Zugewandte Orte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (
 The adjective "old" was introduced after the
The adjective "old" was introduced after the
 The
The


 The ''(Alte) Eidgenossenschaft'' was initially united not by a single pact, but by overlapping pacts and bilateral treaties between members. The parties generally agreed to preserve the peace, aid in military endeavours and arbitrate disputes. Slowly, the members began to see the confederation as a unifying entity. In the ''Pfaffenbrief'', a treaty of 1370 among six of the eight members (Glarus and Bern did not participate) forbidding feuds and denying clerical courts jurisdiction over the confederacy, the cantons for the first time used the term ''Eidgenossenschaft''. The first treaty uniting the eight members of the confederacy was the '' Sempacherbrief'' of 1393, concluded after victories over the Habsburgs at
The ''(Alte) Eidgenossenschaft'' was initially united not by a single pact, but by overlapping pacts and bilateral treaties between members. The parties generally agreed to preserve the peace, aid in military endeavours and arbitrate disputes. Slowly, the members began to see the confederation as a unifying entity. In the ''Pfaffenbrief'', a treaty of 1370 among six of the eight members (Glarus and Bern did not participate) forbidding feuds and denying clerical courts jurisdiction over the confederacy, the cantons for the first time used the term ''Eidgenossenschaft''. The first treaty uniting the eight members of the confederacy was the '' Sempacherbrief'' of 1393, concluded after victories over the Habsburgs at  The ''Tagsatzung'' was the confederation council, typically meeting several times a year. Each canton delegated two representatives (including the associate states, which had no vote). The canton where the delegates met initially chaired the gathering, but during the 16th century Zürich permanently assumed the chair (''Vorort'') and
The ''Tagsatzung'' was the confederation council, typically meeting several times a year. Each canton delegated two representatives (including the associate states, which had no vote). The canton where the delegates met initially chaired the gathering, but during the 16th century Zürich permanently assumed the chair (''Vorort'') and

 The confederation expanded in several stages: first to the Eight Cantons (''Acht Orte''), then in 1481 to ten, in 1501 to twelve, and finally to thirteen cantons (''Dreizehn Orte'').Im Hof, U.. ''Geschichte der Schweiz'', 7th ed., Stuttgart: W. Kohlhammer, 1974/2001. .
*Founding cantons ('' Urkantone''):
**
The confederation expanded in several stages: first to the Eight Cantons (''Acht Orte''), then in 1481 to ten, in 1501 to twelve, and finally to thirteen cantons (''Dreizehn Orte'').Im Hof, U.. ''Geschichte der Schweiz'', 7th ed., Stuttgart: W. Kohlhammer, 1974/2001. .
*Founding cantons ('' Urkantone''):
**  Uri, founding canton named in the
Uri, founding canton named in the 

 Lucerne, city canton, since 1332
**
Lucerne, city canton, since 1332
** 


 Bern, city canton, since 1353; associate since 1323
*15th century: expansion to the ''Zehnörtige Eidgenossenschaft'' following the
Bern, city canton, since 1353; associate since 1323
*15th century: expansion to the ''Zehnörtige Eidgenossenschaft'' following the 



 Appenzell, rural canton, since 1513; associate since 1411
Appenzell, rural canton, since 1513; associate since 1411
 Associates ''(Zugewandte Orte)'' were close allies of the Old Swiss Confederacy, connected to the union by alliance treaties with all or some of the individual members of the confederacy.
Associates ''(Zugewandte Orte)'' were close allies of the Old Swiss Confederacy, connected to the union by alliance treaties with all or some of the individual members of the confederacy.

 Imperial
Imperial 
 Sieben Zenden, an independent federation in the
Sieben Zenden, an independent federation in the 



 Republic of Geneva – 1536 treaty with Bern and a 1584 treaty with Zürich and Bern, remaining so until events of the
Republic of Geneva – 1536 treaty with Bern and a 1584 treaty with Zürich and Bern, remaining so until events of the
 County of Neuchâtel – 1406 and 1526 treaties with Bern and Solothurn, 1495 treaty with Fribourg and 1501 treaty with Lucerne.
*
County of Neuchâtel – 1406 and 1526 treaties with Bern and Solothurn, 1495 treaty with Fribourg and 1501 treaty with Lucerne.
*  Imperial Valley of
Imperial Valley of 

 Payerne – from 1353 by treaty with Bern; annexed by Bern in 1536.
*
Payerne – from 1353 by treaty with Bern; annexed by Bern in 1536.
* 
 Barony of Sax-Forstegg – from 1458 by treaty with Zürich; annexed by Zürich in 1615
*
Barony of Sax-Forstegg – from 1458 by treaty with Zürich; annexed by Zürich in 1615
* 
 County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:
** Lower Gruyère – from 1475 by treaty with Fribourg
** Upper Gruyère – from 1403 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1555:
***
County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:
** Lower Gruyère – from 1475 by treaty with Fribourg
** Upper Gruyère – from 1403 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1555:
***  Imperial Valley of
Imperial Valley of  Imperial Valley of
Imperial Valley of  County of Werdenberg – from 1493 by treaty with Lucerne; annexed by Glarus in 1517.
*
County of Werdenberg – from 1493 by treaty with Lucerne; annexed by Glarus in 1517.
*  Imperial City of Rottweil – from 1519–1632 through a treaty with all 13 members; a first treaty on military cooperation had already been concluded in 1463. In 1632, the treaty was renewed with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
*
Imperial City of Rottweil – from 1519–1632 through a treaty with all 13 members; a first treaty on military cooperation had already been concluded in 1463. In 1632, the treaty was renewed with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
*  Bishopric of Basel – 1579–1735 by treaty with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
Bishopric of Basel – 1579–1735 by treaty with Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Zug, Solothurn and Fribourg.
 Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
** Upper Freiamt was governed by the ''Acht Orte'';
** Lower Freiamt was governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus alone.
*
Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
** Upper Freiamt was governed by the ''Acht Orte'';
** Lower Freiamt was governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus alone.
*  County of Baden – conquered 1415; from 1712 governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus.
*
County of Baden – conquered 1415; from 1712 governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus.
* 
 Landgraviate of Thurgau – from 1460
*
Landgraviate of Thurgau – from 1460
*  Vogtei of Rheintal – from 1490, ''Acht Orte'' minus Bern, plus the
Vogtei of Rheintal – from 1490, ''Acht Orte'' minus Bern, plus the
 County of Grasburg /
County of Grasburg / 



 , Windegg / Gaster – from 1438
*
, Windegg / Gaster – from 1438
* 


 Engelberg Abbey – protectorate of Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden from 1425
*
Engelberg Abbey – protectorate of Lucerne, Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden from 1425
* 
 Imperial
Imperial  Republic of Gersau, an independent village – allied with Schwyz since 1332; Lucerne, Uri and Unterwalden were also protecting powers.
*
Republic of Gersau, an independent village – allied with Schwyz since 1332; Lucerne, Uri and Unterwalden were also protecting powers.
* 




 Valley of
Valley of  Valley of
Valley of



 Höfe (1440)
Höfe (1440)
 County of Werdenberg (1485 / 1517); annexed to Lucerne in 1485; to Glarus in 1517
County of Werdenberg (1485 / 1517); annexed to Lucerne in 1485; to Glarus in 1517
 St-Maurice (1475 / 77)
*
St-Maurice (1475 / 77)
* 
 Nendaz-Hérémence (1475 / 77)
*
Nendaz-Hérémence (1475 / 77)
*  Port Valais/Vionnaz
*
Port Valais/Vionnaz
*


Modern German
New High German (NHG; german: Neuhochdeutsch (Nhd.)) is the term used for the most recent period in the history of the German language, starting in the 17th century. It is a loan translation of the German (). The most important characteristic o ...
: ; historically , after the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or In the charters of the 14th century described as "communities" (, ), the German term ''Orte'' becomes common in the early 15th century, used alongside "estate" after the Reformation. The French term is used in Fribourg in 1475, and after 1490 is increasingly used in French and Italian documents. It only enters occasional German usage after 1648, and only gains official status as synonym of with the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
of 1803. ), initially within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.
It formed during the 14th century, from a nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
in what is now Central Switzerland
Central Switzerland is the region of the Alpine Foothills geographically the heart and historically the origin of Switzerland, with the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Obwalden, Nidwalden, Lucerne and Zug.
Central Switzerland is one of the NUTS 2 Stat ...
, expanding to include the cities of Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
and Bern by the middle of the century. This formed a rare union of rural and urban communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, relig ...
, all of which enjoyed imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
in the Holy Roman Empire.
This confederation of eight cantons () was politically and militarily successful for more than a century, culminating in the Burgundy Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in th ...
of the 1470s which established it as a power in the complicated political landscape dominated by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the Habsburgs. Its success resulted in the addition of more confederates, increasing the number of cantons to thirteen () by 1513. The confederacy pledged neutrality in 1647 (under the threat of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
), although many Swiss served privately as mercenaries in the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
and during the early modern period.
After the Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
of 1499 the confederacy was a ''de facto'' independent state throughout the early modern period, although still nominally part of the Holy Roman Empire until 1648 when the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
ended the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
. The Swiss Reformation divided the confederates into Reformed and Catholic parties, resulting in internal conflict from the 16th to the 18th centuries; as a result, the federal diet () was often paralysed by hostility between the factions. The Swiss Confederacy fell to invasion by the French Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army (french: Armée révolutionnaire française) was the French land force that fought the French Revolutionary Wars from 1792 to 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary fervour, their poor equipme ...
in 1798, after which it became the short-lived Helvetic Republic.
Name
 The adjective "old" was introduced after the
The adjective "old" was introduced after the Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislativ ...
with , retronym
A retronym is a newer name for an existing thing that helps differentiate the original form/version from a more recent one. It is thus a word or phrase created to avoid confusion between older and newer types, whereas previously (before there were ...
s distinguishing the pre-Napoleonic from the restored confederation. During its existence the confederacy was known as or ("oath fellowship"), in reference to treaties among cantons; this term was first used in the 1370 . Territories of the confederacy came to be known collectively as ''Schweiz'' or ''Schweizerland'' (''Schwytzerland'' in contemporary spelling), with the English '' Switzerland'' beginning during the mid-16th century. From that time the Confederacy was seen as a single state, also known as the Swiss Republic (, and by Josias Simmler
Josias Simmler (Josiah Simler; la, Iosias Simlerus) (6 November 1530 – 2 July 1576) was a Swiss theologian and classicist, author of the first book relating solely to the Alps.
Life
The son of the former prior of the Cistercian convent of ...
in 1576) after the fashion of calling individual urban cantons republics
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
(such as the Republics of Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, Berne
Bern () or Berne; in other Swiss languages, gsw, Bärn ; frp, Bèrna ; it, Berna ; rm, Berna is the ''de facto'' Capital city, capital of Switzerland, referred to as the "federal city" (in german: Bundesstadt, link=no, french: ville fédérale ...
and Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
).
History

Foundation
The nucleus of the Old Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of thecentral Alps
The Alps form a large mountain range dominating Central Europe, including parts of Italy, France, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Slovenia, Germany and possibly Hungary (if one includes the Kőszeg Mountains).
This article describes the d ...
to facilitate management of common interests (such as trade) and ensure peace along trade routes through the mountains. The foundation of the Confederacy is marked by the Rütlischwur (dated to 1307 by Aegidius Tschudi
Aegidius (or Giles or Glig) Tschudi (5 February 150528 February 1572) was a Swiss statesman and historian, an eminent member of the Tschudi family of Glarus, Switzerland. His best known work is the Chronicon Helveticum, a history of the earl ...
) or the 1315 Pact of Brunnen The Pact of Brunnen (''Bund von Brunnen'') is a historical treaty between the cantons of
Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, concluded in Brunnen on 9 December 1315.
Representatives of the four territories (Unterwalden was composed of Obwalden and Nidw ...
.
Since 1889, the Federal Charter of 1291
The Federal Charter or Letter of Alliance (german: Bundesbrief) is one of the earliest constitutional documents of Switzerland. A treaty of alliance from 1291 between the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, the Charter is one of a series ...
among the rural communes of Uri, Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
, and Unterwalden
Unterwalden, translated from the Latin ''inter silvas''(''between the forests''), is the old name of a forest-canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy in central Switzerland, south of Lake Lucerne, consisting of two valleys or '' Talschaften'', no ...
has been considered the founding document of the confederacy.Schwabe & Co.: ''Geschichte der Schweiz und der Schweizer'', Schwabe & Co 1986/2004.
Expansion
The initial pact was augmented by pacts with the cities of Lucerne,Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, and Bern. This union of rural and urban communes, which enjoyed the status of imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, was engendered by pressure from Habsburg dukes and kings who had ruled much of the land. In several battles with Habsburg armies, the Swiss were victorious; they conquered the rural areas of Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
and Zug
, neighboring_municipalities = Cham, Baar, Walchwil, Steinhausen, Unterägeri
, twintowns = Fürstenfeld (Austria), Kalesija (Bosnia-Herzegowina)
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; french: Zoug it, Zugo r ...
, which became members of the confederacy.
From 1353 to 1481, the federation of eight cantons—known in German as the ''Acht Orte'' (Eight Cantons)—consolidated its position. The members (especially the cities) enlarged their territory at the expense of local counts—primarily by buying judicial rights
High, middle and low justices are notions dating from Western feudalism to indicate descending degrees of judicial power to administer justice by the maximal punishment the holders could inflict upon their subjects and other dependents.
Low just ...
, but sometimes by force. The ''Eidgenossenschaft'', as a whole, expanded through military conquest: the Aargau was conquered in 1415 and the Thurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
in 1460. In both cases, the Swiss profited from weakness in the Habsburg dukes. In the south, Uri led a military territorial expansion that (after many setbacks) would by 1515 lead to the conquest of the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
.
None of these territories became members of the confederacy; they had the status of condominiums (regions administered by several cantons).
At this time, the eight cantons gradually increased their influence on neighbouring cities and regions through additional alliances. Individual cantons concluded pacts with Fribourg
, neighboring_municipalities= Düdingen, Givisiez, Granges-Paccot, Marly, Pierrafortscha, Sankt Ursen, Tafers, Villars-sur-Glâne
, twintowns = Rueil-Malmaison (France)
, website = www.ville-fribourg.ch
, Location of , Location of ()
() ...
, Appenzell, Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
, the abbot and the city of St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
, Biel
, french: Biennois(e)
, neighboring_municipalities= Brügg, Ipsach, Leubringen/Magglingen (''Evilard/Macolin''), Nidau, Orpund, Orvin, Pieterlen, Port, Safnern, Tüscherz-Alfermée, Vauffelin
, twintowns = Iserlohn (Germany) ...
, Rottweil, Mulhouse and others. These allies (known as the ''Zugewandte Orte'') became closely associated with the confederacy, but were not accepted as full members.
The Burgundy Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in th ...
prompted a further enlargement of the confederacy; Fribourg and Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
were accepted in 1481. In the Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
against Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I, the Swiss were victorious and exempted from imperial legislation. The associated cities of Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
and Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
joined the confederacy as a result of that conflict, and Appenzell followed suit in 1513 as the thirteenth member. The federation of thirteen cantons (''Dreizehn Orte'') constituted the Old Swiss Confederacy until its demise in 1798.
The expansion of the confederacy was stopped by the Swiss defeat in the 1515 Battle of Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was the last major engagement of the War of the League of Cambrai and took place on 13–14 September 1515, near the town now called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan. It pitted the French army, composed of the b ...
. Only Bern and Fribourg were still able to conquer the Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms b ...
in 1536; the latter primarily became part of the canton of Bern, with a small portion under the jurisdiction of Fribourg.
Reformation
 The
The Reformation in Switzerland
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matte ...
led to doctrinal division amongst the cantons. Zürich, Bern, Basel, Schaffhausen and associates Biel, Mulhouse, Neuchâtel, Geneva and the city of St. Gallen became Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
; other members of the confederation and the Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
remained Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. In Glarus, Appenzell, in the Grisons and in most condominiums both religions coexisted; Appenzell split in 1597 into a Catholic Appenzell Innerrhoden and a Protestant Appenzell Ausserrhoden.
The division led to civil war (the Wars of Kappel) and separate alliances with foreign powers by the Catholic and Protestant factions, but the confederacy as a whole continued to exist. A common foreign policy was blocked, however, by the impasse. During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
, religious disagreements among the cantons kept the confederacy neutral and spared it from belligerents. At the Peace of Westphalia, the Swiss delegation was granted formal recognition of the confederacy as a state independent of the Holy Roman Empire.
Early modern period
Growing social differences and an increasing absolutism in the city cantons during the Ancien Régime led to local popular revolts. An uprising during the post-war depression after the Thirty Years' War escalated to theSwiss peasant war of 1653
The Swiss peasant war of 1653 () was a popular revolt in the Old Swiss Confederacy at the time of the Ancien Régime. A devaluation of Bernese money caused a tax revolt that spread from the Entlebuch valley in the Canton of Lucerne to the Emmen ...
in Lucerne, Bern, Basel, Solothurn and the Aargau. The revolt was put down swiftly by force and with the help of many cantons.
Religious differences were accentuated by a growing economic discrepancy. The Catholic, predominantly rural central-Swiss cantons were surrounded by Protestant cantons with increasingly commercial economies. The politically dominant cantons were Zürich and Bern (both Protestant), but the Catholic cantons were influential since the Second War of Kappel in 1531. A 1655 attempt (led by Zürich) to restructure the federation was blocked by Catholic opposition, which led to the first battle of Villmergen
The First War of Villmergen Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Zwitserland. §5.2 Reformatie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. was a Swiss religious war which lasted from 5 January until 7 March 1656, at the time of the ...
in 1656; the Catholic party won, cementing the ''status quo''.
The problems remained unsolved, erupting again in 1712 with the second battle of Villmergen. This time the Protestant cantons won, dominating the confederation. True reform, however, was impossible; the individual interests of the thirteen members were too diverse, and the absolutist cantonal governments resisted all attempts at confederation-wide administration. Foreign policy remained fragmented.
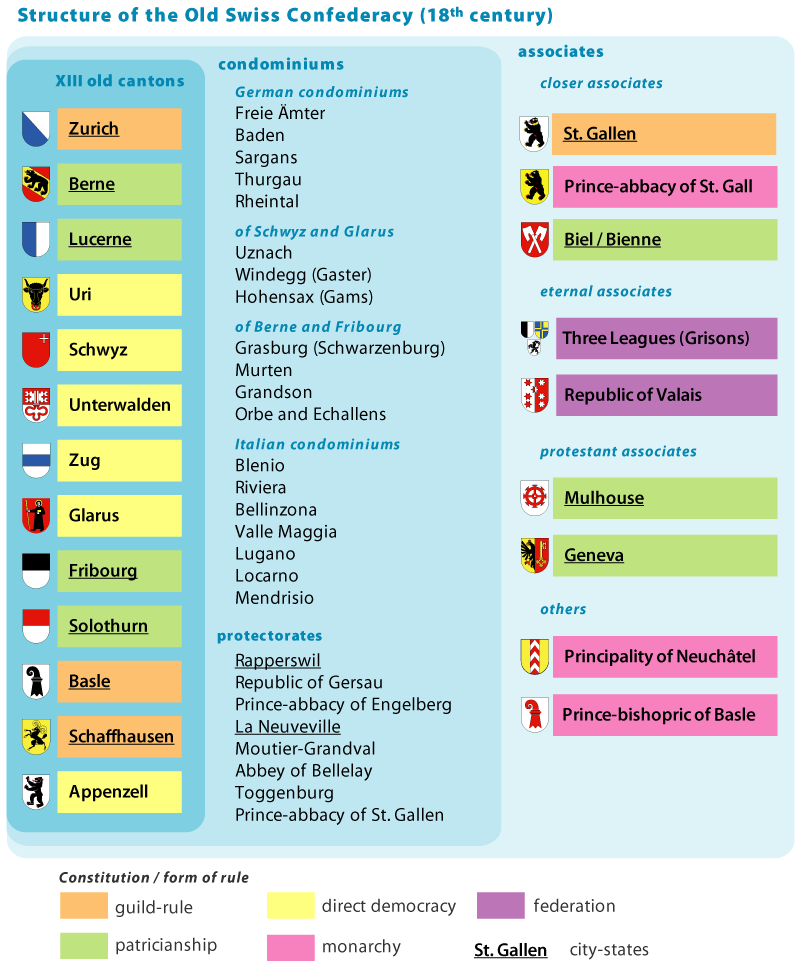
Structure


