|
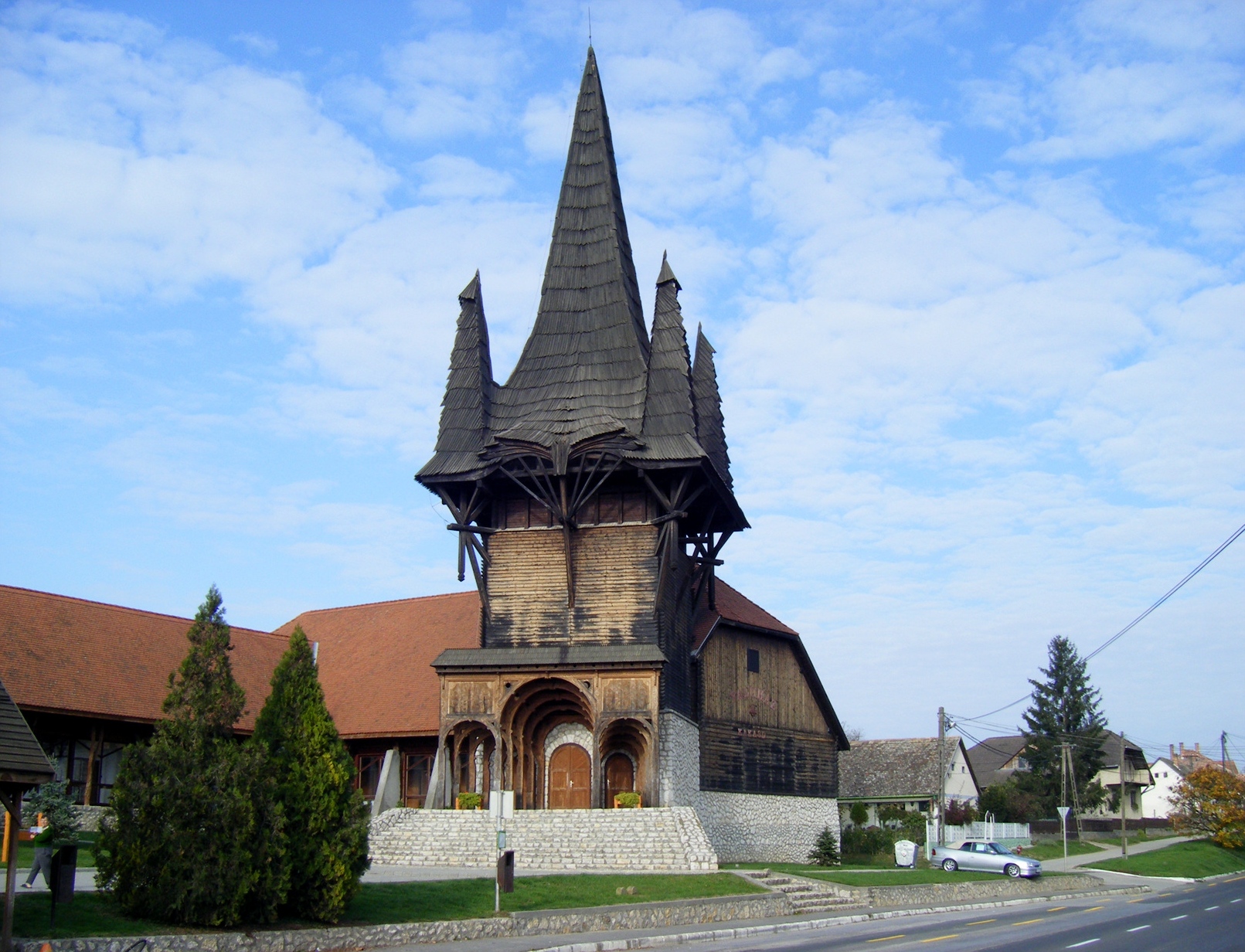
ÃrpÃĄd VezÃĐr Grammar School
The ÃrpÃĄd VezÃĐr Grammar School is a secondary school in SÃĄrospatak, Hungary. Etymology The school was named for ÃrpÃĄd vezÃĐr, who was a prominent figure in Hungarian history in the ninth century. He led the Settlement of the Magyars. The school's coat of arms recalls the period, depicting of trees from the settlement of Magyars. This tree of life symbolizes the tight and unbreakable relation between past and future, tradition and modernity. The ArpÃĄd VezÃĐr Grammar School is one of the youngest local secondary schools. Educational work started in 1993. The building was designed by Imre Makovecz. The main objectives are: * modern general education of students * successful preparation of higher education institutions. The school plays an important role in information technology, foreign language education, and talent management. Students perform successfully in national academic and sports competitions, graduate, and meet preliminary, ECDL exams and language requirements. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SÃĄrospatak
SÃĄrospatak (; ; Serbian language, Serbian: ÐŅÐī ÐĄŅŅÐĩаО; Slovak language, Slovakian: ''Å ariÅĄskÃ― Potok, BlatnÃ― Potok)'' History The area has been inhabited since ancient times. SÃĄrospatak was granted town status in 1201 by Emeric of Hungary, King Emeric. In the Middle Ages it was an important place due to its proximity to an important trade route leading to Poland. Castle of SÃĄrospatak 13th century Its castle, built by Andrew II of Hungary, Andrew II, is traditionally identified as the birthplace of his daughter Saint Elizabeth of Hungary, Saint Elizabeth. 15th and 16th centuries SÃĄrospatak was elevated to the rank of free royal town by Sigismund of Hungary, King Sigismund. In 1460, during the reign of Matthias I of Hungary, King Matthias it received the right to hold a Market town, market. In the 15th and 16th centuries, it was owned by the PÃĄlÃģczi (PÃĄlÃģczy) family, until baron Antal PÃĄlÃģczi was killed at the first Battle of MohÃĄcs in 1526, which preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
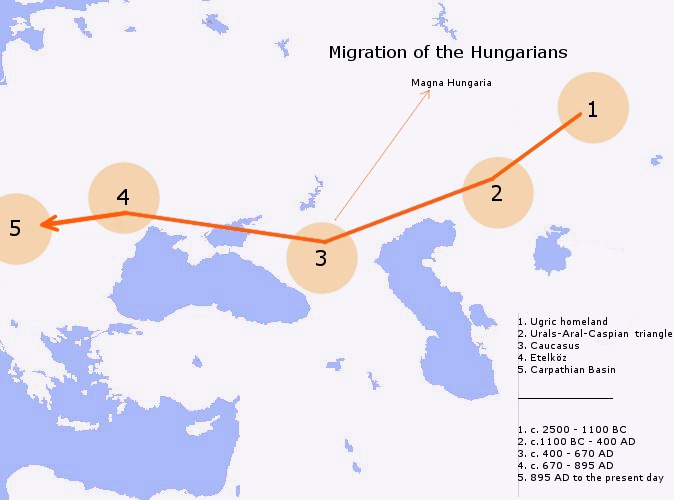
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty and Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. In addition, significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina, and therefore constitute the Hungarian diaspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imre Makovecz
Imre Makovecz (November 20, 1935 â September 27, 2011) was a Hungary, Hungarian architect active in Europe from the late 1950s onward. Makovecz was born and died in Budapest. He attended the Technical University of Budapest. He was founder and "eternal and executive president" of the Hungarian Academy of Arts. He was an award-winning architect, having won Ybl Prize, Kossuth Prize, Steindl Imre Prize and Prima Primissima Award among many others. Makovecz was one of the most prominent proponents of organic architecture. As such, his buildings attempt to work with the natural surroundings rather than triumph over them. Frank Lloyd Wright and Rudolf Steiner are both strong influences, as is traditional Hungarian art. His work began as a critique of communist ideology and the brutal uniformity of system building, but after the fall of the Communist regime in 1989, it became a comment on the nature of globalisation and corporate culture. In its attempts to refer to and build on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KoÅĄice
KoÅĄice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river HornÃĄd at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, KoÅĄice is the second-largest city in Slovakia, after the capital Bratislava. Being the economic and cultural centre of eastern Slovakia, KoÅĄice is the seat of the KoÅĄice Region and KoÅĄice Self-governing Region, it belongs to the :sk:KoÅĄicko-preÅĄovskÃĄ aglomerÃĄcia, KoÅĄice-PreÅĄov agglomeration, and is home to the Constitutional Court of Slovakia, Slovak Constitutional Court, three universities, various dioceses, and many museums, galleries, and theatres. In 2013, KoÅĄice was the European Capital of Culture, together with Marseille, France. KoÅĄice is an important industrial centre of Slovakia, and the U. S. Steel KoÅĄice, s.r.o., U.S. Steel KoÅĄice steel mill is the largest employer in the city. The town has extensive railway connections and an KoÅĄice Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VeÄūkÃĐ KapuÅĄany
VeÄūkÃĐ KapuÅĄany (; ) is a small town on the eastern plains of Slovakia, not far from the Ukrainian border. Name The name "KapuÅĄany" is probably derived from the Hungarian word ''kapu'', meaning "gate". History The territory of the town has been settled since time immemorial (findings from the Neolithic period). From the second half of the 10th century until 1918, it was part of the Kingdom of Hungary. The first written references to the settlement stems from 1211 ("Kapos") and 1214 ("Copus"). The settlement was awarded town status in 1430. The town was the second largest settlement (after Uzhhorod) of the Ung County and frequently served as a temporary or permanent station for migrants (Germans, Rusyns, Poles, Hungarians etc.) from the east to the west. In the town square there is a garden with a plaque commemorating the day the Germans marched into VeÄūkÃĐ KapuÅĄany in 1944. This is significant as both Jews and Romas were persecuted and murdered by the Nazis during World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KrÃĄÄūovskÃ― Chlmec
KrÃĄÄūovskÃ― Chlmec (; until 1948 ''KrÃĄÄūovskÃ― Chlumec'', ) is a town in the TrebiÅĄov District in the KoÅĄice Region of south-eastern Slovakia. It has a population of 7,462. Etymology The name means "Royal Hill". Slovak ''chlm'', Czech ''chlum'', Polish ''cheÅm'' are derived from a Proto-Slavic ''chŅlmŅ'' - a hill, ''chlmec'' - a smaller hill, an elevated location. History The town was first mentioned in 1214 as ''Helmech''. In 1848-1849, residents of KrÃĄÄūovskÃ― Chlmec took part in the Civic Revolution and War of Independence. After the Treaty of Trianon in 1920, the town became part of Czechoslovakia. It was annexed again by Hungary in 1938 as a result of the First Vienna Award. After the Second world war it became part of Czechoslovakia again in 1945, officially in 1947, according to the Paris Peace Treaties. Geography KrÃĄÄūovskÃ― Chlmec lies at an altitude of above sea level and covers an area of . It is located in the southern part of the Eastern Slovak Lowland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TimiČoara
TimiČoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of TimiČ County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, TimiČoara is considered the informal capital city of the historical Banat region. From 1848 to 1860 it was the capital of the Serbian Vojvodina and the Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar. With 250,849 inhabitants at the 2021 Romanian census, 2021 census, TimiČoara is the country's List of cities and towns in Romania, fifth most populous city. It is home to around 400,000 inhabitants in its TimiČoara metropolitan area, metropolitan area, while the TimiČoaraâArad metropolis concentrates more than 70% of the population of TimiČ and Arad County, Arad counties. TimiČoara is a multicultural city, home to 21 ethnic groups and 18 religious denominations. Historically, the most numerous were the Banat Swabians, Swabian Germans, Jews and Hungarians, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristuru Secuiesc
Cristuru Secuiesc (; , ) is a town in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the SzÃĐkely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania. The town administers two villages: BeteČti (''Betfalva''), part of Mugeni until 2004, and FiliaČ (''Fiatfalva''). Location Cristuru Secuiesc lies on the Transylvanian Plateau, in the area where the river Goagiu flows into the TÃĒrnava Mare. It is located in the southwestern part of the county, on the border with MureČ County. The town is crossed by national road ; Odorheiu Secuiesc is to the east, while the county seat, Miercurea Ciuc, is in that direction. History The town was part of the SzÃĐkely Land area of the historical Transylvania province. It belonged to UdvarhelyszÃĐk until the administrative reform of Transylvania in 1876, when it fell within the Udvarhely County of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the aftermath of World War I and the HungarianâRomanian War of 1918â1919, it passed under Romanian administration; after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |