ZZ diboson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ZZ dibosons are rare pairs of Z bosons. They were first observed by the experiments at the
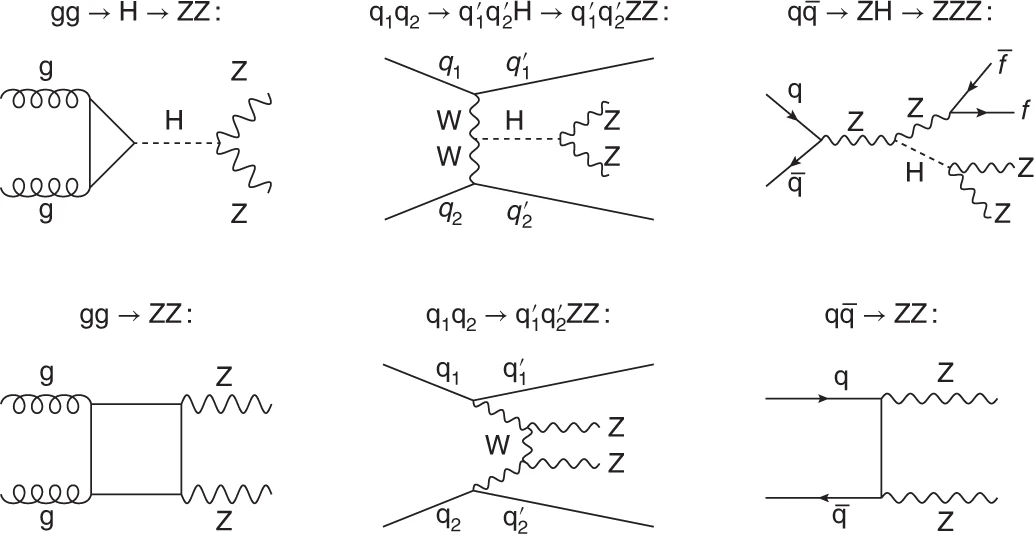 ZZ dibosons are force-carrying particles observed as products of proton–
ZZ dibosons are force-carrying particles observed as products of proton–
Large Electron–Positron Collider
The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) was one of the largest particle accelerators ever constructed. It was built at CERN, a multi-national centre for research in nuclear and particle physics near Geneva, Switzerland.
LEP collided elect ...
(ALEPH, DELPHI, L3 and OPAL). The first observation in a hadron collider was made by the scientists of DØ collaboration at Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been opera ...
.
Discussion
 ZZ dibosons are force-carrying particles observed as products of proton–
ZZ dibosons are force-carrying particles observed as products of proton–antiproton
The antiproton, , (pronounced ''p-bar'') is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived, since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy.
The exis ...
collisions at the Tevatron
The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator (active until 2011) in the United States, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as ''Fermilab''), east of Batavia, Illinois, and is the second highest energy particle collider ...
, the world's second highest-energy particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams.
Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle ...
(after the CERN Large Hadron Collider). The first observation of the ZZ dibosons was announced at a Fermilab seminar on 30 July 2008.
The rarest diboson processes after ZZ dibosons are those involving the Higgs boson, so seeing ZZ diboson is an essential step in demonstrating the ability to see the Higgs boson. ZZ dibosons are the latest in a series of observations of pairs of gauge bosons
In particle physics, a gauge boson is a bosonic elementary particle that acts as the force carrier for elementary fermions. Elementary particles, whose interactions are described by a gauge theory, interact with each other by the exchange of gauge ...
(force-carrying particles) by DØ and its sister experiment CDF (also at Tevatron).
Final analysis of the data for this discovery was done by a team of international researchers including scientists of American, Belgian, British, Georgian, Italian, and Russian nationalities. The observations began with the study of the already-rare production of W boson
In particle physics, the W and Z bosons are vector bosons that are together known as the weak bosons or more generally as the intermediate vector bosons. These elementary particles mediate the weak interaction; the respective symbols are , , and ...
s plus photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they a ...
s (); then Z bosons plus photons (); then observation of W pairs (); then a mix of W and Z boson (). The ZZ () is the combination which has the lowest predicted likelihood of production in the Standard Model due to the smaller couplings.
See also
*Dineutron
Neutronium (sometimes shortened to neutrium, also referred to as neutrite) is a hypothetical substance composed purely of neutrons. The word was coined by scientist Andreas von Antropoff in 1926 (before the 1932 discovery of the neutron) for the ...
*Diproton
Although there are nine known isotopes of helium (2He) ( standard atomic weight: ), only helium-3 () and helium-4 () are stable. All radioisotopes are short-lived, the longest-lived being with a half-life of . The least stable is , with a half- ...
*Pauli exclusion principle
In quantum mechanics, the Pauli exclusion principle states that two or more identical particles with half-integer spins (i.e. fermions) cannot occupy the same quantum state within a quantum system simultaneously. This principle was formulat ...
* Higgs boson
*List of particles
This is a list of known and hypothesized particles.
Elementary particles
Elementary particles are particles with no measurable internal structure; that is, it is unknown whether they are composed of other particles. They are the fundamental ob ...
References
External links
* * * * * Bosons Electroweak theory {{particle-stub