|
1974 In Science
The year 1974 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy and space exploration * February 8 – After 84 days in space, the last crew of the temporary American space station Skylab return to Earth. * February 13–15 – Sagittarius A*, thought to be the location of a supermassive black hole, is identified by Bruce Balick and Robert Brown using the baseline interferometer of the United States National Radio Astronomy Observatory. * November 16 – Arecibo message transmitted from Arecibo Observatory (Puerto Rico) to Messier 13. * Hawking radiation is predicted by Stephen Hawking. Computer Science * The Mark-8 microcomputer based on the Intel 8008 microprocessor is designed by Jonathan Titus. It is announced on the cover of the July 1974 issue of Radio-Electronics as "Your Personal Minicomputer". History of science * F. W. Winterbotham publishes ''The Ultra secret: the inside story of Operation Ultra, Bletchley Park and Enigma'', the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive (though indeed present-day mainframes such as the IBM System z machines use one or more custom microprocessors as their CPUs). Many microcomputers (when equipped with a keyboard and screen for input and output) are also personal computers (in the generic sense). An early use of the term "personal computer" in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. ''(See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below)''. A "microcomputer" used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable input and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perinatal
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth. The term "prenate" is used to describe an unborn offspring at any stage of gestation. In human pregnancy, prenatal development is also called antenatal development. The development of the human embryo follows fertilization, and continues as fetal development. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age, the embryo has acquired its basic form and is referred to as a fetus. The next period is that of fetal development where many organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age. The very early stages of embryonic development are the same in all mammals, but later stages of development, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Jobe
Frank Wilson Jobe (July 16, 1925 – March 6, 2014) was an American Orthopedic surgery, orthopedic surgeon and co-founder of the Kerlan-Jobe Orthopaedic Clinic. Jobe pioneered both elbow ligament replacement and major reconstructive shoulder surgery for baseball players. In 1974, Jobe performed the first "Tommy John surgery" on then-Los Angeles Dodgers pitcher Tommy John. The procedure has become so prevalent an estimated one-third of all major league pitchers have undergone it. Jobe also performed the first major reconstructive shoulder surgery on a big league player in 1990, which allowed Dodger star Orel Hershiser to continue his career. Jobe served as a special medical adviser to the Dodgers until his death. Early life Frank Jobe was born in 1925 in Greensboro, North Carolina. After graduating from Collegedale Academy in Collegedale, Tennessee in 1943, he enlisted in the United States Army and reported to Camp Barkeley for training. Serving in World War II as a medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) or internal lateral ligament is a thick triangular ligament at the medial aspect of the elbow uniting the distal aspect of the humerus to the proximal aspect of the ulna. Structure It consists of two portions, an anterior and posterior united by a thinner intermediate portion. Note that this ligament is also referred to as the medial collateral ligament and should not be confused with the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL). The ''anterior portion'', directed obliquely forward, is attached, above, by its apex, to the front part of the medial epicondyle of the humerus; and, below, by its broad base to the medial margin of the coronoid process of the ulna. The ''posterior portion'', also of triangular form, is attached, above, by its apex, to the lower and back part of the medial epicondyle; below, to the medial margin of the olecranon. Between these two bands a few intermediate fibers descend from the medial epicondyle to blend with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tommy John Surgery
Ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction, sometimes referred to as Tommy John surgery is a surgical graft procedure where the ulnar collateral ligament in the medial elbow is replaced with either a tendon from elsewhere in the patient's body, or with one from a deceased donor. The procedure is common among collegiate and professional athletes in several sports, particularly in baseball. The surgery is performed to restore optimal function for repetitive elbow movements or specifically throwing ability, often extending the careers of professional athletes. In many athletes, the surgery is done more than once during their careers. The procedure was devised in 1974 by orthopedic surgeon Frank Jobe, a Los Angeles Dodgers team physician who served as a special advisor to the team until his death in 2014. It is named after the first baseball player to undergo the surgery, major league pitcher Tommy John, who played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for 26 seasons. The initial operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frey Curve
In mathematics, a Frey curve or Frey–Hellegouarch curve is the elliptic curve y^2 = x(x - \alpha)(x + \beta) associated with an ABC triple \alpha+\beta=\gamma . This relates properties of solutions of equations to elliptic curves. This curve was popularized in its application to Fermat’s Last Theorem where one investigates a (hypothetical) solution of Fermat's equation :a^\ell + b^\ell = c^\ell. The curve is named after Gerhard Frey and (sometimes) . History came up with the idea of associating solutions (a,b,c) of Fermat's equation with a completely different mathematical object: an elliptic curve. If ℓ is an odd prime and ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are positive integers such that a^\ell + b^\ell = c^\ell, then a corresponding Frey curve is an algebraic curve given by the equation y^2 = x(x - a^\ell)(x + b^\ell), or, equivalently y^2 = x(x - a^\ell)(x - c^\ell). This is a nonsingular algebraic curve of genus one defined over Q, and its projective completion is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermat's Last Theorem
In number theory, Fermat's Last Theorem (sometimes called Fermat's conjecture, especially in older texts) states that no three positive number, positive integers , , and satisfy the equation for any integer value of greater than . The cases and have been known since antiquity to have infinitely many solutions.Singh, pp. 18–20 The proposition was first stated as a theorem by Pierre de Fermat around 1637 in the margin of a copy of ''Arithmetica''. Fermat added that he had a proof that was too large to fit in the margin. Although other statements claimed by Fermat without proof were subsequently proven by others and credited as theorems of Fermat (for example, Fermat's theorem on sums of two squares), Fermat's Last Theorem resisted proof, leading to doubt that Fermat ever had a correct proof. Consequently, the proposition became known as a conjecture rather than a theorem. After 358 years of effort by mathematicians, Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, the first success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
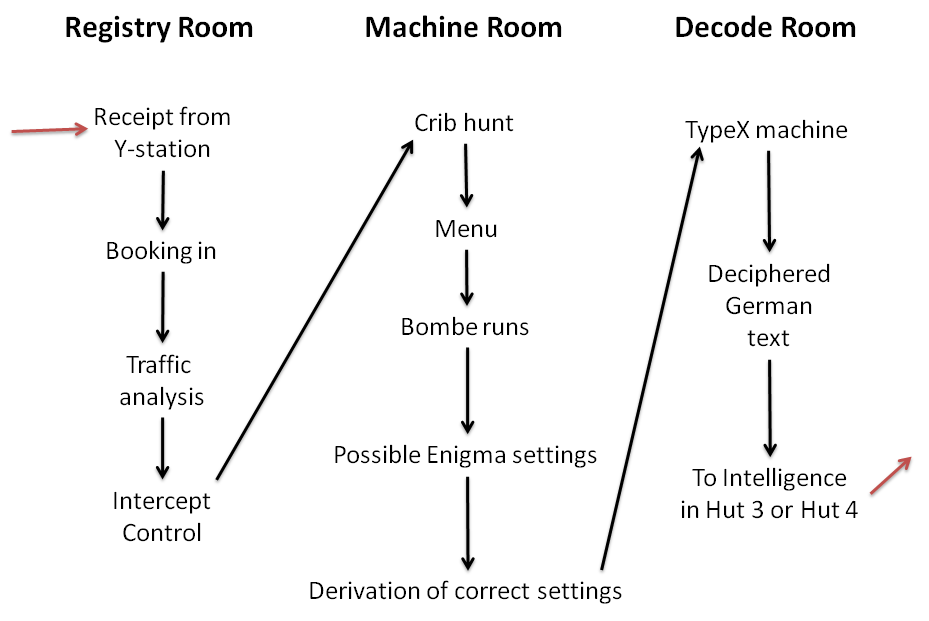
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the Second World War. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powers most importantly the German Enigma machine, Enigma and Lorenz cipher, Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included John Tiltman, Dilwyn Knox, Alan Turing, Harry Golombek, Gordon Welchman, Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander, Hugh Alexander, Donald Michie, W. T. Tutte, Bill Tutte and Stuart Milner-Barry. The team at Bletchley Park devised automatic machinery to help with decryption, culminating in the development of Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's first programmable digital electronic computer. Codebreaking operations at Bletchley Park ended in 1946 and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing Communication protocol, protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (confidentiality, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, Smart card#EMV, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, password, computer passwords, and military communications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |