with vision problems. History The Inuit and Yupik carved snow goggles from the antlers of caribou, wood, and shell to help prevent snow blindness. The goggles were curved to fit the user's face and had a large groove cut in the back to allow for the nose. A long thin slit was cut through the goggles to allow in a small amount of light, diminishing subsequent ultraviolet rays. The goggles were held to the head by a cord made of caribou sinew. In the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms, known as temples or temple pieces, that rest over the ears for support. Glasses are typically used for vision correction, such as with reading glasses and glasses used for nearsightedness; however, without the specialized lenses, they are sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Safety glasses are eye protection, a form of personal protective equipment ( PPE) that are worn by workers around their eyes for protection. Safety glasses act as a shield to protect the eyes from any type of foreign debris that may cause irritation or injury; these glasses may have protection on the sides of the eyes as well as in the lenses. Some types of safety glasses are used to protect against visible and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Protection
Eye protection is protective gear for the eyes, and sometimes face, designed to reduce the risk of injury. Examples of risks requiring eye protection can include: impact from particles or debris, light or radiation, wind blast, heat, sea spray or impact from some type of ball or puck used in sports. Eye protection are typically separated into categories based on the style of eye wear and the hazard they are designed to reduce. There categories include: Spectacles with side protection; Goggles; Welding helmet; Welding Hand Shields; Non-Rigid Helmets (hoods); Face shield; and Respirator Face pieces. Styles Spectacles Safety glasses or spectacles, although often used as a catch-all term for all types of eye protection, specifically revers to protective equipment that closely resembles common eye wear. To meet most national standards, spectacles must include side shields to reduce the ability of debris to get behind the lenses from the side. Safety glasses can often moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Glove
Medical gloves are disposable gloves used during medical examinations and procedures to help prevent cross-contamination between caregivers and patients. Medical gloves are made of different polymers including latex, nitrile rubber, polyvinyl chloride and neoprene; they come unpowdered, or powdered with corn starch to lubricate the gloves, making them easier to put on the hands. Corn starch replaced tissue-irritating lycopodium powder and talc, but even corn starch can impede healing if it gets into tissues (as during surgery). As such, unpowdered gloves are used more often during surgery and other sensitive procedures. Special manufacturing processes are used to compensate for the lack of powder. There are two main types of medical gloves: examination and surgical. Surgical gloves have more precise sizing with a better precision and sensitivity and are made to a higher standard. Examination gloves are available either sterile or non-sterile, while surgical gloves are generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |