|
1998 FIVB Women's World Championship
The 1998 FIVB Women's Volleyball World Championship, FIVB Women's World Championship was the thirteenth edition of the tournament, organized by the world's governing body, the FIVB. It was held from 3 to 12 November 1998 in Tokyo, Tokuyama, Yamaguchi, Tokuyama, Matsumoto, Nagano, Matsumoto, Kagoshima, Nagoya, Fukuoka, and Osaka, Japan. Qualification Source:Official website Squads Venues Source: Format The tournament was played in three different stages (the first, second, and final rounds). In the , the 16 participants were divided into four groups of four teams each. A Round-robin tournament, single round-robin format was played within each group to determine the teams' group position; the three best teams of each group (a total of 12 teams) progressed to the next round. In the , the 12 teams were divided into two groups of six teams. A Round-robin tournament, single round-robin format was played within each group to determine the teams' group position; matches already p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akihito
Akihito (born 23 December 1933) is a member of the Imperial House of Japan who reigned as the 125th emperor of Japan from 1989 until 2019 Japanese imperial transition, his abdication in 2019. The era of his rule was named the Heisei era, Heisei being an expression of achieving peace worldwide. Born in 1933, Akihito is the fifth child and first son of Hirohito, Emperor Shōwa and Empress Nagako, Empress Kōjun. During the Second World War, he moved out of Tokyo with his classmates and remained in Nikkō until 1945. In 1952, his Coming-of-Age ceremony and investiture as crown prince were held, and he began to undertake official duties in his capacity as crown prince. The next year, he made his first journey overseas and represented Japan at the coronation of Elizabeth II in London. He completed his university education in 1956. In April 1959, he married Empress Michiko, Michiko Shōda, a commoner; it was the first imperial wedding to be televised in Japan, drawing about 15 mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
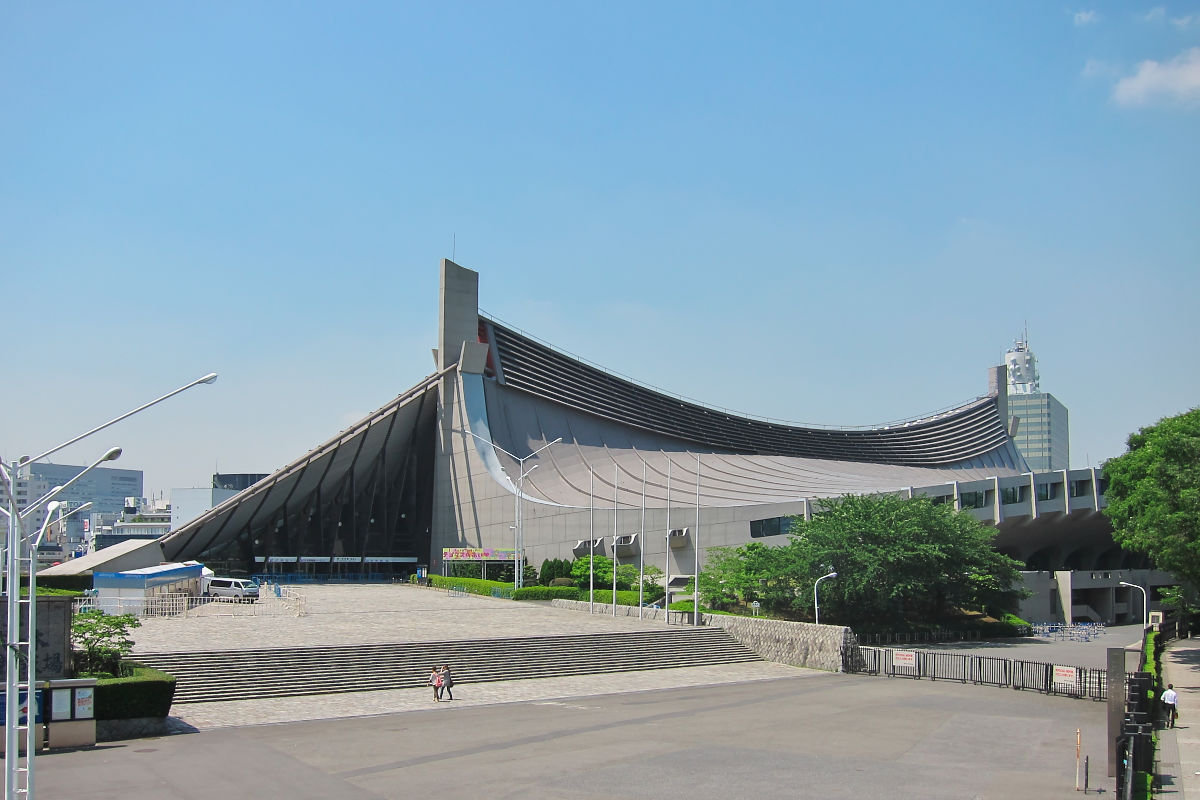
Nagoya City Sports Complex 01
is the largest city in the Chūbu region of Japan. It is the fourth-most populous city in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020, and the principal city of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, which is the third-most populous metropolitan area in Japan with a population of 10.11million. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and most populous city of Aichi Prefecture, with the Port of Nagoya being Japan's largest seaport. In 1610, the warlord Tokugawa Ieyasu, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, moved the capital of Owari Province from Kiyosu to Nagoya. This period saw the renovation of Nagoya Castle. The arrival of the 20th century brought a convergence of economic factors that fueled rapid growth in Nagoya during the Meiji Restoration, and it became a major industrial hub for Japan. The traditional manufactures of timepieces, bicycles, and sewing machines were followed by the production of special steels, ceramic, chemicals, oil, and petrochemicals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Round
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units (SI) is more precise: The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. As the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. The definition that is based on of a rotation of the earth is still used by the Universal Time 1 (UT1) system. Etymology "Minute" co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Équipe
''L'Équipe'' (, French for "the team") is a French nationwide daily newspaper devoted to sport, owned by Éditions Philippe Amaury. The paper is noted for coverage of association football, rugby, motorsport, and cycling. Its predecessor, ''L'Auto'', was founded by wealthy conservative industrialists to undermine '' Le Vélo'', which they found too progressive. It was a general sports paper that also covered the auto racing which was gaining popularity at the turn of the twentieth century. ''L'Auto'' launched the Tour de France road cycling stage race in 1903 as a circulation booster. The race leader's yellow jersey () was instituted in 1919, reflecting the distinctive yellow newsprint on which ''L'Auto'' was published. The European Champion Clubs' Cup, the competition that would later be rebranded as the UEFA Champions League, was also the brainchild of a ''L'Équipe'' journalist, Gabriel Hanot. The participating clubs in the first season were selected by ''L'Équipe' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Standard Time
, or , is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time. Japan Standard Time is equivalent to Time in South Korea, Korean Standard Time, Time in North Korea, Pyongyang Time (North Korea), Time in Indonesia, Eastern Indonesia Standard Time, Time in East Timor, East-Timorese Standard Time, Time in Palau, Palau Time, and Yakutsk Time (Russia). History Before the Meiji (era), Meiji era (1868–1912), each local region had its own time zone in which noon was when the sun was exactly at its culmination. As modern transportation methods, such as trains, were adopted, this practice became a source of confusion. For example, there is a difference of about 5 degrees longitude between Tokyo and Osaka and because of this, a train that departed from Tokyo would arrive at Osaka 20 minu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIVB World Rankings
The FIVB Senior World Rankings is a ranking system for men's and women's national teams in volleyball. The teams of the member nations of Fédération Internationale de Volleyball (FIVB), volleyball's world governing body, are ranked based on their game results with the most successful teams being ranked highest. A points system is used, with points being awarded based on the results of all FIVB-recognised full international matches. The rankings are used in international competitions to define the seeded teams and arrange them in pools. Specific procedures for seeding and pooling are established by the FIVB in each competition's formula, but the method usually employed is the serpentine system. The ranking system has been revamped in 2020, responding to criticism that the preceding calculation method did not effectively reflect the relative strengths of the national teams. The old version of the ranking system was finally used on 31 January 2020. As of 8 January 2025, the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine System
The serpentine system, also known as snake seeding, is a method of organization used in competitions to define the seeded teams and arrange them into pools. The ''n'' ranked teams that will be involved in the tournament are distributed in ''m'' pools according to the following algorithm In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...: For instance, 12 teams would be organized in four-team pools as follows: To improve competitivity, this method is sometimes used in conjunction with the drawing of lots. The serpentine system is used only for some of the teams involved in the competition ("seeds"), and the rest are distributed in pools following a drawing of lots. Sports terminology Tournament systems {{Sport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-elimination Tournament
A single-elimination knockout, or sudden-death tournament is a type of elimination tournament where the loser of a match-up is immediately eliminated from the tournament. Each winner will play another in the next round, until the final match-up, whose winner becomes the tournament champion(s). Some match-ups may be a single match or several, for example two-legged ties in European sports or best-of series in North American pro sports. Defeated competitors may play no further part after losing, or may participate in "consolation" or "classification" matches against other losers to determine the lower final rankings; for example, a third place playoff between losing semi-finalists. In a shootout poker tournament, there are more than two players competing at each table, and sometimes more than one progresses to the next round. Some competitions are held with a pure single-elimination tournament system. Others have many phases, with the last being a single-elimination final stage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round-robin Tournament
A round-robin tournament or all-play-all tournament is a competition format in which each contestant meets every other participant, usually in turn.''Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1971, G. & C. Merriam Co), p.1980. A round-robin contrasts with an elimination tournament, wherein participants are eliminated after a certain number of wins or losses. Terminology The term ''round-robin'' is derived from the French term ('ribbon'). Over time, the term became idiomized to ''robin''. In a ''single round-robin'' schedule, each participant plays every other participant once. If each participant plays all others twice, this is frequently called a ''double round-robin''. The term is rarely used when all participants play one another more than twice, and is never used when one participant plays others an unequal number of times, as is the case in almost all of the major North American professional sports leagues. In the United Kingdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Messe
in Hakata-ku, Fukuoka, Japan is a collection of three separate buildings operated by the Fukuoka Convention Center Foundation. Fukuoka Kokusai Center The Fukuoka Kokusai Center opened in . A Sumo Tournament is held here every November. Many Grand Sumo Tournaments are held here and all attract many visitors. Marine Messe Fukuoka Marine Messe Fukuoka opened in for the 1995 Summer Universiade. One of its main uses is as an indoor sporting arena. The capacity of the arena is up to 15,000 people for sports events and up to 13,000 people for concerts. It hosted the 1999 Asian Basketball Championship, the 2001 World Aquatics Championships and the preliminary rounds during the 2006 Volleyball World Championship Japanese musicians Misia, Koda Kumi, and Ayumi Hamasaki commonly play here for arena tours. Fukuoka International Congress Center The Fukuoka International Congress Center opened in . Events Past events * 1997 Celine Dion Céline Marie Claudette Dion (born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |