William Seward on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as
 After graduation, Seward spent much of the following two years studying law in Goshen and New York City with attorneys John Duer, John Anthon and
After graduation, Seward spent much of the following two years studying law in Goshen and New York City with attorneys John Duer, John Anthon and
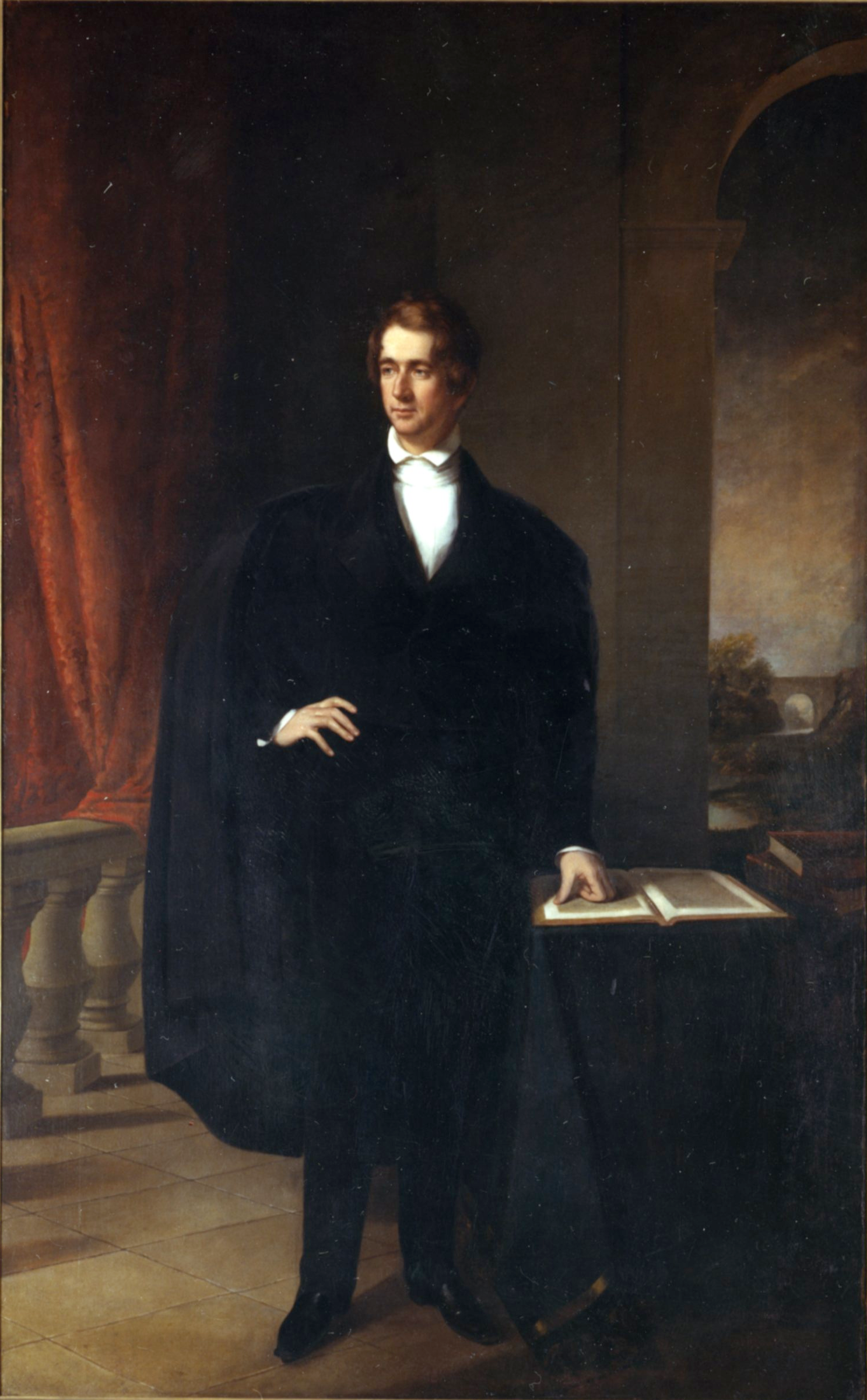 William Seward was sworn in as governor of New York on January 1, 1839, and inaugurated in front of a crowd of jubilant Whigs. In that era, the annual message by the New York governor was published and discussed to the extent of that of a president. Seward biographer Walter Stahr wrote that his address "brimmed with his youth, energy, ambition, and optimism." Seward took note of America's great unexploited resources and stated that immigration should be encouraged in order to take advantage of them. He urged that citizenship and religious liberty be granted to those who came to New York's shores. At the time, New York City's public schools were run by Protestants, and used Protestant texts, including the
William Seward was sworn in as governor of New York on January 1, 1839, and inaugurated in front of a crowd of jubilant Whigs. In that era, the annual message by the New York governor was published and discussed to the extent of that of a president. Seward biographer Walter Stahr wrote that his address "brimmed with his youth, energy, ambition, and optimism." Seward took note of America's great unexploited resources and stated that immigration should be encouraged in order to take advantage of them. He urged that citizenship and religious liberty be granted to those who came to New York's shores. At the time, New York City's public schools were run by Protestants, and used Protestant texts, including the
 As governor, Seward incurred considerable personal debt not only because he had to live beyond his salary to maintain the lifestyle expected of the office, but also because he could not pay down his obligation from the land company purchase. At the time he left office, he owed $200,000. Returning to Auburn, he absorbed himself in a profitable law practice. He did not abandon politics and received former president Adams at the Seward family home in 1843.
According to his biographer, John M. Taylor, Seward picked a good time to absent himself from electoral politics, as the Whig Party was in turmoil. President Tyler, a former Democrat, and Senator Clay each claimed leadership of the Whig Party and, as the two men differed over such issues as whether to re-establish the Bank of the United States, party support was divided. The
As governor, Seward incurred considerable personal debt not only because he had to live beyond his salary to maintain the lifestyle expected of the office, but also because he could not pay down his obligation from the land company purchase. At the time he left office, he owed $200,000. Returning to Auburn, he absorbed himself in a profitable law practice. He did not abandon politics and received former president Adams at the Seward family home in 1843.
According to his biographer, John M. Taylor, Seward picked a good time to absent himself from electoral politics, as the Whig Party was in turmoil. President Tyler, a former Democrat, and Senator Clay each claimed leadership of the Whig Party and, as the two men differed over such issues as whether to re-establish the Bank of the United States, party support was divided. The
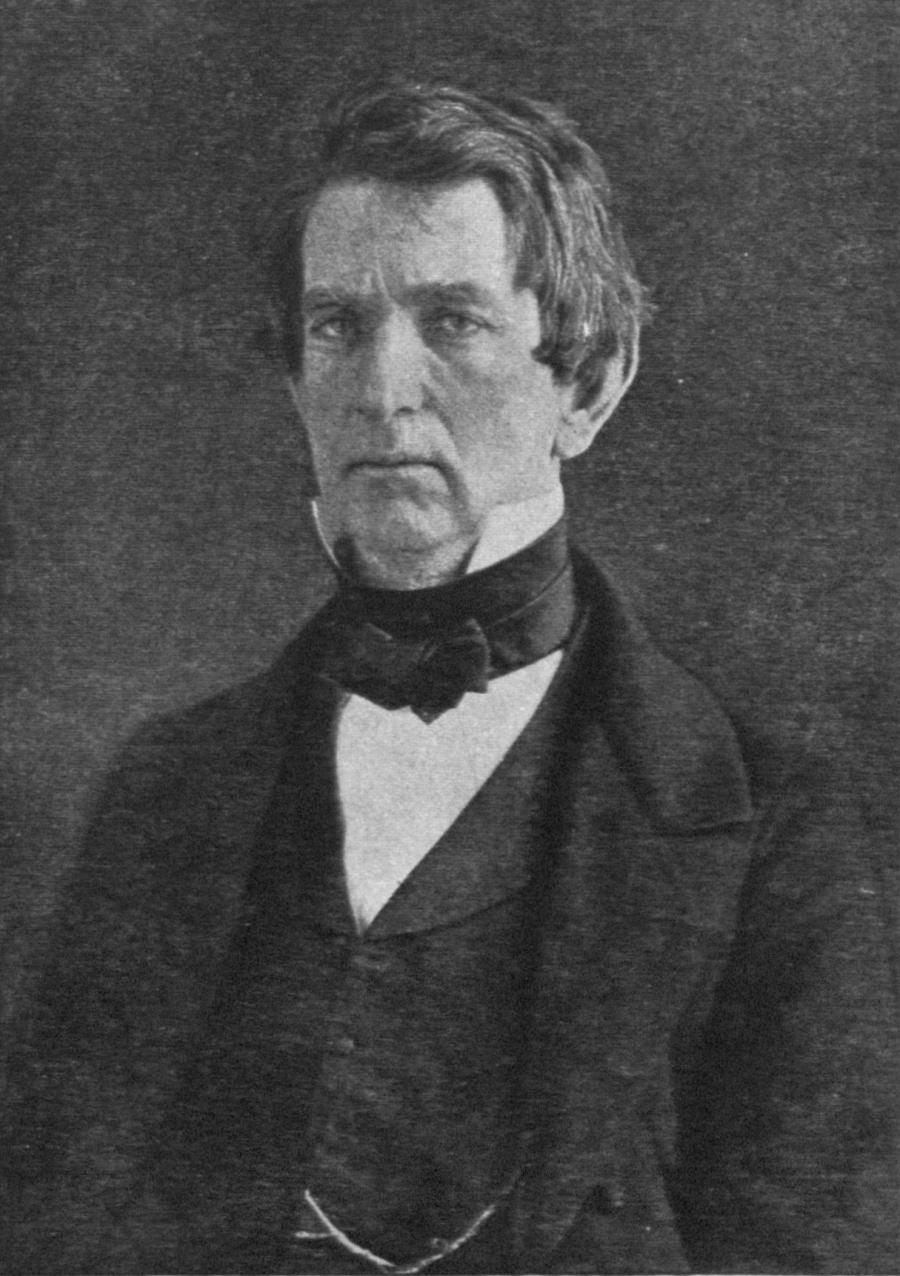 Although Clay had hoped the Compromise would be a final settlement on the matter of slavery that could unite the nation, it divided his Whig Party, especially when the 1852 Whig National Convention endorsed it to the anger of liberal northerners like Seward. The major candidates for the presidential nomination were President Fillmore, Senator Daniel Webster, and General Scott. Seward supported Scott, who he hoped would, like Harrison, unite enough voters behind a military hero to win the election. Scott gained the nomination, and Seward campaigned for him. The Whigs were unable to reconcile over slavery, whereas the Democrats could unite behind the Compromise; the Whigs won only four states, and former New Hampshire senator
Although Clay had hoped the Compromise would be a final settlement on the matter of slavery that could unite the nation, it divided his Whig Party, especially when the 1852 Whig National Convention endorsed it to the anger of liberal northerners like Seward. The major candidates for the presidential nomination were President Fillmore, Senator Daniel Webster, and General Scott. Seward supported Scott, who he hoped would, like Harrison, unite enough voters behind a military hero to win the election. Scott gained the nomination, and Seward campaigned for him. The Whigs were unable to reconcile over slavery, whereas the Democrats could unite behind the Compromise; the Whigs won only four states, and former New Hampshire senator
 The political turmoil engendered by the North–South divide split both major parties and led to the founding of new ones. The American Party (known as the Know Nothings) contained many nativists and pursued an anti-immigrant agenda. The Know Nothings did not publicly discuss party deliberations (thus, they knew nothing). They disliked Seward, and an uncertain number of Know Nothings sought the Whig nomination to legislative seats. Some made clear their stance by pledging to vote against Seward's re-election, but others did not. Although the Whigs won a majority in both houses of the state legislature, the extent of their support for Seward as a US senator was unclear. When
The political turmoil engendered by the North–South divide split both major parties and led to the founding of new ones. The American Party (known as the Know Nothings) contained many nativists and pursued an anti-immigrant agenda. The Know Nothings did not publicly discuss party deliberations (thus, they knew nothing). They disliked Seward, and an uncertain number of Know Nothings sought the Whig nomination to legislative seats. Some made clear their stance by pledging to vote against Seward's re-election, but others did not. Although the Whigs won a majority in both houses of the state legislature, the extent of their support for Seward as a US senator was unclear. When
 In 1859, Seward was advised by his political supporters that he would be better off avoiding additional controversial statements, and left the country for an eight-month tour of Europe and the Middle East. Seward spent two months in London, meeting with the Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, and was presented at Court to
In 1859, Seward was advised by his political supporters that he would be better off avoiding additional controversial statements, and left the country for an eight-month tour of Europe and the Middle East. Seward spent two months in London, meeting with the Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, and was presented at Court to
 Enemies such as publisher and former Seward ally
Enemies such as publisher and former Seward ally
 From the start of the war until early 1862, when responsibility was passed to the War Department, Seward was in charge of determining who should be detained without charges or trial. Approximately 800 men and a few women, believed to be Southern sympathizers or spies, were detained, usually at the initiation of local officials. Once Seward was informed, he would often order that the prisoner be transferred to federal authorities. Seward was reported to have boasted to Lord Lyons that "I can touch a bell on my right hand, and order the arrest of a citizen ... and no power on earth, except that of the President, can release them. Can the Queen of England do so much?"
In September 1861, Maryland legislators planned to vote to leave the Union. Seward took action against them: his son Frederick, the United States Assistant Secretary of State, reported to his father that the disloyal legislators were in prison. On the evidence provided by detective Allen Pinkerton, Seward in 1862 ordered the arrest of
From the start of the war until early 1862, when responsibility was passed to the War Department, Seward was in charge of determining who should be detained without charges or trial. Approximately 800 men and a few women, believed to be Southern sympathizers or spies, were detained, usually at the initiation of local officials. Once Seward was informed, he would often order that the prisoner be transferred to federal authorities. Seward was reported to have boasted to Lord Lyons that "I can touch a bell on my right hand, and order the arrest of a citizen ... and no power on earth, except that of the President, can release them. Can the Queen of England do so much?"
In September 1861, Maryland legislators planned to vote to leave the Union. Seward took action against them: his son Frederick, the United States Assistant Secretary of State, reported to his father that the disloyal legislators were in prison. On the evidence provided by detective Allen Pinkerton, Seward in 1862 ordered the arrest of
Image:Emancipation proclamation.jpg, left, Lincoln meeting with his Cabinet for the first reading of the
Other cabinet members became resentful of Seward, who seemed to be always present when they discussed their departments' concerns with Lincoln, yet they were never allowed to be there when the two men discussed foreign affairs. Seward announced when cabinet meetings would be; his colleagues eventually persuaded Lincoln to set a regular date and time for those sessions. Seward's position on the Emancipation Proclamation when Lincoln read it to his cabinet in July 1862 is uncertain; Secretary of War Edwin Stanton wrote at the time that Seward opposed it in principle, feeling the slaves should simply be freed as Union armies advanced. Two later accounts indicate that Seward felt that it was not yet time to issue it, and Lincoln did wait until after the bloody stalemate at Antietam that ended Confederate General
 In January 1865,
In January 1865,
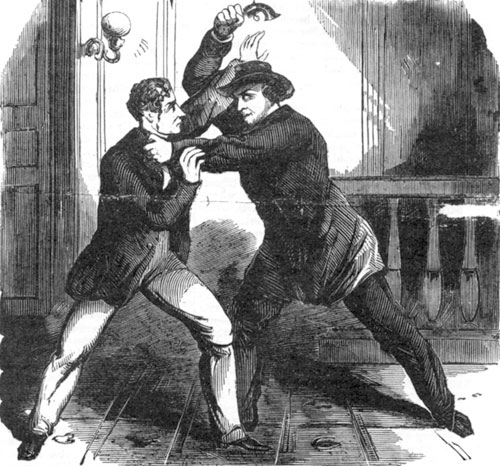 John Wilkes Booth had originally planned to kidnap Lincoln, and recruited conspirators, including Lewis Powell, to help him. Having found no opportunity to abduct the president, on April 14, 1865, Booth assigned Powell to assassinate Seward, with George Atzerodt to kill Vice President Johnson and himself to kill Lincoln, which would slay the three senior members of the Executive Branch. Accordingly, another member of the conspiracy, David Herold, led Powell to the Seward home on horseback and was responsible for holding Powell's horse while he committed the attack. Seward had been hurt in an accident some days before, and Powell gained entry to the home on the excuse he was delivering medicine to the injured man, but was stopped at the top of the stairs by Seward's son Frederick, who insisted Powell give him the medicine. Powell instead attempted to fire on Frederick and beat him over the head with the barrel of his gun when it misfired. Powell burst through the door, threw Fanny Seward (Seward's daughter) to one side, jumped on the bed, and stabbed William Seward in the face and neck five times. A soldier assigned to guard and nurse the secretary, Private George F. Robinson, jumped on Powell, forcing him from the bed. Private Robinson and Augustus Henry Seward, another of Seward's sons, were also injured in their struggle with the would-be assassin. Ultimately, Powell fled, stabbing a messenger, Emerick Hansell, as he went, only to find that Herold, panicked by the screams from the house, had left with both horses. Seward was at first thought dead, but revived enough to instruct Robinson to send for the police and lock the house until they arrived.
John Wilkes Booth had originally planned to kidnap Lincoln, and recruited conspirators, including Lewis Powell, to help him. Having found no opportunity to abduct the president, on April 14, 1865, Booth assigned Powell to assassinate Seward, with George Atzerodt to kill Vice President Johnson and himself to kill Lincoln, which would slay the three senior members of the Executive Branch. Accordingly, another member of the conspiracy, David Herold, led Powell to the Seward home on horseback and was responsible for holding Powell's horse while he committed the attack. Seward had been hurt in an accident some days before, and Powell gained entry to the home on the excuse he was delivering medicine to the injured man, but was stopped at the top of the stairs by Seward's son Frederick, who insisted Powell give him the medicine. Powell instead attempted to fire on Frederick and beat him over the head with the barrel of his gun when it misfired. Powell burst through the door, threw Fanny Seward (Seward's daughter) to one side, jumped on the bed, and stabbed William Seward in the face and neck five times. A soldier assigned to guard and nurse the secretary, Private George F. Robinson, jumped on Powell, forcing him from the bed. Private Robinson and Augustus Henry Seward, another of Seward's sons, were also injured in their struggle with the would-be assassin. Ultimately, Powell fled, stabbing a messenger, Emerick Hansell, as he went, only to find that Herold, panicked by the screams from the house, had left with both horses. Seward was at first thought dead, but revived enough to instruct Robinson to send for the police and lock the house until they arrived.
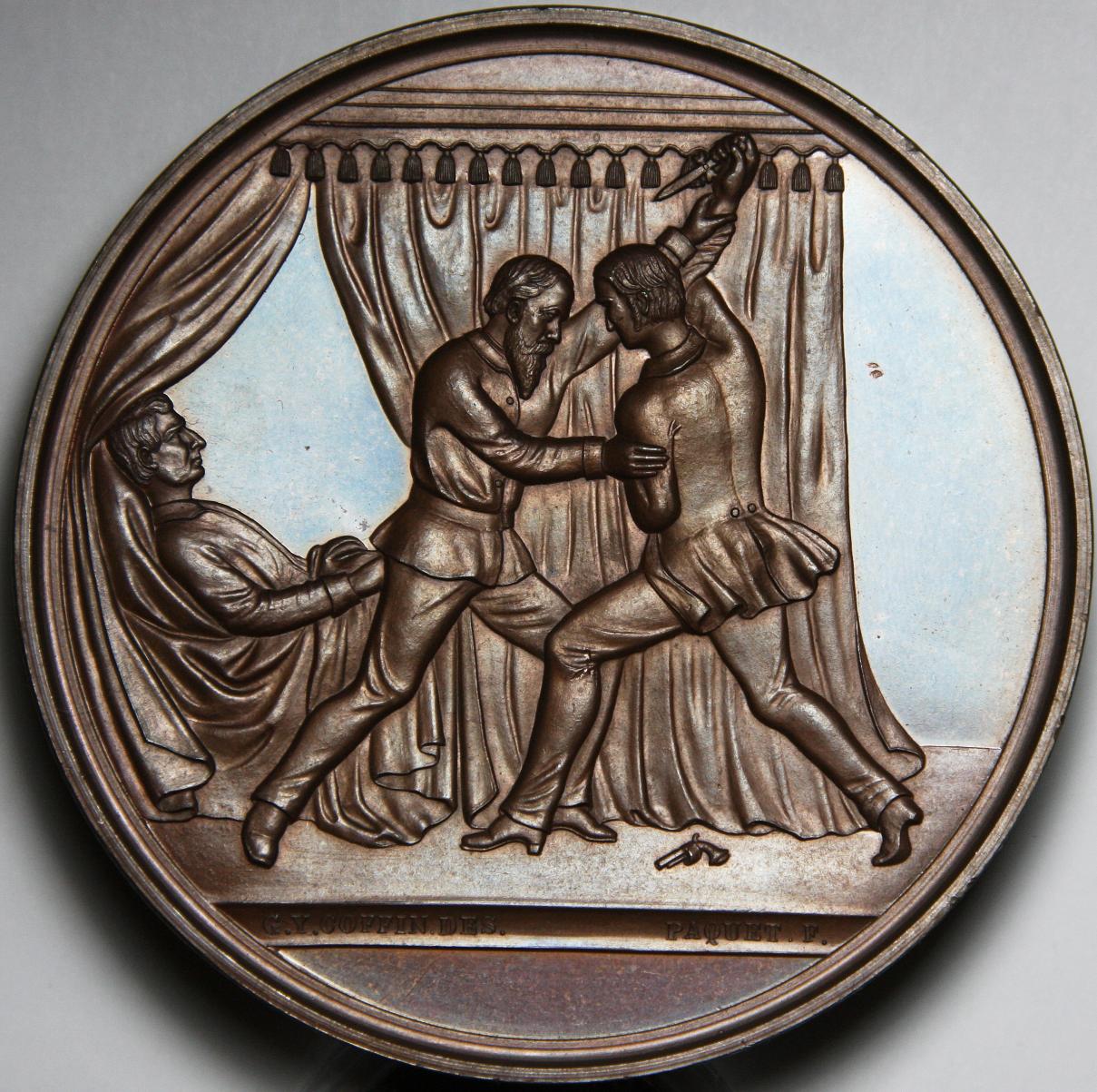 Almost simultaneously with the attack on Seward, Booth had mortally wounded Lincoln at Ford's Theatre. Atzerodt, however, decided not to go through with the attack on Johnson. When Secretary of War Edwin Stanton and Navy Secretary Gideon Welles hurried to Seward's home to find out what had happened, they found blood everywhere.
All five men injured that night at the Seward home survived. Powell was captured the next day at the boarding house of
Almost simultaneously with the attack on Seward, Booth had mortally wounded Lincoln at Ford's Theatre. Atzerodt, however, decided not to go through with the attack on Johnson. When Secretary of War Edwin Stanton and Navy Secretary Gideon Welles hurried to Seward's home to find out what had happened, they found blood everywhere.
All five men injured that night at the Seward home survived. Powell was captured the next day at the boarding house of
 In the first months of the new Johnson administration, Seward did not work much with the president. Seward was at first recovering from his injuries, and Johnson was ill for a time in the summer of 1865. Seward was likely in accord with Johnson's relatively gentle terms for the South's re-entry to the Union, and with his pardon of all Confederates but those of high rank.
In the first months of the new Johnson administration, Seward did not work much with the president. Seward was at first recovering from his injuries, and Johnson was ill for a time in the summer of 1865. Seward was likely in accord with Johnson's relatively gentle terms for the South's re-entry to the Union, and with his pardon of all Confederates but those of high rank.  Johnson hoped the public would elect congressmen who agreed with him in the 1866 midterm elections, and embarked on a trip, dubbed the
Johnson hoped the public would elect congressmen who agreed with him in the 1866 midterm elections, and embarked on a trip, dubbed the
 Although in speeches Seward had predicted all of North America joining the Union, he had, as a senator, opposed the
Although in speeches Seward had predicted all of North America joining the Union, he had, as a senator, opposed the 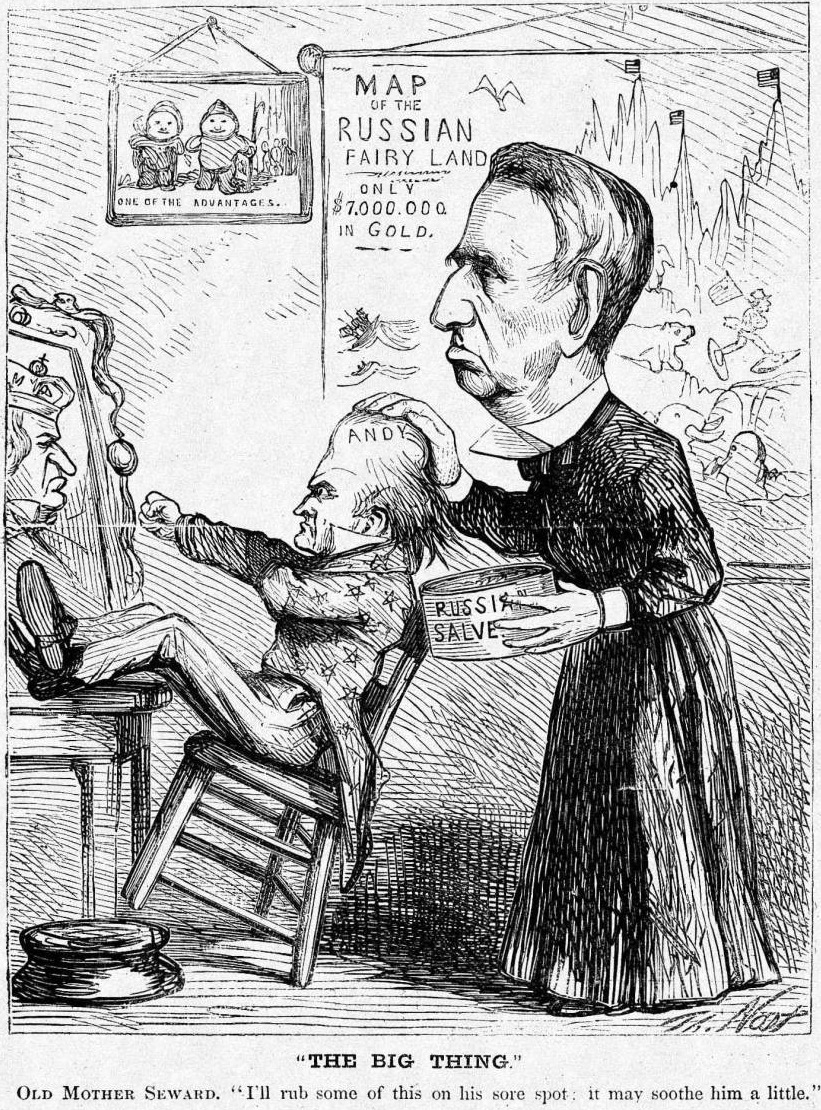 Seward had been interested in whaling as a senator; his interest in Russian America was a byproduct of this. In his speech prior to the 1860 convention, he predicted the territory would become part of the U.S., and when he learned in 1864 that it might be for sale, he pressed the Russians for negotiations. Russian minister Baron Eduard de Stoeckl recommended the sale. The territory was a money loser, and the Russian-American Company itself allowed its charter to expire in 1861. Russia could use the money more efficiently for its expansion in Siberia or Central Asia. Keeping it ran the risk of it being captured in war by the British, or overrun by American settlers. Stoeckl was given the authority to make the sale and when he returned in March 1867, negotiated with the Secretary of State. Seward initially offered $5 million; the two men settled on $7 million and on March 15, Seward presented a draft treaty to the Cabinet. Stoeckl's superiors raised several concerns; to induce him to waive them, the final purchase price was increased to $7.2 million. The treaty was signed in the early morning of March 30, 1867, and ratified by the Senate on April 10. Stevens sent the secretary a note of congratulations, predicting that the
Seward had been interested in whaling as a senator; his interest in Russian America was a byproduct of this. In his speech prior to the 1860 convention, he predicted the territory would become part of the U.S., and when he learned in 1864 that it might be for sale, he pressed the Russians for negotiations. Russian minister Baron Eduard de Stoeckl recommended the sale. The territory was a money loser, and the Russian-American Company itself allowed its charter to expire in 1861. Russia could use the money more efficiently for its expansion in Siberia or Central Asia. Keeping it ran the risk of it being captured in war by the British, or overrun by American settlers. Stoeckl was given the authority to make the sale and when he returned in March 1867, negotiated with the Secretary of State. Seward initially offered $5 million; the two men settled on $7 million and on March 15, Seward presented a draft treaty to the Cabinet. Stoeckl's superiors raised several concerns; to induce him to waive them, the final purchase price was increased to $7.2 million. The treaty was signed in the early morning of March 30, 1867, and ratified by the Senate on April 10. Stevens sent the secretary a note of congratulations, predicting that the
 Seward's reputation, controversial in life, remained so in death, dividing his contemporaries. Former Navy Secretary Gideon Welles argued that not only did Seward lack principles, Welles was unable to understand how Seward had fooled Lincoln into thinking that he did, gaining entry to the Cabinet thereby. Charles Francis Adams, minister in London during Seward's tenure as secretary, deemed him "more of a politician than a statesman", but
Seward's reputation, controversial in life, remained so in death, dividing his contemporaries. Former Navy Secretary Gideon Welles argued that not only did Seward lack principles, Welles was unable to understand how Seward had fooled Lincoln into thinking that he did, gaining entry to the Cabinet thereby. Charles Francis Adams, minister in London during Seward's tenure as secretary, deemed him "more of a politician than a statesman", but
Frances Seward
Wife Of Secretary Of State William Seward * Retrieved on 2009-04-30 * *
Joseph Gerald Whelan, William Seward as Expansionist (Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rochester, 1959)
* *
William H. Seward Letter, W. S. Hoole Special Collections Library, The University of Alabama
* ttp://www.americanabolitionists.com/abolitionists-and-anti-slavery-activists.html American Abolitionists and Antislavery Activists comprehensive website featuring abolitionist and anti-slavery activists in the United States, including political leaders; also provides list of antislavery organizations.
Seward Family Digital Archive
Letters and photographs by and about members of the Seward family. , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Seward, William H. 1801 births 1872 deaths 19th-century American Episcopalians 19th-century American politicians American militia generals Andrew Johnson administration cabinet members Anti-Masonic Party politicians from New York (state) Burials in New York (state) Candidates in the 1856 United States presidential election Candidates in the 1860 United States presidential election Christian abolitionists Governors of New York (state) History of the foreign relations of the United States Lincoln administration cabinet members New York (state) lawyers New York (state) Republicans New York (state) state senators New York (state) Whigs People associated with the assassination of Abraham Lincoln People from Florida, Orange County, New York People from Goshen, New York People of New York (state) in the American Civil War People of pre-statehood Alaska Politicians from Auburn, New York Politicians from Orange County, New York Radical Republicans Republican Party United States senators from New York (state) Seward family Stabbing attacks in the United States Stabbing survivors Underground Railroad people Union College (New York) alumni Union (American Civil War) political leaders United States Secretaries of State Whig Party state governors of the United States Whig Party United States senators
United States Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York
The governor of New York is the head of government of the U.S. state of New York. The governor is the head of the executive branch of New York's state government and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor h ...
and as a United States Senator
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and po ...
. A determined opponent of the spread of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in the years leading up to the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
, he was a prominent figure in the Republican Party in its formative years, and was praised for his work on behalf of the Union as Secretary of State during the Civil War. He also negotiated the treaty for the United States to purchase the Alaskan Territory.
Seward was born in 1801 in the village of Florida, in Orange County, New York, where his father was a farmer and owned slaves. He was educated as a lawyer and moved to the Central New York town of Auburn. Seward was elected to the New York State Senate
The New York State Senate is the upper house of the New York State Legislature; the New York State Assembly is its lower house. Its members are elected to two-year terms; there are no term limits. There are 63 seats in the Senate.
Partisan comp ...
in 1830 as an Anti-Mason. Four years later, he became the gubernatorial nominee of the Whig Party. Though he was not successful in that race, Seward was elected governor in 1838
Events
January–March
* January 10 – A fire destroys Lloyd's Coffee House and the Royal Exchange in London.
* January 11 – At Morristown, New Jersey, Samuel Morse, Alfred Vail and Leonard Gale give the first public demonstration o ...
and won a second two-year term in 1840. During this period, he signed several laws that advanced the rights of and opportunities for black residents, as well as guaranteeing jury trial
A jury trial, or trial by jury, is a legal proceeding in which a jury makes a decision or findings of fact. It is distinguished from a bench trial in which a judge or panel of judges makes all decisions.
Jury trials are used in a signific ...
s for fugitive slaves in the state. The legislation protected abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
, and he used his position to intervene in cases of freed black people who were enslaved in the South.
After many years of practicing law in Auburn, he was elected by the state legislature
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Sta ...
to the U.S. Senate in 1849. Seward's strong stances and provocative words against slavery brought him hatred in the South. He was re-elected to the Senate in 1855, and soon joined the nascent Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
* Republican Party (Liberia)
*Republican Party ...
, becoming one of its leading figures. As the 1860 presidential election approached, he was regarded as the leading candidate for the Republican nomination. Several factors, including attitudes to his vocal opposition to slavery, his support for immigrants and Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, and his association with editor and political boss Thurlow Weed
Edward Thurlow Weed (November 15, 1797 – November 22, 1882) was a printer, New York newspaper publisher, and Whig and Republican politician. He was the principal political advisor to prominent New York politician William H. Seward and was i ...
, worked against him, and Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
secured the presidential nomination. Although devastated by his loss, he campaigned for Lincoln, who appointed him Secretary of State after winning the election.
Seward did his best to stop the southern states from seceding; once that failed, he devoted himself wholeheartedly to the Union cause. His firm stance against foreign intervention in the Civil War helped deter the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
from recognizing the independence of the Confederate States. He was one of the targets of the 1865 assassination plot that killed Lincoln and was seriously wounded by conspirator Lewis Powell. Seward remained in his post through the presidency of Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a De ...
, during which he negotiated the Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
in 1867 and supported Johnson during his impeachment
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
. His contemporary Carl Schurz
Carl Schurz (; March 2, 1829 – May 14, 1906) was a German revolutionary and an American statesman, journalist, and reformer. He immigrated to the United States after the German revolutions of 1848–1849 and became a prominent member of the new ...
described Seward as "one of those spirits who sometimes will go ahead of public opinion instead of tamely following its footprints".
Early life
Seward was born on May 16, 1801, in the small community of Florida, New York, in Orange County. He was the fourth son of Samuel Sweezy Seward and his wife Mary (Jennings) Seward. Samuel Seward was a wealthy landowner and slaveholder inNew York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. sta ...
; slavery was not fully abolished in the state until 1827. Florida was located some north of New York City, west of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
, and was a small rural village of perhaps a dozen homes. Young Seward attended school there, and also in the nearby county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ...
of Goshen. He was a bright student who enjoyed his studies. In later years, one of the former family slaves would relate that instead of running away from school to go home, Seward would run away from home to go to school.
At the age of 15, Henry—he was known by his middle name as a boy—was sent to Union College
Union College is a private liberal arts college in Schenectady, New York. Founded in 1795, it was the first institution of higher learning chartered by the New York State Board of Regents, and second in the state of New York, after Columbia Co ...
in Schenectady, New York
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Yo ...
. Admitted to the sophomore
In the United States, a sophomore ( or ) is a person in the second year at an educational institution; usually at a secondary school or at the college and university level, but also in other forms of post-secondary educational institutions. In ...
class, Seward was an outstanding student and was elected to Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States, and the most prestigious, due in part to its long history and academic selectivity. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal ...
. Seward's fellow students included Richard M. Blatchford
Richard Milford Blatchford (August 17, 1859 – August 31, 1934) was a career officer in the United States Army. A veteran of the Spanish–American War, Philippine–American War, Pancho Villa Expedition, and World War I, he attained the rank ...
, who became a lifelong legal and political associate. Samuel Seward kept his son short on cash, and in December 1818—during the middle of Henry's final year at Union—the two quarreled about money. The younger Seward returned to Schenectady but soon left school in company with a fellow student, Alvah Wilson. The two took a ship from New York to Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, where Wilson had been offered a job as rector, or principal, of a new academy in rural Putnam County. En route, Wilson took a job at another school, leaving Seward to continue on to Eatonton in Putnam County. The trustees interviewed the 17-year-old Seward, and found his qualifications acceptable.
Seward enjoyed his time in Georgia, where he was accepted as an adult for the first time. He was treated hospitably, but also witnessed the ill-treatment of slaves. Seward was persuaded to return to New York by his family and did so in June 1819. As it was too late for him to graduate with his class, he studied law at an attorney's office in Goshen before returning to Union College, securing his degree with highest honors in June 1820.
Lawyer and state senator
Early career and involvement in politics
 After graduation, Seward spent much of the following two years studying law in Goshen and New York City with attorneys John Duer, John Anthon and
After graduation, Seward spent much of the following two years studying law in Goshen and New York City with attorneys John Duer, John Anthon and Ogden Hoffman
Ogden Hoffman (October 13, 1794 – May 1, 1856) was an American lawyer and politician who served two terms in the United States House of Representatives.
Life
Ogden Hoffman was born on October 13, 1794, the son of New York Attorney General Jos ...
. He passed the bar examination
A bar examination is an examination administered by the bar association of a jurisdiction that a lawyer must pass in order to be admitted to the bar of that jurisdiction.
Australia
Administering bar exams is the responsibility of the bar associ ...
in late 1822. He could have practiced in Goshen, but he disliked the town and sought a practice in growing Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY i ...
. Seward decided upon Auburn in Cayuga County, which was about west of Albany and northwest of Goshen. He joined the practice of retired judge Elijah Miller
Elijah Miller (April 11, 1772 – November 13, 1851) was a lawyer and judge in Auburn, New York, Auburn, New York (state), New York.
Early life and career
Miller was born on April 11, 1772. He was the son of Josiah Miller (1749–1817). He ...
, whose daughter Frances Adeline Miller was a classmate of his sister Cornelia at Emma Willard's Troy Female Seminary
The Emma Willard School, originally called Troy Female Seminary and often referred to simply as Emma, is an independent university-preparatory day and boarding school for young women, located in Troy, New York, on Mount Ida, offering grades 9– ...
. Seward married Frances Miller on October 20, 1824.
In 1824, Seward was journeying with his wife to Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the Canada–United States border, border between the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Ontario in Canada and the U.S. state, state ...
when one of the wheels on his carriage was damaged while they passed through Rochester. Among those who came to their aid was local newspaper publisher Thurlow Weed
Edward Thurlow Weed (November 15, 1797 – November 22, 1882) was a printer, New York newspaper publisher, and Whig and Republican politician. He was the principal political advisor to prominent New York politician William H. Seward and was i ...
. Seward and Weed would become closer in the years ahead as they found they shared a belief that government policies should promote infrastructure improvements, such as roads and canals. Weed, deemed by some to be one of the earliest political bosses, would become a major ally of Seward. Despite the benefits to Seward's career from Weed's support, perceptions that Seward was too much controlled by Weed became a factor in the former's defeat for the Republican nomination for president in 1860.
Almost from the time he settled in Auburn, Seward involved himself in politics. At that time, the political system was in flux as new parties evolved. In New York State, there were generally two factions, which went by varying names, but were characterized by the fact that Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; nl, Maarten van Buren; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the eighth president of the United States from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party, he ...
led one element, and the other opposed him. Van Buren, over a quarter century, held a series of senior posts, generally in the federal government. His allies were dubbed the Albany Regency, as they governed for Van Buren while he was away.
Seward originally supported the Regency, but by 1824 had broken from it, concluding that it was corrupt. He became part of the Anti-Masonic Party
The Anti-Masonic Party was the earliest third party in the United States. Formally a single-issue party, it strongly opposed Freemasonry, but later aspired to become a major party by expanding its platform to take positions on other issues. After ...
, which became widespread in 1826 after the disappearance and death of William Morgan, a Mason in Upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York (state), New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York metropolitan area, New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upsta ...
; he was most likely killed by fellow Masons for publishing a book revealing the order's secret rites. Since the leading candidate in opposition to President John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States ...
was General Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, a Mason who mocked opponents of the order, Anti-Masonry became closely associated with opposition to Jackson, and to his policies once he was elected president in 1828.
Governor DeWitt Clinton
DeWitt Clinton (March 2, 1769February 11, 1828) was an American politician and naturalist. He served as a United States senator, as the mayor of New York City, and as the seventh governor of New York. In this last capacity, he was largely re ...
had nominated Seward as Cayuga County Surrogate
A surrogate is a substitute or deputy for another person in a specific role and may refer to:
Relationships
* Surrogacy, an arrangement where a woman agrees to carry and give birth to a child for another person who will become its parent at bir ...
in late 1827 or early 1828, but as Seward was unwilling to support Jackson, he was not confirmed by the state Senate. During the 1828 campaign, Seward made speeches in support of President Adams's re-election. Seward was nominated for the federal House of Representatives by the Anti-Masons, but withdrew, deeming the fight hopeless. In 1829, Seward was offered the local nomination for New York State Assembly
The New York State Assembly is the lower house of the New York State Legislature, with the New York State Senate being the upper house. There are 150 seats in the Assembly. Assembly members serve two-year terms without term limits.
The Ass ...
, but again felt there was no prospect of winning. In 1830, with Weed's aid, he gained the Anti-Masonic nomination for state senator for the local district. Seward had appeared in court throughout the district, and had spoken in favor of government support for infrastructure improvements, a position popular there. Weed had moved his operations to Albany, where his newspaper, the '' Albany Evening Journal'', advocated for Seward, who was elected by about 2,000 votes.
State senator and gubernatorial candidate
Seward was sworn in as state senator in January 1831. He left Frances and their children in Auburn and wrote to her of his experiences. These included meeting former vice presidentAaron Burr
Aaron Burr Jr. (February 6, 1756 – September 14, 1836) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the third vice president of the United States from 1801 to 1805. Burr's legacy is defined by his famous personal conflict with Alexand ...
, who had returned to practicing law in New York following a self-imposed exile in Europe after his duel with Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charle ...
and treason trial. The Regency (or the Democrats, as the national party led by Jackson and supported by Van Buren, was becoming known) controlled the Senate. Seward and his party allied with dissident Democrats and others to pass some legislation, including penal reform measures, for which Seward would become known.
During his term as state senator, Seward traveled extensively, visiting other anti-Jackson leaders, including former president Adams. He also accompanied his father Samuel Seward on a trip to Europe, where they met the political men of the day. Seward hoped that the Anti-Masons would nominate Supreme Court Justice John McLean
John McLean (March 11, 1785 – April 4, 1861) was an American jurist and politician who served in the United States Congress, as U.S. Postmaster General, and as a justice of the Ohio and U.S. Supreme Courts. He was often discussed for t ...
for president against Jackson's re-election bid in 1832, but the nomination fell to former Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
William Wirt. Kentucky Senator Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seven ...
, an opponent of Jackson, was a Mason, and thus unacceptable as party standard-bearer. In the aftermath of Jackson's easy victory, many of those who opposed him believed that a united front was necessary to defeat the Democrats, and the Whig Party gradually came into being. The Whigs believed in legislative action to develop the country and opposed Jackson's unilateral actions as president, which they deemed imperial. Many Anti-Masons, including Seward and Weed, readily joined the new party.
In preparation for the 1834 election, New York's Whigs met in Utica to determine a gubernatorial candidate. Democratic Governor William Marcy
William Learned Marcy (December 12, 1786July 4, 1857) was an American lawyer, politician, and judge who served as U.S. Senator, Governor of New York, U.S. Secretary of War and U.S. Secretary of State. In the latter office, he negotiated the G ...
was heavily favored to be re-elected, and few prominent Whigs were anxious to run a campaign that would most likely be lost. Seward's wife and father wanted him to retire from politics to increase the income from his law practice, and Weed urged him to seek re-election to the state Senate. Nevertheless, the reluctance of others to run caused Seward to emerge as a major candidate. Weed procured Seward's triumph at the Utica convention. The election turned on national issues, most importantly President Jackson's policies. These were then popular, and in a strong year for Democrats, Seward was defeated by some 11,000 votes—Weed wrote that the Whigs were overwhelmed by illegally cast ballots.
Defeated for governor and with his term in the state Senate having expired, Seward returned to Auburn and the practice of law at the start of 1835. That year, Seward and his wife undertook a lengthy trip, going as far south as Virginia. Although they were hospitably received by southerners, the Sewards saw scenes of slavery which confirmed them as its opponents. The following year, Seward accepted a position as agent for the new owners of the Holland Land Company, which owned large tracts of land in Western New York, upon which many settlers were purchasing real estate on installment. The new owners were viewed as less forgiving landlords than the old, and when there was unrest, they hired Seward, popular in Western New York, in hopes of adjusting the matter. He was successful, and when the Panic of 1837
The Panic of 1837 was a financial crisis in the United States that touched off a major depression, which lasted until the mid-1840s. Profits, prices, and wages went down, westward expansion was stalled, unemployment went up, and pessimism abound ...
began, persuaded the owners to avoid foreclosures where possible. He also, in 1838, arranged the purchase of the company's holdings by a consortium that included himself.
Van Buren had been elected president in 1836; even with his other activities, Seward had found time to campaign against him. The economic crisis came soon after the inauguration and threatened the Regency's control of New York politics. Seward had not run for governor in 1836, but with the Democrats unpopular, saw a path to victory in 1838 (the term was then two years). Other prominent Whigs also sought the nomination. Weed persuaded delegates to the convention that Seward had run ahead of other Whig candidates in 1834; Seward was nominated on the fourth ballot. Seward's opponent was again Marcy, and the economy the principal issue. The Whigs argued that the Democrats were responsible for the recession. As it was thought improper for candidates for major office to campaign in person, Seward left most of that to Weed. Seward was elected by a margin of about 10,000 votes out of 400,000 cast. The victory was the most significant for the Whig Party to that point, and eliminated the Regency from power in New York, permanently.
Governor of New York
 William Seward was sworn in as governor of New York on January 1, 1839, and inaugurated in front of a crowd of jubilant Whigs. In that era, the annual message by the New York governor was published and discussed to the extent of that of a president. Seward biographer Walter Stahr wrote that his address "brimmed with his youth, energy, ambition, and optimism." Seward took note of America's great unexploited resources and stated that immigration should be encouraged in order to take advantage of them. He urged that citizenship and religious liberty be granted to those who came to New York's shores. At the time, New York City's public schools were run by Protestants, and used Protestant texts, including the
William Seward was sworn in as governor of New York on January 1, 1839, and inaugurated in front of a crowd of jubilant Whigs. In that era, the annual message by the New York governor was published and discussed to the extent of that of a president. Seward biographer Walter Stahr wrote that his address "brimmed with his youth, energy, ambition, and optimism." Seward took note of America's great unexploited resources and stated that immigration should be encouraged in order to take advantage of them. He urged that citizenship and religious liberty be granted to those who came to New York's shores. At the time, New York City's public schools were run by Protestants, and used Protestant texts, including the King James Bible
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of ...
. Seward believed the current system was a barrier to literacy for immigrants' children and proposed legislation to change it. Education, he stated, "banishes the distinctions, old as time, of rich and poor, master and slave. It banishes ignorance and lays axe to the root of crime." Seward's stance was popular among immigrants, but was disliked by nativists
Nativism is the political policy of promoting or protecting the interests of native or indigenous inhabitants over those of immigrants, including the support of immigration-restriction measures.
In scholarly studies, ''nativism'' is a standa ...
; their opposition would eventually help defeat his bid for the Republican presidential nomination in 1860.
Although the Assembly had a Whig majority at the start of Seward's first term as governor, the party had only 13 legislators out of 32 in the state Senate. The Democrats refused to co-operate with Governor Seward except on the most urgent matters, and he initially found himself unable to advance much of his agenda. Accordingly, the 1839 legislative elections were crucial to Seward's legislative hopes, and to advancing the nominations of many Whigs to state office whose posts required Senate confirmation. Both Seward and President Van Buren gave several speeches across New York State that summer. Henry Clay, one of the hopefuls for the Whig nomination for president, spent part of the summer in Upstate New York, and the two men met by chance on a ferry. Seward refused to formally visit Clay at his vacation home in Saratoga Springs in the interests of neutrality, beginning a difficult relationship between the two men. After the 1839 election, the Whigs had 19 seats, allowing the party full control of state government.
Following the election, there was unrest near Albany among tenant farmers on the land owned by Dutch-descended patroons of the van Rensselaer family
The Van Rensselaer family () is a family of Dutch descent that was prominent during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries in the area now known as the state of New York. Members of this family played a critical role in the formation of the Unit ...
. These tenancies allowed the landlords privileges such as enlisting the unpaid labor of tenants, and any breach could result in termination of tenure without compensation for improvements. When sheriff's deputies in Albany County were obstructed from serving eviction writs, Seward was asked to call out the militia. After an all-night cabinet meeting, he did so, though quietly assuring the tenants that he would intervene with the legislature. This mollified the settlers, though Seward proved unable to get the legislature to pass reforming laws. This question of tenants' rights was not settled until after Seward had left office.
In September 1839, a ship sailing from Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia B ...
, to New York City was discovered to have an escaped slave on board. The slave was returned to his owner pursuant to the Fugitive Slave Clause
The Fugitive Slave Clause in the United States Constitution, also known as either the Slave Clause or the Fugitives From Labor Clause, is Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3, which requires a "person held to service or labor" (usually a slave, appre ...
of the Constitution, but Virginia also demanded that three free black sailors, said to have concealed the fugitive aboard ship, be surrendered to its custody. This Seward would not do, and the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 16 ...
passed legislation inhibiting trade with New York. With Seward's encouragement, the New York legislature passed acts in 1840 protecting the rights of blacks against Southern slave-catchers. One guaranteed alleged fugitive slaves the right of a jury trial in New York to establish whether they were slaves, and another pledged the aid of the state to recover free blacks kidnapped into slavery.
Seward and Van Buren were both up for re-election in 1840. Seward did not attend the December 1839 Whig National Convention in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the 9th largest city and 15th largest municipality in ...
, but Weed did on his behalf. They were determined to support General Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
for president, but when Weed concluded Scott could not win, he threw New York's support behind the eventual winner, General William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was an American military officer and politician who served as the ninth president of the United States. Harrison died just 31 days after his inauguration in 1841, and had the shortest pres ...
. This action outraged supporters of Senator Clay. These grievances would not be quickly forgotten—one supporter of the Kentuckian wrote in 1847 that he was intent on seeing the "punishment of Seward & Co. for defrauding the country of Mr. Clay in 1840".
Seward was renominated for a second term by the Whig convention against Democrat William C. Bouck
William Christian Bouck (January 7, 1786 – April 19, 1859) was an American politician from New York. He was the 13th Governor of New York from 1843 to 1844.
A native of Fultonham, New York, Bouck was educated in the local schools while w ...
, a former state legislator. Seward did not campaign in person, but ran affairs behind the scenes with Weed and made his views known to voters through a Fourth of July speech and lengthy letters, declining invitations to speak, printed in the papers. In one, Seward expounded upon the importance of the log cabin
A log cabin is a small log house, especially a less finished or less architecturally sophisticated structure. Log cabins have an ancient history in Europe, and in America are often associated with first generation home building by settlers.
Eur ...
—a structure evoking the common man and a theme that the Whigs used heavily in Harrison's campaign—where Seward had always found a far warmer welcome than in the marble palaces of the well-to-do (evoking Van Buren). Both Harrison and Seward were elected. Although Seward would serve for nearly thirty more years in public life, his name would never again pass before the voters.
In his second term, Seward was involved with the trial of Alexander McLeod, who had boasted of involvement in the 1837 ''Caroline'' Affair, in which Canadians came across the Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York in the United States (on the east). There are diffe ...
and sank the ''Caroline'', a steamboat being used to supply William Lyon Mackenzie's fighters during the Upper Canada Rebellion
The Upper Canada Rebellion was an insurrection against the oligarchic government of the British colony of Upper Canada (present-day Ontario) in December 1837. While public grievances had existed for years, it was the rebellion in Lower Canada (p ...
. McLeod was arrested, but the British Foreign Minister, Lord Palmerston, demanded his release. McLeod, who was part of the Canadian colonial militia, could not be held responsible for actions taken under orders. Although the Van Buren administration
The presidency of Martin Van Buren began on March 4, 1837, when Martin Van Buren was inaugurated as President of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1841. Van Buren, the incumbent vice president and chosen successor of President Andrew Jack ...
had agreed with Seward that McLeod should be tried under state law, its successor did not and urged that charges against McLeod be dropped. A series of testy letters were exchanged between Governor Seward and Harrison's Secretary of State Daniel Webster, and also between the governor and the new president John Tyler
John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States, serving from 1841 to 1845, after briefly holding office as the tenth vice president in 1841. He was elected vice president on the 1840 Whig tick ...
, who succeeded on Harrison's death after a month in office. McLeod was tried and acquitted in late 1841. Stahr pointed out that Seward got his way in having McLeod tried in a state court, and the diplomatic experience served him well as Secretary of State.
Seward continued his support of blacks, signing legislation in 1841 to repeal a "nine-month law" that allowed slaveholders to bring their slaves into the state for a period of nine months before they were considered free. After this, slaves brought to the state were immediately considered freed. Seward also signed legislation to establish public education for all children, leaving it up to local jurisdictions as to how that would be supplied (some had segregated schools).
Out of office
 As governor, Seward incurred considerable personal debt not only because he had to live beyond his salary to maintain the lifestyle expected of the office, but also because he could not pay down his obligation from the land company purchase. At the time he left office, he owed $200,000. Returning to Auburn, he absorbed himself in a profitable law practice. He did not abandon politics and received former president Adams at the Seward family home in 1843.
According to his biographer, John M. Taylor, Seward picked a good time to absent himself from electoral politics, as the Whig Party was in turmoil. President Tyler, a former Democrat, and Senator Clay each claimed leadership of the Whig Party and, as the two men differed over such issues as whether to re-establish the Bank of the United States, party support was divided. The
As governor, Seward incurred considerable personal debt not only because he had to live beyond his salary to maintain the lifestyle expected of the office, but also because he could not pay down his obligation from the land company purchase. At the time he left office, he owed $200,000. Returning to Auburn, he absorbed himself in a profitable law practice. He did not abandon politics and received former president Adams at the Seward family home in 1843.
According to his biographer, John M. Taylor, Seward picked a good time to absent himself from electoral politics, as the Whig Party was in turmoil. President Tyler, a former Democrat, and Senator Clay each claimed leadership of the Whig Party and, as the two men differed over such issues as whether to re-establish the Bank of the United States, party support was divided. The abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
movement attracted those who did not want to be part of a party led by slavery-supporting southerners. In 1844
In the Philippines, it was the only leap year with 365 days, as December 31 was skipped when 1845 began after December 30.
Events
January–March
* January 15 – The University of Notre Dame, based in the city of the same name, receives ...
, Seward was asked to run for president by members of the Liberty Party; he declined and reluctantly supported the Whig nominee, Clay. The Kentuckian was defeated by Democrat James K. Polk. The major event of Polk's administration was the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the ...
; Seward did not support this, feeling that the price in blood was not worth the increase in territory, especially as southerners were promoting this acquisition to expand territory for slavery.
In 1846, Seward became the center of controversy in Auburn when he defended, in separate cases, two felons accused of murder. Henry Wyatt, a white man, was charged with fatally stabbing a fellow inmate in prison; William Freeman, a black, was accused of breaking into a house after his release and stabbing four people to death. In both cases, the defendants were likely mentally ill and had been abused while in prison. Seward, having long been an advocate of prison reform and better treatment for the insane, sought to prevent each man from being executed by using the relatively new defense of insanity. Seward gained a hung jury in Wyatt's first trial, though he was subsequently convicted in a retrial and executed despite Seward's efforts to secure clemency. Freeman was convicted, though Seward gained a reversal on appeal. There was no second Freeman trial, as officials were convinced of his insanity. Freeman died in prison in late 1846. In the Freeman case, invoking mental illness and racial issues, Seward argued, "he is still your brother, and mine, in form and color accepted and approved by his Father, and yours, and mine, and bears equally with us the proudest inheritance of our race—the image of our Maker. Hold him then to be a Man."
Although they were locally contentious, the trials boosted Seward's image across the North. He gained further publicity in association with Ohioan Salmon P. Chase
Salmon Portland Chase (January 13, 1808May 7, 1873) was an American politician and jurist who served as the sixth chief justice of the United States. He also served as the 23rd governor of Ohio, represented Ohio in the United States Senate, a ...
when handling the unsuccessful appeal in the United States Supreme Court of John Van Zandt
John Van Zandt (died 1847) was an American abolitionist who aided the Underground Railroad resistance movement in Ohio after having been a slaveholder in Kentucky. Sued for monetary damages by a slaveholder whose escaped slaves he aided, he was ...
, an anti-slavery advocate sued by a slaveowner for assisting blacks in escaping on the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
. Chase was impressed with Seward, writing that the former New York governor "was one of the very first public men in our country. Who but himself would have done what he did for the poor wretch Freeman?"
The main Whig contenders in 1848 were Clay again, and two war hero generals with little political experience, Winfield Scott and Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader who served as the 12th president of the United States from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to th ...
. Seward supported General Taylor. The former governor was less enthusiastic about the vice-presidential candidate, New York State Comptroller
The New York State Comptroller is an elected constitutional officer of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and head of the government of New York (state), New York state government's Department of Audit and Control. The New York State C ...
Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
, a rival of his from Buffalo. Nevertheless, he campaigned widely for the Whigs against the Democratic presidential candidate, former Michigan senator Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was an American military officer, politician, and statesman. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He w ...
. The two major parties did not make slavery an issue in the campaign. The Free Soil Party
The Free Soil Party was a short-lived coalition political party in the United States active from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was largely focused on the single issue of opposing the expansion of slavery int ...
, mostly Liberty Party members and some Northern Democrats, nominated former president Van Buren. The Taylor/Fillmore ticket was elected, and the split in the New York Democratic Party allowed the Whigs to capture the legislature.
State legislatures elected U.S. Senators until the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913. One of New York's seats was up for election in 1849, and a Whig would likely be elected to replace John Adams Dix. Seward, with Weed's counsel, decided to seek the seat. When legislators convened in January 1849, he was spoken of as the favorite. Some opposed him as too extreme on slavery issues and intimated that he would not support the slaveholding President-elect Taylor, a Louisianan. Weed and Seward worked to dispel these concerns, and when the vote for the Senate seat took place, the former governor received five times the vote of the nearest other candidate, gaining election on the first ballot.
U.S. Senator
First term
William Seward was sworn in as senator from New York on March 5, 1849, during the brief special session called to confirm President Taylor'sCabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
nominees. Seward was seen as having influence over Taylor: taking advantage of an acquaintance with Taylor's brother. Seward met with the former general several times before Inauguration Day (March 4) and was friendly with Cabinet officers. Taylor hoped to gain the admission of California to the Union, and Seward worked to advance his agenda in the Senate.
The regular session of Congress that began in December 1849 was dominated by the issue of slavery. Senator Clay advanced a series of resolutions, which became known as the Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Am ...
, giving victories to both North and South. Seward opposed the pro-slavery elements of the Compromise, and in a speech on the Senate floor on March 11, 1850, invoked a "higher law than the Constitution". The speech was widely reprinted and made Seward the leading anti-slavery advocate in the Senate. President Taylor took a stance sympathetic to the North, but his death in July 1850 caused the accession of the pro-Compromise Fillmore and ended Seward's influence over patronage. The Compromise passed, and many Seward adherents in federal office in New York were replaced by Fillmore appointees.
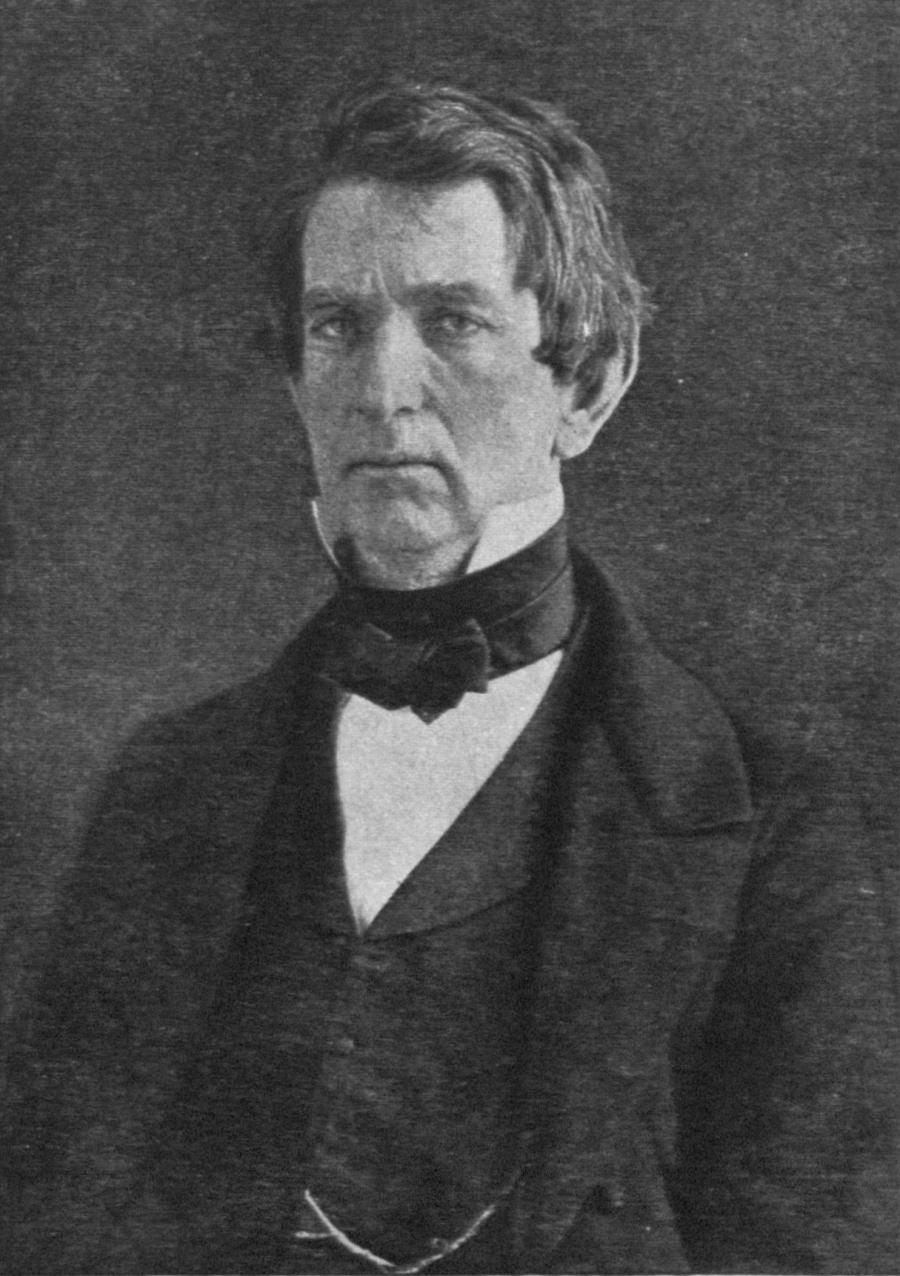 Although Clay had hoped the Compromise would be a final settlement on the matter of slavery that could unite the nation, it divided his Whig Party, especially when the 1852 Whig National Convention endorsed it to the anger of liberal northerners like Seward. The major candidates for the presidential nomination were President Fillmore, Senator Daniel Webster, and General Scott. Seward supported Scott, who he hoped would, like Harrison, unite enough voters behind a military hero to win the election. Scott gained the nomination, and Seward campaigned for him. The Whigs were unable to reconcile over slavery, whereas the Democrats could unite behind the Compromise; the Whigs won only four states, and former New Hampshire senator
Although Clay had hoped the Compromise would be a final settlement on the matter of slavery that could unite the nation, it divided his Whig Party, especially when the 1852 Whig National Convention endorsed it to the anger of liberal northerners like Seward. The major candidates for the presidential nomination were President Fillmore, Senator Daniel Webster, and General Scott. Seward supported Scott, who he hoped would, like Harrison, unite enough voters behind a military hero to win the election. Scott gained the nomination, and Seward campaigned for him. The Whigs were unable to reconcile over slavery, whereas the Democrats could unite behind the Compromise; the Whigs won only four states, and former New Hampshire senator Franklin Pierce
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. He was a northern Democrat who believed that the abolitionist movement was a fundamental threat to the nation's unity ...
was elected president. Other events, such as the 1852 publication of ''Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U ...
'' and Northern anger over the enforcement of the Fugitive Slave Act
A fugitive (or runaway) is a person who is fleeing from custody, whether it be from jail, a government arrest, government or non-government questioning, vigilante violence, or outraged private individuals. A fugitive from justice, also know ...
(an element of the Compromise), widened the divide between North and South.
Seward's wife Frances was deeply committed to the abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
movement. In the 1850s, the Seward family opened their Auburn home as a safehouse to fugitive slaves on the Underground Railroad. Seward's frequent travel and political work suggest that it was Frances who played the more active role in Auburn abolitionist activities. In the excitement following the rescue and safe transport of fugitive slave William "Jerry" Henry in Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
* Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
* Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
** North Syracuse, New York
* Syracuse, Indiana
*Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, M ...
on October 1, 1851, Frances wrote to her husband, "two fugitives have gone to Canada—one of them our acquaintance John". Another time she wrote, "A man by the name of William Johnson will apply to you for assistance to purchase the freedom of his daughter. You will see that I have given him something by his book. I told him I thought you would give him more."
In January 1854, Democratic Illinois Senator Stephen A. Douglas introduced his Kansas–Nebraska Bill. This would permit territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
to choose whether to join the Union as free or slave states, and effectively repeal the Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a Slave states an ...
forbidding slavery in new states north of 36° 30′ North latitude. Seward was determined to defeat what he called "this infamous Nebraska Bill," and worked to ensure the final version of the bill would be unpalatable to enough senators, North and South, to defeat it. Seward spoke against the bill both on initial consideration in the Senate and when the bill returned after reconciliation with the House. The bill passed into law, but northerners had found a standard around which they could rally. Those in the South defended the new law, arguing that they should have an equal stake through slavery in the territories their blood and money had helped secure.
Second term
 The political turmoil engendered by the North–South divide split both major parties and led to the founding of new ones. The American Party (known as the Know Nothings) contained many nativists and pursued an anti-immigrant agenda. The Know Nothings did not publicly discuss party deliberations (thus, they knew nothing). They disliked Seward, and an uncertain number of Know Nothings sought the Whig nomination to legislative seats. Some made clear their stance by pledging to vote against Seward's re-election, but others did not. Although the Whigs won a majority in both houses of the state legislature, the extent of their support for Seward as a US senator was unclear. When
The political turmoil engendered by the North–South divide split both major parties and led to the founding of new ones. The American Party (known as the Know Nothings) contained many nativists and pursued an anti-immigrant agenda. The Know Nothings did not publicly discuss party deliberations (thus, they knew nothing). They disliked Seward, and an uncertain number of Know Nothings sought the Whig nomination to legislative seats. Some made clear their stance by pledging to vote against Seward's re-election, but others did not. Although the Whigs won a majority in both houses of the state legislature, the extent of their support for Seward as a US senator was unclear. When the election
''The Election'' () is a political drama series produced by Hong Kong Television Network (HKTV). With a budget of HK$15 million, filming started in July 2014 and wrapped up on 28 October 2014. Popularly voted to be the inaugural drama of ...
was held by the legislature in February 1855, Seward won a narrow majority in each house. The opposition was scattered, and a Know Nothing party organ denounced two dozen legislators as "traitors".
The Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
* Republican Party (Liberia)
*Republican Party ...
had been founded in 1854, in reaction to the Kansas–Nebraska Act. Its anti-slavery stance was attractive to Seward, but he needed the Whig structure in New York to get re-elected. In September 1855, the New York Whig and Republican parties held simultaneous conventions that quickly merged into one. Seward was the most prominent figure to join the new party and was spoken of as a possible presidential candidate in 1856. Weed, however, did not feel that the new party was strong enough on a national level to secure the presidency, and advised Seward to wait until 1860. When Seward's name was mentioned at the 1856 Republican National Convention, a huge ovation broke out. In the 1856 presidential election, the Democratic candidate, former Pennsylvania senator James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861. He previously served as secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and repr ...
, defeated the Republican, former California senator John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 ...
, and the Know Nothing candidate, former president Fillmore.
The 1856 campaign played out against the backdrop of "Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
", the violent efforts of pro- and anti-slavery forces to control the government in Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the free state of Kansas.
...
and determine whether it would be admitted as a slave or free state. This violence spilled over into the Senate chamber itself after Republican Massachusetts Senator Charles Sumner delivered an incendiary speech against slavery, making personal comments against South Carolina Senator Andrew P. Butler. Sumner had read a draft of the speech to Seward, who had advised him to omit the personal references. Two days after the speech, Butler's nephew, Congressman Preston Brooks entered the chamber and beat Sumner with a cane, injuring him severely. Although some southerners feared the propaganda value of the incident in the North, most lionized Brooks as a hero. Many northerners were outraged, though some, including Seward, felt that Sumner's words against Butler had unnecessarily provoked the attack. Some Southern newspapers felt that the Sumner precedent might usefully be applied to Seward; the ''Petersburg Intelligencer'', a Virginia periodical, suggested that "it will be very well to give Seward a double dose at least every other day".
In a message to Congress in December 1857, President Buchanan advocated the admission of Kansas as a slave state under the Lecompton Constitution, passed under dubious circumstances. This split the Democrats: the administration wanted Kansas admitted; Senator Douglas demanded a fair ratification vote. The Senate debated the matter through much of early 1858, though few Republicans spoke at first, content to watch the Democrats tear their party to shreds over the issue of slavery. The issue was complicated by the Supreme Court's ruling the previous year in '' Dred Scott v. Sandford'' that neither Congress nor a local government could ban slavery in the territories.
In a speech on March 3 in the Senate, Seward "delighted Republican ears and utterly appalled administration Democrats, especially the Southerners". Discussing ''Dred Scott'', Seward accused Buchanan and Chief Justice Roger B. Taney of conspiring to gain the result and threatened to reform the courts to eliminate Southern power. Taney later told a friend that if Seward had been elected in 1860, he would have refused to administer the oath of office. Buchanan reportedly denied the senator access to the White House. Seward predicted slavery was doomed:
Southerners saw this as a threat, by the man deemed the likely Republican nominee in 1860, to force change on the South whether it liked it or not. Statehood for Kansas failed for the time being, but Seward's words were repeatedly cited by Southern senators as the secession crisis grew. Nevertheless, Seward remained on excellent personal terms with individual southerners such as Mississippi's Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
. His dinner parties, where those from both sides of the sectional divide mingled, were a Washington legend.
With an eye to a presidential bid in 1860, Seward tried to appear a statesman who could be trusted by both North and South. Seward did not believe the federal government could mandate emancipation but that it would develop by action of the slave states as the nation urbanized and slavery became uneconomical, as it had in New York. Southerners still believed that he was threatening the forcible ending of slavery. While campaigning for Republicans in the 1858 midterm elections, Seward gave a speech at Rochester that proved divisive and quotable, alleging that the U.S. had two "antagonistic systems hatare continually coming into closer contact, and collision results ... It is an irrepressible conflict between opposing and enduring forces, and it means that the United States must and will, sooner or later, become entirely either a slave-holding nation, or entirely a free-labor nation." White southerners saw the "irrepressible conflict" speech as a declaration of war, and Seward's vehemence ultimately damaged his chances of gaining the presidential nomination.
Election of 1860
Candidate for the nomination
 In 1859, Seward was advised by his political supporters that he would be better off avoiding additional controversial statements, and left the country for an eight-month tour of Europe and the Middle East. Seward spent two months in London, meeting with the Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, and was presented at Court to
In 1859, Seward was advised by his political supporters that he would be better off avoiding additional controversial statements, and left the country for an eight-month tour of Europe and the Middle East. Seward spent two months in London, meeting with the Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, and was presented at Court to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
. Seward returned to Washington in January 1860 to find controversy: that some southerners blamed him for his rhetoric, which they believed had inspired John Brown to try to start a slave insurrection. Brown was captured and executed; nevertheless, Mississippi representatives Reuben Davis and Otho Singleton each stated that if Seward or another Radical Republican
The Radical Republicans (later also known as "Stalwarts") were a faction within the Republican Party, originating from the party's founding in 1854, some 6 years before the Civil War, until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Recon ...
was elected, he would meet with the resistance of a united South. To rebut such allegations, and to set forth his views in the hope of receiving the nomination, Seward made a major speech in the Senate on February 29, 1860, which most praised, though white southerners were offended, and some abolitionists also objected because the senator, in his speech, said that Brown was justly punished. The Republican National Committee
The Republican National Committee (RNC) is a U.S. political committee that assists the Republican Party of the United States. It is responsible for developing and promoting the Republican brand and political platform, as well as assisting in ...
ordered 250,000 copies in pamphlet form, and eventually twice that many were printed.
Weed sometimes expressed certainty that Seward would be nominated; at other times he expressed gloom at the thought of the convention fight. He had some reason for doubt, as word from Weed's agents across the country was mixed. Many in the Midwest did not want the issue of slavery to dominate the campaign, and with Seward as the nominee, it inevitably would. The Know Nothing Party was still alive in the Northeast, and was hostile to Seward for his pro-immigrant stance, creating doubts as to whether Seward could win Pennsylvania and New Jersey, where there were many nativists, in the general election. These states were crucial to a Republican nominee faced with a Solid South
The Solid South or Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especial ...
. Conservative factions in the evolving Republican Party opposed Seward.
Convention
There were noprimaries
Primary elections, or direct primary are a voting process by which voters can indicate their preference for their party's candidate, or a candidate in general, in an upcoming general election, local election, or by-election. Depending on the c ...
in 1860, no way to be certain how many delegates a candidate might receive. Nevertheless, going into the 1860 Republican National Convention
The 1860 Republican National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met May 16-18 in Chicago, Illinois. It was held to nominate the Republican Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1860 election. The conve ...
in May in Chicago, Seward was seen as the overwhelming favorite. Others spoken of for the nomination included Ohio Governor Salmon P. Chase, former Missouri congressman Edward Bates
Edward Bates (September 4, 1793 – March 25, 1869) was a lawyer and politician. He represented Missouri in the US House of Representatives and served as the U.S. Attorney General under President Abraham Lincoln. A member of the influentia ...
, and former Illinois congressman Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
.
Seward stayed in Auburn during the convention; Weed was present on his behalf and worked to shore up Seward's support. He was amply supplied with money: business owners had eagerly given, expecting Seward to be the next president. Weed's reputation was not entirely positive; he was believed corrupt by some, and his association both helped and hurt Seward.
 Enemies such as publisher and former Seward ally
Enemies such as publisher and former Seward ally Horace Greeley
Horace Greeley (February 3, 1811 – November 29, 1872) was an American newspaper editor and publisher who was the founder and editor of the '' New-York Tribune''. Long active in politics, he served briefly as a congressman from New York ...
cast doubts as to Seward's electability in the battleground states of Illinois, Indiana, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey. Lincoln had worked hard to gain a reputation as a moderate in the party and hoped to be seen as a consensus second choice, who might be successful in those critical states, of which the Republicans had to win three to secure the election. Lincoln's men, led by his friend David Davis, were active on his behalf. As Lincoln had not been seen as a major candidate, his supporters had been able to influence the decision to hold the convention in his home state, and surrounded the New York delegation, pro-Seward, with Lincoln loyalists. They were eventually successful in gaining the support of the delegations from the other battleground states, boosting delegates' perceptions of Lincoln's electability. Although Lincoln and Seward shared many views, Lincoln, out of office since 1849, had not excited opposition as Seward had in the South and among Know Nothings. Lincoln's views on nativism, which he opposed, were not public.
On the first ballot, Seward had 173½ votes to Lincoln's 102, with 233 needed to nominate. Pennsylvania shifted its vote to Lincoln on the second ballot, and Seward's lead was cut to 184½ to 181. On the third, Lincoln had 231½ to Seward's 180 after the roll call, but Ohio changed four votes from Chase to Lincoln, giving the Illinoian the nomination and starting a small stampede; the nomination was eventually made unanimous. By the accounts of witnesses, when word reached Seward by telegraph he calmly remarked that Lincoln had some of the attributes needed to be president, and would certainly be elected.
Campaigning for Lincoln
Despite his public nonchalance, Seward was devastated by his convention loss, as were many of his supporters. The New Yorker was the best-known and most popular Republican, and his defeat shocked many in the North, who felt that Lincoln had been nominated through chicanery. Although Seward sent a letter stating Weed was not to blame, Seward's political manager took the defeat hard. Seward was initially inclined to retire from public life but received many letters from supporters: distrustful of Lincoln, they urged Seward to remain involved in politics. On his way to Washington to return to Senate duties, he stopped in Albany to confer with Weed, who had gone to Lincoln's home inSpringfield, Illinois
Springfield is the capital of the U.S. state of Illinois and the county seat and largest city of Sangamon County. The city's population was 114,394 at the 2020 census, which makes it the state's seventh most-populous city, the second largest ...
, to meet with the candidate, and had been very impressed at Lincoln's political understanding. At the Capitol, Seward received sympathy even from sectional foes such as Jefferson Davis.
Lincoln faced three major opponents. A split in the Democratic Party had led northerners to nominate Senator Douglas, while southerners chose Vice President John C. Breckinridge. The Constitutional Union Party, a new party consisting mostly of former Southern Whigs, selected former Tennessee senator John Bell. As Lincoln would not even be on the ballot in ten southern states, he needed to win almost every northern state to take the presidency. Douglas was said to be strong in Illinois and Indiana, and if he took those, the election might be thrown into the House of Representatives. Seward was urged to undertake a campaign tour of the Midwest in support of Lincoln and did so for five weeks in September and October, attracting huge crowds. He journeyed by rail and boat as far north as Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul (abbreviated St. Paul) is the capital of the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Ramsey County. Situated on high bluffs overlooking a bend in the Mississippi River, Saint Paul is a regional business hub and the center ...
, into the border state of Missouri at St. Louis, and even to Kansas Territory, though it had no electoral votes to cast in the election. When the train passed through Springfield, Seward and Lincoln were introduced, with Lincoln appearing "embarrassed" and Seward "constrained". In his oratory, Seward spoke of the U.S. as a "tower of freedom", a Union that might even come to include Canada, Latin America, and Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
.
New York was key to the election; a Lincoln loss there would deadlock the Electoral College. Soon after his return from his Midwest tour, Seward embarked on another, speaking to large crowds across the state of New York. At Weed's urging, he went to New York City and gave a patriotic speech before a large crowd on November 3, only three days before the election. On Election Day, Lincoln carried most Northern states, while Breckinridge took the Deep South, Bell three border states, and Douglas won Missouri—the only state Seward campaigned in that Lincoln did not win. Lincoln was elected.
Secession crisis
Lincoln's election had been anticipated in Southern states, and South Carolina and otherDeep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the wa ...
states began to call conventions for the purpose of secession. In the North, there was dissent over whether to offer concessions to the South to preserve the Union, and if conciliation failed, whether to allow the South to depart in peace. Seward favored compromise. He had hoped to remain at home until the New Year, but with the deepening crisis left for Washington in time for the new session of Congress in early December.
The usual tradition was for the leading figure of the winning party to be offered the position of Secretary of State, the most senior Cabinet post. Seward was that person, and around December 12, the vice president-elect, Maine Senator Hannibal Hamlin
Hannibal Hamlin (August 27, 1809 – July 4, 1891) was an American attorney and politician who served as the 15th vice president of the United States from 1861 to 1865, during President Abraham Lincoln's first term. He was the first Republic ...
, offered Seward the position on Lincoln's behalf. At Weed's advice, Seward was slow to formally accept, doing so on December 28, 1860, though well before Inauguration Day, March 4, 1861. Lincoln remained in Illinois until mid-February, and he and Seward communicated by letter.
As states in the Deep South prepared to secede in late 1860, Seward met with important figures from both sides of the sectional divide. Seward introduced a proposed constitutional amendment preventing federal interference with slavery. This was done at Lincoln's private request; the president-elect hoped that the amendment, and a change to the Fugitive Slave Act to allow those captured a jury trial, would satisfy both sides. Congressmen introduced many such proposals, and Seward was appointed to a committee of 13 senators to consider them. Lincoln was willing to guarantee the security of slavery in the states that currently had it, but he rejected any proposal that would allow slavery to expand. It was increasingly clear that the deep South was committed to secession; the Republican hope was to provide compromises to keep the border slave states in the Union. Seward voted against the Crittenden Compromise
The Crittenden Compromise was an unsuccessful proposal to permanently enshrine slavery in the United States Constitution, and thereby make it unconstitutional for future congresses to end slavery. It was introduced by United States Senator J ...
on December 28, but quietly continued to seek a compromise that would keep the border states in the Union.
Seward gave a major speech on January 12, 1861. By then, he was known to be Lincoln's choice as Secretary of State, and with Lincoln staying silent, it was widely expected that he would propound the new administration's plan to save the Union. Accordingly, he spoke to a crowded Senate, where even Jefferson Davis attended despite Mississippi's secession, and to packed galleries. He urged the preservation of the Union, and supported an amendment such as the one he had introduced, or a constitutional convention, once passions had cooled. He hinted that New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of '' Nuevo México'' becomin ...
might be a slave state, and urged the construction of two transcontinental railroads, one northern, one southern. He suggested the passage of legislation to bar interstate invasions such as that by John Brown. Although Seward's speech was widely applauded, it gained a mixed reaction in the border states to which he had tried to appeal. Radical Republicans were not willing to make concessions to the South, and were angered by the speech. Pennsylvania Congressman Thaddeus Stevens
Thaddeus Stevens (April 4, 1792August 11, 1868) was a member of the United States House of Representatives from Pennsylvania, one of the leaders of the Radical Republican faction of the Republican Party during the 1860s. A fierce opponent of sla ...
, a radical, warned that if Lincoln, like Seward, ignored the Republican platform and tried to purchase peace through concessions, he would retire, as too old to bear the years of warfare in the Republican Party that would result.
Lincoln applauded Seward's speech, which he read in Springfield, but refused to approve any compromise that could lead to a further expansion of slavery. Once Lincoln left Springfield on February 11, he gave speeches, stating in Indianapolis that it would not be coercing a state if the federal government insisted on retaining or retaking property that belonged to it. This came as the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
still held Fort Sumter; the president-elect's words upset moderate southerners. Virginia Congressman Sherrard Clemens
Sherrard Clemens (April 28, 1820 – June 30, 1881) was a nineteenth-century politician and lawyer from Virginia and Missouri. He was a cousin to author Samuel L. Clemens (a.k.a. Mark Twain). The unincorporated community of Sherrard in M ...
wrote,
Lincoln arrived in Washington, unannounced and incognito, early on the morning of February 23, 1861. Seward had been advised by General Winfield Scott that there was a plot to assassinate Lincoln in Baltimore when he passed through the city. Senator Seward sent his son Frederick to warn Lincoln in Philadelphia, and the president-elect decided to travel alone but for well-armed bodyguards. Lincoln travelled without incident and came to regret his decision as he was widely mocked for it. Later that morning, Seward accompanied Lincoln to the White House, where he introduced the Illinoisan to President Buchanan.
Seward and Lincoln differed over two issues in the days before the inauguration: the composition of Lincoln's cabinet, and his inaugural address. Given a draft of the address, Seward softened it to make it less confrontational toward the South; Lincoln accepted many of the changes, though he gave it, according to Seward biographer Glyndon G. Van Deusen, "a simplicity and a poetic quality lacking in Seward's draft". The differences regarding the Cabinet revolved around the inclusion of Salmon Chase, a radical. Lincoln wanted all elements of the party, as well as representation from outside it; Seward opposed Chase, as well as former Democrats such as Gideon Welles and Montgomery Blair
Montgomery Blair (May 10, 1813 – July 27, 1883) was an American politician and lawyer from Maryland. He served in the Lincoln administration cabinet as Postmaster-General from 1861 to 1864, during the Civil War. He was the son of Francis Pres ...
. Seward did not get his way, and gave Lincoln a letter declining the post of Secretary of State. Lincoln felt, as he told his private secretary, John Nicolay, that he could not "afford to let Seward take the first trick". No reply or acknowledgment was made by Lincoln until after the inaugural ceremonies were over on March 4, when he asked Seward to remain. Seward did and was both nominated and confirmed by the Senate, with minimal debate, on March 5, 1861.
Secretary of State
Lincoln administration
War breaks out
Lincoln faced the question of what to do about Fort Sumter in Charleston harbor, held by the Army against the will of South Carolinians, who had blockaded it. The fort's commander, Major Robert Anderson, had sent word that he would run out of supplies. Seward, backed by most of the Cabinet, recommended to Lincoln that an attempt to resupply Sumter would be provocative to the border states, that Lincoln hoped to keep from seceding. Seward hinted to the commissioners who had come to Washington on behalf of the Confederacy that Sumter would be surrendered. Lincoln was loath to give up Sumter, feeling it would only encourage the South in its insurgency. With the Sumter issue unresolved, Seward sent Lincoln a memorandum on April 1, proposing various courses of action, including possibly declaring war on France and Spain if certain conditions were not met, and reinforcing the forts along theGulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
. In any event, vigorous policies were needed and the president must either establish them himself or allow a Cabinet member to do so, with Seward making it clear he was willing to do it. Lincoln drafted a reply indicating that whatever policy was adopted, "I must do it", though he never sent it, but met with Seward instead, and what passed between them is not known. Seward's biographers make the point that the note was sent to a Lincoln who had not yet proved himself in office.
Lincoln decided on expeditions to try to relieve Sumter and Florida's Fort Pickens. Meanwhile, Seward was assuring Justice John Archibald Campbell, the intermediary with the Confederate commissioners who had come to Washington in an attempt to secure recognition, that no hostile action would be taken. Lincoln sent a notification to South Carolina's governor of the expedition, and on April 12, Charleston's batteries began firing on Sumter, beginning the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
.
Diplomacy
When the war started, Seward turned his attention to making sure that foreign powers did not interfere in the conflict. When, in April 1861, the Confederacy announced that it would authorizeprivateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s, Seward sent word to the American representatives abroad that the U.S. would become party to the Paris Declaration Respecting Maritime Law of 1856. This would outlaw such vessels, but Britain required that, if the U.S. were to become a party, the ratification would not require action to be taken against Confederate vessels.
The Palmerston government considered recognizing the Confederacy as an independent nation. Seward was willing to wage war against Britain if it did and drafted a strong letter for the American Minister in London, Charles Francis Adams, to read to the Foreign Secretary, Lord Russell. Seward submitted it to Lincoln, who, realizing that the Union was in no position to battle both the South and Britain, toned it down considerably, and made it merely a memorandum for Adams's guidance.
In May 1861, Britain and France declared the South to be belligerent
A belligerent is an individual, group, country, or other entity that acts in a hostile manner, such as engaging in combat. The term comes from the Latin ''bellum gerere'' ("to wage war"). Unlike the use of ''belligerent'' as an adjective meaning ...
s by international law, and their ships were entitled to the same rights as U.S.-flagged vessels, including the right to remain 24 hours in neutral ports. Nevertheless, Seward was pleased that both nations would not meet with Confederate commissioners or recognize the South as a nation. Britain did not challenge the Union blockade of Confederate ports, and Seward wrote that if Britain continued to avoid interfering in the war, he would not be overly sensitive to what wording they used to describe their policies.
In November 1861, the , commanded by Captain Charles Wilkes
Charles Wilkes (April 3, 1798 – February 8, 1877) was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842).
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), he commanded ' during the ...
, intercepted the British mail ship RMS ''Trent'' and removed two Confederate diplomats, James Mason
James Neville Mason (; 15 May 190927 July 1984) was an English actor. He achieved considerable success in British cinema before becoming a star in Hollywood. He was the top box-office attraction in the UK in 1944 and 1945; his British films inc ...
and John Slidell. They were held in Boston amid jubilation in the North and outrage in Britain. The British minister in Washington, Lord Lyons, demanded their release, as the U.S. had no right to stop a British-flagged ship traveling between neutral ports. The British drew up war plans to attack New York and sent reinforcements to Canada. Seward worked to defuse the situation. He persuaded Lyons to postpone delivering an ultimatum and told Lincoln that the prisoners would have to be released. Lincoln did let them go, reluctantly, on technical grounds. Relations between the U.S. and Britain soon improved; in April 1862, Seward and Lyons signed a treaty they had negotiated allowing each nation to inspect the other's ships for contraband slaves. In November 1862, with America's image in Britain improved by the issuance of the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War, Civil War. The Proclamation c ...
, the British cabinet decided against recognition of the Confederacy as a nation.
Confederate agents in Britain had arranged for the construction of Confederate ships; most notably the CSS ''Alabama'', which ravaged Union shipping after her construction in 1862. With two more such vessels under construction the following year, supposedly for French interests, Seward pressed Palmerston not to allow them to leave port, and, nearly complete, they were seized by British officials in October 1863.
Involvement in wartime detentions
 From the start of the war until early 1862, when responsibility was passed to the War Department, Seward was in charge of determining who should be detained without charges or trial. Approximately 800 men and a few women, believed to be Southern sympathizers or spies, were detained, usually at the initiation of local officials. Once Seward was informed, he would often order that the prisoner be transferred to federal authorities. Seward was reported to have boasted to Lord Lyons that "I can touch a bell on my right hand, and order the arrest of a citizen ... and no power on earth, except that of the President, can release them. Can the Queen of England do so much?"
In September 1861, Maryland legislators planned to vote to leave the Union. Seward took action against them: his son Frederick, the United States Assistant Secretary of State, reported to his father that the disloyal legislators were in prison. On the evidence provided by detective Allen Pinkerton, Seward in 1862 ordered the arrest of
From the start of the war until early 1862, when responsibility was passed to the War Department, Seward was in charge of determining who should be detained without charges or trial. Approximately 800 men and a few women, believed to be Southern sympathizers or spies, were detained, usually at the initiation of local officials. Once Seward was informed, he would often order that the prisoner be transferred to federal authorities. Seward was reported to have boasted to Lord Lyons that "I can touch a bell on my right hand, and order the arrest of a citizen ... and no power on earth, except that of the President, can release them. Can the Queen of England do so much?"
In September 1861, Maryland legislators planned to vote to leave the Union. Seward took action against them: his son Frederick, the United States Assistant Secretary of State, reported to his father that the disloyal legislators were in prison. On the evidence provided by detective Allen Pinkerton, Seward in 1862 ordered the arrest of Rose Greenhow
Rose O'Neal Greenhow (1813– October 1, 1864) was a renowned Confederate spy during the American Civil War. A socialite in Washington, D.C., during the period before the war, she moved in important political circles and cultivated friendsh ...
, a Washington socialite with Confederate sympathies. Greenhow had sent a stream of reports south, which continued even after she was placed under house arrest. From Washington's Old Capitol Prison
The Old Brick Capitol in Washington, D.C., served as the temporary Capitol of the United States from 1815 to 1819. The building was a private school, a boarding house, and, during the American Civil War, a prison known as the Old Capitol Pris ...
, the "Rebel Rose" provided newspaper interviews until she was allowed to cross into Confederate territory.
When Seward received allegations that former president Pierce was involved in a plot against the Union, he asked Pierce for an explanation. Pierce indignantly denied it. The matter proved to be a hoax, and the administration was embarrassed. On February 14, 1862, Lincoln ordered that responsibility for detentions be transferred to the War Department, ending Seward's part in them.
Relationship with Lincoln
Seward had mixed feelings about the man who had blocked him from the presidency. One story is that when Seward was told that to denyCarl Schurz
Carl Schurz (; March 2, 1829 – May 14, 1906) was a German revolutionary and an American statesman, journalist, and reformer. He immigrated to the United States after the German revolutions of 1848–1849 and became a prominent member of the new ...
an office would disappoint him, Seward angrily stated, "Disappointment! You speak to me of disappointment! To me, who was justly entitled to the Republican nomination for the presidency, and who had to stand aside and see it given to a little Illinois lawyer!" Despite his initial reservations about Lincoln's abilities, he came to admire Lincoln as the president grew more confident in his job. Seward wrote to his wife in June 1861, "Executive skill and vigor are rare qualities. The President is the best of us, but he needs constant and assiduous cooperation." According to Goodwin, "Seward would become his most faithful ally in the cabinet ... Seward's mortification at not having received his party's nomination never fully abated, but he no longer felt compelled to belittle Lincoln to ease his pain." Lincoln, a one-term congressman, was inexperienced in Washington ways and relied on Seward's advice on protocol and social etiquette.
The two men built a close personal and professional relationship. Lincoln fell into the habit of entrusting Seward with tasks not within the remit of the State Department, for example asking him to examine a treaty with the Delaware Indians. Lincoln would come to Seward's house and the two lawyers would relax before the fire, chatting. Seward began to feature in the president's humorous stories. For example, Lincoln would tell of Seward remonstrating with the president, whom he found polishing his boots, "In Washington, we do not blacken our own boots," with Lincoln's response, "Indeed, then whose boots ''do'' you blacken, Mr. Secretary?"
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War, Civil War. The Proclamation c ...
draft on July 22, 1862. Seward is seated at mid-right. Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and a ...
by Francis Carpenter.''(Clickable image—use cursor to identify.)''
poly 269 892 254 775 193 738 130 723 44 613 19 480 49 453 75 434 58 376 113 344 133 362 143 423 212 531 307 657 357 675 409 876 Edwin Stanton
poly 169 282 172 244 244 201 244 148 265 117 292 125 305 166 304 204 321 235 355 296 374 348 338 395 341 469 Salmon Chase
poly 569 893 535 708 427 613 357 562 377 456 393 404 468 351 451 317 473 259 520 256 544 283 530 339 526 374 559 401 594 431 639 494 715 542 692 551 693 579 672 546 623 552 596 617 698 629 680 852 Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
poly 692 514 740 441 788 407 772 350 800 303 831 297 861 329 867 381 868 409 913 430 913 471 847 532 816 533 709 533 Gideon Welles
poly 703 783 752 769 825 627 907 620 929 569 905 538 886 563 833 563 873 502 930 450 1043 407 1043 389 1036 382 1042 363 1058 335 1052 333 1052 324 1081 318 1124 338 1133 374 1116 412 1132 466 1145 509 1117 588 1087 632 1083 706 William Seward
poly 905 418 941 328 987 295 995 284 982 244 990 206 1036 207 1046 247 1047 284 1066 312 1071 314 1049 327 1044 354 1033 383 1033 407 921 453 Caleb Smith
poly 1081 308 1102 255 1095 220 1093 181 1109 161 1145 160 1169 191 1153 227 1153 246 1199 268 1230 310 1239 377 1237 443 1220 486 1125 451 1118 412 1136 378 1124 342 Montgomery Blair
Montgomery Blair (May 10, 1813 – July 27, 1883) was an American politician and lawyer from Maryland. He served in the Lincoln administration cabinet as Postmaster-General from 1861 to 1864, during the Civil War. He was the son of Francis Pres ...
poly 1224 479 1298 416 1304 379 1295 329 1325 310 1360 324 1370 359 1371 385 1371 397 1413 425 1422 497 1440 563 1348 555 1232 517 Edward Bates
Edward Bates (September 4, 1793 – March 25, 1869) was a lawyer and politician. He represented Missouri in the US House of Representatives and served as the U.S. Attorney General under President Abraham Lincoln. A member of the influentia ...
poly 625 555 595 620 699 625 730 550 Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War, Civil War. The Proclamation c ...
poly 120 80 120 300 3 300 3 80 Portrait of Simon Cameron
poly 752 196 961 189 948 8 735 10 Portrait of Andrew Jackson
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
's incursion into the North to issue it. In the interim, Seward cautiously investigated how foreign powers might react to such a proclamation, and learned it would make them less likely to interfere in the conflict.
Seward was not close to Lincoln's wife Mary, who by some accounts had opposed his appointment as Secretary of State. Mary Lincoln developed such a dislike for Seward that she instructed her coachman to avoid passing by the Seward residence. The Secretary of State enjoyed the company of the younger Lincoln boys, Willie
Willy or Willie is a masculine, male given name, often a diminutive form of William or Wilhelm, and occasionally a nickname. It may refer to:
People Given name or nickname
* Willie Aames (born 1960), American actor, television director, and sc ...
and Tad, presenting them with two cats from his assortment of pets.
Seward accompanied Lincoln to Gettysburg, Pennsylvania
Gettysburg (; non-locally ) is a borough and the county seat of Adams County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The Battle of Gettysburg (1863) and President Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address are named for this town.
Gettysburg is home to ...
, in November 1863, where Lincoln was to deliver a short speech, that would become famous as the Gettysburg Address
The Gettysburg Address is a speech that U.S. President Abraham Lincoln delivered during the American Civil War at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery, now known as Gettysburg National Cemetery, in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania on the ...
. The night before the speech, Lincoln met with Seward. There is no surviving evidence that Seward authored any changes: he stated after the address, when asked if had had any hand in it, that only Lincoln could have made that speech. Seward also proposed to Lincoln that he proclaim a day of national thanksgiving, and drafted a proclamation to that effect. Although post-harvest thanksgiving celebrations had long been held, this first formalized Thanksgiving Day
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden and ...
as a national observance.
1864 election; Hampton Roads Conference
It was far from certain that Lincoln would even be nominated in 1864, let alone re-elected, as the tide of war, though generally favoring the North, washed back and forth. Lincoln sought nomination by the National Union Party, composed of Republicans and War Democrats. No one proved willing to oppose Lincoln, who was nominated. Seward was by then unpopular among many Republicans and opponents sought to prompt his replacement by making Lincoln's running mate former New York Democratic senatorDaniel S. Dickinson
Daniel Stevens Dickinson (September 11, 1800April 12, 1866) was an American politician and lawyer, most notable as a United States senator from 1844 to 1851.
Biography
Born in Goshen, Connecticut, he moved with his parents to Guilford, Chenan ...
; under the political customs of the time, one state could not hold two positions as prestigious as vice president and Secretary of State. Administration forces turned back Dickinson's bid, nominating instead Military Governor of Tennessee Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a De ...
, with whom Seward had served in the Senate. Lincoln was re-elected in November; Seward sat with Lincoln and the assistant presidential secretary, John Hay
John Milton Hay (October 8, 1838July 1, 1905) was an American statesman and official whose career in government stretched over almost half a century. Beginning as a private secretary and assistant to Abraham Lincoln, Hay's highest office was U ...
, as the returns came in.
 In January 1865,
In January 1865, Francis Preston Blair
Francis Preston Blair Sr. (April 12, 1791 – October 18, 1876) was an American journalist, newspaper editor, and influential figure in national politics advising several U.S. presidents across party lines.
Blair was an early member of the De ...
, father of former Lincoln Postmaster General
A Postmaster General, in Anglosphere countries, is the chief executive officer of the postal service of that country, a ministerial office responsible for overseeing all other postmasters. The practice of having a government official responsib ...
Montgomery Blair, went, with Lincoln's knowledge, to the Confederate capital of Richmond to propose to Davis that North and South unite to expel the French from their domination of Mexico. Davis appointed commissioners (Vice President Alexander Stephens, former U.S. Supreme Court justice Campbell, and former Confederate Secretary of State Robert M. T. Hunter) to negotiate. They met with Lincoln and Seward at the Hampton Roads Conference
The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and representatives of the unrecognized breakaway Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat ''River Queen'' in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to disc ...
the following month. Lincoln would settle for nothing short of a cessation of resistance to the federal government and an end to slavery; the Confederates would not even concede that they and the Union were one nation. There was much friendly talk, as most of them had served together in Washington, but no agreement. After the conference broke up, Seward sent a bucket of champagne to the Confederates, conveyed by a black oarsman in a rowboat, and called to the southerners, "keep the champagne, but return the Negro."
Assassination attempt
 John Wilkes Booth had originally planned to kidnap Lincoln, and recruited conspirators, including Lewis Powell, to help him. Having found no opportunity to abduct the president, on April 14, 1865, Booth assigned Powell to assassinate Seward, with George Atzerodt to kill Vice President Johnson and himself to kill Lincoln, which would slay the three senior members of the Executive Branch. Accordingly, another member of the conspiracy, David Herold, led Powell to the Seward home on horseback and was responsible for holding Powell's horse while he committed the attack. Seward had been hurt in an accident some days before, and Powell gained entry to the home on the excuse he was delivering medicine to the injured man, but was stopped at the top of the stairs by Seward's son Frederick, who insisted Powell give him the medicine. Powell instead attempted to fire on Frederick and beat him over the head with the barrel of his gun when it misfired. Powell burst through the door, threw Fanny Seward (Seward's daughter) to one side, jumped on the bed, and stabbed William Seward in the face and neck five times. A soldier assigned to guard and nurse the secretary, Private George F. Robinson, jumped on Powell, forcing him from the bed. Private Robinson and Augustus Henry Seward, another of Seward's sons, were also injured in their struggle with the would-be assassin. Ultimately, Powell fled, stabbing a messenger, Emerick Hansell, as he went, only to find that Herold, panicked by the screams from the house, had left with both horses. Seward was at first thought dead, but revived enough to instruct Robinson to send for the police and lock the house until they arrived.
John Wilkes Booth had originally planned to kidnap Lincoln, and recruited conspirators, including Lewis Powell, to help him. Having found no opportunity to abduct the president, on April 14, 1865, Booth assigned Powell to assassinate Seward, with George Atzerodt to kill Vice President Johnson and himself to kill Lincoln, which would slay the three senior members of the Executive Branch. Accordingly, another member of the conspiracy, David Herold, led Powell to the Seward home on horseback and was responsible for holding Powell's horse while he committed the attack. Seward had been hurt in an accident some days before, and Powell gained entry to the home on the excuse he was delivering medicine to the injured man, but was stopped at the top of the stairs by Seward's son Frederick, who insisted Powell give him the medicine. Powell instead attempted to fire on Frederick and beat him over the head with the barrel of his gun when it misfired. Powell burst through the door, threw Fanny Seward (Seward's daughter) to one side, jumped on the bed, and stabbed William Seward in the face and neck five times. A soldier assigned to guard and nurse the secretary, Private George F. Robinson, jumped on Powell, forcing him from the bed. Private Robinson and Augustus Henry Seward, another of Seward's sons, were also injured in their struggle with the would-be assassin. Ultimately, Powell fled, stabbing a messenger, Emerick Hansell, as he went, only to find that Herold, panicked by the screams from the house, had left with both horses. Seward was at first thought dead, but revived enough to instruct Robinson to send for the police and lock the house until they arrived.
 Almost simultaneously with the attack on Seward, Booth had mortally wounded Lincoln at Ford's Theatre. Atzerodt, however, decided not to go through with the attack on Johnson. When Secretary of War Edwin Stanton and Navy Secretary Gideon Welles hurried to Seward's home to find out what had happened, they found blood everywhere.
All five men injured that night at the Seward home survived. Powell was captured the next day at the boarding house of
Almost simultaneously with the attack on Seward, Booth had mortally wounded Lincoln at Ford's Theatre. Atzerodt, however, decided not to go through with the attack on Johnson. When Secretary of War Edwin Stanton and Navy Secretary Gideon Welles hurried to Seward's home to find out what had happened, they found blood everywhere.
All five men injured that night at the Seward home survived. Powell was captured the next day at the boarding house of Mary Surratt
Mary Elizabeth Jenkins SurrattCashin, p. 287.Steers, 2010, p. 516. (1820 or May 1823 – July 7, 1865) was an American boarding house owner in Washington, D.C., who was convicted of taking part in the conspiracy which led to the assassi ...
. He was hanged
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging ...
on July 7, 1865, along with Herold, Atzerodt, and Surratt, convicted as conspirators in the Lincoln assassination. Their deaths occurred only weeks after that of Seward's wife Frances, who never recovered from the shock of the assassination attempt.
Johnson administration
Reconstruction and impeachment
 In the first months of the new Johnson administration, Seward did not work much with the president. Seward was at first recovering from his injuries, and Johnson was ill for a time in the summer of 1865. Seward was likely in accord with Johnson's relatively gentle terms for the South's re-entry to the Union, and with his pardon of all Confederates but those of high rank.
In the first months of the new Johnson administration, Seward did not work much with the president. Seward was at first recovering from his injuries, and Johnson was ill for a time in the summer of 1865. Seward was likely in accord with Johnson's relatively gentle terms for the South's re-entry to the Union, and with his pardon of all Confederates but those of high rank. Radical Republicans
The Radical Republicans (later also known as "Stalwarts") were a faction within the Republican Party, originating from the party's founding in 1854, some 6 years before the Civil War, until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Recons ...
such as Stanton and Pennsylvania Representative Thaddeus Stevens proposed that the freed slaves be given the vote, but Seward was content to leave that to the states (few Northern states gave African-Americans the ballot), believing the priority should be reconciling the power-holding white populations of the North and South to each other.
Unlike Lincoln, who had a close rapport with Seward, Johnson kept his own counsel and generally did not take advantage of Seward's political advice as Congress prepared to meet in December 1865. Johnson had issued proclamations allowing for the southern states to reform their state governments and hold elections; they mostly elected men who had served as prewar or wartime leaders. Seward advised Johnson to state, in his first annual message to Congress, that southern states meet three conditions for readmission to the Union: repeal of secession, repudiation of the war debt incurred by the rebel governments, and ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment. Johnson, hoping to appeal to both Republicans and Democrats, did not take the suggestion. Congress did not seat southerners but appointed a joint committee of both houses to make recommendations on the issue. Johnson opposed the committee; Seward was prepared to wait and see.
In early 1866, Congress and president battled over the extension of the authorization of the Freedmen's Bureau
The Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands, usually referred to as simply the Freedmen's Bureau, was an agency of early Reconstruction, assisting freedmen in the South. It was established on March 3, 1865, and operated briefly as a ...
. Both sides agreed that the bureau should end after the states were re-admitted, the question was whether that would be soon. With Seward's support, Johnson vetoed the bill. Republicans in Congress were angry with both men, and tried but failed to override Johnson's veto. Johnson vetoed the Civil Rights Bill, which was to grant citizenship to the freedmen. Seward advised a conciliatory veto message; Johnson ignored him, telling Congress it had no right to pass bills affecting the South until it seated the region's congressmen. This time Congress overrode his veto, gaining the necessary two-thirds majority of each house, the first time this had been done on a major piece of legislation in American history.
 Johnson hoped the public would elect congressmen who agreed with him in the 1866 midterm elections, and embarked on a trip, dubbed the
Johnson hoped the public would elect congressmen who agreed with him in the 1866 midterm elections, and embarked on a trip, dubbed the Swing Around the Circle
Swing Around the Circle is the nickname for a speaking campaign undertaken by President of the United States, United States President Andrew Johnson between August 27 and September 15, 1866, in which he tried to gain support for his mild Reconstru ...
, giving speeches in a number of cities that summer. Seward was among the officials who went with him. The trip was a disaster for Johnson; he made a number of ill-considered statements about his opponents that were criticized in the press. The Radical Republicans were strengthened by the results of the elections. The Republican anger against Johnson extended to his Secretary of State—Maine Senator William P. Fessenden
William Pitt Fessenden (October 16, 1806September 8, 1869) was an American politician from the U.S. state of Maine. Fessenden was a Whig (later a Republican) and member of the Fessenden political family. He served in the United States House ...
said of Johnson, "he began by meaning well, but I fear that Seward's evil counsels have carried him beyond the reach of salvation".
In February 1867, both houses of Congress passed the Tenure of Office Bill, purporting to restrict Johnson in the removal of presidential appointees. Johnson suspended, then fired, Stanton over Reconstruction policy differences, leading to the president's impeachment for allegedly violating the Tenure of Office Act. Seward recommended that Johnson hire the renowned attorney, William M. Evarts
William Maxwell Evarts (February 6, 1818February 28, 1901) was an American lawyer and statesman from New York who served as U.S. Secretary of State, U.S. Attorney General and U.S. Senator from New York. He was renowned for his skills as a litig ...
, and, with Weed, raised funds for the president's successful defense.
Mexico
Mexico was strife-torn in the early 1860s, as it often had been in the fifty years since its independence. There had been 36 changes of government and 73 presidents, and a refusal to pay foreign debts. France, Spain, and Great Britain joined together to intervene in 1861 on the pretext of protecting their nationals, and to secure repayment of debt. Spain and the British soon withdrew, but France remained. Seward realized that a challenge to France at this point might provoke its intervention on the Confederate side, so he stayed quiet. In 1864, French emperorNapoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
set his cousin, Archduke Maximilian of Austria on the Mexican throne, with French military support. Seward used strident language publicly but was privately conciliatory toward the French.
The Confederates had been supportive of France's actions. Upon returning to work after the assassination attempt, Seward warned France that the U.S. still wanted the French gone from Mexico. Napoleon feared that the large, battle-tested American army would be used against his troops. Seward remained conciliatory, and in January 1866, Napoleon agreed to withdraw his troops after a twelve- to eighteen-month period, during which time Maximilian could consolidate his position against the insurgency led by Benito Juárez.
In December 1865, Seward bluntly told Napoleon that the United States desired friendship, but, "this policy would be brought into imminent Jeopardy unless France could deem it consistent with her interest and honor to desist from the prosecution of armed intervention in Mexico." Napoleon tried to postpone the French departure, but the Americans had General Phil Sheridan and an experienced combat army on the north bank of the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
and Seward held firm. Napoleon suggested a new Mexican government that would exclude both Maximilian and Juárez. The Americans had recognized Juárez as the legitimate president and were not willing to consider this. In the meantime, Juárez, with the help of American military aid, was advancing through northeast Mexico. The French withdrew in early 1867. Maximilian stayed behind but was soon captured by Juárez's troops. Although both the U.S. and France urged Juárez against it, the deposed emperor was executed by firing squad on June 19, 1867.
Territorial expansion and Alaska
 Although in speeches Seward had predicted all of North America joining the Union, he had, as a senator, opposed the
Although in speeches Seward had predicted all of North America joining the Union, he had, as a senator, opposed the Gadsden Purchase
The Gadsden Purchase ( es, region=MX, la Venta de La Mesilla "The Sale of La Mesilla") is a region of present-day southern Arizona and southwestern New Mexico that the United States acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Mesilla, which took effe ...
obtaining land from Mexico, and Buchanan's attempts to purchase Cuba from Spain. Those stands were because the land to be secured would become slave territory. After the Civil War, this was no longer an issue, and Seward became an ardent expansionist and even contemplated the purchase of Greenland and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
. The Union Navy had been hampered due to the lack of overseas bases during the war, and Seward also believed that American trade would be helped by the purchase of overseas territory.
Believing, along with Lincoln, that the U.S. needed a naval base in the Caribbean, in January 1865, Seward offered to purchase the Danish West Indies (today the United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
). Late that year, Seward sailed for the Caribbean on a naval vessel. Among the ports of call was St. Thomas in the Danish West Indies, where Seward admired the large, easily defended harbor. Another stop was in the Dominican Republic, where he opened talks to obtain Samaná Bay. When Congress reconvened in December 1866, Seward caused a sensation by entering the chamber of the House of Representatives and sitting down with the administration's enemy, Congressman Stevens, persuading him to support an appropriation for more money to expedite the purchase of Samaná, and sent his son Frederick to the Dominican Republic to negotiate a treaty. Both attempts fell through; the Senate, in the dying days of the Johnson administration, failed to ratify a treaty for the purchase of the Danish possessions, while negotiations with the Dominican Republic were not successful.
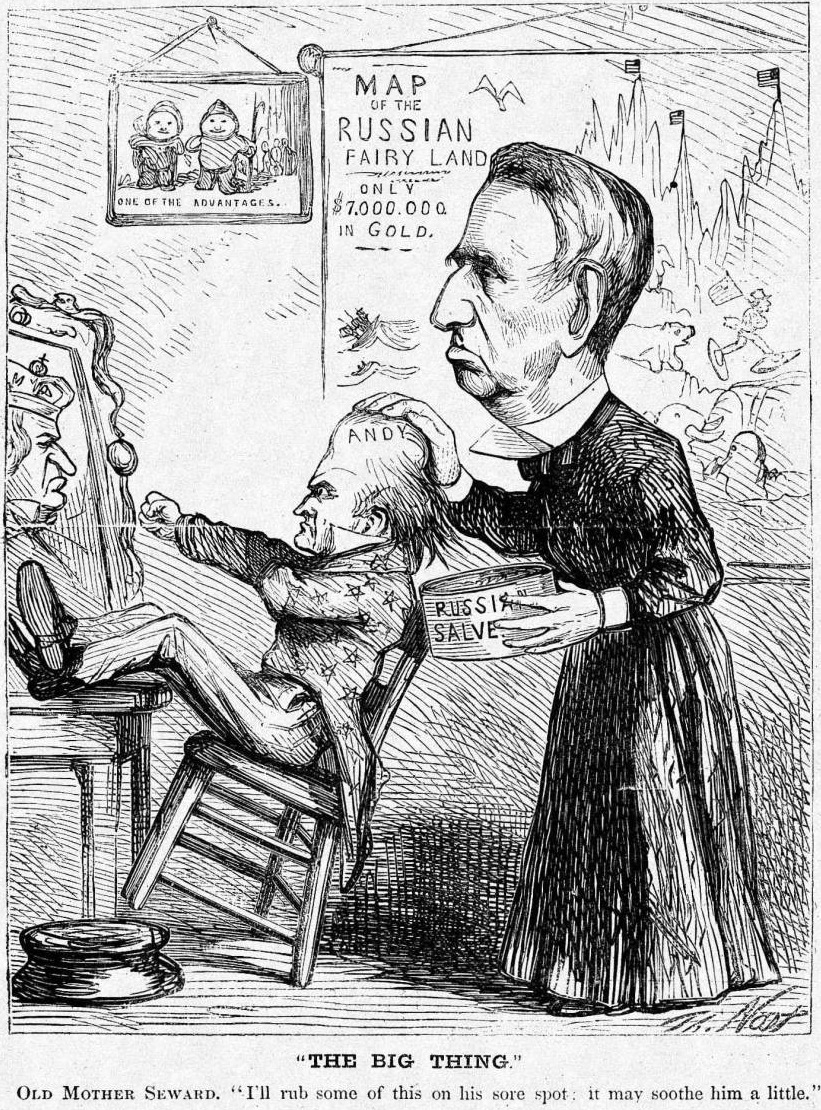 Seward had been interested in whaling as a senator; his interest in Russian America was a byproduct of this. In his speech prior to the 1860 convention, he predicted the territory would become part of the U.S., and when he learned in 1864 that it might be for sale, he pressed the Russians for negotiations. Russian minister Baron Eduard de Stoeckl recommended the sale. The territory was a money loser, and the Russian-American Company itself allowed its charter to expire in 1861. Russia could use the money more efficiently for its expansion in Siberia or Central Asia. Keeping it ran the risk of it being captured in war by the British, or overrun by American settlers. Stoeckl was given the authority to make the sale and when he returned in March 1867, negotiated with the Secretary of State. Seward initially offered $5 million; the two men settled on $7 million and on March 15, Seward presented a draft treaty to the Cabinet. Stoeckl's superiors raised several concerns; to induce him to waive them, the final purchase price was increased to $7.2 million. The treaty was signed in the early morning of March 30, 1867, and ratified by the Senate on April 10. Stevens sent the secretary a note of congratulations, predicting that the
Seward had been interested in whaling as a senator; his interest in Russian America was a byproduct of this. In his speech prior to the 1860 convention, he predicted the territory would become part of the U.S., and when he learned in 1864 that it might be for sale, he pressed the Russians for negotiations. Russian minister Baron Eduard de Stoeckl recommended the sale. The territory was a money loser, and the Russian-American Company itself allowed its charter to expire in 1861. Russia could use the money more efficiently for its expansion in Siberia or Central Asia. Keeping it ran the risk of it being captured in war by the British, or overrun by American settlers. Stoeckl was given the authority to make the sale and when he returned in March 1867, negotiated with the Secretary of State. Seward initially offered $5 million; the two men settled on $7 million and on March 15, Seward presented a draft treaty to the Cabinet. Stoeckl's superiors raised several concerns; to induce him to waive them, the final purchase price was increased to $7.2 million. The treaty was signed in the early morning of March 30, 1867, and ratified by the Senate on April 10. Stevens sent the secretary a note of congratulations, predicting that the Alaska Purchase
The Alaska Purchase (russian: Продажа Аляски, Prodazha Alyaski, Sale of Alaska) was the United States' acquisition of Alaska from the Russian Empire. Alaska was formally transferred to the United States on October 18, 1867, through a ...
would be seen as one of Seward's greatest accomplishments.
1868 election, retirement and death
Seward hoped that Johnson would be nominated at the1868 Democratic National Convention
The 1868 Democratic National Convention was held at Tammany Hall in New York City between July 4, and July 9, 1868. The first Democratic convention after the conclusion of the American Civil War, the convention was notable for the return of Democ ...
, but the delegates chose former New York Governor Horatio Seymour. The Republicans chose General Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
, who had a hostile relationship with Johnson. Seward gave a major speech on the eve of the election
''The Election'' () is a political drama series produced by Hong Kong Television Network (HKTV). With a budget of HK$15 million, filming started in July 2014 and wrapped up on 28 October 2014. Popularly voted to be the inaugural drama of ...
, endorsing Grant, who was easily elected. Seward met twice with Grant after the election, leading to speculation that he was seeking to remain as secretary for a third presidential term. However, the president-elect had no interest in retaining Seward, and the secretary resigned himself to retirement. Grant refused to have anything to do with Johnson, even declining to ride to his inauguration in the same carriage as the outgoing president, as was customary. Despite Seward's attempts to persuade him to attend Grant's swearing-in, Johnson and his Cabinet spent the morning of March 4, 1869, at the White House dealing with last-minute business, then left once the time for Grant to be sworn in had passed. Seward returned to Auburn.
Restless in Auburn, Seward embarked on a trip across North America by the new transcontinental railroad. In Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
, Utah Territory, he met with Brigham Young
Brigham Young (; June 1, 1801August 29, 1877) was an American religious leader and politician. He was the second president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), from 1847 until his death in 1877. During his time as chu ...
, President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, who had worked as a carpenter on Seward's house (then belonging to Judge Miller) as a young man. On reaching the Pacific Coast, the Seward party sailed north on the steamer '' Active'' to visit Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, Department of Alaska, part of the vast wilderness Seward had acquired for the U.S. After spending time in Oregon and California, the party went to Mexico, where he was given a hero's welcome. After a visit to Cuba, he returned to the U.S., concluding his nine-month trip in March 1870.
In August 1870, Seward embarked on another trip, this time westbound around the world. With him was Olive Risley, daughter of a Treasury Department official, to whom he became close in his final year in Washington. They visited Japan, then China, where they walked on the Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against Eurasian noma ...
. During the trip, they decided that Seward would adopt Olive, and he did so, thus putting an end to gossip and the fears of his sons that Seward would remarry late in life. They spent three months in India, then journeyed through the Middle East and Europe, not returning to Auburn until October 1871.
Back in Auburn, Seward began his memoirs, but only reached his thirties before putting it aside to write of his travels. In these months he was steadily growing weaker. On October 10, 1872, he worked at his desk in the morning as usual, then complained of trouble breathing. Seward grew worse during the day, as his family gathered around him. Asked if he had any final words, he said, "Love one another". Seward died that afternoon. His funeral a few days later was preceded by the people of Auburn and nearby filing past his open casket for four hours. Thurlow Weed was there for the burial of his friend, and Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman (born Araminta Ross, March 10, 1913) was an American abolitionist and social activist. Born into slavery, Tubman escaped and subsequently made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 slaves, including family and friends, u ...
, a former slave whom the Sewards had aided, sent flowers. President Grant sent his regrets he could not be there. William Seward rests with his wife Frances and daughter Fanny (1844–1866), in Fort Hill Cemetery in Auburn.
Legacy and historical view
 Seward's reputation, controversial in life, remained so in death, dividing his contemporaries. Former Navy Secretary Gideon Welles argued that not only did Seward lack principles, Welles was unable to understand how Seward had fooled Lincoln into thinking that he did, gaining entry to the Cabinet thereby. Charles Francis Adams, minister in London during Seward's tenure as secretary, deemed him "more of a politician than a statesman", but
Seward's reputation, controversial in life, remained so in death, dividing his contemporaries. Former Navy Secretary Gideon Welles argued that not only did Seward lack principles, Welles was unable to understand how Seward had fooled Lincoln into thinking that he did, gaining entry to the Cabinet thereby. Charles Francis Adams, minister in London during Seward's tenure as secretary, deemed him "more of a politician than a statesman", but Charles Anderson Dana
Charles Anderson Dana (August 8, 1819 – October 17, 1897) was an American journalist, author, and senior government official. He was a top aide to Horace Greeley as the managing editor of the powerful Republican newspaper '' New-York Tribun ...
, former Assistant Secretary of War, disagreed, writing that Seward had "the most cultivated and comprehensive intellect in the administration" and "what is very rare in a lawyer, a politician, or a statesman—imagination".
Scholars of history have generally praised Seward for his work as Secretary of State; in 1973, Ernest N. Paolino deemed him "the one outstanding Secretary of State after John Quincy Adams". Seward has been given high marks by historians both for his achievements in office, and for his foresight in anticipating the future needs of the U.S. According to his biographer Van Deusen, "his foreign policy built for the future. He wished to prepare America for the great era which lay ahead. So he sought bases, naval stations and, peacefully, additional territory."
Seward's biographers suggested that there are two faces to Seward. One, "John Quincy Adams Seward", dreamed big dreams and tried to convey them in speeches, working to achieve education for all, a fair deal for immigrants, an end to slavery, and an expanded America. The other, "Thurlow Weed Seward", cut backroom deals over cigars and a bottle, and was a pragmatist who often settled for half a loaf when the whole was not achievable. Daniel S. Crofts, in Seward's entry in the ''American National Biography
The ''American National Biography'' (ANB) is a 24-volume biographical encyclopedia set that contains about 17,400 entries and 20 million words, first published in 1999 by Oxford University Press under the auspices of the American Council of Le ...
'' argued, "Each Seward was, of course, a caricature, and both tendencies, at once symbiotic and contradictory, existed in tandem."
The praise Seward has received extends to his work during the Civil War. Stahr wrote that Seward "skillfully managed the nation's foreign affairs, avoiding the foreign intervention that would have ensured that the Confederacy would become a separate nation". Nevertheless, historians, focusing on the battlefields of the Civil War, have given him relatively little attention. Seward has a dozen biographers, while thousands of books focus on Lincoln. According to Crofts, "Seward and Lincoln were the two most important leaders spawned by the intersection of antebellum idealism and partisan politics. Lincoln, of course, will always overshadow Seward. Before 1860, however, Seward eclipsed Lincoln."
Lincoln's assassination helped to seal his greatness, and according to Seward biographer John M. Taylor, to relegate "his associates ... to the status of bit players." Dozens of biographies extolling Lincoln as the quintessential American were written in the decades after the president's death, placing Lincoln on a pedestal of public esteem Seward could not climb. Seward realized this even in life; by one account, when asked to show his scars from the attempt on his life, Seward regretted he had not been martyred along with Lincoln, "I think I deserved the reward of dying there".
Despite his being an ardent supporter of American expansionism during his time in the Cabinet, only Alaska was added to U.S. territory during Seward's service as Secretary of State. (It should be remembered that the purchase of Alaska from Russia was not inevitable; the land had the same latitude as Siberia and was very difficult to farm, while neither gold nor oil nor any other important mineral was discovered there until years after Seward's death.) Nevertheless, his influence extended to later American acquisitions. One of his friends, Hamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American politician who served as the 16th Governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States Senator from New York from 1851 to 1857 and the 26th United States Secretary of State fro ...
, in 1875 signed the trade reciprocity treaty with the Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent islan ...
that eventually led to the American annexation of the islands. William Everts, another Seward friend, in 1877 signed a treaty of friendship with the Samoan Islands
The Samoan Islands ( sm, Motu o Sāmoa) are an archipelago covering in the central South Pacific, forming part of Polynesia and of the wider region of Oceania. Administratively, the archipelago comprises all of the Independent State of Samoa an ...
, laying the groundwork for another American acquisition. A young friend and protege of Seward, Lincoln's assistant private secretary, John Hay, served as a successor to Seward from 1898 to 1905, during which time the U.S. acquired Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
, the Philippines, and the Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone ( es, Zona del Canal de Panamá), also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the ter ...
.
Stahr believes that Seward's influence is still felt today:
See also
* Sites and works regarding William H. SewardReferences
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * Temple, William H. "William H. Seward: Secretary of State March 5, 1861, to March 4, 1869 " in Samuel Flagg Bemis, ed. ''The American Secretaries of State and their Diplomacy'' (1928) vol VII pp 3–115. * *External links
Frances Seward
Wife Of Secretary Of State William Seward * Retrieved on 2009-04-30 * *
Joseph Gerald Whelan, William Seward as Expansionist (Ph.D. Thesis, University of Rochester, 1959)
* *
William H. Seward Letter, W. S. Hoole Special Collections Library, The University of Alabama
* ttp://www.americanabolitionists.com/abolitionists-and-anti-slavery-activists.html American Abolitionists and Antislavery Activists comprehensive website featuring abolitionist and anti-slavery activists in the United States, including political leaders; also provides list of antislavery organizations.
Seward Family Digital Archive
Letters and photographs by and about members of the Seward family. , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Seward, William H. 1801 births 1872 deaths 19th-century American Episcopalians 19th-century American politicians American militia generals Andrew Johnson administration cabinet members Anti-Masonic Party politicians from New York (state) Burials in New York (state) Candidates in the 1856 United States presidential election Candidates in the 1860 United States presidential election Christian abolitionists Governors of New York (state) History of the foreign relations of the United States Lincoln administration cabinet members New York (state) lawyers New York (state) Republicans New York (state) state senators New York (state) Whigs People associated with the assassination of Abraham Lincoln People from Florida, Orange County, New York People from Goshen, New York People of New York (state) in the American Civil War People of pre-statehood Alaska Politicians from Auburn, New York Politicians from Orange County, New York Radical Republicans Republican Party United States senators from New York (state) Seward family Stabbing attacks in the United States Stabbing survivors Underground Railroad people Union College (New York) alumni Union (American Civil War) political leaders United States Secretaries of State Whig Party state governors of the United States Whig Party United States senators