Women's health differs from that of men in many unique ways. Women's health is an example of
population health
Population health has been defined as "the health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of such outcomes within the group". It is an approach to health that aims to improve the health of an entire human population. It ha ...
, where health is defined by the
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". Often treated as simply women's
reproductive health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
, many groups argue for a broader definition pertaining to the overall health of women, better expressed as "The health of women". These differences are further exacerbated in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
where women, whose health includes both their risks and experiences, are further disadvantaged.
Although women in
industrialised countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
have narrowed the
gender gap
A gender gap, a relative disparity between people of different genders, is reflected in a variety of sectors in many societies. There exist differences between men and women as reflected in social, political, intellectual, cultural, scientific or e ...
in
life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
and now live longer than men, in many areas of health they experience earlier and more severe disease with poorer outcomes. Gender remains an important
social determinant of health, since women's health is influenced not just by their biology but also by conditions such as
poverty, employment, and family responsibilities. Women have long been disadvantaged in many respects such as social and economic power which restricts their access to the necessities of life including
health care, and the greater the level of disadvantage, such as in developing countries, the greater adverse impact on health.
Women's reproductive and
sexual health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
has a distinct difference compared to men's health. Even in
developed countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
and
childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
are associated with substantial risks to women with
maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
accounting for more than a quarter of a million deaths per year, with large gaps between the developing and developed countries.
Comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity - from Latin morbus ("sickness"), co ("together"), -ity (as if - several sicknesses together) - is the presence of one or more additional conditions often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary ...
from other non reproductive disease such as
cardiovascular disease contribute to both the mortality and
morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
of pregnancy, including
preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
.
Sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral ...
have serious consequences for women and infants, with
mother-to-child transmission
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It can ...
leading to outcomes such as
stillbirths
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term ...
and
neonatal death
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion ...
s, and
pelvic inflammatory disease leading to
infertility. In addition infertility from many other causes,
birth control,
unplanned pregnancy
Unintended pregnancies are pregnancies that are mistimed, unplanned or unwanted at the time of conception.
Sexual activity without the use of effective contraception through choice or coercion is the predominant cause of unintended pregnancy. W ...
,
unconsensual sexual activity and the struggle for access to
abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
create other burdens for women.
While the rates of the leading causes of death,
cardiovascular disease,
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and
lung disease
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
, are similar in women and men, women have different experiences.
Lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
has overtaken all other types of cancer as the leading cause of cancer death in women, followed by
breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
,
colorectal
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being ...
,
ovarian
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body ...
,
uterine
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
and
cervical
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings:
# of or pertaining to any neck.
# of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus.
*Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are
**cervical collar
**cerv ...
cancers. While
smoking is the major cause of lung cancer, amongst nonsmoking women the risk of developing cancer is three times greater than among nonsmoking men. Despite this, breast cancer remains the commonest cancer in women in developed countries, and is one of the more important
chronic diseases
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three mon ...
of women, while cervical cancer remains one of the commonest cancers in developing countries, associated with
human papilloma virus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
(HPV), an important
sexually transmitted disease
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral ...
.
HPV vaccine together with
screening offers the promise of controlling these diseases. Other important health issues for women include cardiovascular disease,
depression,
dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
,
osteoporosis and
anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
. A major impediment to advancing women's health has been their underrepresentation in research studies, an
inequity being addressed in the United States and other western nations by the establishment of
centers of excellence in women's health research and large scale
clinical trials such as the
Women's Health Initiative
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three ...
.
Definitions and scope
Women's experience of health and disease differ from those of men, due to unique biological, social and behavioral conditions. Biological differences vary from
phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
s to the
cellular biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
, and manifest
unique risks for the development of ill health.
[ The ]World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO) defines health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". Women's health is an example of population health
Population health has been defined as "the health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of such outcomes within the group". It is an approach to health that aims to improve the health of an entire human population. It ha ...
, the health of a specific defined population.
Women's health has been described as "a patchwork quilt with gaps". Although many of the issues around women's health relate to their reproductive health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
, including maternal
]
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of gestat ...
and child birth, child health, genital health and breast health, and endocrine (hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required f ...
) health, including menstruation, birth control and menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
, a broader understanding of women's health to include all aspects of the health of women has been urged, replacing "Women's Health" with "The Health of Women". The WHO considers that an undue emphasis on reproductive health has been a major barrier to ensuring access to good quality health care for all women.[ Conditions that affect both men and women, such as cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, also manifest differently in women. Women's health issues also include medical situations in which women face problems not directly related to their biology, such as gender-differentiated access to medical treatment and other ]socioeconomic
Socioeconomics (also known as social economics) is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how modern societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their l ...
factors. Women's health is of particular concern due to widespread discrimination against women in the world, leaving them disadvantaged
The "disadvantaged" is a generic term for individuals or groups of people who:
* Face special problems such as physical or mental disability
* Lack money or economic supportKingdom of Nepal: Economic and Social Inclusion of the Disadvantaged Poo ...
.[
A number of health and medical research advocates, such as the Society for Women's Health Research in the United States, support this broader definition, rather than merely issues specific to human female anatomy to include areas where biological sex differences between women and men exist. Women also need health care more and access the health care system more than do men. While part of this is due to their reproductive and sexual health needs, they also have more chronic non-reproductive health issues such as cardiovascular disease, ]cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, mental illness, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
and osteoporosis. Another important perspective is realising that events across the entire life cycle
Life cycle, life-cycle, or lifecycle may refer to:
Science and academia
*Biological life cycle, the sequence of life stages that an organism undergoes from birth to reproduction ending with the production of the offspring
* Life-cycle hypothesis ...
(or life-course), from ''in utero
''In Utero'' is the third and final studio album by American rock band Nirvana. It was released on September 21, 1993, by DGC Records. After breaking into the mainstream with their second album, ''Nevermind'' (1991), Nirvana hired Steve Albin ...
'' to aging effect the growth, development and health of women. The life course perspective is one of the key strategies of the World Health Organization.[
]
Global perspective
Gender differences in susceptibility and symptoms of disease and response to treatment in many areas of health are particularly true when viewed from a global perspective. Much of the available information comes from developed countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, yet there are marked differences between developed and developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
in terms of women's roles and health. The global viewpoint is defined as the "area for study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving health equity for all people worldwide". In 2015 the World Health Organization identified the top ten issues in women's health as being cancer, reproductive health, maternal health, human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immun ...
(HIV), sexually transmitted infections, violence, mental health, non communicable diseases, youth and aging.
Life expectancy
Women's life expectancy is greater than that of men, and they have lower death rates throughout life, regardless of race and geographic region. Historically though, women had higher rates of mortality, primarily from maternal deaths
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
(death in childbirth). In industrialised countries, particularly the most advanced, the gender gap narrowed and was reversed following the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
.
Despite these differences, in many areas of health, women experience earlier and more severe disease, and experience poorer outcomes.
Despite these differences, the leading causes of death in the United States are remarkably similar for men and women, headed by heart disease, which accounts for a quarter of all deaths, followed by cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, lung disease
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
and stroke. While women have a lower incidence of death from unintentional injury
An accident is an unintended, normally unwanted event that was not directly caused by humans. The term ''accident'' implies that nobody should be blamed, but the event may have been caused by unrecognized or unaddressed risks. Most researche ...
(see below) and suicide, they have a higher incidence of dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
(Gronowski and Schindler, Table I).[
The major differences in life expectancy for women between developed and developing countries lie in the childbearing years. If a woman survives this period, the differences between the two regions become less marked, since in later life ]non-communicable diseases
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, oste ...
(NCDs) become the major causes of death in women throughout the world, with cardiovascular deaths accounting for 45% of deaths in older women, followed by cancer (15%) and lung disease (10%). These create additional burdens on the resources of developing countries. Changing lifestyles, including diet, physical activity and cultural factors that favour larger body size in women, are contributing to an increasing problem with obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
and diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
amongst women in these countries and increasing the risks of cardiovascular disease and other NCDs.
Women who are socially marginalized are more likely to die at younger ages than women who are not. Women who have substance abuse disorders, who are homeless, who are sex workers, and/or who are imprisoned have significantly shorter lives than other women. At any given age, women in these overlapping, stigmatized groups are approximately 10 to 13 times more likely to die than typical women of the same age.
Social and cultural factors
 Women's health is positioned within a wider body of knowledge cited by, amongst others, the
Women's health is positioned within a wider body of knowledge cited by, amongst others, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
, which places importance on gender as a social determinant of health.[ While women's health is affected by their biology, it is also affected by their social conditions, such as poverty, employment, and family responsibilities, and these aspects should not be overshadowed.
Women have traditionally been disadvantaged in terms of economic and social status and power, which in turn reduces their access to the necessities of life including health care. Despite recent improvements in western nations, women remain disadvantaged with respect to men. The gender gap in health is even more acute in ]developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
where women are relatively more disadvantaged. In addition to gender inequity, there remain specific disease processes uniquely associated with being a woman which create specific challenges in both prevention and health care.
Even after succeeding in accessing health care, women have been discriminated against, a process that Iris Young has called "internal exclusion", as opposed to "external exclusion", the barriers to access. This invisibility effectively masks the grievances of groups already disadvantaged by power inequity, further entrenching injustice.
Behavioral differences also play a role, in which women display lower risk taking including consume less tobacco, alcohol, and drugs, reducing their risk of mortality from associated diseases, including lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
and cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
. Other risk factors that are lower for women include motor vehicle accidents. Occupational differences have exposed women to less industrial injuries
An occupational injury is bodily damage resulting from working. The most common organs involved are the spine, hands, the head, lungs, eyes, skeleton, and skin. Occupational injuries can result from exposure to occupational hazards ( physic ...
, although this is likely to change, as is risk of injury or death in war. Overall such injuries contributed to 3.5% of deaths in women compared to 6.2% in the United States in 2009. Suicide rates are also less in women.[
The social view of health combined with the acknowledgement that gender is a social determinant of health inform women's health service delivery in countries around the world. Women's health services such as ]Leichhardt Leichhardt may refer to:
* Division of Leichhardt, electoral District for the Australian House of Representatives
* Leichhardt Highway, a highway of Queensland, Australia
* Leichhardt Way, an Australian road route
* Leichhardt, New South Wales, inn ...
Women's Community Health Centre which was established in 1974 and was the first women's health centre established in Australia is an example of women's health approach to service delivery.
Women's health is an issue which has been taken up by many feminists
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social equality of the sexes. Feminism incorporates the position that society prioritizes the male poi ...
, especially where reproductive health
Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, healthcare, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual wellbeing during all stages of their life.
The term can also be further de ...
is concerned and the international women's movement was responsible for much of the adoption of agendas to improve women's health.
Biological factors
Factors that specifically affect the health of women vs. men
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chro ...
are most evident in those related to reproduction, but sex differences have been identified from the molecular to the behavioral scale. Some of these differences are subtle and difficult to explain, partly due to the fact that it is difficult to separate the health effects of inherent biological factors from the effects of the surrounding environment they exist in. Women's XX sex chromosomes
A sex chromosome (also referred to as an allosome, heterotypical chromosome, gonosome, heterochromosome, or idiochromosome) is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical ...
compliment, hormonal environment, as well as sex-specific lifestyles, metabolism, immune system function, and sensitivity to environmental factors are believed to contribute to sex differences in health at the levels of physiology, perception, and cognition. Women can have distinct responses to drugs and thresholds for diagnostic parameters. All of these necessitate caution in extrapolating information derived from biomarkers
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pa ...
from one sex to the other. Young women and adolescents are at risk from STIs, pregnancy and unsafe abortion, while older women often have few resources and are disadvantaged with respect to men, and also are at risk of dementia and abuse, and generally poor health.
Reproductive and sexual health
Women experience many unique health issues related to reproduction and sexuality and these are responsible for a third of all health problems experienced by women during their reproductive years (aged 15–44), of which unsafe sex is a major risk factor, especially in developing countries. Reproductive health includes a wide range of issues including the health and function of structures and systems involved in reproduction, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
, childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
and child rearing, including antenatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
and perinatal care.[ Global women's health has a much larger focus on reproductive health than that of developed countries alone, but also infectious diseases such as ]malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
in pregnancy and non-communicable diseases
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, oste ...
(NCD). Many of the issues that face women and girls in resource poor regions are relatively unknown in developed countries, such as female genital cutting, and further lack access to the appropriate diagnostic and clinical resources.
Maternal health
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
presents substantial health risks, even in developed countries, and despite advances in obstetrical
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surg ...
science and practice.[ ]Maternal mortality
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pre ...
remains a major problem in global health
Global health is the health of the populations in the worldwide context; it has been defined as "the area of study, research and practice that places a priority on improving health and achieving equity in health for all people worldwide". Problem ...
and is considered a sentinel event in judging the quality of health care systems. Adolescent pregnancy represents a particular problem, whether intended or unintended, and whether within marriage or a union or not. Pregnancy results in major changes in a girl's life, physically, emotionally, socially and economically and jeopardises her transition into adulthood. Adolescent pregnancy, more often than not, stems from a girl's lack of choices. or abuse. Child marriage (see below) is a major contributor worldwide, since 90% of births to girls aged 15–19 occur within marriage.
Maternal death
In 2013 about 289,000 women (800 per day) in the world died due to pregnancy-related causes, with large differences between developed and developing countries. Maternal mortality in western nations had been steadily falling, and forms the subject of annual reports and reviews.[ Yet, between 1987 and 2011, maternal mortality in the United States rose from 7.2 to 17.8 deaths per 100,000 live births, this is reflected in the ]Maternal Mortality Ratio
The maternal mortality ratio is a key performance indicator (KPI) for efforts to improve the health and safety of mothers before, during, and after childbirth per country worldwide. Often referred to as MMR, it is the annual number of female death ...
(MMR).[ By contrast rates as high as 1,000 per birth are reported in the rest of the world, with the highest rates in Sub-Saharan Africa and ]South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, which account for 86% of such deaths. These deaths are rarely investigated, yet the World Health Organization considers that 99% of these deaths, the majority of which occur within 24 hours of childbirth, are preventable if the appropriate infrastructure, training, and facilities were in place.[ In these resource-poor countries, maternal health is further eroded by poverty and adverse economic factors which impact the roads, health care facilities, equipment and supplies in addition to limited skilled personnel. Other problems include cultural attitudes towards sexuality, contraception, ]child marriage
Child marriage is a marriage or similar union, formal or informal, between a child under a certain age – typically 18 years – and an adult or another child.
*
*
*
* The vast majority of child marriages are between a female child and a mal ...
, home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
and the ability to recognise medical emergencies. The direct causes of these maternal deaths are hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, v ...
, eclampsia
Eclampsia is the onset of seizures (convulsions) in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is one of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy that presents with three main features: new onset of high blood pressure, large amounts of protein in ...
, obstructed labor
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include Perinatal asphyxia, not getting enoug ...
, sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
and unskilled abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
. In addition malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
and AIDS complicate pregnancy. In the period 2003–2009 hemorrhage was the leading cause of death, accounting for 27% of deaths in developing countries and 16% in developed countries.
Non-reproductive health remains an important predictor of maternal health. In the United States, the leading causes of maternal death are cardiovascular disease (15% of deaths), endocrine, respiratory and gastrointestinal disorders, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
, hemorrhage and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (Gronowski and Schindler, Table II).
In 2000, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
created Millennium Development Goal
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenni ...
(MDG) 5 to improve maternal health.[ Target 5A sought to reduce maternal mortality by three quarters from 1990 to 2015, using two indicators, 5.1 the MMR and 5.2 the proportion of deliveries attended by skilled health personnel (physician, nurse or midwife). Early reports indicated MDG 5 had made the least progress of all MDGs.][ By the target date of 2015 the MMR had only declined by 45%, from 380 to 210, most of which occurred after 2000. However this improvement occurred across all regions, but the highest MMRs were still in Africa and Asia, although South Asia witnessed the largest fall, from 530 to 190 (64%). The smallest decline was seen in the developed countries, from 26 to 16 (37%). In terms of assisted births, this proportion had risen globally from 59 to 71%. Although the numbers were similar for both developed and developing regions, there were wide variations in the latter from 52% in South Asia to 100% in ]East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
. The risks of dying in pregnancy in developing countries remains fourteen times higher than in developed countries, but in Sub-Saharan Africa, where the MMR is highest, the risk is 175 times higher. In setting the MDG targets, skilled assisted birth was considered a key strategy, but also an indicator of access to care and closely reflect mortality rates. There are also marked differences within regions with a 31% lower rate in rural areas of developing countries (56 vs. 87%), yet there is no difference in East Asia but a 52% difference in Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo ...
(32 vs. 84%). With the completion of the MDG campaign in 2015, new targets are being set for 2030 under the Sustainable Development Goals campaign. Maternal health is placed under Goal 3, Health, with the target being to reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70.[ Amongst tools being developed to meet these targets is the WHO Safe Childbirth Checklist.][
Improvements in maternal health, in addition to professional assistance at delivery, will require routine antenatal care, basic emergency obstetric care, including the availability of ]antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
, oxytocics, anticonvulsants, the ability to manually remove a retained placenta
Retained placenta is a condition in which all or part of the placenta or membranes remain in the uterus during the third stage of labour. Retained placenta can be broadly divided into:
* failed separation of the placenta from the uterine lining
* p ...
, perform instrumented deliveries, and postpartum care
Postpartum care or postnatal care is a service provided to individuals in the postpartum period, to help with postpartum recuperation and restoration.
Traditional postpartum care
Many traditional forms of postpartum confinement exist throughout ...
. Research has shown the most effective programmes are those focussing on patient and community education, prenatal care, emergency obstetrics (including access to cesarean sections
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
) and transportation. As with women's health in general, solutions to maternal health require a broad view encompassing many of the other MDG goals, such as poverty and status, and given that most deaths occur in the immediate intrapartum period, it has been recommended that intrapartum care (delivery) be a core strategy. New guidelines on antenatal care were issued by WHO in November 2016.[
]
Complications of pregnancy
In addition to death occurring in pregnancy and childbirth, pregnancy can result in many non-fatal health problems including obstetrical fistulae, ectopic pregnancy, preterm labor
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
, gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of ...
, hyperemesis gravidarum, hypertensive states including preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
, and anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
.[ Globally, complications of pregnancy vastly outway maternal deaths, with an estimated 9.5 million cases of pregnancy-related illness and 1.4 million near-misses (survival from severe life-threatening complications). Complications of pregnancy may be physical, mental, economic and social. It is estimated that 10–20 million women will develop physical or mental disability every year, resulting from complications of pregnancy or inadequate care. Consequently, international agencies have developed standards for obstetric care.][
]
= Obstetrical fistula
=
 Of near miss events, obstetrical fistulae (OF), including vesicovaginal and
Of near miss events, obstetrical fistulae (OF), including vesicovaginal and rectovaginal fistula
A rectovaginal fistula is a medical condition where there is a fistula or abnormal connection between the rectum and the vagina.
Rectovaginal fistulae may be extremely debilitating. If the opening between the rectum and vagina is wide it will allo ...
e, remain one of the most serious and tragic. Although corrective surgery is possible it is often not available and OF is considered completely preventable. If repaired, subsequent pregnancies will require cesarean section.[ While unusual in developed countries, it is estimated that up to 100,000 cases occur every year in the world, and that about 2 million women are currently living with this condition, with the highest incidence occurring in Africa and parts of Asia.][ OF results from prolonged ]obstructed labor
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically block during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include Perinatal asphyxia, not getting enoug ...
without intervention, when continued pressure from the fetus in the birth canal
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hyme ...
restricts blood supply to the surrounding tissues, with eventual fetal death
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion o ...
, necrosis and expulsion. The damaged pelvic organs then develop a connection (fistula) allowing urine or feces, or both, to be discharged through the vagina with associated urinary
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, co ...
and fecal incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents, both liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. When this loss includes flatus (gas), it is referre ...
, vaginal stenosis, nerve damage and infertility. Severe social and mental consequences are also likely to follow, with shunning of the women. Apart from lack of access to care, causes include young age, and malnourishment
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
.[ The ]UNFPA
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, is a UN agency aimed at improving reproductive and maternal health worldwide. Its work includes developing national healthcare strategies ...
has made prevention of OF a priority and is the lead agency in the Campaign to End Fistula, which issues annual reports[ and the United Nations observes May 23 as the International Day to End Obstetric Fistula every year.][ Prevention includes discouraging teenage pregnancy and child marriage, adequate nutrition, and access to skilled care, including caesarean section.
]
Sexual health
Contraception
 The ability to determine if and when to become pregnant, is vital to a woman's autonomy and well-being, and contraception can protect girls and young women from the risks of early pregnancy and older women from the increased risks of unintended pregnancy. Adequate access to contraception can limit multiple pregnancies, reduce the need for potentially unsafe abortion and reduce maternal and infant mortality and morbidity. Some barrier forms of contraception such as
The ability to determine if and when to become pregnant, is vital to a woman's autonomy and well-being, and contraception can protect girls and young women from the risks of early pregnancy and older women from the increased risks of unintended pregnancy. Adequate access to contraception can limit multiple pregnancies, reduce the need for potentially unsafe abortion and reduce maternal and infant mortality and morbidity. Some barrier forms of contraception such as condoms
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of inte ...
, also reduce the risk of STIs and HIV infection. Access to contraception allows women to make informed choices about their reproductive and sexual health, increases empowerment, and enhances choices in education, careers and participation in public life. At the societal level, access to contraception is a key factor in controlling population growth, with resultant impact on the economy, the environment and regional development.[ Consequently, the United Nations considers access to contraception a ]human right
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
that is central to gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
and women's empowerment
Women's empowerment (or female empowerment) may be defined in several ways, including accepting women's viewpoints, making an effort to seek them and raising the status of women through education, awareness, literacy, and training.Kabeer, Naila ...
that saves lives and reduces poverty,[ and birth control has been considered amongst the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century.][
To optimise women's control over pregnancy, it is essential that culturally appropriate contraceptive advice and means are widely, easily, and affordably available to anyone that is sexually active, including adolescents. In many parts of the world access to contraception and family planning services is very difficult or non existent and even in developed counties cultural and religious traditions can create barriers to access. Reported usage of adequate contraception by women has risen only slightly between 1990 and 2014, with considerable regional variability. Although global usage is around 55%, it may be as low as 25% in Africa. Worldwide 222 million women have no or limited access to ]contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. Some caution is needed in interpreting available data, since contraceptive prevalence is often defined as "the percentage of women currently using any method of contraception among all women of reproductive age (''i.e.'', those aged 15 to 49 years, unless otherwise stated) who are married or in a union. The "in-union" group includes women living with their partner in the same household and who are not married according to the marriage laws or customs of a country." This definition is more suited to the more restrictive concept of family planning, but omits the contraceptive needs of all other women and girls who are or are likely to be sexually active, are at risk of pregnancy and are not married or "in-union".[
Three related targets of MDG5 were adolescent birth rate, contraceptive prevalence and unmet need for family planning (where prevalence+unmet need = total need), which were monitored by the Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs.][ Contraceptive use was part of Goal 5B (universal access to reproductive health), as Indicator 5.3.][ The evaluation of MDG5 in 2015 showed that amongst couples usage had increased worldwide from 55% to 64%. with one of the largest increases in Subsaharan Africa (13 to 28%). The corollary, unmet need, declined slightly worldwide (15 to 12%). In 2015 these targets became part of SDG5 (gender equality and empowerment) under Target 5.6: Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights, where Indicator 5.6.1 is the proportion of women aged 15–49 years who make their own informed decisions regarding sexual relations, contraceptive use and reproductive health care (p. 31).][
There remain significant barriers to accessing contraception for many women in both developing and developed regions. These include legislative, administrative, cultural, religious and economic barriers in addition to those dealing with access to and quality of health services. Much of the attention has been focussed on preventing adolescent pregnancy. The ]Overseas Development Institute
ODI (formerly the 'Overseas Development Institute') is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the ...
(ODI) has identified a number of key barriers, on both the supply
Supply may refer to:
*The amount of a resource that is available
**Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers
**Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission
*Supply, as in confidenc ...
and demand side, including internalising socio-cultural values, pressure from family members, and cognitive barriers (lack of knowledge), which need addressing.[ Even in developed regions many women, particularly those who are ]disadvantaged
The "disadvantaged" is a generic term for individuals or groups of people who:
* Face special problems such as physical or mental disability
* Lack money or economic supportKingdom of Nepal: Economic and Social Inclusion of the Disadvantaged Poo ...
, may face substantial difficulties in access that may be financial and geographic but may also face religious and political discrimination.[ Women have also mounted campaigns against potentially dangerous forms of contraception such as defective intrauterine devices (IUD)s, particularly the Dalkon Shield.
]
Abortion
 Abortion is the intentional termination of pregnancy, as compared to spontaneous termination ( miscarriage). Abortion is closely allied to contraception in terms of women's control and regulation of their reproduction, and is often subject to similar cultural, religious, legislative and economic constraints. Where access to contraception is limited, women turn to abortion. Consequently, abortion rates may be used to estimate unmet needs for contraception. However the available procedures have carried great risk for women throughout most of history, and still do in the developing world, or where legal restrictions force women to seek clandestine facilities. Access to safe legal abortion places undue burdens on lower socioeconomic groups and in jurisdictions that create significant barriers. These issues have frequently been the subject of political and feminist campaigns where differing viewpoints pit health against moral values.
Globally, there were 87 million unwanted pregnancies in 2005, of those 46 million resorted to abortion, of which 18 million were considered unsafe, resulting in 68,000 deaths. The majority of these deaths occurred in the developing world. The United Nations considers these avoidable with access to safe abortion and post-abortion care. While abortion rates have fallen in developed countries, but not in developing countries. Between 2010 and 2014 there were 35 abortions per 1000 women aged 15–44, a total of 56 million abortions per year. The United nations has prepared recommendations for health care workers to provide more accessible and safe abortion and post-abortion care. An inherent part of post-abortion care involves provision of adequate contraception.
Abortion is the intentional termination of pregnancy, as compared to spontaneous termination ( miscarriage). Abortion is closely allied to contraception in terms of women's control and regulation of their reproduction, and is often subject to similar cultural, religious, legislative and economic constraints. Where access to contraception is limited, women turn to abortion. Consequently, abortion rates may be used to estimate unmet needs for contraception. However the available procedures have carried great risk for women throughout most of history, and still do in the developing world, or where legal restrictions force women to seek clandestine facilities. Access to safe legal abortion places undue burdens on lower socioeconomic groups and in jurisdictions that create significant barriers. These issues have frequently been the subject of political and feminist campaigns where differing viewpoints pit health against moral values.
Globally, there were 87 million unwanted pregnancies in 2005, of those 46 million resorted to abortion, of which 18 million were considered unsafe, resulting in 68,000 deaths. The majority of these deaths occurred in the developing world. The United Nations considers these avoidable with access to safe abortion and post-abortion care. While abortion rates have fallen in developed countries, but not in developing countries. Between 2010 and 2014 there were 35 abortions per 1000 women aged 15–44, a total of 56 million abortions per year. The United nations has prepared recommendations for health care workers to provide more accessible and safe abortion and post-abortion care. An inherent part of post-abortion care involves provision of adequate contraception.
Sexually transmitted infections
Important sexual health issues for women include Sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and oral ...
(STIs) and female genital cutting (FGC). STIs are a global health priority because they have serious consequences for women and infants. Mother-to-child transmission
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses that use mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It can ...
of STIs can lead to stillbirths
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term ...
, neonatal death
Perinatal mortality (PNM) refers to the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. Variations in the precise definition of the perinatal mortality exist, specifically concerning the issue of inclusion ...
, low-birth-weight and prematurity, sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, neonatal conjunctivitis
Neonatal conjunctivitis is a form of conjunctivitis (inflammation of the outer eye) which affects newborn babies following birth. It is typically due to neonatal bacterial infection, although can also be non-infectious (e.g. chemical exposure). I ...
, and congenital deformities
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can r ...
. Syphilis in pregnancy results in over 300,000 fetal and neonatal deaths per year, and 215,000 infants with an increased risk of death from prematurity, low-birth-weight or congenital disease.[
Diseases such as ]chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several we ...
and gonorrhoea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with ur ...
are also important causes of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and subsequent infertility in women. Another important consequence of some STIs such as genital herpes
Genital herpes is an infection by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) of the genitals. Most people either have no or mild symptoms and thus do not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they typically include small blisters that break open ...
and syphilis increase the risk of acquiring HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
by three-fold, and can also influence its transmission progression.[ Worldwide, women and girls are at greater risk of ]HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
. STIs are in turn associated with unsafe sexual activity that is often unconsensual.[
]
Female genital mutilation
 Female genital mutilation (also referred to as female genital cutting) is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the
Female genital mutilation (also referred to as female genital cutting) is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval ...
, or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons". It has sometimes been referred to as female circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Top ...
, although this term is misleading because it implies it is analogous to the circumcision of the foreskin
In male human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce, is the double-layered fold of skin, mucosal and muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans and the urinary meatus. The foreskin is attached to the ...
from the male penis.[ Consequently, the term mutilation was adopted to emphasise the gravity of the act and its place as a violation of human rights. Subsequently, the term cutting was advanced to avoid offending cultural sensibility that would interfere with dialogue for change. To recognise these points of view some agencies use the composite female genital mutilation/cutting (FMG/C).][
It has affected more than 200 million women and girls who are alive today. The practice is concentrated in some 30 countries in Africa, the Middle East and Asia.][ FGC affects many religious faiths, nationalities, and socioeconomic classes and is highly controversial. The main arguments advanced to justify FGC are hygiene, fertility, the preservation of ]chastity
Chastity, also known as purity, is a virtue related to temperance. Someone who is ''chaste'' refrains either from sexual activity considered immoral or any sexual activity, according to their state of life. In some contexts, for example when ma ...
, an important rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
, marriageability and enhanced sexual pleasure of male partners. The amount of tissue removed varies considerably, leading the WHO and other bodies to classify FGC into four types. These range from the partial or total removal of the clitoris with or without the prepuce (clitoridectomy
Clitoridectomy or clitorectomy is the surgical removal, reduction, or partial removal of the clitoris. It is rarely used as a therapeutic medical procedure, such as when cancer has developed in or spread to the clitoris. It is often performed on i ...
) in Type I, to the additional removal of the labia minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', singular: ''labium minus'', 'smaller lip'), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips or nymphae are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening in the vulva, situated b ...
, with or without excision of the labia majora
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva.
The labia majo ...
(Type II) to narrowing of the vaginal orifice (introitus
An introitus is an entrance into a canal or hollow organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Elec ...
) with the creation of a covering seal by suturing the remaining labial tissue over the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra c ...
and introitus, with or without excision of the clitoris (infibulation
Infibulation is the ritual removal of the external female genitalia and the suturing of the vulva, a practice found mainly in northeastern Africa, particularly in Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan. The World Health Organization refer ...
). In this type a small opening is created to allow urine and menstrual blood to be discharged. Type 4 involves all other procedures, usually relatively minor alterations such as piercing
Body piercing, which is a form of body modification, is the practice of puncturing or cutting a part of the human body, creating an opening in which jewelry
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal ...
.[
While defended by those cultures in which it constitutes a tradition, FGC is opposed by many medical and cultural organizations on the grounds that it is unnecessary and harmful. Short-term health effects may include hemorrhage, infection, sepsis, and even result in death, while long term effects include dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea, ]vaginitis
Vaginitis, also known as vulvovaginitis, is inflammation of the vagina and vulva. Symptoms may include itching, burning, pain, discharge, and a bad smell. Certain types of vaginitis may result in complications during pregnancy.
The three main ...
and cystitis
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney ...
. In addition FGC leads to complications with pregnancy, labor and delivery. Reversal (defibulation) by skilled personnel may be required to open the scarred tissue. Amongst those opposing the practice are local grassroots groups, and national and international organisations including WHO, UNICEF,[ UNFPA][ and Amnesty International. Legislative efforts to ban FGC have rarely been successful and the preferred approach is education and empowerment and the provision of information about the adverse health effects as well the ]human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
aspects.
Progress has been made but girls 14 and younger represent 44 million of those who have been cut, and in some regions 50% of all girls aged 11 and younger have been cut.[ Ending FGC has been considered one of the necessary goals in achieving the targets of the Millennium Development Goals, while the United Nations has declared ending FGC a target of the Sustainable Development Goals, and for February 6 to known as the International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, concentrating on 17 African countries and the 5 million girls between the ages of 15 and 19 that would otherwise be cut by 2030.][
]
Infertility
In the United States, infertility affects 1.5 million couples.[ Many couples seek assisted reproductive technology (ART) for infertility.][ In the United States in 2010, 147,260 ]in vitro fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) f ...
(IVF) procedures were carried out, with 47,090 live births resulting. In 2013 these numbers had increased to 160,521 and 53,252. However, about a half of IVF pregnancies result in multiple-birth deliveries, which in turn are associated with an increase in both morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
and mortality of the mother and the infant. Causes for this include increased maternal blood pressure, premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 2 ...
and low birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an
infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal inten ...
. In addition, more women are waiting longer to conceive and seeking ART.
Child marriage

Child marriage
Child marriage is a marriage or similar union, formal or informal, between a child under a certain age – typically 18 years – and an adult or another child.
*
*
*
* The vast majority of child marriages are between a female child and a mal ...
(including union or cohabitation
Cohabitation is an arrangement where people who are not married, usually couples, live together. They are often involved in a romantic or sexually intimate relationship on a long-term or permanent basis. Such arrangements have become increas ...
)[ is defined as ]marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
under the age of eighteen and is an ancient custom. In 2010 it was estimated that 67 million women, then, in their twenties had been married before they turned eighteen, and that 150 million would be in the next decade, equivalent to 15 million per year. This number had increased to 70 million by 2012. In developing countries one third of girls are married under age, and 1:9 before 15. The practice is commonest in South Asia (48% of women), Africa (42%) and Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
and the Caribbean (29%). The highest prevalence is in Western and Sub-Saharan Africa. The percentage of girls married before the age of eighteen is as high as 75% in countries such as Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mal ...](_blank)
the ratio of girls to boys is 72:1, while in countries such as the United States the ratio is 8:1. Marriage may occur as early as birth, with the girl being sent to her husbands home as early as age seven.
There are a number of cultural factors that reinforce this practice. These include the child's financial future, her dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
, social ties and social status, prevention of premarital sex
Premarital sex is sexual activity which is practiced by people before they are married. Premarital sex is considered a sin by a number of religions and also considered a moral issue which is taboo in many cultures. Since the Sexual Revolutio ...
, extramarital pregnancy and STIs. The arguments against it include interruption of education and loss of employment prospects, and hence economic status, as well as loss of normal childhood and its emotional maturation and social isolation. Child marriage places the girl in a relationship where she is in a major imbalance of power and perpetuates the gender inequality that contributed to the practice in the first place.[ Also in the case of minors, there are the issues of human rights, non-consensual sexual activity and ]forced marriage
Forced marriage is a marriage in which one or more of the parties is married without their consent or against their will. A marriage can also become a forced marriage even if both parties enter with full consent if one or both are later force ...
and a 2016 joint report of the WHO and Inter-Parliamentary Union places the two concepts together as Child, Early and Forced Marriage (CEFM), as did the 2014 Girl Summit (see below). In addition the likely pregnancies at a young age are associated with higher medical risks for both mother and child, multiple pregnancies and less access to care[ with pregnancy being amongst the leading causes of death amongst girls aged 15–19. Girls married under age are also more likely to be the victims of domestic violence.
There has been an international effort to reduce this practice, and in many countries eighteen is the legal age of marriage. Organizations with campaigns to end child marriage include the United Nations][ and its agencies, such as the ]Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nati ...
, UNFPA,[ UNICEF][ and WHO. Like many global issues affecting women's health, poverty and gender inequality are root causes, and any campaign to change cultural attitudes has to address these.][ Child marriage is the subject of international conventions and agreements such as The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW, 1979) (article 16)][ and the ]Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, ...
[ and in 2014 a ]summit conference
A summit meeting (or just summit) is an international meeting of heads of state or government, usually with considerable media exposure, tight security, and a prearranged agenda. Notable summit meetings include those of Franklin D. Roosevelt, Wi ...
( Girl Summit) co-hosted by UNICEF and the UK was held in London (see illustration) to address this issue together with FGM/C. Later that same year the General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presb ...
of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
passed a resolution, which '' inter alia''
Amongst non-governmental organizations (NGOs) working to end child marriage are Girls not Brides, Young Women's Christian Association
The Young Women's Christian Association (YWCA) is a nonprofit organization with a focus on empowerment, leadership, and rights of women, young women, and girls in more than 100 countries.
The World office is currently based in Geneva, Swi ...
(YWCA), the International Center for Research on Women (ICRW) and Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
(HRW). Although not explicitly included in the original Millennium Development Goals, considerable pressure was applied to include ending child marriage in the successor Sustainable Development Goals adopted in September 2015, where ending this practice by 2030 is a target of SDG 5 Gender Equality (see above).[ While some progress is being made in reducing child marriage, particularly for girls under fifteen, the prospects are daunting. The indicator for this will be the percentage of women aged 20–24 who were married or in a union before the age of eighteen. Efforts to end child marriage include legislation and ensuring enforcement together with empowering women and girls.][ To raise awareness, the inaugural UN ]International Day of the Girl Child
International Day of the Girl Child is an international observance day declared by the United Nations; it is also called the Day of Girls and the International Day of the Girl. October 11, 2012, was the first Day of the Girl Child. The observatio ...
in 2012 was dedicated to ending child marriage.[
]
Menstrual cycle
 Women's menstrual cycles, the approximately monthly cycle of changes in the reproductive system, can pose significant challenges for women in their reproductive years (the early teens to about 50 years of age). These include the physiological changes that can effect physical and mental health, symptoms of
Women's menstrual cycles, the approximately monthly cycle of changes in the reproductive system, can pose significant challenges for women in their reproductive years (the early teens to about 50 years of age). These include the physiological changes that can effect physical and mental health, symptoms of ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
and the regular shedding of the inner lining of the uterus ( endometrium) accompanied by vaginal bleeding (menses or menstruation). The onset of menstruation ( menarche) may be alarming to unprepared girls and mistaken for illness. Menstruation can place undue burdens on women in terms of their ability to participate in activities, and access to menstrual aids such as tampons
A tampon is a menstrual product designed to absorb blood and vaginal secretions by insertion into the vagina during menstruation. Unlike a pad, it is placed internally, inside of the vaginal canal. Once inserted correctly, a tampon is held ...
and sanitary pads. This is particularly acute amongst poorer socioeconomic groups where they may represent a financial burden and in developing countries where menstruation can be an impediment to a girl's education.[
Equally challenging for women are the physiological and emotional changes associated with the cessation of menses (]menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
or climacteric). While typically occurring gradually towards the end of the fifth decade in life marked by irregular bleeding the cessation of ovulation and menstruation is accompanied by marked changes in hormonal activity, both by the ovary itself (oestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
and progesterone) and the pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypoph ...
gland ( follicle stimulating hormone or FSH and luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) ...
or LH). These hormonal changes may be associated with both systemic sensations such as hot flashes
Hot flashes (also known as hot flushes) are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and ...
and local changes to the reproductive tract such as reduced vaginal secretions and lubrication. While menopause may bring relief from symptoms of menstruation and fear of pregnancy it may also be accompanied by emotional and psychological changes associated with the symbolism of the loss of fertility and a reminder of aging and possible loss of desirability
Desires are states of mind that are expressed by terms like "wanting", " wishing", "longing" or "craving". A great variety of features is commonly associated with desires. They are seen as propositional attitudes towards conceivable states of aff ...
. While menopause generally occurs naturally as a physiological process it may occur earlier (premature menopause
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) (also called premature ovarian insufficiency, premature menopause, and premature ovarian failure) is the partial or total loss of reproductive and hormonal function of the ovaries before age 40 because of fol ...
) as a result of disease or from medical or surgical intervention. When menopause occurs prematurely the adverse consequences may be more severe.[
]
Other issues
Other reproductive and sexual health issues include sex education
Sex education, also known as sexual education, sexuality education or sex ed, is the instruction of issues relating to human sexuality, including emotional relations and responsibilities, human sexual anatomy, sexual activity, sexual reproduc ...
, puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a bo ...
, sexuality and sexual function Sexual function is how the body reacts in different stages of the sexual response cycle, or as a result of sexual dysfunction. Relevant aspects of sexual function are defined on the basis of a modified version of Masters and Johnson's work. The aspe ...
. Women also experience a number of issues related to the health of their breasts and genital tract, which fall into the scope of gynaecology.
Non-reproductive health
Women and men have different experiences of the same illnesses, especially cardiovascular disease, cancer, depression and dementia, and are more prone to urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidne ...
than men.[
]
Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death (30%) amongst women in the United States, and the leading cause of chronic disease amongst them, affecting nearly 40% (Gronowski and Schindler, Tables I and IV). The onset occurs at a later age in women than in men. For instance the incidence of stroke in women under the age of 80 is less than that in men, but higher in those aged over 80. Overall the lifetime risk of stroke in women exceeds that in men.[ The risk of cardiovascular disease amongst those with diabetes and amongst smokers is also higher in women than in men. Many aspects of cardiovascular disease vary between women and men, including risk factors, prevalence, physiology, symptoms, response to intervention and outcome.
]
Cancer
Women and men have approximately equal risk of dying from cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, which accounts for about a quarter of all deaths, and is the second leading cause of death. However the relative incidence of different cancers varies between women and men. In the United States the three commonest types of cancer of women in 2012 were lung, breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
and colorectal
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being ...
cancers. In addition other important cancers in women, in order of importance, are ovarian
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body ...
, uterine
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
(including endometrial
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer ...
and cervical
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings:
# of or pertaining to any neck.
# of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus.
*Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are
**cervical collar
**cerv ...
cancers (Gronowski and Schindler, Table III). Similar figures were reported in 2016. While cancer death rates rose rapidly during the twentieth century, the increase was less and later in women due to differences in smoking rates. More recently cancer death rates have started to decline as the use of tobacco becomes less common. Between 1991 and 2012, the death rate in women declined by 19% (less than in men). In the early twentieth century death from uterine ( uterine body and cervix) cancers was the leading cause of cancer death in women, who had a higher cancer mortality than men. From the 1930s onwards, uterine cancer deaths declined, primarily due to lower death rates from cervical cancer following the availability of the Papanicolaou (Pap) screening test. This resulted in an overall reduction of cancer deaths in women between the 1940s and 1970s, when rising rates of lung cancer led to an overall increase. By the 1950s the decline in uterine cancer left breast cancer as the leading cause of cancer death until it was overtaken by lung cancer in the 1980s. All three cancers (lung, breast, uterus) are now declining in cancer death rates (Siegel ''et al.'' Figure 8), but more women die from lung cancer every year than from breast, ovarian, and uterine cancers combined. Overall about 20% of people found to have lung cancer are never smokers, yet amongst nonsmoking women the risk of developing lung cancer is three times greater than amongst men who never smoked.
In addition to mortality, cancer is a cause of considerable morbidity in women. Women have a lower lifetime probability of being diagnosed with cancer (38% vs 45% for men), but are more likely to be diagnosed with cancer at an earlier age.
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in the world and the most common among women. It is also among the ten most common chronic diseases
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three mon ...
of women, and a substantial contributor to loss of quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
(Gronowski and Schindler, Table IV). Globally, it accounts for 25% of all cancers. In 2016, breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed among women in both developed and developing countries, accounting for nearly 30% of all cases, and worldwide accounts for one and a half million cases and over half a million deaths, being the fifth most common cause of cancer death overall and the second in developed regions. Geographic variation in incidence is the opposite of that of cervical cancer, being highest in Northern America and lowest in Eastern and Middle Africa, but mortality rates are relatively constant, resulting in a wide variance in case mortality, ranging from 25% in developed regions to 37% in developing regions, and with 62% of deaths occurring in developing countries.[
]
Cervical cancer
Globally, cervical cancer is the fourth commonest cancer amongst women, particularly those of lower socioeconomic status. Women in this group have reduced access to health care, high rates of child and forced marriage, parity, polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is ...
and exposure to STIs from multiple sexual contacts of male partners. All of these factors place them at higher risk. In developing countries, cervical cancer accounts for 12% of cancer cases amongst women and is the second leading cause of death, where about 85% of the global burden of over 500,000 cases and 250,000 deaths from this disease occurred in 2012. The highest incidence occurs in Eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
, where with Middle Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Eq ...
, cervical cancer is the commonest cancer in women. The case fatality rate
In epidemiology, case fatality rate (CFR) – or sometimes more accurately case-fatality risk – is the proportion of people diagnosed with a certain disease, who end up dying of it. Unlike a disease's mortality rate, the CFR does not take int ...
of 52% is also higher in developing countries than in developed countries (43%), and the mortality rate varies by 18-fold between regions of the world.[
Cervical cancer is associated with ]human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and res ...
(HPV), which has also been implicated in cancers of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulv ...
, vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
, anus, and oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
. Almost 300 million women worldwide have been infected with HPV, one of the commoner sexually transmitted infections, and 5% of the 13 million new cases of cancer in the world have been attributed to HPV.[ In developed countries, screening for cervical cancer using the Pap test has identified pre-cancerous changes in the cervix, at least in those women with access to health care. Also an HPV vaccine programme is available in 45 countries. Screening and prevention programmes have limited availability in developing countries although inexpensive low technology programmes are being developed, but access to treatment is also limited. If applied globally, HPV vaccination at 70% coverage could save the lives of 4 million women from cervical cancer, since most cases occur in developing countries.
]
Ovarian cancer
By contrast, ovarian cancer, the leading cause of reproductive organ cancer deaths, and the fifth commonest cause of cancer deaths in women in the United States, lacks an effective screening programme, and is predominantly a disease of women in industrialised countries. Because it is largely asymptomatic in its earliest stages, more than 50% of women have stage III or higher cancer (spread beyond the ovaries) by the time they are diagnosed, with a consequent poor prognosis.
Mental health
Almost 25% of women will experience mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental hea ...
issues over their lifetime. Women are at higher risk than men from anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, depression, and psychosomatic complaints. Globally, depression is the leading disease burden. In the United States, women have depression twice as often as men. The economic costs of depression in American women are estimated to be $20 billion every year. The risks of depression in women have been linked to changing hormonal environment that women experience, including puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, childbirth and the menopause. Women also metabolise drugs used to treat depression differently to men. Suicide rates are less in women than men (<1% vs. 2.4%),[ but are a leading cause of death for women under the age of 60. In the United Kingdom, the Women's Mental Health Taskforce was formed aiming to address differences in mental health experiences and needs between women and men.]
Dementia
The prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in the United States is estimated at 5.1 million, and of these two thirds are women. Furthermore, women are far more likely to be the primary caregivers of adult family members with depression, so that they bear both the risks and burdens of this disease. The lifetime risk for a woman of developing Alzheimer's disease is twice that of men. Part of this difference may be due to life expectancy, but changing hormonal status over their lifetime may also play a par as may differences in gene expression. Deaths due to dementia are higher in women than men (4.5% of deaths vs. 2.0%).
Bone health
Osteoporosis ranks sixth amongst chronic diseases of women in the United States, with an overall prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of 18%, and a much higher rate involving the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
, neck or lumbar spine
The lumbar vertebrae are, in human anatomy, the five vertebrae between the rib cage and the pelvis. They are the largest segments of the vertebral column and are characterized by the absence of the foramen transversarium within the transverse p ...
amongst women (16%) than men (4%), over the age of 50 (Gronowski and Schindler, Table IV). Osteoporosis is a risk factor for bone fracture and about 20% of senior citizens who sustain a hip fracture
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.
They most often occur as a res ...
die within a year. The gender gap is largely the result of the reduction of estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
levels in women following the menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
. Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vaginal ...
(HRT) has been shown to reduce this risk by 25–30%, and was a common reason for prescribing it during the 1980s and 1990s. However the Women's Health Initiative
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three ...
(WHI) study that demonstrated that the risks of HRT outweighed the benefits has since led to a decline in HRT usage.
Anaemia
Anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
is a major global health problem for women. Women are affected more than men, in which up to 30% of women being found to be anaemic and 42% of pregnant women. Anaemia is linked to a number of adverse health outcomes including a poor pregnancy outcome and impaired cognitive function
Cognitive skills, also called cognitive functions, cognitive abilities or cognitive capacities, are brain-based skills which are needed in acquisition of knowledge, manipulation of information and reasoning. They have more to do with the mechanisms ...
(decreased concentration and attention). The main cause of anaemia is iron deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key ...
. In United States women iron deficiency anaemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, shor ...
(IDA) affects 37% of pregnant women, but globally the prevalence is as high as 80%. IDA starts in adolescence, from excess menstrual
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs a ...
blood loss, compounded by the increased demand for iron in growth and suboptimal dietary intake. In the adult woman, pregnancy leads to further iron depletion.
Violence
Women experience structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such ...
and personal violence differently than men. The United Nations has defined violence against women as;
Violence against women may take many forms, including physical, sexual
Sex is the biological distinction of an organism between male and female.
Sex or SEX may also refer to:
Biology and behaviour
*Animal sexual behaviour
**Copulation (zoology)
**Human sexual activity
**Non-penetrative sex, or sexual outercourse
** ...
, emotional and psychological and may occur throughout the life-course. Structural violence may be embedded in legislation or policy, or be systematic misogyny
Misogyny () is hatred of, contempt for, or prejudice against women. It is a form of sexism that is used to keep women at a lower social status than men, thus maintaining the societal roles of patriarchy. Misogyny has been widely practice ...
by organisations against groups of women. Perpetrators of personal violence include state actors, strangers, acquaintances, relatives and intimate partners and manifests itself across a spectrum from discrimination, through harassment, sexual assault and rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault usually involving sexual intercourse or other forms of sexual penetration carried out against a person without their consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or ...
, and physical harm to murder (femicide
Femicide or feminicide is a hate crime which is broadly defined as "the intentional killing of women or girls because they are female," but definitions of it vary depending on cultural context. In 1976, the feminist author Diana E. H. Russ ...
). It may also include cultural practices such as female genital cutting.[
Non-fatal violence against women has severe implications for women's physical, mental and reproductive health, and is seen as not simply isolated events but rather a systematic pattern of behaviour that both violates their rights but also limits their role in society and requires a systematic approach.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 35% of women in the world have experienced physical or sexual violence over their lifetime and that the commonest situation is intimate partner violence. 30% of women in relationships report such experience, and 38% of murders of women are due to intimate partners. These figures may be as high as 70% in some regions.][ Risk factors include low educational achievement, a parental experience of violence, childhood abuse, gender inequality and cultural attitudes that allow violence to be considered more acceptable.][
Violence was declared a global health priority by the WHO at its assembly in 1996, drawing on both the United Nations ]Declaration on the elimination of violence against women
The Declaration on the Elimination of Violence Against Women (abbreviated as DEVAW) was adopted without a vote by the United Nations General Assembly in the 48/104 resolution of 20 December 1993. Contained within it is the recognition of "the ur ...
(1993) and the recommendations of both the International Conference on Population and Development
The United Nations coordinated an International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) in Cairo, Egypt, on 5–13 September 1994. Its resulting Programme of Action is the steering document for the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) ...
(Cairo, 1994) and the Fourth World Conference on Women
The Fourth World Conference on Women: Action for Equality, Development and Peace was the name given for a conference convened by the United Nations during 4–15 September 1995 in Beijing, China.
At this conference, governments from around the ...
(Beijing, 1995) This was followed by its 2002 World Report on Violence and Health, which focusses on intimate partner and sexual violence. Meanwhile, the UN embedded these in an action plan when its General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presb ...
passed the Millennium Declaration
On 8 September 2000, following a three-day Millennium Summit of world leaders gathered in New York at the headquarters of the United Nations, the UN General Assembly
adopted some 60 goals regarding peace; development; environment; human rights; t ...
in September 2000, which resolved '' inter alia'' "to combat all forms of violence against women and to implement the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women". One of the Millennium Goals (MDG 3) was the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of women, which sought to eliminate all forms of violence against women as well as implementing CEDAW.[ This recognised that eliminating violence, including discrimination was a prerequisite to achieving all other goals of improving women's health. However it was later criticised for not including violence as an explicit target, the "missing target".][ In the evaluation of MDG 3, violence remained a major barrier to achieving the goals. In the successor Sustainable Development Goals, which also explicitly list the related issues of discrimination, child marriage and genital cutting, one target is listed as "Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls in the public and private spheres" by 2030.][
]UN Women
The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women, also known as UN Women, is a United Nations entity working for gender equality and the empowerment of women. UN Women advocates for the rights of women and girls, and foc ...
believe that violence against women "is rooted in gender-based discrimination and social norms and gender stereotypes that perpetuate such violence", and advocate moving from supporting victims to prevention, through addressing root and structural causes. They recommend programmes that start early in life and are directed towards both genders to promote respect and equality, an area often overlooked in public policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to solve or address relevant and real-world problems, guided by a conception and often implemented by programs. Public p ...
. This strategy, which involves broad educational and cultural change, also involves implementing the recommendations of the 57th session of the UN Commission on the Status of Women
The Commission on the Status of Women (CSW or UNCSW) is a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), one of the main UN organs within the United Nations. CSW has been described as the UN organ promoting gend ...
(2013).[ To that end the 2014 UN International Day of the Girl Child was dedicated to ending the cycle of violence.][ In 2016, the World Health Assembly also adopted a plan of action to combat violence against women, globally.][
]
Women in health research
 Changes in the way
Changes in the way research ethics
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
was visualised in the wake of the Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg trials were held by the Allies against representatives of the defeated Nazi Germany, for plotting and carrying out invasions of other countries, and other crimes, in World War II.
Between 1939 and 1945, Nazi Germany invaded m ...
(1946), led to an atmosphere of protectionism of groups deemed to be vulnerable that was often legislated or regulated. This resulted in the relative underrepresentation of women in clinical trials. The position of women in research was further compromised in 1977, when in response to the tragedies resulting from thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is a medication used to treat a number of cancers (including multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and a number of skin conditions including complications o ...
and diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a ...
(DES), the United States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) prohibited women of child-bearing years from participation in early stage clinical trials. In practice this ban was often applied very widely to exclude all women. Women, at least those in the child-bearing years, were also deemed unsuitable research subjects due to their fluctuating hormonal levels during the menstrual cycle. However, research has demonstrated significant biological differences between the sexes in rates of susceptibility, symptoms and response to treatment in many major areas of health, including heart disease and some cancers. These exclusions pose a threat to the application of evidence-based medicine to women, and compromise to care offered to both women and men.
The increasing focus on Women's Rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
in the United States during the 1980s focused attention on the fact that many drugs being prescribed for women had never actually been tested in women of child-bearing potential, and that there was a relative paucity of basic research into women's health. In response to this the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
(NIH) created the Office of Research on Women's Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. It comprises 27 sep ...
(ORWH) in 1990 to address these inequities. In 1993 the National Institutes of Health Revitalisation Act officially reversed US policy by requiring NIH funded phase III clinical trials
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases ...
to include women. This resulted in an increase in women recruited into research studies. The next phase was the specific funding of large scale epidemiology studies and clinical trials focussing on women's health such as the Women's Health Initiative
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three ...
(1991), the largest disease prevention study conducted in the US. Its role was to study the major causes of death, disability and frailty in older women. Despite this apparent progress, women remain underrepresented. In 2006 women accounted for less than 25% of clinical trials published in 2004, A follow up study by the same authors five years later found little evidence of improvement. Another study found between 10 and 47% of women in heart disease clinical trials, despite the prevalence of heart disease in women. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death amongst women, but while the number of women enrolled in lung cancer studies is increasing, they are still far less likely to be enrolled than men.
One of the challenges in assessing progress in this area is the number of clinical studies that either do not report the gender of the subjects or lack the statistical power to detect gender differences. These were still issues in 2014, and further compounded by the fact that the majority of animal studies also exclude females or fail to account for differences in sex and gender. for instance despite the higher incidence of depression amongst women, less than half of the animal studies use female animals. Consequently, a number of funding agencies and scientific journals are asking researchers to explicitly address issues of sex and gender in their research.
A related issue is the inclusion of pregnant women in clinical studies. Since other illnesses can exist concurrently with pregnancy, information is needed on the response to and efficacy of interventions during pregnancy, but ethical issues relative to the fetus, make this more complex. This gender bias is partly offset by the initiation of large scale epidemiology studies of women, such as the Nurses' Health Study
The Nurses Health Study is a series of prospective studies that examine epidemiology and the long-term effects of nutrition, hormones, environment, and nurses' work-life on health and disease development. The studies have been among the largest in ...
(1976), Women's Health Initiative
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) was a series of clinical studies initiated by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 1991, to address major health issues causing morbidity and mortality in postmenopausal women. It consisted of three ...
and Black Women's Health Study
The Black Women's Health Study (BWHS) is a long-term observational study conducted at Boston University's Slone Epidemiology Center since 1995 to investigate the health problems of Black women over a long time period, with the ultimate goal of imp ...
.
Women have also been the subject of abuse in health care research, such as the situation revealed in the Cartwright Inquiry
The Cartwright Inquiry was a committee of inquiry held in New Zealand from 1987 to 1988 that was commissioned by the Minister of Health, Michael Bassett, to investigate whether, as alleged in an article in ''Metro'' magazine, there had been a f ...
in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
(1988), in which research by two feminist journalists revealed that women with cervical
In anatomy, cervical is an adjective that has two meanings:
# of or pertaining to any neck.
# of or pertaining to the female cervix: i.e., the ''neck'' of the uterus.
*Commonly used medical phrases involving the neck are
**cervical collar
**cerv ...
abnormalities were not receiving treatment, as part of an experiment. The women were not told of the abnormalities and several later died.
National and international initiatives
 In addition to addressing gender inequity in research, a number of countries have made women's health the subject of national initiatives. For instance in 1991 in the United States, the
In addition to addressing gender inequity in research, a number of countries have made women's health the subject of national initiatives. For instance in 1991 in the United States, the Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
established an Office on Women's Health (OWH) with the goal of improving the health of women in America, through coordinating the women's health agenda throughout the department, and other agencies. In the twenty first century the Office has focussed on underserviced women.[ Also, in 1994 the ]Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
(CDC) established its own Office of Women's Health (OWH), which was formally authorised by the 2010 Affordable Health Care Act (ACA).[
Internationally, many ]United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
agencies such as the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO), United Nations Population Fund
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, is a UN agency aimed at improving reproductive and maternal health worldwide. Its work includes developing national healthcare strategies a ...
(UNFPA) and UNICEF
UNICEF (), originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to ...
maintain specific programs on women's health, or maternal, sexual and reproductive health.[ In addition the United Nations global goals address many issues related to women's health, both directly and indirectly. These include the 2000 ]Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenn ...
(MDG) and their successor, the Sustainable Development Goals adopted in September 2015, following the report on progress towards the MDGs (''The Millennium Development Goals Report 2015'').[ For instance the eight MDG goals, eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, achieving universal primary education, promoting gender equality and empowering women, reducing child mortality rates, improving maternal health, combating HIV/AIDS malaria and other diseases, ensuring environmental sustainability, and developing a global partnership for development, all impact on women's health, as do all seventeen SDG goals, in addition to the specific SDG5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.][
]
Goals and challenges
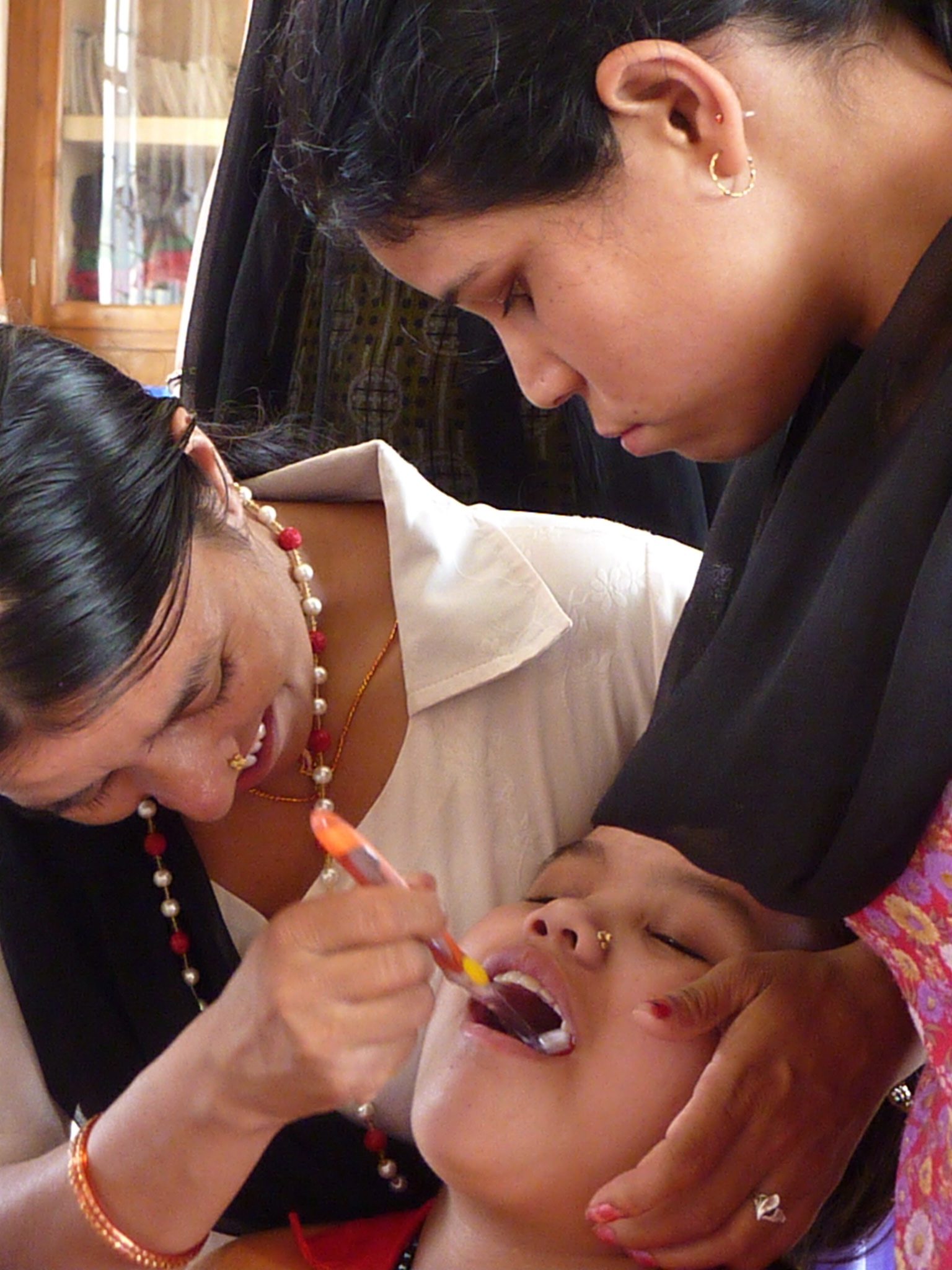 Research is a priority in terms of improving women's health. Research needs include diseases unique to women, more serious in women and those that differ in risk factors between women and men. The balance of gender in research studies needs to be balanced appropriately to allow analysis that will detect interactions between gender and other factors. Gronowski and Schindler suggest that
Research is a priority in terms of improving women's health. Research needs include diseases unique to women, more serious in women and those that differ in risk factors between women and men. The balance of gender in research studies needs to be balanced appropriately to allow analysis that will detect interactions between gender and other factors. Gronowski and Schindler suggest that scientific journals
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research.
Content
Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as s ...
make documentation of gender a requirement when reporting the results of animal studies, and that funding agencies require justification from investigators for any gender inequity in their grant proposals, giving preference to those that are inclusive. They also suggest it is the role of health organisations to encourage women to enroll in clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of healthcare science that determines the safety and effectiveness ( efficacy) of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. These may be used for prevention, treatm ...
. However, there has been progress in terms of large scale studies such as the WHI, and in 2006 the Society for Women's Health Research founded the Organization for the Study of Sex Differences and the journal ''Biology of Sex Differences'' to further the study of sex differences.
Research findings can take some time before becoming routinely implemented into clinical practice
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
. Clinical medicine needs to incorporate the information already available from research studies as to the different ways in which diseases affect women and men. Many "normal" laboratory values have not been properly established for the female population separately, and similarly the "normal" criteria for growth and development. Drug dosing needs to take gender differences in drug metabolism into account.
 Globally, women's access to health care remains a challenge, both in developing and developed countries. In the United States, before the Affordable Health Care Act came into effect, 25% of women of child-bearing age lacked health insurance. In the absence of adequate insurance, women are likely to avoid important steps to self care such as routine physical examination, screening and prevention testing, and prenatal care. The situation is aggravated by the fact that women living below the
Globally, women's access to health care remains a challenge, both in developing and developed countries. In the United States, before the Affordable Health Care Act came into effect, 25% of women of child-bearing age lacked health insurance. In the absence of adequate insurance, women are likely to avoid important steps to self care such as routine physical examination, screening and prevention testing, and prenatal care. The situation is aggravated by the fact that women living below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for t ...
are at greater risk of unplanned pregnancy
Unintended pregnancies are pregnancies that are mistimed, unplanned or unwanted at the time of conception.
Sexual activity without the use of effective contraception through choice or coercion is the predominant cause of unintended pregnancy. W ...
, unplanned delivery and elective abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
. Added to the financial burden in this group are poor educational achievement, lack of transportation, inflexible work schedules and difficulty obtaining child care, all of which function to create barriers to accessing health care. These problems are much worse in developing countries. Under 50% of childbirths in these countries are assisted by healthcare providers (''e.g.'' midwives
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialization known as midwifery.
The education and training for a midwife concentrates extensively on the care of women throughout their lifespan; co ...
, nurses, doctors) which accounts for higher rates of maternal death, up to 1:1,000 live births. This is despite the WHO setting standards, such as a minimum of four antenatal visits.[ A lack of healthcare providers, facilities, and resources such as formularies all contribute to high levels of morbidity amongst women from avoidable conditions such as obstetrical fistulae, sexually transmitted diseases and cervical cancer.
These challenges are included in the goals of the Office of Research on Women's Health, in the United States, as is the goal of facilitating women's access to careers in ]biomedicine
Biomedicine (also referred to as Western medicine, mainstream medicine or conventional medicine) . The ORWH believes that one of the best ways to advance research in women's health is to increase the proportion of women involved in healthcare and health research, as well as assuming leadership in government, centres of higher learning, and in the private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The ...
. This goal acknowledges the glass ceiling
A glass ceiling is a metaphor usually applied to women, used to represent an invisible barrier that prevents a given demographic from rising beyond a certain level in a hierarchy.Federal Glass Ceiling Commission''Solid Investments: Making Full ...
that women face in careers in science and in obtaining resources from grant funding
A grant is a fund given by an end entity grant – often a public body, charitable foundation, or a specialised grant-making institution – to an individual or another entity (usually, a non-profit organisation, sometimes a business or a loc ...
to salaries and laboratory space. The National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
in the United States states that women only gain half of the doctorates
A doctorate (from Latin ''docere'', "to teach"), doctor's degree (from Latin ''doctor'', "teacher"), or doctoral degree is an academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism ''l ...
awarded in science and engineering, fill only 21% of full-time professor positions in science and 5% of those in engineering, while earning only 82% of the remuneration their male colleagues make. These figures are even lower in Europe.
See also
* European Institute of Women's Health
The European Institute of Women's Health (EIWH) is a women's health and family health policy development institution. It was established in 1996, primarily to ensure women's health. All aspects of family health and well-being were on the Europea ...
* Gynaecology
* Gender discrimination
Sexism is prejudice or discrimination based on one's sex or gender. Sexism can affect anyone, but it primarily affects women and girls.There is a clear and broad consensus among academic scholars in multiple fields that sexism refers primaril ...
* Health equity
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequiti ...
* Men's health
''Men's Health'' (''MH''), published by Hearst, is the world's largest men's magazine brand, with 35 editions in 59 countries. It is also the best-selling men's magazine on U.S. newsstands.
Started as a men's health magazine by Rodale, Inc. ...
* Reproductive Health Supplies Coalition
The Reproductive Health Supplies Coalition (RHSC) is a global partnership of public, private and non-governmental organizations. Its aim is to ensure that all people in low- and middle-income countries can choose, obtain and use the supplies and a ...
* Social determinants of health
* Women and smoking
Tobacco smoking has serious negative effects on the body. A wide variety of diseases and medical phenomena affect the sexes differently, and the same holds true for the effects of tobacco. Since the proliferation of tobacco, many cultures have ...
* Women in medicine
The presence of women in medicine, particularly in the practicing fields of surgery and as physicians, has been traced to the earliest of history. Women have historically had lower participation levels in medical fields compared to men with occu ...
Women's health by country
* Women's health in China
* Women's health in Ethiopia
* Women's health in India
Publications
* ''Global Library of Women's Medicine
The ''Global Library of Women's Medicine'' is a free and publicly available resource of clinical information on women’s health launched on 20 November 2008. Its purpose is to provide expert support to obstetricians, gynecologists, and reproduct ...
''
* ''Health Care for Women International
''Health Care for Women International'' is a monthly peer-reviewed healthcare journal covering health care and related topics that concern women around the globe.
It is the official journal for Women's Health Issues and it is published by Taylor ...
''
* ''Journal of Women's Health
The ''Journal of Women's Health'' is a monthly peer-reviewed healthcare journal focusing on women's health care, including advancements in diagnostic procedures, therapeutic protocols for the management of diseases, and research in gender-based b ...
''
* ''Our Bodies, Ourselves
''Our Bodies, Ourselves'' is a book about women's health and sexuality produced by the nonprofit organization Our Bodies Ourselves (originally called the Boston Women's Health Book Collective). First published in 1970, it contains information rel ...
''
* '' Women & Health''
* '' Women's Health Issues''
Notes
References
Bibliography
Symposia and series
*
*
*
Articles
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* , in
*
*
*
*
*
* , in
*
*
*
* , in
*
* , in
* , in
*
* , in
*
*
*
*
*
* }
*
*
*
*
* , in
Reproductive and sexual health
* , in
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Maternal health
*
*
*
*
*
Books
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Chapters
* , in
* , in
* , in
* , in
Reports and documents
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
United Nations reports
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Websites
*
*
*
*
*
News
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Women's health research
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Organizations
* see American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
* see Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
*
* see Overseas Development Institute
ODI (formerly the 'Overseas Development Institute') is a global affairs think tank, founded in 1960. Its mission is "to inspire people to act on injustice and inequality through collaborative research and ideas that matter for people and the ...
* see Save the Children
The Save the Children Fund, commonly known as Save the Children, is an international non-governmental organization established in the United Kingdom in 1919 to improve the lives of children through better education, health care, and economic ...
*
= Women's health providers
=
*
*
*
= United Nations Web sites
=
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
WHO
*
** , in
**
**
**
**
**
**
= CDC
=
*
** , in
** , in
Further reading
*
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Women's Health
Feminism and health
Maternal health
 Women's health is positioned within a wider body of knowledge cited by, amongst others, the
Women's health is positioned within a wider body of knowledge cited by, amongst others, the  Of near miss events, obstetrical fistulae (OF), including vesicovaginal and
Of near miss events, obstetrical fistulae (OF), including vesicovaginal and  The ability to determine if and when to become pregnant, is vital to a woman's autonomy and well-being, and contraception can protect girls and young women from the risks of early pregnancy and older women from the increased risks of unintended pregnancy. Adequate access to contraception can limit multiple pregnancies, reduce the need for potentially unsafe abortion and reduce maternal and infant mortality and morbidity. Some barrier forms of contraception such as
The ability to determine if and when to become pregnant, is vital to a woman's autonomy and well-being, and contraception can protect girls and young women from the risks of early pregnancy and older women from the increased risks of unintended pregnancy. Adequate access to contraception can limit multiple pregnancies, reduce the need for potentially unsafe abortion and reduce maternal and infant mortality and morbidity. Some barrier forms of contraception such as  Abortion is the intentional termination of pregnancy, as compared to spontaneous termination ( miscarriage). Abortion is closely allied to contraception in terms of women's control and regulation of their reproduction, and is often subject to similar cultural, religious, legislative and economic constraints. Where access to contraception is limited, women turn to abortion. Consequently, abortion rates may be used to estimate unmet needs for contraception. However the available procedures have carried great risk for women throughout most of history, and still do in the developing world, or where legal restrictions force women to seek clandestine facilities. Access to safe legal abortion places undue burdens on lower socioeconomic groups and in jurisdictions that create significant barriers. These issues have frequently been the subject of political and feminist campaigns where differing viewpoints pit health against moral values.
Globally, there were 87 million unwanted pregnancies in 2005, of those 46 million resorted to abortion, of which 18 million were considered unsafe, resulting in 68,000 deaths. The majority of these deaths occurred in the developing world. The United Nations considers these avoidable with access to safe abortion and post-abortion care. While abortion rates have fallen in developed countries, but not in developing countries. Between 2010 and 2014 there were 35 abortions per 1000 women aged 15–44, a total of 56 million abortions per year. The United nations has prepared recommendations for health care workers to provide more accessible and safe abortion and post-abortion care. An inherent part of post-abortion care involves provision of adequate contraception.
Abortion is the intentional termination of pregnancy, as compared to spontaneous termination ( miscarriage). Abortion is closely allied to contraception in terms of women's control and regulation of their reproduction, and is often subject to similar cultural, religious, legislative and economic constraints. Where access to contraception is limited, women turn to abortion. Consequently, abortion rates may be used to estimate unmet needs for contraception. However the available procedures have carried great risk for women throughout most of history, and still do in the developing world, or where legal restrictions force women to seek clandestine facilities. Access to safe legal abortion places undue burdens on lower socioeconomic groups and in jurisdictions that create significant barriers. These issues have frequently been the subject of political and feminist campaigns where differing viewpoints pit health against moral values.
Globally, there were 87 million unwanted pregnancies in 2005, of those 46 million resorted to abortion, of which 18 million were considered unsafe, resulting in 68,000 deaths. The majority of these deaths occurred in the developing world. The United Nations considers these avoidable with access to safe abortion and post-abortion care. While abortion rates have fallen in developed countries, but not in developing countries. Between 2010 and 2014 there were 35 abortions per 1000 women aged 15–44, a total of 56 million abortions per year. The United nations has prepared recommendations for health care workers to provide more accessible and safe abortion and post-abortion care. An inherent part of post-abortion care involves provision of adequate contraception.
 Female genital mutilation (also referred to as female genital cutting) is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the
Female genital mutilation (also referred to as female genital cutting) is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the 
 Changes in the way
Changes in the way  Research is a priority in terms of improving women's health. Research needs include diseases unique to women, more serious in women and those that differ in risk factors between women and men. The balance of gender in research studies needs to be balanced appropriately to allow analysis that will detect interactions between gender and other factors. Gronowski and Schindler suggest that
Research is a priority in terms of improving women's health. Research needs include diseases unique to women, more serious in women and those that differ in risk factors between women and men. The balance of gender in research studies needs to be balanced appropriately to allow analysis that will detect interactions between gender and other factors. Gronowski and Schindler suggest that  Globally, women's access to health care remains a challenge, both in developing and developed countries. In the United States, before the Affordable Health Care Act came into effect, 25% of women of child-bearing age lacked health insurance. In the absence of adequate insurance, women are likely to avoid important steps to self care such as routine physical examination, screening and prevention testing, and prenatal care. The situation is aggravated by the fact that women living below the
Globally, women's access to health care remains a challenge, both in developing and developed countries. In the United States, before the Affordable Health Care Act came into effect, 25% of women of child-bearing age lacked health insurance. In the absence of adequate insurance, women are likely to avoid important steps to self care such as routine physical examination, screening and prevention testing, and prenatal care. The situation is aggravated by the fact that women living below the