|
ÃnÊe Et Lavinie (Dauvergne)
''ÃnÊe et Lavinie'' (''Aeneas and Lavinia'') is an opera by the French composer Antoine Dauvergne, first performed at the AcadÊmie Royale de Musique (the Paris OpÊra) on 14 February 1758. It takes the form of a ''tragÊdie lyrique'' in five acts. It is a resetting of a libretto by Bernard Le Bovier de Fontenelle, which was originally set by Pascal Collasse in 1690. The story is taken from the later books of Virgil's ''Aeneid''. Roles Synopsis Aeneas, fleeing the destruction of Troy, has arrived in Latium in Italy. The King of Latium wants to marry his daughter Lavinia to Aeneas, but the Trojan has a rival in the local prince Turnus, who is favoured by the queen and the goddess Juno. Juno provokes Turnus to fight the Trojans. The king consults the oracle of his father, the god Faunus, who says that Lavinia must choose her husband for herself and then there will be peace. The ghost of Dido warns Lavinia not to trust her faithless lover Aeneas. The god Bacchus also inspires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amata
According to Roman mythology, Amata (also called Palanto) was the wife of Latinus, king of the Latins, and the mother of their only child, Lavinia. In the Aeneid of Virgil, she commits suicide during the conflict between Aeneas and Turnus over which of them would marry Lavinia. When Aeneas asks for Lavinia's hand, Amata objects, because she has already been promised to Turnus, the king of the Rutulians. Hiding her daughter in the woods, she enlists the other Latin women to instigate a war between the two. Turnus, and his ally Mezentius, leader of the Etruscans, are defeated by Aeneas with the assistance of the Pelasgian colonists from Arcadia and Italic natives of Pallantium, led by that city's founder, the Arcadian Evander of Pallene. The story of this conflict fills the greater part of the seventh book of Virgil's ''Aeneid''. When Amata believes that Turnus had fallen in battle, she hangs herself. In Dante's ''Divine Comedy'' In Canto 17 of Dante Alighieri's '' Purgat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebe (mythology)
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Hebe (; ) is the goddess of youth or of the prime of life. She was the cup-bearer for the gods of Mount Olympus, serving their nectar and ambrosia. On Sicyon, she was worshipped as a goddess of forgiveness or mercy. She was often given the epithet ''Ganymeda'' (). Hebe is a daughter of Zeus and Hera, and the divine wife of Heracles (Roman mythology, Roman equivalent: Hercules). She had influence over eternal youth and the ability to restore youth to mortals, a power that appears exclusive to her, as in Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', some gods lament the aging of their favoured mortals. According to Philostratus the Elder, Hebe was the youngest of the gods and the one responsible for keeping them eternally young, and thus was the most revered by them. Her role of ensuring the eternal youth of the other gods is appropriate to her role of serving as cup-bearer, as the word ''ambrosia'' has been linked to a possible Proto-Indo-Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophie Arnould
Sophie Arnould (13 February 1740, in Paris, France â 18 October 1802, in Paris, France) was a French operatic soprano. Biography Born Magdeleine Sophie Arnould, she studied in Paris with Marie Fel and La Clairon, and made her stage debut at the OpÊra de Paris The Paris Opera ( ) is the primary opera and ballet company of France. It was founded in 1669 by Louis XIV as the , and shortly thereafter was placed under the leadership of Jean-Baptiste Lully and officially renamed the , but continued to be kn ... on 15 December 1757 and sang there for 20 years. She created for Christoph Wilibald Gluck the roles of Eurydice in '' OrphÊe et Eurydice'' and the title role in ''IphigÊnie en Aulide''. She also obtained considerable success in operas by Jean-Philippe Rameau, François Francoeur, and Pierre-Alexandre Monsigny. Her love life was extremely colorful. Her tumultuous relationship with Louis-LÊon de Brancas, Louis-LÊon de Brancas, duc de Lauragais, resulted in four chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faunus
In Religion in ancient Rome, ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, myth, Faunus was the rustic god of the forest, plains and fields; when he made cattle fertile, he was called Inuus. He came to be equated in literature with the Greek god Pan (god), Pan, after which Romans depicted him as a horned deity, horned god. Faunus was one of the oldest Roman deities, known as the ''di indigetes''. According to the epic poet Virgil, he was a legendary king of the Latins. His shade was consulted as a goddess of prophecy under the name of Fatuus, with oracles in the sacred grove of Tibur, around the well Albunea, and on the Aventine Hill in ancient Rome itself.Peck, Harry (1897). âFaunalia Faustina.â ''Harper's Dictionary of Classical Literature and Antiquities.'' Harper & Brothers Publishers. 662-663. Marcus Terentius Varro asserted that the oracular responses were given in Saturnian (poetry), Saturnian verse. Faunus revealed the future in dreams and voices that were Incubation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faun
The faun (, ; , ) is a half-human and half-goat mythological creature appearing in Greek and Roman mythology. Originally fauns of Roman mythology were ghosts ( genii) of rustic places, lesser versions of their chief, the god Faunus. Before their conflation with Greek satyrs, they and Faunus were represented as naked men (e.g. the Barberini Faun). Later fauns became copies of the satyrs of Greek mythology, who themselves were originally shown as part-horse rather than part-goat. By the Renaissance, fauns were depicted as two-footed creatures with the horns, legs, and tail of a goat and the head, torso, and arms of a human; they are often depicted with pointed ears. These late-form mythological creatures borrowed their look from the satyrs, who in turn borrowed their look from the god Pan of the Greek pantheon. They were symbols of peace and fertility, and their Greek chieftain, Silenus, was a minor deity of Greek mythology. Origins Romans believed fauns stirred fear in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianuarius''). According to ancient Roman farmers' almanacs, Juno was mistaken as the tutelary deity of the month of January, but Juno is the tutelary deity of the month of June. Janus presided over the beginning and ending of conflict, and hence war and peace. The gates of the Temple of Janus in Rome were opened in time of war and closed to mark the arrival of peace. As a god of transitions, he had functions pertaining to birth and to journeys and exchange, and in his association with Portunus, a similar harbor and gateway god, he was concerned with travelling, trading, and shipping. Janus had no flamen or specialised priest ''( sacerdos)'' assigned to him, but the King of the Sacred Rites ''( rex sacrorum)'' himself carried out his cerem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-contre
The ''haute-contre'' (plural ''hautes-contre'') was the primary French operatic tenor voice, predominant in French Baroque and Classical opera, from the middle of the seventeenth century until the latter part of the eighteenth century. History This voice was predominantly used in male solo roles, typically heroic and amatory ones, but also in comic parts, even '' en travesti'' (see apropos the portrait reproduced below and representing Pierre JÊlyotte made up for the female title role of Rameau's ''PlatÊe ''PlatÊe'' is an opera in a prologue and three acts by Jean-Philippe Rameau with a libretto by Adrien-Joseph Le Valois d'Orville. Rameau bought the rights to the libretto ''PlatÊe ou Junon jalouse'' (''Plataea, or Juno Jealous'') by Jacques Autr ...''). Lully wrote 8 out of 14 leading male roles for the voice; Charpentier, who was an haute-contre himself, composed extensively for the voice-part, as did Rameau and, later, Gluck. The leading ''hautes-contre'' of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas ( , ; from ) was a Troy, Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus (mythology), Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy (both being grandsons of Ilus (son of Tros), Ilus, founder of Troy), making Aeneas a second cousin to Priam's List of children of Priam, children (such as Hector and Paris (mythology), Paris). He is a minor character in Greek mythology and is mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad''. Aeneas receives full treatment in Roman mythology, most extensively in Virgil's ''Aeneid'', where he is cast as an ancestor of Romulus and Remus. He became the first true hero of Rome. Snorri Sturluson identifies him with the Norse god VÃðarr of the Ãsir.The Prose Edda of Snorri Sturlson Translated by Arthur Gilchrist Brodeur [1916] Prologue II at Internet Sacred Texts Archive. Accessed 11/14/17 Etymology Aeneas is the Romanization of Greek, Romanization of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dido (Queen Of Carthage)
Dido ( ; , ), also known as Elissa ( , ), was the legendary founder and first queen of the Phoenician city-state of Carthage (located in Tunisia), in 814 BC. In most accounts, she was the queen of the Phoenician city-state of Tyre (located in Lebanon) who fled tyranny to found her own city in northwest Africa. Known only through ancient Greek and Roman sources, all of which were written well after Carthage's founding, her historicity remains uncertain. The oldest references to Dido are attributed to Timaeus, who lived in Taormina in Sicily, and died around 260 BC, which is about five centuries after the date given for the foundation of Carthage. Timaeus told the legends surrounding the founding of Carthage by Dido in his Sicilian ''History''. By his account, Dido founded Carthage in 814 BC, around the same time as the foundation of Rome, and he alluded to the growing conflict between the two cities in his own day. Details about Dido's character, life, and role in the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camilla (mythology)
In Virgil's ''Aeneid'', Camilla of the Volsci is a warrior who fights against the Trojans during the war in Latium. She stars in Book 11, where she leads a battle against the Trojans and is eventually killed. Camilla is the daughter of King Metabus and Queen Casmilla. ''Aeneid'' Camilla appears in books 7 and 11 of the ''Aeneid''. Virgil says that Camilla was so fast on her feet that she could run over a field of wheat without breaking the tops of the plants, or over the ocean without wetting her feet. When Camilla was an infant, her father Metabus was driven from his throne and chased into the wilderness by armed Volsci, holding Camilla in his hands. The river Amasenus blocked his path, and, fearing for the child's welfare, Metabus bound Camilla to a spear. He promised Diana that Camilla would be her servant, a warrior virgin. He then safely threw her to the other side, and swam across to retrieve her. The baby Camilla was suckled by a mare, and once her "first firm steps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
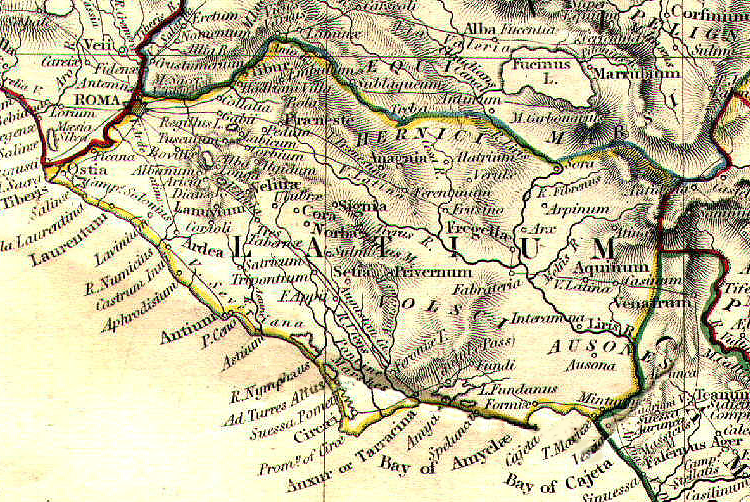
Rutuli
The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome. Thought to have been descended from the Umbri and the Pelasgians, according to modern scholars they were more probably connected with the Etruscan or Ligurian peoples. Mythological history In Virgil's ''Aeneid'', and also according to Livy, the Rutuli are led by Turnus, a young prince to whom Latinus, king of the Latins, had promised the hand of his daughter Lavinia in marriage. When the Trojans arrived in Italy, Latinus decided to give his daughter to Aeneas instead because of instructions he had received from the gods to marry his daughter to a foreigner. Turnus was outraged and led his people as well as several other Italian tribes against the Trojans in war. Virgil's text ends when Aeneas defeats Turnus in single combat and therefore confirms his right to marry Lavinia. In some other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |