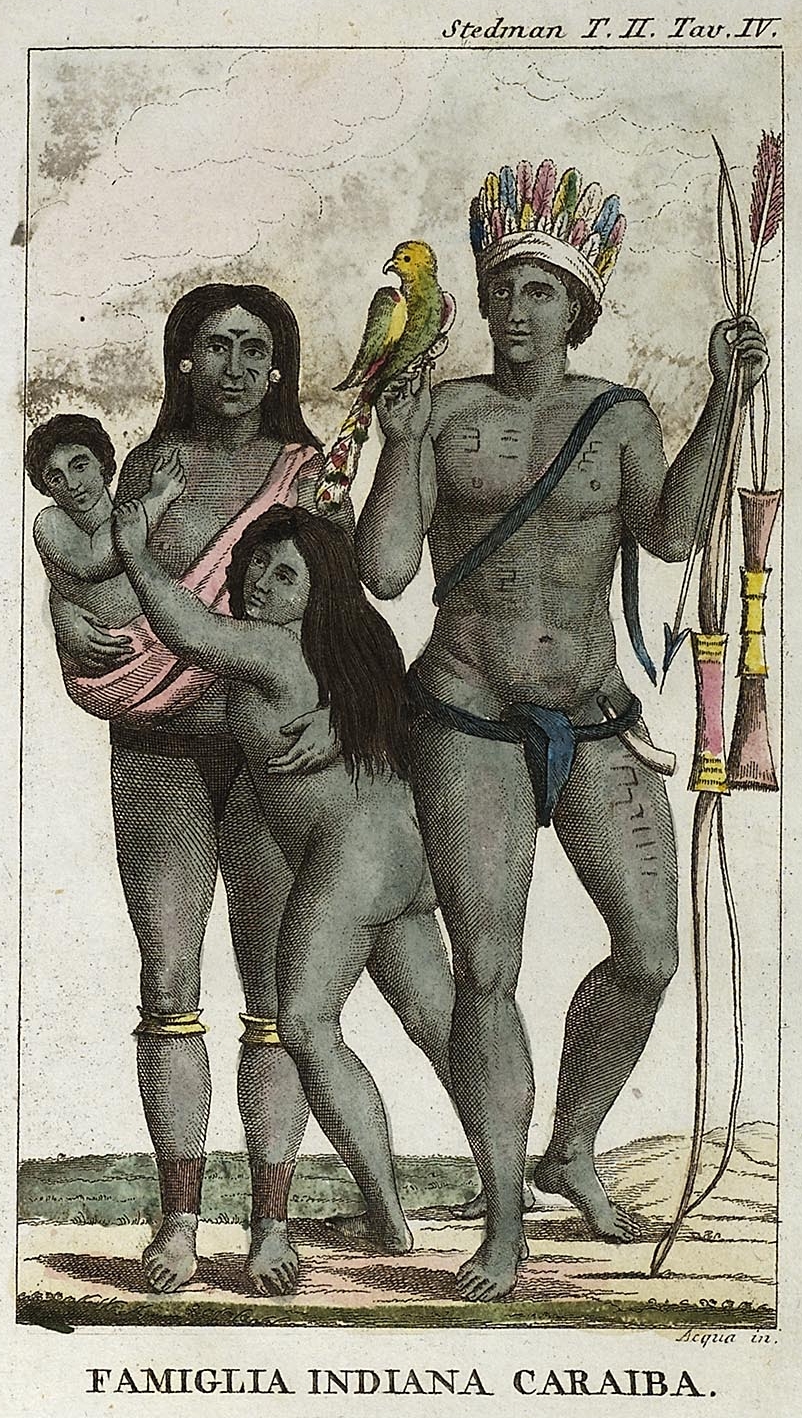|
ĂŽles Des Saintes
The Îles des Saintes (; ), also known as Les Saintes (, ), is a group of small islands in the archipelago of Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. It is part of the Canton of Trois-Rivières and is divided into two communes: Terre-de-Haut and Terre-de-Bas. It is in the arrondissement of Basse-Terre and also in Guadeloupe's 4th constituency. History Pre-Columbian ''Les Saintes'', due to their location in the heart of the Lesser Antilles, were frequented first by Indian tribes coming from Caribbean and Central America. ''Caaroucaëra'' (the Arawak name of ''Îles des Saintes''), although uninhabited due to the lack of spring water, were regularly visited by Arawak peoples then Kalinagos living on the neighbourhood islands of Guadeloupe and Dominica around the 9th century. They went there to practise hunting and fishing. The archaeological remains of war axes and pottery dug up on the site of ''Anse Rodrigue's Beach'' and stored at "Fort Napoléon" museum test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French-based Creole Language
A French creole, or French-based creole language, is a creole for which French is the lexifier. Most often this lexifier is not modern French but rather a 17th- or 18th-century koiné of French from Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the nascent French colonies. This article also contains information on French pidgin languages, contact languages that lack native speakers. These contact languages are not to be confused with creolized varieties of French outside of Europe that date to colonial times, such as Acadian, Louisiana, New England or Quebec French. There are over 15.5 million speakers of some form of French-based creole languages. Haitian Creole is the most spoken creole language in the world, with over 12 million speakers. History Throughout the 17th century, French Creoles became established as a unique ethnicity originating from the mix of French, Indian, and African cultures. These French Creoles held a distinct ethno-cultural identity, a shared antique la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Commune Of France
A () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondissements of its largest cities, the are the lowest level of administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Houël Du Petit Pré
Charles Houël du Petit Pré (; 161622 April 1682) was a French governor of Guadeloupe from 1643 to 1664. He was also knight and lord. He became, by a royal proclamation dated August 1645, the first of the island judicial officer. He is named Marquis de Guadeloupe by Louis XIV. On 4 September 1649, Charles Houël, who partnered with his brother in law John Boisseret Herblay, bought the bankrupt Compagnie Guadeloupe, Marie-Galante, La Désirade and Les Saintes for 60,000 books pétun (tobacco) and was committed to deliver 600 pounds of sugar per year. In order to secure the site and solidify its grip on the population, he built Fort Saint-Charles () in 1650. Despite the 1640 peace treaty between Indians and France, clashes with the Caribbean continued. On 31 March 1660, Charles Houël signed a treaty with the Caribbean, who abandoned the majority of the island to the French and retreated to the island of Dominica. However, a small number of Indians took refuge north and east of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Colonial And Departmental Heads Of Guadeloupe
(Dates in italics indicate ''de facto'' continuation of office) Note: currently, the Prefect (France), prefect is not the true departmental head, which is the President of the General Council. The prefect is merely the representative of the national government. Ancien regime Governors under the Ancien RĂ©gime were: Revolution and First Empire Restoration, Second Republic, Second Empire Third, Fourth, Fifth republics Notes Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Colonial And Departmental Heads Of Guadeloupe Governors of Guadeloupe, Lists of French colonial governors and administrators, Guadeloupe Prefects of Guadeloupe, * Guadeloupe-related lists, Colonial and Departmental Heads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
All Saints' Day
All Saints' Day, also known as All Hallows' Day, the Feast of All Saints, the Feast of All Hallows, the Solemnity of All Saints, and Hallowmas, is a Christian solemnity celebrated in honour of all the saints of the Church, whether they are known or unknown. From the 4th century, feasts commemorating all Christian martyrs were held in various places, on various dates near Easter and Pentecost. In the 9th century, some churches in the British Isles began holding the commemoration of all saints on 1 November, and in the 9th century this was extended to the whole Catholic Church by Pope Gregory IV. In Western Christianity, it is still celebrated on 1 November by the Western Catholic Church as well as by many Protestant churches, such as the Lutheran, Anglican, and Methodist traditions. The Eastern Orthodox Church and associated Eastern Catholic and Eastern Lutheran churches celebrate it on the first Sunday after Pentecost. The Syro-Malabar Church and the Chaldean Catholic C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening the way for the widespread European Age of Discovery, exploration and colonization of the Americas. His expeditions were the first known European contact with the Caribbean and Central and South America. The name ''Christopher Columbus'' is the Anglicisation (linguistics), anglicization of the Latin . Growing up on the coast of Liguria, he went to sea at a young age and traveled widely, as far north as the British Isles and as far south as what is now Ghana. He married Portuguese noblewoman Filipa Moniz Perestrelo, who bore a son, Diego Columbus, Diego, and was based in Lisbon for several years. He later took a Castilian mistress, Beatriz EnrĂquez de Arana, who bore a son, Ferdinand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fort Napoléon Des Saintes
Fort Napoléon (in French: ''Fort Napoléon des Saintes'') is a fortification, located on Terre-de-Haut Island, in the Îles des Saintes, Guadeloupe. Property of the Departmental Council of Guadeloupe, it has been classified as a historical monument since the December 15, 1997. Fort Napoléon was built on the ''morne'' (Caribbean French language, French word for "Hill, bluff") called ''Mire'', it was originally named ''Fort Louis''. It was destroyed by UK, British forces in 1809. It was rebuilt in 1867, and named after Napoleon III, but never saw use in battle, and was instead used as a Prison, penitentiary. It has now been turned into a museum dedicated to the Saintes’ history, culture, and environment. It also has contains the Jardin exotique du Fort Napoléon, a botanical garden dedicated to local succulent plants and iguanas. History From 1759 to 1763, the English took possession of Saintes, Charente-Maritime, Saintes and part of mainland Guadeloupe. The archipelago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Island Caribs