 The ''(Alte) Eidgenossenschaft'' was initially united not by a single pact, but by overlapping pacts and bilateral treaties between members. The parties generally agreed to preserve the peace, aid in military endeavours and arbitrate disputes. Slowly, the members began to see the confederation as a unifying entity. In the ''Pfaffenbrief'', a treaty of 1370 among six of the eight members (Glarus and Bern did not participate) forbidding feuds and denying clerical courts jurisdiction over the confederacy, the cantons for the first time used the term ''Eidgenossenschaft''. The first treaty uniting the eight members of the confederacy was the '' Sempacherbrief'' of 1393, concluded after victories over the Habsburgs at
The ''(Alte) Eidgenossenschaft'' was initially united not by a single pact, but by overlapping pacts and bilateral treaties between members. The parties generally agreed to preserve the peace, aid in military endeavours and arbitrate disputes. Slowly, the members began to see the confederation as a unifying entity. In the ''Pfaffenbrief'', a treaty of 1370 among six of the eight members (Glarus and Bern did not participate) forbidding feuds and denying clerical courts jurisdiction over the confederacy, the cantons for the first time used the term ''Eidgenossenschaft''. The first treaty uniting the eight members of the confederacy was the '' Sempacherbrief'' of 1393, concluded after victories over the Habsburgs at Sempach
Sempach is a municipality in the district of Sursee in the canton of Lucerne in Switzerland.
History
It has retained some traces of its medieval appearance, especially the main gateway, beneath a watch tower, and reached by a bridge over th ...
in 1386 and Näfels
Näfels is a former municipality in the canton of Glarus in Switzerland. Effective from 1 January 2011, Näfels is part of the municipality of Glarus Nord.
History
Näfels is first mentioned in 1240 as ''Nevels''.
In 1388, the Swiss Confederates ...
in 1388, which forbade a member from unilaterally beginning a war without the consent of the other cantons. A federal diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
, the ''Tagsatzung
The Federal Diet of Switzerland (german: Tagsatzung, ; french: Diète fédérale; it, Dieta federale) was the legislative and executive council of the Old Swiss Confederacy and existed in various forms from the beginnings of Swiss independen ...
'', developed during the 15th century.
Pacts and renewals (or modernizations) of earlier alliances reinforced the confederacy. The individual interests of the cantons clashed in the Old Zürich War
The Old Zurich War (german: Alter Zürichkrieg), 1440–46, was a conflict between the canton of Zurich and the other seven cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy over the succession to the Count of Toggenburg.
In 1436, Count Friedrich VII of T ...
(1436–1450), caused by territorial conflict among Zürich and the central Swiss cantons over the succession of the Count of Toggenburg. Although Zürich entered an alliance with the Habsburg dukes, it then rejoined the confederacy. The confederation had become so close a political alliance that it no longer tolerated separatist tendencies in its members.
 The ''Tagsatzung'' was the confederation council, typically meeting several times a year. Each canton delegated two representatives (including the associate states, which had no vote). The canton where the delegates met initially chaired the gathering, but during the 16th century Zürich permanently assumed the chair (''Vorort'') and
The ''Tagsatzung'' was the confederation council, typically meeting several times a year. Each canton delegated two representatives (including the associate states, which had no vote). The canton where the delegates met initially chaired the gathering, but during the 16th century Zürich permanently assumed the chair (''Vorort'') and Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
became the seat. The Tagsatzung dealt with inter-cantonal affairs and was the court of last resort in disputes between member states, imposing sanctions on dissenting members. It also administered the condominiums; the reeves were delegated for two years, each time by a different canton.
A unifying treaty of the Old Swiss Confederacy was the '' Stanser Verkommnis'' of 1481. Conflicts between rural and urban cantons and disagreements over the bounty of the Burgundian Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in t ...
had led to skirmishes. The city-states of Fribourg and Solothurn wanted to join the confederacy, but were mistrusted by the central Swiss rural cantons. The compromise by the ''Tagsatzung'' in the ''Stanser Verkommnis'' restored order and assuaged the rural cantons' complaints, with Fribourg and Solothurn accepted into the confederation. While the treaty restricted freedom of assembly (many skirmishes arose from unauthorised expeditions by soldiers from the Burgundian Wars), it reinforced agreements amongst the cantons in the earlier ''Sempacherbrief'' and ''Pfaffenbrief''.
The civil war during the Reformation ended in a stalemate. The Catholic cantons could block council decisions but, due to geographic and economic factors, could not prevail over the Protestant cantons. Both factions began to hold separate councils, still meeting at a common ''Tagsatzung'' (although the common council was deadlocked by disagreements between both factions until 1712, when the Protestant cantons gained power after their victory in the second war of Villmergen). The Catholic cantons were excluded from administering the condominiums in the Aargau, the Thurgau and the Rhine valley; in their place, Bern became co-sovereign of these regions.
List of territories
Cantons

 The confederation expanded in several stages: first to the Eight Cantons (''Acht Orte''), then in 1481 to ten, in 1501 to twelve, and finally to thirteen cantons (''Dreizehn Orte'').Im Hof, U.. ''Geschichte der Schweiz'', 7th ed., Stuttgart: W. Kohlhammer, 1974/2001. .
*Founding cantons ('' Urkantone''):
**
The confederation expanded in several stages: first to the Eight Cantons (''Acht Orte''), then in 1481 to ten, in 1501 to twelve, and finally to thirteen cantons (''Dreizehn Orte'').Im Hof, U.. ''Geschichte der Schweiz'', 7th ed., Stuttgart: W. Kohlhammer, 1974/2001. .
*Founding cantons ('' Urkantone''):
** Federal Charter of 1291
The Federal Charter or Letter of Alliance (german: Bundesbrief) is one of the earliest constitutional documents of Switzerland. A treaty of alliance from 1291 between the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, the Charter is one of a series ...
** Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
** Unterwalden
Unterwalden, translated from the Latin ''inter silvas''(''between the forests''), is the old name of a forest-canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy in central Switzerland, south of Lake Lucerne, consisting of two valleys or '' Talschaften'', no ...
, founding canton named in the Federal Charter of 1291
*14th century: expansion to the ''Achtörtige Eidgenossenschaft'' following the battles of Morgarten and Laupen:
** Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, city canton, since 1351
** Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
, rural canton, since 1352
** Zug
, neighboring_municipalities = Cham, Baar, Walchwil, Steinhausen, Unterägeri
, twintowns = Fürstenfeld (Austria), Kalesija (Bosnia-Herzegowina)
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; french: Zoug it, Zugo r ...
, city canton, since 1352
** Burgundian Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in t ...
:
** Fribourg
, neighboring_municipalities= Düdingen, Givisiez, Granges-Paccot, Marly, Pierrafortscha, Sankt Ursen, Tafers, Villars-sur-Glâne
, twintowns = Rueil-Malmaison (France)
, website = www.ville-fribourg.ch
, Location of , Location of ()
() ...
, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1454
** Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
, city canton, since 1481; associate since 1353
*16th century: expansion to the ''Dreizehnörtige Eidgenossenschaft'' following the Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
:
** Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
, city canton, since 1501
** Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
, city canton, since 1501; associate since 1454
** Associates
 Associates ''(Zugewandte Orte)'' were close allies of the Old Swiss Confederacy, connected to the union by alliance treaties with all or some of the individual members of the confederacy.
Associates ''(Zugewandte Orte)'' were close allies of the Old Swiss Confederacy, connected to the union by alliance treaties with all or some of the individual members of the confederacy.
Closest associates
Three of the associates were known as ': *Biel
, french: Biennois(e)
, neighboring_municipalities= Brügg, Ipsach, Leubringen/Magglingen (''Evilard/Macolin''), Nidau, Orpund, Orvin, Pieterlen, Port, Safnern, Tüscherz-Alfermée, Vauffelin
, twintowns = Iserlohn (Germany) ...
– 1344–82 treaties with Fribourg, Bern and Solothurn. Nominally, Biel was subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
* Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
en – 1451 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus, renewed in 1479 and 1490. The abbey was simultaneously a protectorate.
* Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
of St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
– 1454 treaty with Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich, Glarus, Zug and Bern.
Eternal associates
Two federations were known as ': *Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
– Became a ''Zugewandter Ort'' in 1416 through an alliance with Uri, Unterwalden and Lucerne, followed by a treaty with Bern in 1446.
* Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
were independent federations on the territory of the Grisons and became an associates of the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1497/98 through the events of the Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
. The Three Leagues together concluded an alliance pact with Bern in 1602.
** Grey League
The Grey League (german: Grauer Bund, it, Lega Grigia, rm, Ligia Grischa or ), sometimes called ''Oberbund'', formed in 1395 in the ''Vorderrhein'' and '' Hinterrhein'' valleys, Raetia. The name Grey League is derived from the homespun grey cl ...
, who had been allied with Glarus, Uri and Obwalden through pacts from 1400, 1407 and 1419, entered an alliance with seven of the old eight cantons (the ''Acht Orte'' without Bern) in 1497
** League of God's House
The League of God's House (German: ''Gotteshausbund'', Italian: ''Lega Caddea'', rm, ) was formed in what is now Switzerland on 29 January 1367, to resist the rising power of the Bishopric of Chur and the House of Habsburg. The League allied wi ...
(''Gotteshausbund'') followed suit a year later.
** League of the Ten Jurisdictions
The League of the Ten Jurisdictions was the last of the Three Leagues founded during the Middle Ages in what is now Graubünden, Canton Graubünden of Switzerland. The League was created in the County of Toggenburg after the counts of Toggenbur ...
, the third of the leagues, entered an alliance with Zürich and Glarus in 1590.
Protestant associates
There were two ': *Republic of Mulhouse
The Republic of Mulhouse (in German: ''Stadtrepublik Mülhausen)'' was a protestant associate of the Old Swiss Confederation.
Mulhouse had been a free city of the Empire since 1275. It became a Republic in 1347 with the election of its first burg ...
– Concluded a first treaty with some cantons in 1466 and became an associate in 1515 through a treaty with all 13 members of the Confederacy, remaining so until events of the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia ...
in 1798.
* French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia ...
in 1798.
Other
*Urseren
The Urseren (also ''Ursern'') is the valley of the upper Reuss in Uri, Switzerland, running southwest to northeast, from Realp to Hospental and Andermatt.
Separated from the main valley of Uri, it connects to the Valais via the Furkapass, t ...
– 1317 treaty with Uri; annexed by Uri in 1410.
* 
Weggis
Weggis is a municipality in the district of Lucerne in the canton of Lucerne in Switzerland.
It forms part of the northern shore of Lake Lucerne. The official language is German.
History
In about 800 the monastery of Pfäfers acquired the court o ...
– 1332–1380 by treaties with Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Lucerne; annexed by Lucerne in 1480.
* 
Murten
Murten (German) or Morat (French, ; frp, Morât ) is a bilingual municipality and a city in the See district of the canton of Fribourg in Switzerland.
It is located on the southern shores of Lake Morat (also known as Lake Murten). Morat is si ...
– from 1353 by treaty with Bern; became a confederal condominium in 1475.
* County of Sargans
The County of Sargans was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1458 until the French Revolutionary War in 1798, Sargans became a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy, administered jointly by the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Lucer ...
– from 1437 by treaty with Glarus and Schwyz; became a confederal condominium in 1483.
* 
Stein am Rhein
Stein am Rhein (abbreviated as Stein a. R.) is a historic town and a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland.
The town's medieval centre retains the ancient street plan. The site of the city wall, and the city gates are preserve ...
– from 1459 by treaty with Zürich and Schaffhausen; annexed by Zürich in 1484.
*  County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:
** Lower Gruyère – from 1475 by treaty with Fribourg
** Upper Gruyère – from 1403 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1555:
***
County of Gruyère – had been allied with Fribourg and Berne since the early 14th century, becoming a full associate of the Confederation in 1548. When the counts fell bankrupt in 1555, the country was partitioned in twain:
** Lower Gruyère – from 1475 by treaty with Fribourg
** Upper Gruyère – from 1403 by treaty with Berne; annexed by Berne in 1555:
*** Saanen
Saanen (french: Gessenay; Highest Alemannic: ''Saanä'') is a municipality in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is the capital of the Obersimmental-Saanen administrative district.
History
The village was first mentioned in 1228 as ''Gi ...
*** Château-d'Œx
Château-d'Œx () is a municipality in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is in the district of Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut.
History
Château-d'Œx is first mentioned in 1115 as ''Oit'', ''Oyz'', ''Oix'' and ''Oyez''.
Prehistoric settlements
Du ...
* Condominiums
Condominiums (german: Gemeine Herrschaften) were common subject territories under the administration of several cantons. They were governed by reeves (''Vögte'') delegated for two years, each time from another of the responsible cantons. Bern initially did not participate in the administration of some of the eastern condominiums, as it had no part in their conquest and its interests were focused more on the western border. In 1712, Bern replaced the Catholic cantons in the administration of the '' Freie Ämter'' ("Free Districts"), theThurgau
Thurgau (; french: Thurgovie; it, Turgovia), anglicized as Thurgovia, more formally the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital is Frauenfeld.
Thurgau is par ...
, the Rhine valley, and Sargans
Sargans is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Sarganserland in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
Sargans is known for its castle, which dates from before the founding of the Swiss Confederation in 1291. Sargans was al ...
, and furthermore the Catholic cantons were excluded from the administration of the County of Baden.
German bailiwicks
The "German bailiwicks" (german: Deutsche Gemeine Vogteien, Gemeine Herrschaften) were generally governed by the ''Acht Orte'' apart from Bern until 1712, when Bern joined the sovereign powers: * Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
** Upper Freiamt was governed by the ''Acht Orte'';
** Lower Freiamt was governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus alone.
*
Freie Ämter – conquered 1415 and partitioned in 1712:
** Upper Freiamt was governed by the ''Acht Orte'';
** Lower Freiamt was governed by Zürich, Bern and Glarus alone.
* County of Sargans
The County of Sargans was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1458 until the French Revolutionary War in 1798, Sargans became a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy, administered jointly by the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Lucer ...
– from 1460/83
* Imperial Abbey of St Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
. Appenzell added in 1500; Bern added in 1712.
Italian bailiwicks
Severalbailiwicks
A bailiwick () is usually the area of jurisdiction of a bailiff, and once also applied to territories in which a privately appointed bailiff exercised the sheriff's functions under a royal or imperial writ. The bailiwick is probably modelled on the ...
(''Vogteien'') were generally referred to as "transmontane bailiwicks" (german: Ennetbergische Vogteien, it, Baliaggi Ultramontani).
In 1440, Uri conquered the Leventina Valley from the Visconti, dukes of Milan. Some of this territory had previously been annexed between 1403 and 1422. Further territories were acquired in 1500; ''see History of Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
for further details''.
Three bailiwicks, all now in the Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
, were condominiums of the Forest cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Nidwalden:
* Vogtei of Blenio – 1477–80 and from 1495
* Vogtei of Rivera – 1403–22 and from 1495
* Vogtei of Bellinzona – from 1500
Four other Ticinese bailiwicks were condominiums of the ''Zwölf Orte'' (the original 13 cantons, minus Appenzell) from 1512:
* Landvogtei of Valmaggia
The Vallemaggia District is a district of the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. It has a population of (as of ). The capital of the district is Cevio.
Geography
The Vallemaggia District has an area, , of . Of this area, or 1.7% is used for ag ...
* Landvogtei of Lugano
* Landvogtei of Locarno
The Locarno District (also called Locarnese) is a district of Canton Ticino, Switzerland. It has a population of (as of ).
Geography
The Locarno District has an area, , of . Of this area, or 6.4% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 58 ...
* Landvogtei of Mendrisio
Another three bailiwicks were condominiums of the ''Zwölf Orte'' from 1512, but were lost from the Confederacy three years later and are all now ''comuni
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
'' of Lombardy or Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
:
* Travaglia
* Cuvio
Cuvio ( lmo, Cüj, label=Western Lombard) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Varese in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northwest of Milan and about northwest of Varese
Varese ( , , or ; lmo, label=Varesino, Varés ...
* Eschental (now Ossola)
Two-party condominiums
=Bern and Fribourg
= *Schwarzenburg
Schwarzenburg is a municipality in the district of Bern-Mittelland in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It was created on 1 January 2011 through the merger of the municipalities of Wahlern and Albligen.
History Albligen
Albligen is first mentio ...
– from 1423
* 
Murten
Murten (German) or Morat (French, ; frp, Morât ) is a bilingual municipality and a city in the See district of the canton of Fribourg in Switzerland.
It is located on the southern shores of Lake Morat (also known as Lake Murten). Morat is si ...
– from 1475
* Grandson
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
– from 1475
* Orbe
Orbe (; la, Urba; older german: Orbach, ; frp, Orba) is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Vaud. It was the seat of the former district of Orbe and is now part of the district of Jura-Nord Vaudois.
History
Orbe is first mentioned about 2 ...
and Echallens – from 1475
=Glarus and Schwyz
= *Uznach
Uznach is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of See-Gaster in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
History
Uznach is first mentioned in 741 as ''Uzinaa'' in a grant from a noble lady at Benken Abbey to the Abbey of Saint G ...
– from 1437
* 
Hohensax
The noble family von Sax (originally ''de Sacco'') were a medieval noble family in eastern Switzerland. They owned estates and castles on both sides of the Alps in the modern cantons of St. Gallen, Graubünden and Ticino. The origin of the fami ...
/ Gams
Gams is a municipality in the ''Wahlkreis'' (constituency) of Werdenberg in the canton of St. Gallen in Switzerland.
History
Gams is first mentioned in 835 as ''Campesias''. In 1210 it was mentioned as ''Chames'', in 1236 as ''Gamps''. Unt ...
– from 1497
= Condominiums with third-parties
= * Lordship of Tessenberg – from 1388, condominium between Bern and Bishopric of BaselProtectorates
*Bellelay Abbey
Bellelay Abbey is a former Premonstratensian monastery in the Bernese Jura in Switzerland, now a psychiatric clinic. It is a heritage site of national significance and the entire former Abbey complex is part of the Inventory of Swiss Heritage S ...
– protectorate of Bern, Biel and Solothurn from 1414; nominally under the jurisdiction of the Bishopric of Basel
* Einsiedeln Abbey
Einsiedeln Abbey (german: Kloster Einsiedeln) is a Benedictine Catholic monastery in the village of Einsiedeln in the canton of Schwyz, Switzerland. The abbey is dedicated to Our Lady of the Hermits, in recognition of Meinrad of Einsiedeln, a he ...
– protectorate of Schwyz from 1357
* Erguel
Erguël is an medieval seigniory of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Basel, and under protectorate of Biel/Bienne, under military jurisdiction from 1335, in the now called valley of St.-Imier, in the now Bernese Jura, Switzerland.
The Sire of the ...
– protectorate of Biel/Bienne
, french: Biennois(e)
, neighboring_municipalities= Brügg, Ipsach, Leubringen/Magglingen (''Evilard/Macolin''), Nidau, Orpund, Orvin, Pieterlen, Port, Safnern, Tüscherz-Alfermée, Vauffelin
, twintowns = Iserlohn (Germany)
...
under military jurisdiction from 1335; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel
* Abbey of St. Gall
The Abbey of Saint Gall (german: Abtei St. Gallen) is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot ...
en – protectorate of Schwyz, Lucerne, Zürich and Glarus from 1451; the abbey was simultaneously a ''Zugewandter Ort''.
* Moutier-Grandval Abbey
Moutier-Grandval Abbey was a Benedictine abbey near the villages of Moutier and Grandval in today's Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It was founded around 640, when Grandval already existed; Moutier g ...
– protectorate of Bern from 1486; the abbey was also subject to the Bishopric of Basel and, until 1797, the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
* La Neuveville
La Neuveville (; german: Neuenstadt) is a municipality in the Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland, located in the French-speaking Bernese Jura (''Jura Bernois'').
History
La Neuveville is first mention ...
– protectorate of Bern from 1388; also subject to the Bishopric of Basel.
* 
Pfäfers Abbey
Pfäfers Abbey (german: Kloster Pfäfers), also known as St. Pirminsberg from its position on a mountain, was a Benedictine monastery in Pfäfers near Bad Ragaz, in the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland.
Situated at the junction of the Tamina an ...
– protectorate of the ''Acht Orte'' minus Bern from 1460; annexed to the County of Sargans
The County of Sargans was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1458 until the French Revolutionary War in 1798, Sargans became a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy, administered jointly by the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Lucer ...
in 1483
* Rapperswil
Rapperswil (Swiss German: or ;Andres Kristol, ''Rapperswil SG (See)'' in: ''Dictionnaire toponymique des communes suisses – Lexikon der schweizerischen Gemeindenamen – Dizionario toponomastico dei comuni svizzeri (DTS, LSG)'', Centre de dial ...
– protectorate of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Glarus from 1464; of Zürich, Bern and Glarus from 1712
* County of Toggenburg
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
– protectorate of Schwyz and Glarus from 1436; of Zürich and Bern from 1718. The county was simultaneously subject to St Gallen Abbey.
Separate subjects
Some territories were separate subjects of cantons or associates, ':Uri
*Leventina
The Leventina District is one of the eight districts of the largely Italian-speaking canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The capital of the district is Faido but the largest town is Airolo on the southern flank of the Gotthard Pass.
Situated to th ...
(1403, 1439, finally 1480)
* Urseren
The Urseren (also ''Ursern'') is the valley of the upper Reuss in Uri, Switzerland, running southwest to northeast, from Realp to Hospental and Andermatt.
Separated from the main valley of Uri, it connects to the Valais via the Furkapass, t ...
(1440)
Schwyz
*
Küssnacht
Küssnacht am Rigi (official name since 2004: Küssnacht) is a village and a district and a municipality in the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland. The municipality consists of three villages Küssnacht, Immensee, and Merlischachen, the hamlet ''Ha ...
(1402)
* 
Einsiedeln Abbey
Einsiedeln Abbey (german: Kloster Einsiedeln) is a Benedictine Catholic monastery in the village of Einsiedeln in the canton of Schwyz, Switzerland. The abbey is dedicated to Our Lady of the Hermits, in recognition of Meinrad of Einsiedeln, a he ...
(1397 / 1424)
* 
March
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. It is the second of seven months to have a length of 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March ...
(1405 / 36)
*  Höfe (1440)
Höfe (1440)
Glarus
*Valais
*
Monthey
Monthey (; frp, Montê) is the capital of the district of Monthey in the canton of Valais in Switzerland.
History
The castle in the town center was built in 950 on a hill, the first houses of Monthey surrounded it. Monthey is first mention ...
(1536)
* Lötschental
The Lötschental is the largest valley on the northern side of the Rhône valley in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It lies in the Bernese Alps, with the Lonza running down the length of the valley from its source within the Langgletsche ...
(15th century); the five upper ''Zenden''
Three Leagues
*
Bormio
Bormio ( lmo, Bormi, rm, italic=yes, , german: Worms im Veltlintal) is a town and ''comune'' with a population of about 4,100 located in the Province of Sondrio, Lombardy region of the Alps in northern Italy.
The centre of the upper Valtellina ...
(1512-1797)
* Chiavenna (1512-1797)
* Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Toda ...
(1512-1797)
* Drei Pleven (1512–26)
* Maienfeld
Maienfeld ( rm, Maiavilla) is a municipality in the Landquart Region in the Swiss canton of Graubünden. It is a tourist destination in the Alps, both because of the local wine and because it was the setting of the story ''Heidi''.
History ...
( Bündner Herrschaft) (1509–1790); simultaneously a member of the League of the Ten Jurisdictions
The League of the Ten Jurisdictions was the last of the Three Leagues founded during the Middle Ages in what is now Graubünden, Canton Graubünden of Switzerland. The League was created in the County of Toggenburg after the counts of Toggenbur ...
.
Notes and references
Further reading
* Aubert, J.-F.: ''Petite histoire constitutionnelle de la Suisse'', 2nd ed.; Francke Editions, Bern, 1974. * Peyer, H. C.: ''Verfassungsgeschichte der alten Schweiz'', Schulthess Polygraphischer Verlag, Zürich, 1978. .External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Swiss Confederacy States and territories established in 1291 States and territories disestablished in 1798 . . Former confederations Former countries in Europe States of the Holy Roman Empire 1290s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1291 establishments in Europe 1798 disestablishments in Europe * * Former countries History of Switzerland by period Old Swiss Confederacy