XML editor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An XML editor is a
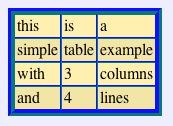 In the above example, a stylesheet is used to color table cells in a particular way. For instance, even rows do not have the same background color as odd rows, in order to make reading easier.
In the above example, a stylesheet is used to color table cells in a particular way. For instance, even rows do not have the same background color as odd rows, in order to make reading easier.
markup language
A markup language is a Encoding, text-encoding system which specifies the structure and formatting of a document and potentially the relationships among its parts. Markup can control the display of a document or enrich its content to facilitate au ...
editor with added functionality to facilitate the editing
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written language, written, Image editing, visual, Audio engineer, audible, or Film editing, cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing p ...
of XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
. This can be done using a plain text
In computing, plain text is a loose term for data (e.g. file contents) that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects ( floating-point numbers, images, etc.). It may also include a lim ...
editor, with all the code visible, but XML editors have added facilities like tag completion and menus and buttons for tasks that are common in XML editing, based on data supplied with document type definition (DTD) or the XML tree.
There are also graphical XML editors that hide the code in the background and present the content to the user in a more user-friendly format, approximating the rendered version or editing forms. This is helpful for situations where people who are not fluent in XML code need to enter information in XML based documents such as time sheets and expenditure reports. And even if the user is familiar with XML, use of such editors, which take care of syntax details, is often faster and more convenient.
Functionality beyond syntax highlighting
An XML editor goes beyond the syntax highlighting offered by many plaintext editors and generic source code editors, verifying the XML source based on anXML schema
An XML schema is a description of a type of XML document, typically expressed in terms of constraints on the structure and content of documents of that type, above and beyond the basic syntactical constraints imposed by XML itself. These constrai ...
or XML DTD, and some can do it as the document is being edited in real time.
Other features of an editor designed specifically for editing XML might include element word completion and automatic appending of a closing tag whenever an opening tag is entered.
These features can help to prevent typographically originating errors in the XML code.
Some XML editors provide for the ability to run an XSLT transform, or series of transforms, over a document. Some of the larger XML packages even offer XSLT debugging features and XSL-FO processors for generation of PDF files from documents.
Graphical editors
Graphical editors based on GUIs may be easier for some people to use than text editors, and may not require knowledge of XML syntax. These are often called WYSIWYG ("What You See Is What You Get") editors, but not all of them are WYSIWYG: graphical XML editors can be WYSIWYG when they try to display the final rendering or WYSIWYM ("What You See Is What You Mean") when they try to display the actual meaning of XML elements. When they are not WYSIWYG, they do not display the (or one of the) graphical end result of a document, but instead focus on conveying the meaning of the text. They use DTDs or XML schemas and/or configuration files to map XML elements to graphical components. These kinds of editors are generally more useful for XML languages for data rather than for storing documents. Documents tend to be fairly free-form in structure, which tends to defy the generally rigid nature of many graphical editors. In the above example, the editor is using a configuration file to know that the TABLE element represents a table, the TR element represents a row of the table, and the TD element represents a cell of the table. It is using this information to display the table based on this structuring information, in order to make editing easier. Schema and configuration files information can also be used to ensure that users do not create invalid documents. For instance, in a text editor, it is possible to create a row with too many cells in the table, while this would not be possible with the above graphical user interface.WYSIWYG editors
WYSIWYG editors let people edit files directly with the tags represented by some form of graphical viewing rather than bare XML code. Often, WYSIWYG editors attempt to emulate the result of some transform or CSS stylesheet application. This emulation may or may not be possible, depending on the transformation from XML into the result. Naive use of a WYSIWYG editor can lead to the creation of documents that do not have the intrinsic semantics of the particular XML language. This comes about if the user is focused on trying to achieve a certain visual presentation with the editor, rather than using the WYSIWYG to make editing the document easier. For instance, someone creating aweb page
A web page (or webpage) is a World Wide Web, Web document that is accessed in a web browser. A website typically consists of many web pages hyperlink, linked together under a common domain name. The term "web page" is therefore a metaphor of pap ...
could use an H2 element (meaning: second level title) instead of H1 (meaning: first level title) because it looks smaller on their current WYSIWYG editor. Such an author is making a choice based on the apparent visual representation, but a visitor to the author's web page can offer a very different rendering in their browser.
However, as long as the underlying meaning of the document is understood by the author, and the author does not make decisions based on the exact look in the WYSIWYG editor, such an editor can be of value to the writer. It is generally much easier to read a document that is being rendered in some fashion than it is to read the raw XML code. Also, editing can be much more intuitive, as the WYSIWYG editor can use tools similar to many word processing applications. Some WYSIWYG editors even allow the user to use a DTD or Schema and define their own user interface for editing.
Usually WYSIWYG editors support CSS but not XSLT, because XSLT transformations can be very complex, and guessing what the user meant when changing the result can be impossible. The WYSIWYG editors that do support XSLT, such as Syntext Serna, will therefore apply changes directly to the original XML, while updating the view by running the XSLT for every change.
 In the above example, a stylesheet is used to color table cells in a particular way. For instance, even rows do not have the same background color as odd rows, in order to make reading easier.
In the above example, a stylesheet is used to color table cells in a particular way. For instance, even rows do not have the same background color as odd rows, in order to make reading easier.
Application domains
*Computer programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of proc ...
* Technical editing
See also
* Comparison of XML editors * Authoring system *Editing
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written language, written, Image editing, visual, Audio engineer, audible, or Film editing, cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing p ...
* Source code editor
* Machine-Readable Documents
; Edited formats
* XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
* Darwin Information Typing Architecture (DITA)
* DocBook
DocBook is a Semantics (computer science), semantic markup language for technical documentation. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software, but it can be used for any other sort of docume ...
* Strategy Markup Language
References
{{Reflist Technical communication tools XML