The Kalinago, also called Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, Indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Kalina people, Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Kalinago language, Kalinago or Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean (the name of which is derived from "Carib", as the Kalinago were once called). They lived throughout north-eastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arawak Peoples
The Arawak are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. The term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to different Indigenous groups, from the Lokono of South America to the TaĂno (Island Arawaks), who lived in the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. All these groups spoke related Arawakan languages. Name Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and ''Kalinago#Name, Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for Indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. In 1871, ethnologist Daniel Garrison Brinton proposed calling the Caribbean populace "Island Arawak" because of their cultural and linguistic similarities with the mainland Arawak. Subsequent scholars shortened this convention to "Arawak", creating confusion between the island and mainland groups. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. Most of Central America falls under the Isthmo-Colombian cultural area. Before the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to the Americas, hundreds of indigenous peoples made their homes in the area. From the year 1502 onwards, Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Guadeloupe's 4th Constituency
The 4th constituency of Guadeloupe () is a French legislative Constituency in the Overseas department of Guadeloupe. Since 2022, is represented by Élie Califer of the Socialist Party. Guadeloupe's fourth constituency consists of Les Saintes and southern Basse-Terre. Deputies Election results 2024 2022 , - , colspan="8" bgcolor="#E9E9E9", , - * Withdrew after the first round. 2017 2012 See also * Arrondissements of Guadeloupe * Cantons of Guadeloupe * Constituency (France) * Deputy (France) Deputies (, ), also known in English as members of Parliament (MPs), are the legislators who sit in the National Assembly (France), National Assembly, the lower house of the French Parliament. The 17th legislature of the French Fifth Republic, 17 ... References External links Guadeloupe department * * * Constituencies of France * * * Description and Atlas of constituencies of France on . {{French National Assembly constituencies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arrondissement Of Basse-Terre
The arrondissement of Basse-Terre is an arrondissement of France in the Guadeloupe department in the Guadeloupe region. It has 18 communes. Its population is 185,012 (2021), and its area is . Composition The communes of the arrondissement of Basse-Terre, and their INSEE codes, are: # Baie-Mahault (97103) # Baillif (97104) # Basse-Terre (97105) # Bouillante (97106) # Capesterre-Belle-Eau (97107) # Deshaies (97111) # Gourbeyre (97109) # Goyave (97114) # Lamentin (97115) # Petit-Bourg (97118) # Pointe-Noire (97121) # Saint-Claude (97124) # Sainte-Rose (97129) # Terre-de-Bas (97130) # Terre-de-Haut (97131) # Trois-Rivières (97132) # Vieux-Fort (97133) # Vieux-Habitants (97134) History The arrondissement of Basse-Terre was established in 1947. The arrondissement of Saint-Martin-Saint-Barthélemy, containing the communes of Saint-Martin and Saint-Barthélemy, was created in 1963 from part of the arrondissement of Basse-Terre. As a result of the reorganisation of the canto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |