Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of
 By the 18th century, the Wyoming Valley was inhabited by the
By the 18th century, the Wyoming Valley was inhabited by the

 Wilkes-Barre's population skyrocketed due to the discovery of
Wilkes-Barre's population skyrocketed due to the discovery of
 Wilkes-Barre is located within Pennsylvania's
Wilkes-Barre is located within Pennsylvania's

 Manufacturing and retail remained Wilkes-Barre's strongest industries, but the city's economy took a major blow from
Manufacturing and retail remained Wilkes-Barre's strongest industries, but the city's economy took a major blow from
 On June 9, 2005, Mayor Thomas M. Leighton unveiled his ''"I believe..."'' campaign for Wilkes-Barre, which was intended to boost the city's spirits. Construction began on a planned downtown theatre complex, which had a grand opening on June 30, 2006. Renovation of the landmark Hotel Sterling was being pursued by CityVest, a nonprofit developer. The expansion of
On June 9, 2005, Mayor Thomas M. Leighton unveiled his ''"I believe..."'' campaign for Wilkes-Barre, which was intended to boost the city's spirits. Construction began on a planned downtown theatre complex, which had a grand opening on June 30, 2006. Renovation of the landmark Hotel Sterling was being pursued by CityVest, a nonprofit developer. The expansion of




 According to the
According to the
 Wilkes-Barre has a Downtown Riverfront Park system that contains 91 acres of open space.
Kirby Park is a public park located along the western bank of the Susquehanna River. Kirby Park is one of the region's most valued recreational resources. Given to the city of Wilkes-Barre by the Kirby Family, the park welcomes hundreds of thousands each year. The park is the setting for the city's annual Cherry Blossom Festival (held during the last weekend of April) and the city's July 4 Celebration. Its amenities include tennis courts, a fitness trail, pond, walking paths, running track, softball fields, parking area, volleyball courts, pavilions, and more.
Nesbitt Park is also located on the west side of the Susquehanna River. It is located across from Kirby Park. Nesbitt is open to the public. It has walking paths and areas for picnicking.
The River Common is located along the eastern bank of the Susquehanna River. The Market Street Bridge bisects the park. The River Common joins with the Luzerne County Courthouse grounds. Its features include a 750-person amphitheater, paved walk-ways, gardens, ornamental trees, seating areas, a fishing pier, and two grand gateways connecting the city to the river.
Wilkes-Barre has a Downtown Riverfront Park system that contains 91 acres of open space.
Kirby Park is a public park located along the western bank of the Susquehanna River. Kirby Park is one of the region's most valued recreational resources. Given to the city of Wilkes-Barre by the Kirby Family, the park welcomes hundreds of thousands each year. The park is the setting for the city's annual Cherry Blossom Festival (held during the last weekend of April) and the city's July 4 Celebration. Its amenities include tennis courts, a fitness trail, pond, walking paths, running track, softball fields, parking area, volleyball courts, pavilions, and more.
Nesbitt Park is also located on the west side of the Susquehanna River. It is located across from Kirby Park. Nesbitt is open to the public. It has walking paths and areas for picnicking.
The River Common is located along the eastern bank of the Susquehanna River. The Market Street Bridge bisects the park. The River Common joins with the Luzerne County Courthouse grounds. Its features include a 750-person amphitheater, paved walk-ways, gardens, ornamental trees, seating areas, a fishing pier, and two grand gateways connecting the city to the river.
 The city's population has been in constant decline since the 1930s, but the decline has been slowing in recent decades, and saw growth as of 2020. As of the 2020 census, there were 44,328 people and 15,581 households residing in the city. The popeulation density was 5,945 per square mile. The racial makeup of the city was 69.80%
The city's population has been in constant decline since the 1930s, but the decline has been slowing in recent decades, and saw growth as of 2020. As of the 2020 census, there were 44,328 people and 15,581 households residing in the city. The popeulation density was 5,945 per square mile. The racial makeup of the city was 69.80%

 The Luzerne County
The Luzerne County




Greater Wilkes-Barre Chamber of Commerce
* {{Authority control 1769 establishments in Pennsylvania Cities in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania Cities in Pennsylvania County seats in Pennsylvania Municipalities of the Anthracite Coal Region of Pennsylvania Populated places established in 1769 Pennsylvania populated places on the Susquehanna River
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ...
of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the second-largest city, after Scranton, in the Scranton–Wilkes-Barre–Hazleton, PA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which had a population of 563,631 as of the 2010 census and is the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Pennsylvania after the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
, Greater Pittsburgh, and the Lehigh Valley with an urban population of 401,884.
Scranton/Wilkes-Barre is the cultural and economic center of a region called Northeastern Pennsylvania, which is home to over 1.3 million residents.
Wilkes-Barre and the surrounding Wyoming Valley are framed by the Pocono Mountains to the east, the Endless Mountains to the north and west, and the Lehigh Valley to the south. The Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
flows through the center of the valley and defines the northwestern border of the city.
Wilkes-Barre was founded in 1769 and formally incorporated as a borough in 1806, and as a city in 1869. The city grew rapidly in the 19th century after the discovery of nearby coal reserves and the arrival of hundreds of thousands of immigrants who provided a labor force for the local mines. The coal mining fueled industrialization in the city, which reached the height of its prosperity in the first half of the 20th century. Its population peaked at more than 86,000 in 1930. Following World War II, the city's economy declined due to the collapse of industry. The Knox Mine disaster
Knox may refer to:
Places United States
* Fort Knox, a United States Army post in Kentucky
** United States Bullion Depository, a high security storage facility commonly called Fort Knox
* Fort Knox (Maine), a fort located on the Penobscot River ...
accelerated this trend after large portions of the area's coal mines were flooded and could not be reopened. Today, the city has around half of its peak population of the 1930s, making it the largest city in Luzerne County and the 13th-largest city in Pennsylvania. The contiguous network of 5 cities and more than 40 boroughs all built in a straight line in Northeastern Pennsylvania's urban area act culturally and logistically as one continuous city, so while the city of Wilkes-Barre itself is a smaller town, the larger unofficial city of Scranton/Wilkes-Barre contains nearly half a million residents in roughly 200 square miles.
Wilkes-Barre is located approximately northwest of Allentown, and northwest of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
.
History
18th century
 By the 18th century, the Wyoming Valley was inhabited by the
By the 18th century, the Wyoming Valley was inhabited by the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
and Delaware Indian (Lenape) tribes. In 1753, the Susquehanna Company was founded in Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the ...
for settling the Wyoming Valley (in modern-day Pennsylvania). Connecticut succeeded in purchasing the land from the Native Americans; however, Pennsylvania already claimed the very same territory through a purchase they made in 1736. In 1762, roughly two hundred Connecticut settlers (Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United S ...
s) established a settlement near Mill Creek. They planted wheat and constructed log cabins. The Yankees returned to New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
for the winter.
The Connecticut settlers returned in the spring of 1763 with their families and additional supplies. A party of Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
also visited the area with the dual purpose of turning the Delaware (Lenape) against the colonists and killing Teedyuscung, a local Delaware chief. On April 19, 1763, the residence of the chief, along with several others, was set ablaze. Chief Teedyuscung perished in the inferno. The Iroquois let the Delaware believe that this atrocity was committed by the settlers. As a result, the Delaware attacked the colonists on October 15, 1763. Thirty settlers were killed, and several others were taken prisoner. Those who managed to escape fled back to New England. The Delaware then burned what was left of the Yankee settlement.
In 1769, the Yankees returned to the Wyoming Valley. Five townships were established by Connecticut. Each one was five square miles and divided amongst forty settlers. Wilkes-Barre Township was one of the original townships; it was named in honor of John Wilkes
John Wilkes (17 October 1725 – 26 December 1797) was an English radical journalist and politician, as well as a magistrate, essayist and soldier. He was first elected a Member of Parliament in 1757. In the Middlesex election dispute, he ...
and Isaac Barré—two British members of Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
who supported colonial America
The colonial history of the United States covers the history of European colonization of North America from the early 17th century until the incorporation of the Thirteen Colonies into the United States after the Revolutionary War. In the ...
. Pennsylvanians (Pennamites) also arrived in the valley that same year.
The Connecticut settlers established Fort Durkee, which was named in honor of their leader (Colonel Durkee). This was immediately followed by a series of skirmishes between the Pennsylvanians and Connecticut settlers. The land changed hands several times between the two groups. The Congress of the Confederation
The Congress of the Confederation, or the Confederation Congress, formally referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, was the governing body of the United States of America during the Confederation period, March 1, 1781 – Mar ...
was asked to resolve the matter. With the Decree of Trenton, on December 30, 1782, the confederation government officially decided that the region belonged to Pennsylvania; the Wyoming Valley became part of Northumberland County.
Pennsylvania ruled that the Connecticut settlers (Yankees) were not citizens of the Commonwealth. Therefore, they could not vote and were ordered to give up their property claims. In May 1784, armed men from Pennsylvania force-marched the Connecticut settlers away from the valley. By November, the Yankees returned with a greater force. They captured and destroyed Fort Dickinson Fort Dickinson was a Pennamite fort with four small blockhouses, armed with four guns, manned by 100 men constructed as part of the Pennamite Wars.
In 1769, Major John Durkee and his men erected Fort Durkee on the eastern bank of the Susquehanna ...
in Wilkes-Barre. With that victory, a new state (which was separate from both Connecticut and Pennsylvania) was proposed. The new state was to be named Westmoreland. To ensure that they didn't lose the land, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania worked out a compromise with the Connecticut (Yankee) settlers. The Yankee settlers would become citizens of Pennsylvania and their property claims would be restored (prior to the Decree of Trenton). As part of the compromise, Pennsylvania would establish a new county in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The Yankees agreed to the terms.
On September 25, 1786, the Pennsylvania General Assembly
The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the legislature of the U.S. commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times (1682–1776), the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania ...
passed a resolution which created Luzerne County. It was formed from a section of Northumberland County and named after Chevalier de la Luzerne, a French soldier and diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or interna ...
during the 18th century. Wilkes-Barre became the seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
for the new territory. This resolution ended the idea of creating a new state.
In 1797, several decades after the community's founding, Louis Philippe, later the King of France from 1830 to 1840, stayed in Wilkes-Barre while traveling to the French Asylum settlement.
19th century

 Wilkes-Barre's population skyrocketed due to the discovery of
Wilkes-Barre's population skyrocketed due to the discovery of anthracite coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the hig ...
in the 19th century. In 1808, Judge Jesse Fell
Jesse Fell was an early political leader in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. He was one of the first Pennsylvanians to successfully burn anthracite on an open air grate. Anthracite differs from wood in that it needs a draft from the bottom, and Judge ...
of Wilkes-Barre discovered a solution to ignite anthracite with the usage of an iron grate; it allowed for the coal to light and burn easier. This invention increased the popularity of anthracite as a fuel source. This led to the expansion of the coal industry in Northeastern Pennsylvania; Wilkes-Barre was nicknamed "The Diamond City" due to its high productivity of mining coal. The growing demand for coal as a domestic heat source resulted in changes to patterns of immigration to Wilkes-Barre in the 19th century. The Pennsylvania guide, compiled by the Writers' Program of the Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; renamed in 1939 as the Work Projects Administration) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to carry out public works projects, i ...
in 1940, noted that:
Throughout the 1800s, canals and railroads were constructed to aid in the mining and transportation of coal. Hundreds of thousands of immigrants flocked to the city; they were seeking jobs in the numerous mines and collieries that sprang up throughout the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
. In 1806, Wilkes-Barre Borough was formed from a segment of Wilkes-Barre Township; it was later incorporated as a city in 1871. This was the direct result of the population boom. At its peak, Wilkes-Barre had a population of over 86,000 in the 1930s and 40s.
New industries were established and the Vulcan Iron Works was a well-known manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1849 to 1954. During Wilkes-Barre's reign as an industrial and economic force in America, several major companies and franchises became based in the city, such as Woolworth's, Sterling Hotels, Miner's Bank, Bell Telephone, Luzerne National Bank, and Stegmaier.
Even though the overall economy was doing very well, the city was still prone to natural disasters. Besides frequent flooding from the Susquehanna River, Wilkes-Barre also endured a devastating F3 tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, alt ...
on August 19, 1890. The twister killed 16 people, injured 50, damaged or destroyed 260 buildings, and cost at least $240,000 (in 1890 money).
20th century
 Wilkes-Barre is located within Pennsylvania's
Wilkes-Barre is located within Pennsylvania's Coal Region
The Coal Region is a region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. It is known for being home to the largest known deposits of anthracite coal in the world with an estimated reserve of seven billion short tons.
The region is typically defined as compris ...
. The anthracite coal mining industry, and its extensive use of child labor in the early 20th century, was one of the industries targeted by the National Child Labor Committee and its hired photographer, Lewis Hine. Many of Hine's subjects were photographed in the mines and coal fields near Wilkes-Barre. The impact of the Hine photographs led to the enactment of child labor laws
Child labour laws are statutes placing restrictions and regulations on the work of minors.
Child labour increased during the Industrial Revolution due to the children's abilities to access smaller spaces and the ability to pay children less wage ...
across the country.
The coal industry continued despite several disasters, including an explosion at Wilkes-Barre's Baltimore Colliery in 1919, which killed 92 miners. The industry declined when the United States switched to other energy sources, and most coal operations had left Wilkes-Barre by the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. The 1959 Knox Mine Disaster
Knox may refer to:
Places United States
* Fort Knox, a United States Army post in Kentucky
** United States Bullion Depository, a high security storage facility commonly called Fort Knox
* Fort Knox (Maine), a fort located on the Penobscot River ...
, resulting in the flooding of numerous mines, marked the end of large-scale coal mining in the area. Industrial restructuring also caused the city to lose jobs and begin a decades-long decline.
In 1926, Planters Peanuts Company was founded in Wilkes-Barre by two Italian immigrants. The company maintained its headquarters in the city until 1961. In 1929, baseball player Babe Ruth
George Herman "Babe" Ruth Jr. (February 6, 1895 – August 16, 1948) was an American professional baseball player whose career in Major League Baseball (MLB) spanned 22 seasons, from 1914 through 1935. Nicknamed "the Bambino" and "the Su ...
hit one of the longest home runs in history at Artillery Park
The Artillery Park (also known as the Churchyard Cemetery and Historical Cemetery 2) is a historic cemetery at North Road and Narragansett Avenue in Jamestown, Rhode Island. It is located at a high point on the southern part of Conanicut Island ...
in Wilkes-Barre.
On November 8, 1972, Wilkes-Barre became the birthplace of modern cable television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with bro ...
programming, when Home Box Office (HBO) launched over the city's Teleservice Cable system (now Service Electric Cable). Around 365 Teleservice subscribers were the first to receive the premium cable service when it commenced broadcasts. (As local ordinances prohibiting direct-to-cable telecasts of theatrical feature films prevented Time-Life from launching HBO over its New York City-based Sterling Manhattan cable franchise, the company initially sought an agreement with Teleservice to launch it on the provider's Allentown system; possible television blackout conflicts for HBO-televised NBA games, as Allentown was located within the Philadelphia 76ers
The Philadelphia 76ers, colloquially known as the Sixers, are an American professional basketball team based in the Philadelphia metropolitan area. The 76ers compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the league's Ea ...
's blackout radius, resulted in Teleservice electing to offer it on its Wilkes-Barre system instead.)
Wilkes-Barre became the site of a mass shooting on September 25, 1982. George Emil Banks killed 13 people and wounded one. Banks was deemed incompetent to be executed, yet currently resides on death row.
Flooding

 Manufacturing and retail remained Wilkes-Barre's strongest industries, but the city's economy took a major blow from
Manufacturing and retail remained Wilkes-Barre's strongest industries, but the city's economy took a major blow from Tropical Storm Agnes The name Agnes has been used for a total of sixteen tropical cyclones worldwide: one in the Atlantic Ocean, thirteen in the Western North Pacific Ocean, one in the South-West Indian Ocean, and one in the South Pacific Ocean.
In the Atlantic:
* Hur ...
in 1972. The storm pushed the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
to a height of nearly , four feet above the city's levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastli ...
s, flooding downtown with nine feet of water. A total of 128 deaths were attributed to the storm. Most drowning deaths were caused by people trapped in their cars. Almost 400,000 homes and businesses were destroyed and 220,000 Pennsylvanians were left homeless (as were hundreds of thousands in other states). Damage was estimated to be $2.1 billion in Pennsylvania alone. President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
sent aid to the area, after flying over in his helicopter on his way to his Camp David
Camp David is the country retreat for the president of the United States of America. It is located in the wooded hills of Catoctin Mountain Park, in Frederick County, Maryland, near the towns of Thurmont and Emmitsburg, about north-northwest ...
retreat (on June 24, 1972).
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Wilkes-Barre attempted to prevent the damage from storms as intense as Agnes by building a levee system that rises ; completed in January 2003, the network of levees cost roughly $250 million. It has successfully resisted other threatening floods in 1996, 2004, and 2006. The Army Corps of Engineers has praised the quality of the levees. In 2006, the city made the front page of national newspapers when 200,000 residents were told to evacuate in the wake of flooding that was forecast to reach levels near that of 1972, though the flooding fell short of predictions.
In late August 2011, Hurricane Irene, centered off the New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
coast, caused the Susquehanna River to rise to flood level, but there was no cause for alarm. Then, from September 6 to 8, heavy rains from the inland remnants of Tropical Storm Lee The name Lee has been used for seven tropical cyclones worldwide. In the Atlantic, it replaced the name ''Lenny''.
In the Atlantic:
* Tropical Storm Lee (2005), a short-lived, minimal tropical storm
* Tropical Storm Lee (2011)
Tropical Storm ...
and Hurricane Katia offshore funneled heavy rain over the Wyoming Valley and into the Susquehanna River watershed. The Susquehanna swelled to record levels across the state. In Wilkes-Barre, it crested on September 9 at an all-time record of , nearly higher than water levels reached during Hurricane Agnes in 1972. The levees protected Wilkes-Barre, but nearby boroughs did not escape, as West Pittston
West Pittston is a borough in the Greater Pittston area of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is located on the Susquehanna River (opposite of Pittston City). In 2020, the population was 4,644.
The town once produced mine screens ...
, Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to ...
, and parts of Plains Township were affected by extreme flooding.
21st century
Revitalization and construction
 On June 9, 2005, Mayor Thomas M. Leighton unveiled his ''"I believe..."'' campaign for Wilkes-Barre, which was intended to boost the city's spirits. Construction began on a planned downtown theatre complex, which had a grand opening on June 30, 2006. Renovation of the landmark Hotel Sterling was being pursued by CityVest, a nonprofit developer. The expansion of
On June 9, 2005, Mayor Thomas M. Leighton unveiled his ''"I believe..."'' campaign for Wilkes-Barre, which was intended to boost the city's spirits. Construction began on a planned downtown theatre complex, which had a grand opening on June 30, 2006. Renovation of the landmark Hotel Sterling was being pursued by CityVest, a nonprofit developer. The expansion of Wilkes University
Wilkes University is a private university in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. It has over 2,200 undergraduates and over 2,200 graduate students (both full and part-time). Wilkes was founded in 1933 as a satellite campus of Bucknell University, and b ...
and King's College took place. Also, the canopy and matching street lights in Public Square and across downtown were removed; they were replaced by new green lampposts.
The city of Wilkes-Barre celebrated its 200th anniversary in 2006. Several events, including a Beach Boys concert, were planned but canceled due to extremely heavy rains. Most of the city's population was ordered to evacuate on June 28, 2006. The Bicentennial __NOTOC__
A bicentennial or bicentenary is the two-hundredth anniversary of a part, or the celebrations thereof. It may refer to:
Europe
* French Revolution bicentennial, commemorating the 200th anniversary of 14 July 1789 uprising, celebrated ...
celebration was postponed to Labor Day weekend, September 3, 2006, and was attended by Pennsylvania Governor Ed Rendell and the Beach Boys.
The Riverfront revitalization project (River Common), broke ground in 2007 and was completed in early 2010. It has made the riverfront accessible to the public. The area also has a new amphitheater for live performances and improved access through ramps and sidewalks. Fountains and color-changing lights have been added underneath two bridges which carry pedestrian traffic across the normally-open levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastli ...
. The project stretches approximately four blocks from the Luzerne County Courthouse to the intersection of South River Street and West South Street. The River Common has since hosted concerts and charity events.
Since completion of the River Common, additional improvements to city infrastructure have been progressing. New crosswalks have been installed downtown, including signage emphasizing that pedestrians have the right-of-way. The completion of the James F. Conahan Intermodal Transportation Facility has added parking and relocated Luzerne County buses from their former Public Square staging sites. This has reduced traffic congestion around the square. Private carrier Martz offers coach bus service from the terminal as well.
The widening and realignment of Coal Street, a major road connecting Wilkes-Barre City with Wilkes-Barre Township, was completed in 2012. The new Coal Street provides four lanes over the original two lanes, making travel between the highly commercial Wilkes-Barre Township and the city much easier. In 2013, Hotel Sterling was demolished due to flood damage in the hotel's basement (which compromised the building's integrity). As of today, several buildings are in the process of being constructed on the site of the former hotel.
Geography


 According to the
According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, the city has a total area of , of which is land and , or 4.60%, is water. The city is bordered by the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
to the west. Most of Downtown is located on a wide floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
. Floodwall
A flood wall (or floodwall) is a primarily vertical artificial barrier designed to temporarily contain the waters of a river or other waterway which may rise to unusual levels during seasonal or extreme weather events. Flood walls are mainly ...
s were constructed to protect a large percentage of the city. The elevation of the downtown area is about above sea level. As you travel inland, away from the river, the elevation rises. Wilkes-Barre Mountain is a physical barrier southeast of the city.
Neighborhoods
Wilkes-Barre houses over one dozen neighborhoods: * Central City: It is also referred to as "Downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business district ...
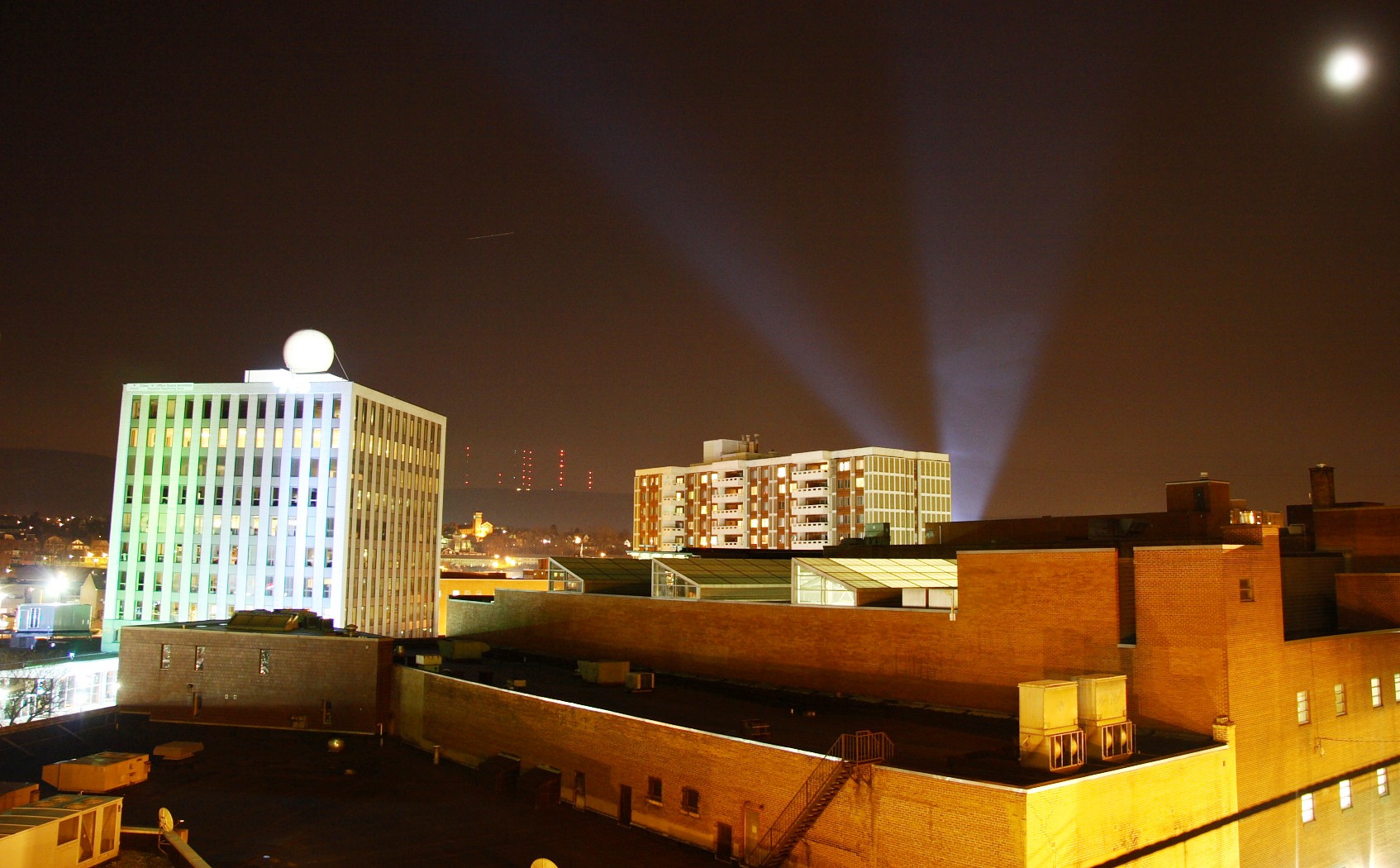
." This section of the city is located between the Susquehanna River and Wilkes-Barre Boulevard, and between South and North Streets. It is the original foundation of Wilkes-Barre (the 16 blocks claimed by the Connecticut settlers who founded the city). The neighborhood is home to most of the city's high-rises and its one Public Square. Throughout the city's history, the area has remained a hub for all of Luzerne County. During the city's boom, this small area was home to the headquarters of more than 100 national corporations. Today, it still houses the NEPA Headquarters for Verizon, Citizen's Bank, Blue Cross, PNC Bank, Luzerne National Bank, Guard Insurance, and a number of other companies. Thousands of people live and/or work in Downtown Wilkes-Barre every day.
* North End: This is the area northeast of Downtown. It comprises a number of urban and suburban communities. North End is renowned for its architecture.
* Parsons: This neighborhood is also northeast of Downtown. This is a quiet part of the city (with a suburban atmosphere). It includes two city parks, a golf course, and a number of factories.
* Miners' Mills: This community was named after a prominent local family (who lived in the area). Miners' Mills is the last neighborhood on the northeastern border of the city.
* East End: This neighborhood is directly east of Downtown. East End, Heights, and Mayflower are fairly new areas compared to the rest of the city, having only been developed in the 20th Century. Old pictures of the Stegmaier Building indicate that everything east of Downtown was undeveloped until the 1900s.
* Heights: This section of the city is located southeast of Downtown. It is centered between East End and Mayflower.
* Mayflower: This area is located south of Downtown. It was once home to numerous mansions owned by various "bigwigs." Today it houses the OKT, Lincoln Plaza, and Park Avenue residential housing communities. The best view of Downtown can be seen from the high streets of Mayflower.
* South Wilkes-Barre: This neighborhood is located directly southwest of Downtown. It was home to the national headquarters of Planter's Peanuts and the Bell Telephone Company (in the 20th Century). One of the tallest churches in Luzerne County, St. Nicholas Roman Catholic Church, dominates the south end skyline (standing at nearly 200 feet).
* Goose Island: This area is located in the southwestern section of the city between South Wilkes-Barre and Rolling Mill Hill.
* Rolling Mill Hill: This neighborhood is also located in the southwestern part of the city.
* Iron Triangle: This is another community southwest of Downtown.
* Other neighborhoods and sub-neighborhoods: There are other smaller neighborhoods and sub-neighborhoods in Wilkes-Barre City (e.g., Brookside, Upper Miners' Mills, Lower Miners' Mills, and Barney Farms).
Adjacent municipalities
* Wilkes-Barre Township (southeast) * Plains Township (east and northeast) * Kingston (north) * Edwardsville (northwest) * Larksville (west) * Hanover Township (southwest) * Bear Creek Township (southwest)Climate
Under theKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, Wilkes-Barre falls within either a hot-summer humid continental climate (''Dfa'') if the isotherm is used or a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(''Cfa'') if the isotherm is used. Summers are hot and winters are moderately cold with wide variations in temperature. Winters are cold with a January average of . The surrounding mountains have an influence on the climate (including both precipitation and temperatures), leading to wide variations within a short distance. On average, temperatures below are infrequent, occurring 2.5 days per year, and there are 34.9 days where the maximum temperature remains below . The average annual snowfall is during the winter (in which severe snowstorms are rare). However, when snowstorms do occur, they can disrupt normal routines for several days.
Summers are warm with a July average of . In an average summer, temperatures exceeding occur on 11.7 days and but rarely exceed . Spring and fall are unpredictable with temperatures ranging from cold to warm (although they are usually mild). On average, Wilkes-Barre receives of precipitation each year, which is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year (though the summer months receive more precipitation). Extreme temperatures range from on January 21, 1994, to on July 9, 1936. Wilkes-Barre averages 2,303 hours of sunshine per year, ranging from a low of 96 hours in December (or 33% of possible sunshine) to 286 hours in July (or 62% of possible sunshine).
Parks and recreation
 Wilkes-Barre has a Downtown Riverfront Park system that contains 91 acres of open space.
Kirby Park is a public park located along the western bank of the Susquehanna River. Kirby Park is one of the region's most valued recreational resources. Given to the city of Wilkes-Barre by the Kirby Family, the park welcomes hundreds of thousands each year. The park is the setting for the city's annual Cherry Blossom Festival (held during the last weekend of April) and the city's July 4 Celebration. Its amenities include tennis courts, a fitness trail, pond, walking paths, running track, softball fields, parking area, volleyball courts, pavilions, and more.
Nesbitt Park is also located on the west side of the Susquehanna River. It is located across from Kirby Park. Nesbitt is open to the public. It has walking paths and areas for picnicking.
The River Common is located along the eastern bank of the Susquehanna River. The Market Street Bridge bisects the park. The River Common joins with the Luzerne County Courthouse grounds. Its features include a 750-person amphitheater, paved walk-ways, gardens, ornamental trees, seating areas, a fishing pier, and two grand gateways connecting the city to the river.
Wilkes-Barre has a Downtown Riverfront Park system that contains 91 acres of open space.
Kirby Park is a public park located along the western bank of the Susquehanna River. Kirby Park is one of the region's most valued recreational resources. Given to the city of Wilkes-Barre by the Kirby Family, the park welcomes hundreds of thousands each year. The park is the setting for the city's annual Cherry Blossom Festival (held during the last weekend of April) and the city's July 4 Celebration. Its amenities include tennis courts, a fitness trail, pond, walking paths, running track, softball fields, parking area, volleyball courts, pavilions, and more.
Nesbitt Park is also located on the west side of the Susquehanna River. It is located across from Kirby Park. Nesbitt is open to the public. It has walking paths and areas for picnicking.
The River Common is located along the eastern bank of the Susquehanna River. The Market Street Bridge bisects the park. The River Common joins with the Luzerne County Courthouse grounds. Its features include a 750-person amphitheater, paved walk-ways, gardens, ornamental trees, seating areas, a fishing pier, and two grand gateways connecting the city to the river.
Demographics
 The city's population has been in constant decline since the 1930s, but the decline has been slowing in recent decades, and saw growth as of 2020. As of the 2020 census, there were 44,328 people and 15,581 households residing in the city. The popeulation density was 5,945 per square mile. The racial makeup of the city was 69.80%
The city's population has been in constant decline since the 1930s, but the decline has been slowing in recent decades, and saw growth as of 2020. As of the 2020 census, there were 44,328 people and 15,581 households residing in the city. The popeulation density was 5,945 per square mile. The racial makeup of the city was 69.80% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
, 14.90% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.40% Native American, 2.4% Asian, 0.20% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
, and 4.60% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
or Latino of any race were 21.0% of the population.
As of the 2010 census, the city was 79.2% White, 10.9% Black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 1.4% Asian, and 2.9% were two or more races. Of the population, 11.3% were of Hispanic or Latino ancestry. The Hispanic population was just 1.58% of the population as of the 2000 census.
As of the 2000 census, there were 43,123 people, 17,961 households, and 9,878 families residing in the city. The population density was 6,296.3 people per square mile (2,430.6/km2). There were 20,294 housing units at an average density of 2,963.1 per square mile (1,143.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 92.30% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
, 5.09% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.11% Native American, 0.79% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
, 0.53% from other races, and 1.15% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
or Latino of any race were 1.58% of the population.
The average household size was 2.42. With population spread of 22.9% under the age of 18, 61.3% between the ages of 19–64, and 15.8% over the age of 65. Females made up 50.6% of the population.
The median household income was $37,902, while 26.6% of the city were found below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
. The per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
was $20,197.
Dialect
The local accent ofAmerican English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances ...
is Northeast Pennsylvania English.
Religion
More than half (59.3%) of the city's population is religious: 43.8%Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 4.4% Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
, 3.1% Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, 2.0% Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
, 1.1% Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestantism, Protestant Charismatic Christianity, Charismatic Christian movementJudaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
, 0.6% Episcopalian
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
, 0.5% Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul c ...
, 0.5% Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, and 0.3% The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
.
Economy
As of March 2019, income per capita in Wilkes-Barre was $18,375, compared to the national average of $31,177. Household income was $32,484, compared to the national average of $57,652. Family median income was $42,782, compared to the national average of $70,850. The city's unemployment rate in March 2019 was 6.4%. Recent job growth was 0.8%. 49% of jobs were in sales, office, administrative support, production, transportation, and material moving sectors. In 2016, 30.1% of residents lived below the poverty line, more than double the Pennsylvania average of 12.9%. Large employers in the city includeGUARD Insurance Group
Berkshire Hathaway GUARD Insurance Companies currently insure over 250,000 businesses in the US.
History
In July 1982, the company's original subsidiaries were formed in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, by Susan and Judd Shoval and a group of priv ...
and Lord & Taylor.
Government
City government

Executive
The city is headed by an electedmayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
, who serves four-year terms. The current mayor is George Brown ( Democrat). He has been in office since 2019. Before becoming mayor he was a business man and a former city councilman.
Legislative
The legislative branch consists of a five-memberCity Council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural coun ...
. They are elected by a single-member district
A single-member district is an electoral district represented by a single officeholder. It contrasts with a multi-member district, which is represented by multiple officeholders. Single-member districts are also sometimes called single-winner vo ...
to four-year terms. The following are current members of the council: Bill Barrett, Mike Belusko, Tony Brooks, Beth Gilbert, and John Marconi.
Audit and Control
The office of Audit and Control is the third branch of Wilkes-Barre City government. It is headed by the City Controller, elected to a four-year term. Darren G. Snyder, the current City Controller, is a Democrat and has been in office since 2016.Judicial
The city of Wilkes-Barre is served by two City Attorneys (Timothy Henry and Maureen Collins). They advise both the mayor and city council. The chance of becoming a victim of either violent or property crime in Wilkes-Barre is 1 in 35. Based on FBI crime data, Wilkes-Barre is not one of the safest communities in America. Relative to Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barre has a crime rate that is higher than 91% of the state's cities and towns of all sizes.County government
 The Luzerne County
The Luzerne County government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government i ...
operates out of Wilkes-Barre. The city is the administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of Luzerne County. The county government is responsible for imposing taxes, providing services to the public, and administering laws and regulations. They govern over a population of nearly 320,000 people. Many government offices are situated within the county courthouse (located at 200 North River Street in Downtown Wilkes-Barre). The Luzerne County Court of Common Pleas also operates out of the same building.
On November 2, 2010, the voters of Luzerne County held a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
on the question of home rule
Home rule is government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governance wi ...
. A total of 51,413 (55.25%) voted in favor of home rule, while another 41,639 (44.75%) voted against the move. This vote was the direct result of the corruption, wasteful spending, higher property taxes, and out-of-control debt facing the county. The home rule charter took effect on January 2, 2012; the Luzerne County Board of Commissioners was abolished and replaced with the new form of government ( council–manager government). This government consists of a county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
. The council chair, who is appointed by his or her fellow council members, is both the highest-ranking officer on the assembly and the head of county government for ceremonial purposes. The council also appoints and works alongside a full-time manager
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activitie ...
(who supervises the county's day-to-day operations).
The county government is also made up of many other officials (e.g., the county controller, district attorney
In the United States, a district attorney (DA), county attorney, state's attorney, prosecuting attorney, commonwealth's attorney, or state attorney is the chief prosecutor and/or chief law enforcement officer representing a U.S. state in a ...
, and sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
).
State and federal representation
State
*Eddie Day Pashinski
Edwin A. "Eddie Day" Pashinski (born July 2, 1945) is a Democratic member of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives for the 121st District who was elected in 2006. His district includes Wilkes-Barre, Wilkes-Barre Township, Ashley, Plains ...
( D) represents Wilkes-Barre in the Pennsylvania House of Representatives
The Pennsylvania House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Pennsylvania General Assembly, the legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. There are 203 members, elected for two-year terms from single member districts.
It ...
.
* John T. Yudichak ( I) represents the city in the Pennsylvania State Senate
The Pennsylvania State Senate is the upper house of the Pennsylvania General Assembly, the Pennsylvania state legislature. The State Senate meets in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Commonwealt ...
.
Federal
*Matthew Cartwright
Matthew Alton Cartwright (born May 1, 1961) is an American politician and lawyer serving as the U.S. representative from Pennsylvania's 8th congressional district since 2013. The district, numbered as the 17th district from 2013 through 2019, ...
( D) represents Wilkes-Barre on the federal level (in the U.S. House of Representatives).
* Bob Casey ( D) and Pat Toomey ( R) represent the entire Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in the U.S. Senate.
Education


High schools
Wilkes-Barre City is part of theWilkes-Barre Area School District
Wilkes–Barre Area School District is an urban public school district located in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. The District encompasses approximately 123 square miles. The district includes the city o ...
. The district operates three high schools:
* James M. Coughlin High School
* G.A.R. (Grand Army of the Republic) Memorial High School
* Elmer L. Meyers High School
In 2020, the 3 High Schools became one, as Wilkes-Barre Area High School was built in nearby Plains Township. They chose the nickname “Wolfpack”.
The Diocese of Scranton also has a high school in Wilkes-Barre— Holy Redeemer High School.
Colleges
The area in and around Wilkes-Barre is home to several colleges and universities: * King's College *Wilkes University
Wilkes University is a private university in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. It has over 2,200 undergraduates and over 2,200 graduate students (both full and part-time). Wilkes was founded in 1933 as a satellite campus of Bucknell University, and b ...
* Misericordia University
Misericordia University is a private Roman Catholic university in Dallas, Pennsylvania. It was founded by the Religious Sisters of Mercy in 1924 as College Misericordia; in 2007 it became a university and changed its name. The university offe ...
* Luzerne County Community College
Luzerne County Community College (LCCC) is a public community college in Nanticoke, Pennsylvania. LCCC offers over 100 academic, technical, and career programs. The institution uses an open admissions policy for most programs, and has over 35,000 ...
* Penn State Wilkes-Barre
Penn State Wilkes-Barre is a commonwealth campus of Pennsylvania State University located in Lehman Township, Pennsylvania.
History
In May 1915, two Penn State graduates, reacting to the needs of the local anthracite mining industry, proposed th ...
* Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine (GCSOM) is a private medical school associated with the Geisinger Health System and located in northeastern and north central Pennsylvania. GCSOM offers a community-based model of medical education wit ...
, Wilkes Barre Campus
Libraries
Along with the libraries associated with the colleges, Wilkes-Barre has several libraries. These include three branches of theOsterhout Free Library
The Luzerne County Library System (LCLS) is an organization that administers ten libraries in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1984, it is headquartered at the Osterhout Free Library in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. Along with hosting vari ...
, with the headquarters for the Luzerne County Library System in the main branch.
Transportation

Airports
Five international airlines fly from the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport in nearby Pittston Township. Smaller, private planes may also use theWilkes-Barre Wyoming Valley Airport
Wilkes-Barre Wyoming Valley Airport is a county-owned, public airport three miles north of Wilkes-Barre, in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, and 10 miles south of Scranton, in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania. The National Plan of Integrated Airpo ...
in Forty Fort.
Highways
Interstate 81 passes north–south near Wilkes-Barre, and the city is also located near the Northeast Extension of the Pennsylvania Turnpike. It is also about north ofInterstate 80
Interstate 80 (I-80) is an east–west transcontinental freeway that crosses the United States from downtown San Francisco, California, to Teaneck, New Jersey, in the New York metropolitan area. The highway was designated in 1956 as one ...
. The North Cross Valley Expressway
Pennsylvania Route 309 (PA 309) is a state highway that runs for 134 miles (216 km) through eastern Pennsylvania. The route runs from an interchange between PA 611 and Cheltenham Avenue on the border of Philadelphia and Cheltenham Townshi ...
, starting at the junction of Interstate 81 and Pennsylvania Route 115, carries Pennsylvania Route 309 through northern Wilkes-Barre, connecting the city to Dallas
Dallas () is the third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 million people. It is the largest city in and seat of Dallas County ...
in the north. Route 115 provides access from the Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike (Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike) is a toll highway operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A controlled-access highway, it runs for across the state. The turnpike's we ...
's Northeast Extension, but it does not enter Wilkes-Barre city limits.
Buses
Public transportation is provided by theLuzerne County Transportation Authority
The Luzerne County Transportation Authority (LCTA) is the operator of mass transportation in the city of Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, and portions of surrounding Luzerne County. Services provided by the LCTA replaced previously offered services ...
. In addition to servicing the city, it provides transportation for the northern half of the county. It also has a connecting bus to Scranton via an interchange at Pittston
Pittston is a city in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is situated between Scranton and Wilkes-Barre in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The city gained prominence in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as an active anthracite coal ...
with the Transit System of Lackawanna County (COLTS), the public transit authority of Lackawanna County. Martz Trailways
Martz Group is a bus company headquartered in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, operating intercity commuter buses, charter buses, and tours. The company operates Martz Trailways, which is a part of the Trailways Transportation System. Martz Trailways ...
provides intercity bus service from the Martz Trailways Bus Terminal in downtown Wilkes-Barre to Scranton, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, Atlantic City
Atlantic City, often known by its initials A.C., is a coastal resort city in Atlantic County, New Jersey, United States. The city is known for its casinos, boardwalk, and beaches. In 2020, the city had a population of 38,497.
, and Wind Creek Bethlehem.
Rail
The city was at one time served by theLehigh Valley Railroad
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Pennsylvania. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846 for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, ...
, Central Railroad of New Jersey, the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad) was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey (and by ferry with New York City), a distance of . Incorporated in ...
(later Erie Lackawanna Railway), Delaware and Hudson Railway, the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
, the Wilkes-Barre and Eastern Railroad, and the Lackawanna and Wyoming Valley Railroad
The Lackawanna & Wyoming Valley Railroad, more commonly known as the Laurel Line, was a Pennsylvania third rail electric interurban streetcar line which operated commuter train service from 1903 to 1952, and freight service until 1976. Its main li ...
(known as the Laurel Line). CNJ trains included the ''Interstate Express
The ''Interstate Express'' was a long-distance passenger train operating between Syracuse, New York, and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, jointly operated by the Reading Railroad, the Central Railroad of New Jersey and the Delaware, Lackawanna and West ...
'' (ending in 1957) and local service to Allentown and Philadelphia. The last Lehigh Valley trains were the '' Black Diamond'' (ending in 1959), ''John Wilkes'' and '' Maple Leaf'' (the last two, ending in 1961).
The Wilkes-Barre Traction Company formed a streetcar line from Georgetown to Nanticoke and over the river into Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to ...
(it ceased operations in the mid-1940s).
The Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31 ...
, which was acquired the former Delaware and Hudson line from successor Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canad ...
) and the Luzerne and Susquehanna Railway
The Luzerne and Susquehanna Railway is a shortline railroad in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. It both serves local traffic and connects to the Reading Blue Mountain and Northern Railroad in Pittston and to the Norfolk Southern Railway at three sep ...
, provides freight service within the city.
Arts and culture

Local attractions
* Dorothy Dickson Darte Center for the Performing Arts, located on the campus of Wilkes University * F. M. Kirby Center for the Performing Arts * Frederick Stegmaier Mansion * Little Theatre of Wilkes-Barre * Luzerne County Convention and Visitors Bureau * Luzerne County Museum *Mohegan Sun Arena at Casey Plaza
Mohegan Sun Arena at Casey Plaza (originally Northeastern Pennsylvania Civic Arena and Convention Center, formerly First Union Arena and Wachovia Arena) is an 8,050-seat multi-purpose arena located in Wilkes-Barre Township, Pennsylvania just no ...
* Mohegan Sun at Pocono Downs
Mohegan Pennsylvania (formerly Mohegan Sun Pocono, Pocono Downs and Mohegan Sun at Pocono Downs) is a racino located in Plains Township on the outskirts of Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. The casino features over 2,300 slots, live tables for blac ...
, Pennsylvania's first slots casino
* River Street Historic District
* Stegmaier Brewery
* Wilkes-Barre station
The Central Railroad of New Jersey Station is a historic railway station located at Wilkes-Barre, Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. It was built in 1868, by the Central Railroad of New Jersey. It is a 2 1/2-story, brick building with 1 1/2-story win ...
* Wyoming Monument
The Wyoming Monument is an American Revolutionary War monument and grave site located in the Borough of Wyoming in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania.
History
Background
The monument marks the location of the bones of victims from the Battle of ...
Media
'' Times Leader'' and '' The Citizens' Voice'' are the two largest daily newspapers in Wilkes-Barre. The Wyoming Valley's NBC affiliate, WBRE-TV 28, is the only television station licensed to Wilkes-Barre, but WNEP-TV 16 ( ABC), WYOU 22 ( CBS), WVIA-TV 44 ( PBS), and WSWB 38 ( CW), all in Scranton,WOLF-TV
WOLF-TV (channel 56) is a television station licensed to Hazleton, Pennsylvania, United States, serving Northeastern Pennsylvania as an affiliate of the Fox network. It is the flagship property of locally based New Age Media, LLC, and is co-ow ...
56 ( Fox) in Hazleton, and WQMY 53 ( MyNetworkTV) in Williamsport also serve the city. Wilkes-Barre's radio market is ranked No. 69 by Arbitron
Nielsen Audio (formerly Arbitron) is a consumer research company in the United States that collects listener data on radio broadcasting audiences. It was founded as the American Research Bureau by Jim Seiler in 1949 and became national by merging ...
's ranking system. There are news, adult alternative, and music radio stations which are receivable in the area.
Popular culture
* Wilkes-Barre's economic plight is featured in the movie '' Capitalism: A Love Story'', directed byMichael Moore
Michael Francis Moore (born April 23, 1954) is an American filmmaker, author and left-wing activist. His works frequently address the topics of globalization and capitalism.
Moore won the 2002 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature for ' ...
.
* The Wilkes-Barre variation (or Traxler variation, as it is more commonly known) of the Two Knights' Defense is named for the Wilkes-Barre chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to dist ...
club.
* In the TV series ''Supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
'' episode 8.13 "Everyone Hates Hitler," the lead protagonists investigate a case in Wilkes-Barre.
* In the TV series ''The Office
''The Office'' is a mockumentary sitcom created by Ricky Gervais and Stephen Merchant, first made in the United Kingdom, then Germany, and subsequently the United States. It has since been remade in ten other countries.
The original ser ...
'', In the episode "Michael's Birthday", Dwight gives Michael a jersey from the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins, a local professional hockey team that plays in Wilkes-Barre. Throughout the series there is a magnet that is on the Kitchen Fridge that reads "Scranton/Wilkes Barre Yankees
The Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders (often abbreviated to SWB RailRiders) are a Minor League Baseball team of the International League (IL) and the Triple-A affiliate of the New York Yankees. They are located in Moosic, Pennsylvania, in the ...
."
* In the TV series ''Days of Our Lives
''Days of Our Lives'' (also stylized as ''Days of our Lives''; simply referred to as ''Days'' or ''DOOL'') is an American television soap opera that streams on the streaming service Peacock. The soap, which aired on the American television net ...
'', Episode 8/31/2021, Phillip tells Belle that Brady and Chloe are in Wilkes-Barre PA. In the end of the episode Phillip tells them to fuel up the jet for Wilkes-Barre PA."
Sports
Notable people
* Jane Alexander, lawyer and Pennsylvania state representative * George Emil Banks, spree killer * Hazel Barnes, philosopher * Douglas Carter Beane, playwright * Al Bedner, NFL player * Ray Black, Pitcher for the Milwaukee Brewers * David Bohm, quantum physicist *Benjamin Burnley
Benjamin Jackson Burnley IV (born March 10, 1978) is an American musician, singer, songwriter, and record producer, best known as the founder and frontman of the American rock band Breaking Benjamin. As the sole constant of the group, Burnley h ...
, lead singer and guitarist for rock band Breaking Benjamin
Breaking Benjamin is an American rock band from Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, formed in 1999 by lead singer and guitarist Benjamin Burnley and drummer Jeremy Hummel. The first lineup of the band also included guitarist Aaron Fink and bassist ...
* Lillian Cahn
Lillian Cahn (née Lenovitz; December 11, 1923 – March 4, 2013) was a Hungarian-born American businessperson who co-founded Coach New York with her husband, Miles Cahn. Lillian Cahn also created Coach's first line of handbags, which remains th ...
, co-founder of Coach, Inc. and Coach handbag designer
* George Catlin
George Catlin (July 26, 1796 – December 23, 1872) was an American adventurer, lawyer, painter, author, and traveler, who specialized in portraits of Native Americans in the Old West.
Traveling to the American West five times during the 18 ...
, artist
* Britton Chance, bio-physicist and Olympic sailor
* Catherine Chandler, poet
* Mark Ciavarella, disgraced judge in kids for cash scandal
* Mark Cohen, street photographer
* Ed Cole, Major League Baseball pitcher
* Colleen Corby, 1960s fashion model
* Mary Helen Peck Crane
Mary Helen Peck Crane (, Peck; April 10, 1827 – December 7, 1891) was a 19th-century American church and temperance activist, as well as a writer. She was the mother of the writer, Stephen Crane. She died in 1891.
Early life and education
Mary ...
(1827–1891), activist, writer; mother of Stephen Crane
* Amasa Dana, former U.S. Congressman
* Charles B. Dougherty, Army National Guard major general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
who commanded the 28th Infantry Division
* Mark Duda
Mark D Duda (born February 4, 1961) is a former professional American football defensive tackle in the National Football League (NFL). He played his entire NFL career with the St. Louis Cardinals from 1983 until 1987.
From 1979 to 1982, Duda pl ...
, NFL player, Lackawanna College football head coach
* Francis A. "Mother" Dunn, football player for the Canton Bulldogs
The Canton Bulldogs were a professional American football team, based in Canton, Ohio. They played in the Ohio League from 1903 to 1906 and 1911 to 1919, and the American Professional Football Association (later renamed the National Football Lea ...
* Benjamin F. Evans Jr. (1912–1991), U.S. Army Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
, U.S. military's chief of joint U.S. military aid mission in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
.
* Pete Elko, Major League Baseball third baseman
* Dave Evans, Hollywood filmmaker most known for the movie '' The Sandlot''
* Jesse Fell
Jesse Fell was an early political leader in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania. He was one of the first Pennsylvanians to successfully burn anthracite on an open air grate. Anthracite differs from wood in that it needs a draft from the bottom, and Judge ...
, early experimenter with anthracite coal
* Pat Finn, game show host whose shows include Lifetime's, The Family Channel's, and PAX's ''Shop 'til You Drop
''Shop 'til You Drop'' is an American game show that was on the air intermittently between 1991 and 2005. Four different series were produced during that time, with the first premiering on Lifetime on July 8, 1991, and the fourth series airing its ...
''
* Ham Fisher
Hammond Edward "Ham" Fisher (September 24, 1900 (some sources indicate 1901) – December 27, 1955) was an American comic strip writer and cartoonist. He is best known for his long, popular run on ''Joe Palooka'', which was launched in 1930 and r ...
, cartoonist
* Tess Gardella, actress
* Billy Goeckel, baseball player
* