Zhang Qian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zhang Qian (; died c. 114) was a Chinese official and diplomat who served as an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the late 2nd century BC during the
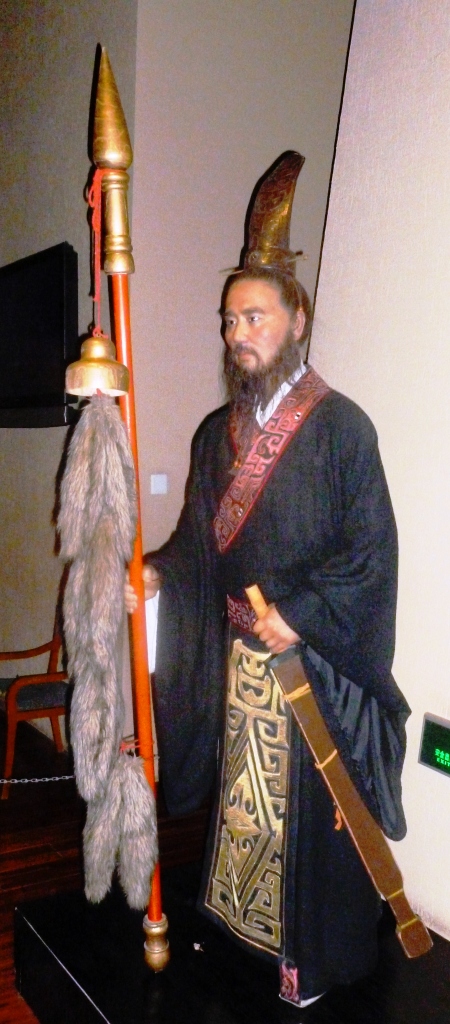 Zhang Qian was born in Chenggu district just east of
Zhang Qian was born in Chenggu district just east of
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
. He was one of the first official diplomats to bring back valuable information about Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, including the Greco-Bactrian remains of the Macedonian Empire
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
as well as the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
, to the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
imperial court, then ruled by Emperor Wu of Han.
He played an important pioneering role for the future Chinese conquest of lands west of Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, including swaths of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
and even lands south of the Hindu Kush (see Protectorate of the Western Regions). This trip created the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
that marked the beginning of globalization between the countries in the east and west.
Zhang Qian's travel was commissioned by Emperor Wu with the major goal of initiating transcontinental trade in the Silk Road, as well as create political protectorates by securing allies. His missions opened trade routes between East and West and exposed different products and kingdoms to each other through trade. Zhang's accounts were compiled by Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years be ...
in the 1st century BC. The Central Asian
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the form ...
parts of the Silk Road routes were expanded around 114 BC largely through the missions of and exploration by Zhang Qian. Today, Zhang is considered a Chinese national hero and revered for the key role he played in opening China and the countries of the known world to the wider opportunity of commercial trade and global alliances. Zhang Qian is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (無雙譜, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang.
Zhang Qian's Missions
 Zhang Qian was born in Chenggu district just east of
Zhang Qian was born in Chenggu district just east of Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west.
The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as ...
in the north-central province of Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. He entered the capital, Chang'an, today's Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
, between 140 BC and 134 BC as a Gentleman (), serving Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
. At the time the nomadic Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
tribes controlled what is now Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
and dominated the Western Regions, Xiyu (), the areas neighbouring the territory of the Han Dynasty. The Han emperor was interested in establishing commercial ties with distant lands but outside contact was prevented by the hostile Xiongnu.
The Han court dispatched Zhang Qian, a military officer who was familiar with the Xiongnu, to the Western Regions in 138 BC with a group of ninety-nine members to make contact and build an alliance with the Yuezhi against the Xiongnu. He was accompanied by a guide named Ganfu (), a Xiongnu who had been captured in war. The objective of Zhang Qian's first mission was to seek a military alliance with the Yuezhi, in modern Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
. However to get to the territory of the Yuezhi he was forced to pass through land controlled by the Xiongnu who captured him (as well as Ganfu) and enslaved him for thirteen years. During this time he married a Xiongnu wife, who bore him a son, and gained the trust of the Xiongnu leader.
Zhang and Ganfu (as well as Zhang's Xiongnu wife and son) were eventually able to escape and, passing Lop Nor
Lop Nur or Lop Nor (from a Mongolian name meaning "Lop Lake", where "Lop" is a toponym of unknown origin) is a former salt lake, now largely dried up, located in the eastern fringe of the Tarim Basin, between the Taklamakan and Kumtag deser ...
and following the northern edge of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
, around the Kunlun Mountains
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
and through small fortified areas in the middle of oases in what is now Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
until they made their way to Dayuan
Dayuan (or Tayuan; ; Middle Chinese ''dâiC-jwɐn'' < : ''dɑh-ʔyɑn'') is the Chinese
 The reports of Zhang Qian's travels are quoted extensively in the 1st century BC Chinese historic chronicles "Records of the Great Historian" ( Shiji) by
The reports of Zhang Qian's travels are quoted extensively in the 1st century BC Chinese historic chronicles "Records of the Great Historian" ( Shiji) by
alfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as ...
for animal fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals (includ ...
. However, the Yuezhi were too settled to desire war against the Xiongnu. Zhang spent a year in Yuezhi and the adjacent Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
n territory, documenting their cultures, lifestyles and economy, before beginning his return trip to China, this time following the southern edge of the Tarim Basin.
On his return trip he was again captured by the Xiongnu who again spared his life because they valued his sense of duty and composure in the face of death. Two years later the Xiongnu leader died and in the midst of chaos and infighting Zhang Qian escaped. Of the original mission of just over a hundred men, only Zhang Qian and Ganfu managed to return to China.
Zhang Qian returned in 125 BC with detailed news for the Emperor, showing that sophisticated civilizations existed to the West, with which China could advantageously develop relations. The Shiji relates that "the Emperor learned of the Dayuan (大宛), Daxia (大夏), Anxi (安息), and the others, all great states rich in unusual products whose people cultivated the land and made their living in much the same way as the Chinese. All these states, he was told, were militarily weak and prized Han goods and wealth". Upon Zhang Qian's return to China he was honoured with a position of palace counsellor. Although he was unable to develop commercial ties between China and these far-off lands, his efforts did eventually result in trade mission to the Wusun people in 119 BC which led to trade between China and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
On his mission Zhang Qian had noticed products from an area now known as northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
. However, the task remained to find a trade route not obstructed by the Xiongnu to India. Zhang Qian set out on a second mission to forge a route from China to India via Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
, but after many attempts this effort proved unsuccessful. In 119–115 BC Zhang Qian was sent on a third mission by the emperor, to develop ties with the Wusun () people.
Zhang Qian's reports
 The reports of Zhang Qian's travels are quoted extensively in the 1st century BC Chinese historic chronicles "Records of the Great Historian" ( Shiji) by
The reports of Zhang Qian's travels are quoted extensively in the 1st century BC Chinese historic chronicles "Records of the Great Historian" ( Shiji) by Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years be ...
. Zhang Qian visited directly the kingdom of Dayuan
Dayuan (or Tayuan; ; Middle Chinese ''dâiC-jwɐn'' < : ''dɑh-ʔyɑn'') is the Chinese
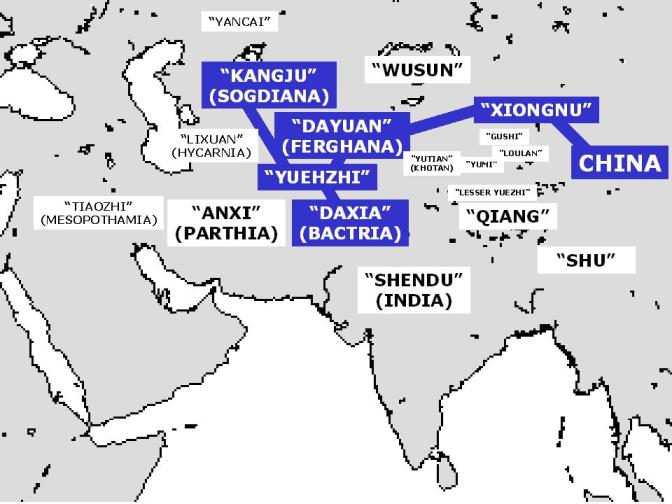 After being released from captivity by Xiongnu, Zhang Qian visited
After being released from captivity by Xiongnu, Zhang Qian visited
Fergana
Fergana ( uz, Fargʻona/Фарғона, ), or Ferghana, is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 420 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km west of Andijan, and less than 20 km ...
, the territories of the Yuezhi () in Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, the Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
n country of Daxia
Daxia, Ta-Hsia, or Ta-Hia (; literally: 'Great Xia') was apparently the name given in antiquity by the Han Chinese to Tukhara or Tokhara: the main part of Bactria, in what is now northern Afghanistan, and parts of southern Tajikistan and Uzbek ...
() with its remnants of Greco-Bactrian rule, and Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
(). He also made reports on neighbouring countries that he did not visit, such as Anxi () ( Arsacid territories), Tiaozhi (條支/条支) (Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
), Shendu () (India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
) and the Wusun ().
Dayuan (大宛, Ferghana)
 After being released from captivity by Xiongnu, Zhang Qian visited
After being released from captivity by Xiongnu, Zhang Qian visited Dayuan
Dayuan (or Tayuan; ; Middle Chinese ''dâiC-jwɐn'' < : ''dɑh-ʔyɑn'') is the Chinese
Fergana
Fergana ( uz, Fargʻona/Фарғона, ), or Ferghana, is a district-level city and the capital of Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan. Fergana is about 420 km east of Tashkent, about 75 km west of Andijan, and less than 20 km ...
region west of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
. The people of Dayuan were being portrayed as sophisticated urban dwellers similar to the Parthians and the Bactrians. The name Dayuan is thought to be a transliteration of the word '' Yona'', the Greek descendants that occupied the region from the 4th to the 2nd century BCE. It was during this stay that Zhang reported the famous tall and powerful "blood-sweating" Ferghana horse. The refusal by Dayuan to offer these horses to Emperor Wu of Han resulted in two punitive campaigns launched by the Han Dynasty to acquire these horses by force.
:"Dayuan lies south-west of the territory of the Xiongnu, some 10,000 '' li'' (5,000 kilometres) directly west of China. The people are settled on the land, ploughing the fields and growing rice and wheat. They also make wine out of grapes. The people live in houses in fortified cities, there being some seventy or more cities of various sizes in the region. The population numbers several hundred thousand" ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Later the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
conquered the region in the War of the Heavenly Horses.
Yuezhi (月氏)
After obtaining the help of the king of Dayuan, Zhang Qian went south-west to the territory of the Yuezhi, with whom he was supposed to obtain a military alliance against the Xiongnu. :"The Great Yuezhi live some 2,000 or 3,000 li (1,000 or 1,500 kilometres) west of Dayuan, north of the Gui (Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
) river. They are bordered to the south by Daxia (Bactria), on the west by Anxi, and on the north by Kangju (康居). They are a nation of nomads, moving place to place with their herds and their customs are like those of the Xiongnu. They have some 100,000 or 200,000 archer warriors." (adapted from Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Zhang Qian also describes the origins of the Yuezhi, explaining they came from the eastern part of the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hyd ...
. This has encouraged some historians to connect them to the Caucasoid mummies of the Tarim. (The question of links between the Yuezhi and the Tocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China). ...
of the Tarim is still debatable.)
:"The Yuezhi originally lived in the area between the Qilian or Heavenly Mountains (Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
) and Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major s ...
, but after they were defeated by the Xiongnu they moved far away to the west, beyond Dayuan (Ferghana), where they attacked the people of Daxia (Bactria) and set up the court of their king on the northern bank of the Gui (Oxus) river." ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
A smaller group of Yuezhi, the "Little Yuezhi", were not able to follow the exodus and reportedly found refuge among the " Qiang barbarians".
Zhang was the first Chinese to write about one humped dromedary camels which he saw in this region.
Daxia (大夏, Bactria)
Zhang Qian probably witnessed the last period of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, as it was being subjugated by the nomadic Yuezhi. Only small powerless chiefs remained, who were apparently vassals to the Yuezhi horde. Their civilization was urban, almost identical to the civilizations of Anxi and Dayuan, and the population was numerous. :"Daxia is situated over 2,000 ''li'' (1,000 kilometres) south-west ofDayuan
Dayuan (or Tayuan; ; Middle Chinese ''dâiC-jwɐn'' < : ''dɑh-ʔyɑn'') is the Chinese
Bactra) where all sorts of goods are bought and sold." ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, translation Burton Watson).
Cloth from Shu (
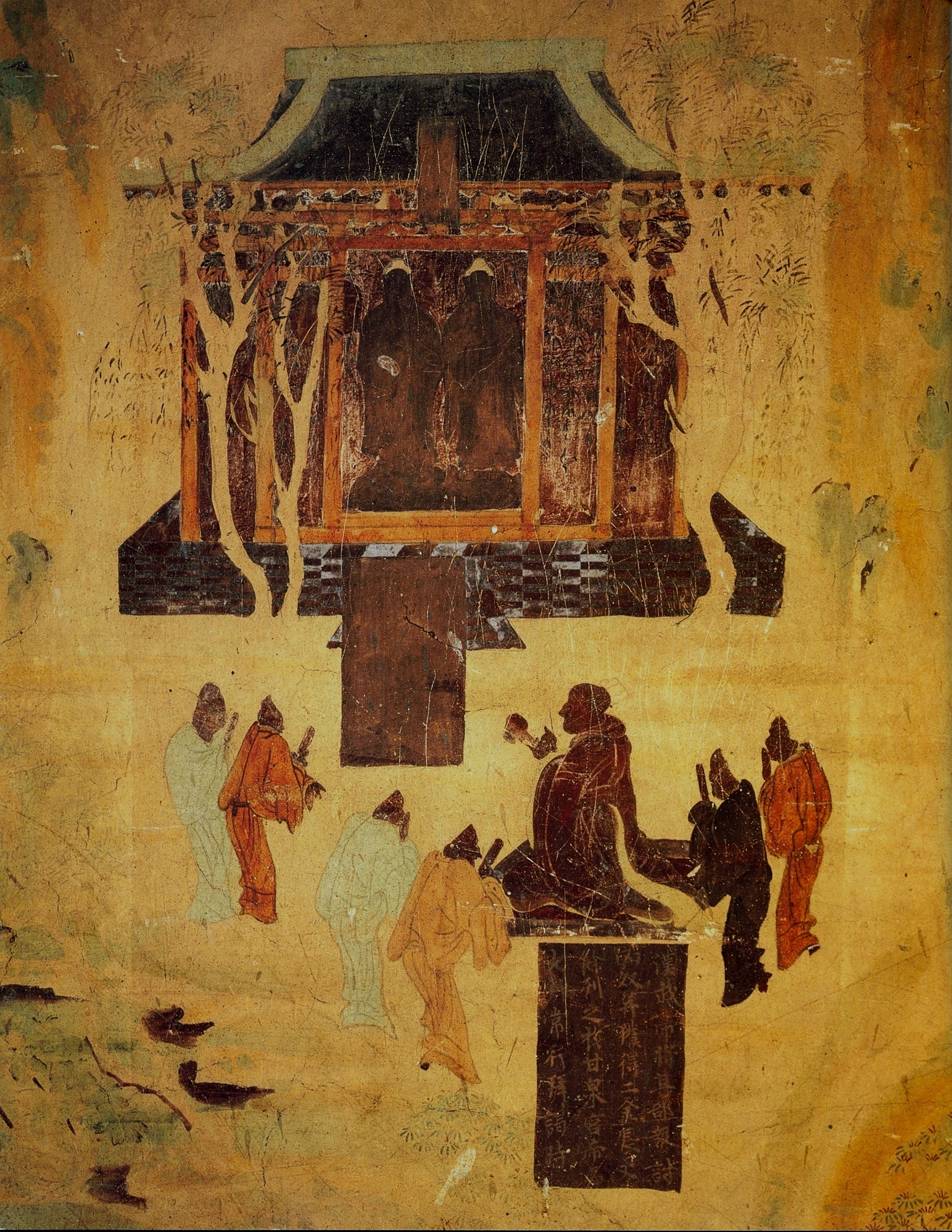 Murals in Mogao Caves in
Murals in Mogao Caves in
The Opening of the Silk Road
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zhang Qian Ancient explorers Chinese explorers Han dynasty diplomats Politicians from Hanzhong Horse in Chinese mythology Han dynasty politicians from Shaanxi 190s BC births 113 BC deaths 200 BC births Emperor Wu of Han Legendary Chinese people
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
) was found there.
Shendu (身毒, India)
Zhang Qian also reports about the existence ofIndia
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
south-east of Bactria. The name ''Shendu'' () comes from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
word "Sindhu", meaning the Indus river. Sindh was one of the richest regions of India at the time, ruled by Indo-Greek Kingdoms, which explains the reported cultural similarity between Bactria and India:
:"Southeast of Daxia is the kingdom of Shendu (India)... Shendu, they told me, lies several thousand ''li'' south-east of Daxia (Bactria). The people cultivate the land and live much like the people of Daxia. The region is said to be hot and damp. The inhabitants ride elephants when they go in battle. The kingdom is situated on a great river (Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
)" ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Anxi (安息, Parthia)
Zhang Qian identifies "Anxi" () as an advanced urban civilization, like Dayuan (Ferghana) and Daxia (Bactria). The name "Anxi" is a transcription of " Arshak" ( Arsaces), the name of the founder ofArsacid Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqueri ...
that ruled the regions along the Silk Road between the Tedzhen river in the east and the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
in the west, and running through Aria
In music, an aria ( Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompa ...
, Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
proper, and Media proper.
:"Anxi is situated several thousand '' li'' west of the region of the Great Yuezhi. The people are settled on the land, cultivating the fields and growing rice and wheat. They also make wine out of grapes. They have walled cities like the people of Dayuan (Ferghana), the region contains several hundred cities of various sizes. The coins of the country are made of silver and bear the face of the king. When the king dies, the currency is immediately changed and new coins issued with the face of his successor. The people keep records by writing on horizontal strips of leather. To the west lies Tiaozhi (Mesopotamia) and to the north Yancai and Lixuan ( Hyrcania)." ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Tiaozhi (条支, Seleucid Empire in Mesopotamia)
Zhang Qian's reports onMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
and the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, or Tiaozhi (), are in tenuous terms. He did not himself visit the region, and was only able to report what others told him.
:"Tiaozhi (Mesopotamia) is situated several thousand ''li'' west of Anxi ( Arsacid territory) and borders the "Western Sea" (which could refer to the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
or Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
). It is hot and damp, and the people live by cultivating the fields and planting rice... The people are very numerous and are ruled by many petty chiefs. The ruler of Anxi (the Arsacids) give orders to these chiefs and regards them as vassals." (adapted from Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Kangju (康居) northwest of Sogdiana (粟特)
Zhang Qian also visited directly the area of Sogdiana (Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
), home to the Sogdian nomads:
:"Kangju is situated some 2,000 li (1,000 kilometres) north-west of Dayuan (Bactria). Its people are nomads and resemble the Yuezhi in their customs. They have 80,000 or 90,000 skilled archer fighters. The country is small, and borders Dayuan. It acknowledges sovereignty to the Yuezhi people in the South and the Xiongnu in the East." (Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Yancai (奄蔡, Vast Steppe)
:"Yancai lies some 2,000 '' li'' (832 km) north-west ofKangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
(centered on Turkestan at Beitian). The people are nomads and their customs are generally similar to those of the people of Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
. The country has over 100,000 archer warriors, and borders a great shore-less lake, perhaps what is now known as the Northern Sea (Aral Sea
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic lake lying between Kazak ...
, distance between Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
to Aralsk
Aral, also known as Aralsk or Aral'sk, ( Kazakh: Арал, ''Aral'', ارال; Russian: Аральск, ''Araljsk'') is a small city in south-western Kazakhstan, located in the ''oblast'' (region) of Kyzylorda. It serves as the administrati ...
is about 866 km)" ( Shiji, 123, Zhang Qian quote, trans. Burton Watson).
Development of East-West contacts
Following Zhang Qian's embassy and report, commercial relations between China and Central as well as Western Asia flourished, as many Chinese missions were sent throughout the end of the 2nd century BC and the 1st century BC, initiating the development of theSilk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
:
:"The largest of these embassies to foreign states numbered several hundred persons, while even the smaller parties included over 100 members... In the course of one year anywhere from five to six to over ten parties would be sent out." (Shiji, trans. Burton Watson).
Many objects were soon exchanged, and travelled as far as Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
in the East, as suggested by the discovery of a Persian box and various artefacts from Central Asia in the 122 BC tomb of King Zhao Mo of Nanyue.
 Murals in Mogao Caves in
Murals in Mogao Caves in Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major s ...
describe the Emperor Han Wudi (156–87 BC) worshipping Buddhist statues, explaining them as "golden men brought in 120 BC by a great Han general in his campaigns against the nomads", although there is no other mention of Han Wudi worshipping the Buddha in Chinese historical literature.
China also sent a mission to Anxi, which were followed up by reciprocal missions from Parthian envoys around 100 BC:
:"When the Han envoy first visited the kingdom of Anxi, the king of Anxi (the Arsacid ruler) dispatched a party of 20,000 horsemen to meet them on the eastern border of the kingdom... When the Han envoys set out again to return to China, the king of Anxi dispatched envoys of his own to accompany them... The emperor was delighted at this." (adapted from Shiji, 123, trans. Burton Watson).
The Roman historian Florus describes the visit of numerous envoys, including '' Seres'' (Chinese or central Asians), to the first Roman Emperor Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, who reigned between 27 BC and 14:
:"Even the rest of the nations of the world which were not subject to the imperial sway were sensible of its grandeur, and looked with reverence to the Roman people, the great conqueror of nations. Thus even Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Sarmatians sent envoys to seek the friendship of Rome. Nay, the Seres came likewise, and the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
ns who dwelt beneath the vertical sun, bringing presents of precious stones and pearls and elephants, but thinking all of less moment than the vastness of the journey which they had undertaken, and which they said had occupied four years. In truth it needed but to look at their complexion to see that they were people of another world than ours." ("Cathay and the way thither", Henry Yule).
In 97 the Chinese general Ban Chao
Ban Chao (; 32–102 CE), courtesy name Zhongsheng, was a Chinese diplomat, explorer, and military general of the Eastern Han Dynasty. He was born in Fufeng, now Xianyang, Shaanxi. Three of his family members—father Ban Biao, elder brother B ...
dispatched an envoy to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
in the person of Gan Ying.
Several Roman embassies to China followed from 166, and are officially recorded in Chinese historical chronicles.
Final years and legacy
The '' Shiji'' reports that Zhang Qian returned from his final expedition to the Wusun in 115 BC. After his return he "was honoured with the post of grand messenger, making him among the nine highest ministers of the government. A year or so later he died.""The indications regarding the year of his passing differ, but Shih Chih-mien (1961), p. 268 shows beyond doubt that he died in 113 B.C. His tomb is situated in Chang-chia ts'un 張家村 near Ch'eng-ku . . . ; during repairs carried out in 1945 a clay mold with the inscription 博望家造 ome of the Bowang (Marquis)was found, as reported by Ch'en Chih (1959), p. 162." Hulsewé and Loewe (1979), p. 218, note 819.
Other achievements
From his missions he brought back many important products, the most important beingalfalfa
Alfalfa () (''Medicago sativa''), also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as ...
seeds (for growing horse fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals (includ ...
), strong horses with hard hooves, and knowledge of the extensive existence of new products, peoples and technologies of the outside world. He died ''c''. 114 BC after spending twenty-five years travelling on these dangerous and strategic missions. Although at a time in his life he was regarded with disgrace for being defeated by the Xiongnu, by the time of his passing he had been bestowed with great honours by the emperor.
Zhang Qian's journeys had promoted a great variety of economic and cultural exchanges between the Han Dynasty and the Western Regions. Because silk became the dominant product traded from China, this great trade route later became known as the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
.
See also
* Seres *Ban Chao
Ban Chao (; 32–102 CE), courtesy name Zhongsheng, was a Chinese diplomat, explorer, and military general of the Eastern Han Dynasty. He was born in Fufeng, now Xianyang, Shaanxi. Three of his family members—father Ban Biao, elder brother B ...
* Faxian
* Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
* Chen Cheng
Chen Cheng (; ; January 4, 1898 – March 5, 1965) was a Chinese political and military leader, and one of the main commanders of the National Revolutionary Army during the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Chinese Civil War.
After movi ...
* Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
* Yi Jing
* Rabban Bar Sauma
* Tianzhu (India)
Tianzhu which also referred as Heaven is the historical East Asian name for India, Originally pronounced as l̥induk or *qʰl'iːn tuɡ 天竺 in Old Chinese, it comes from the Chinese transliteration of unattested Old Persian diminutive *Hi ...
Footnotes
References
*Hulsewé, A. F. P. and Loewe, M. A. N., (1979). ''China in Central Asia: The Early Stage 125 BC – AD 23: an annotated translation of chapters 61 and 96 of the History of the Former Han Dynasty''. Leiden: E. J. Brill. * * Further Readings * Yap, Joseph P, (2019). The Western Regions, Xiongnu and Han, from the Shiji, Hanshu and Hou Hanshu.External links
The Opening of the Silk Road
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zhang Qian Ancient explorers Chinese explorers Han dynasty diplomats Politicians from Hanzhong Horse in Chinese mythology Han dynasty politicians from Shaanxi 190s BC births 113 BC deaths 200 BC births Emperor Wu of Han Legendary Chinese people