Yuly Shokalsky on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Yuly Mikhailovich Shokalsky (russian: Юлий Михайлович Шокальский; October 17, 1856 in
Yuly Mikhailovich Shokalsky (russian: Юлий Михайлович Шокальский; October 17, 1856 in
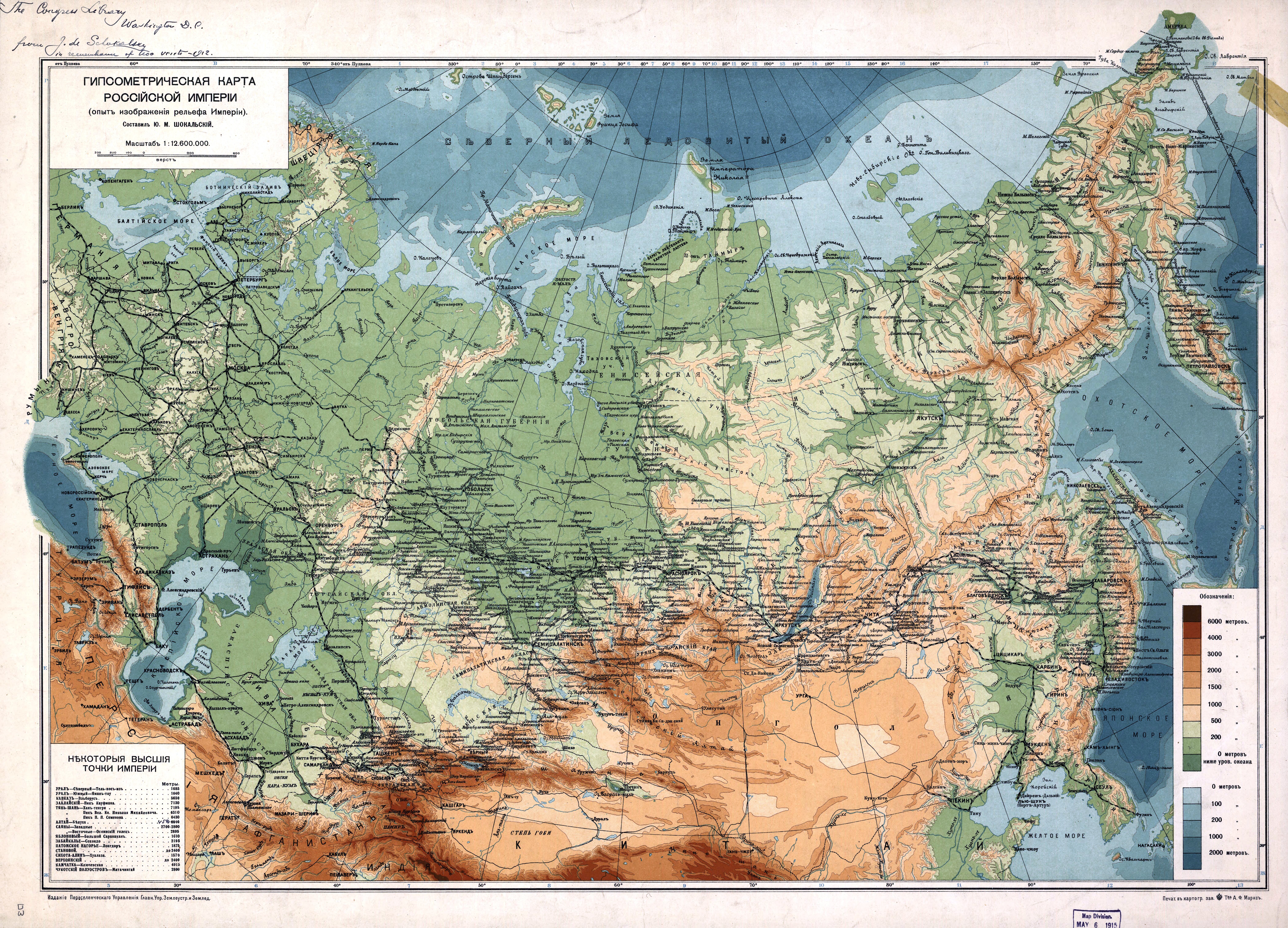 Shokalsky's most important monograph was ''Oceanography'' (1917), a collection of his lectures which examined connection between
Shokalsky's most important monograph was ''Oceanography'' (1917), a collection of his lectures which examined connection between
Biography
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shokalsky, Yuly Mikhailovich 1856 births 1940 deaths Scientists from Saint Petersburg Russian oceanographers Russian hydrographers Cartographers from the Russian Empire Geographers from the Russian Empire Soviet geographers Explorers from the Russian Empire Members of the French Academy of Sciences Corresponding Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925) Corresponding Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Imperial Russian Navy personnel Fellows of the Royal Geographical Society Soviet oceanographers Soviet hydrographers
 Yuly Mikhailovich Shokalsky (russian: Юлий Михайлович Шокальский; October 17, 1856 in
Yuly Mikhailovich Shokalsky (russian: Юлий Михайлович Шокальский; October 17, 1856 in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
– March 26, 1940 in Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
) was a Russian oceanographer
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamic ...
, cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an ...
, and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
.
Career
A grandson of Anna Kern,Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
's celebrated mistress, Shokalsky graduated from the Naval Academy in 1880 and made a career in the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from ...
, helping establish the Sevastopol Marine Observatory and rising to the rank of Lieutenant-General in 1912. At the same time, he developed interest in limnology
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteris ...
and meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
and became the most prolific Russian author on the subjects. In the ''Marine Miscellanies'' alone, he published some 300 articles.  Shokalsky's most important monograph was ''Oceanography'' (1917), a collection of his lectures which examined connection between
Shokalsky's most important monograph was ''Oceanography'' (1917), a collection of his lectures which examined connection between meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
and hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is call ...
and emphasized the importance of monitoring marine phenomena in order to understand global changes of climate. Shokalsky insisted on differentiating oceanography and hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the prima ...
and coined the term "World Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the worl ...
".
In 1904, Shokalsky was elected into the Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
. Ten years later, he was put in charge of the Russian Geographical Society and retained the post until 1931.
Honours
His name was given to the Shokalsky Strait connecting theLaptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, t ...
and the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipel ...
, to the large Shokalsky Island
Shokalsky Island (russian: Остров Шокальского) is an island in the Kara Sea, in Russia. It is located on the eastern side of the mouth of the Ob River, off the tip of the narrow northwestern arm of the Gyda Peninsula. It is separ ...
in the Kara Sea, and to the ship ''Akademik Shokalskiy
MV ''Akademik Shokalskiy'' (russian: Академик Шокальский) is an ''Akademik Shuleykin''-class ice-strengthened ship, built in Finland in 1982 and originally used for oceanographic research. In 1998 she was fully refurbished to s ...
''.
See also
*Aleksey Tillo
Aleksey Tillo (russian: Алексей Андреевич Тилло; Alexei Andreyevitch Tillo) (25 November ( O.S. November 13), 1839, Kiev Governorate – 11 January ( O.S. December 30), 1900, Saint Petersburg) was a prominent Russian geograph ...
External links
Biography
{{DEFAULTSORT:Shokalsky, Yuly Mikhailovich 1856 births 1940 deaths Scientists from Saint Petersburg Russian oceanographers Russian hydrographers Cartographers from the Russian Empire Geographers from the Russian Empire Soviet geographers Explorers from the Russian Empire Members of the French Academy of Sciences Corresponding Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925) Corresponding Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences Imperial Russian Navy personnel Fellows of the Royal Geographical Society Soviet oceanographers Soviet hydrographers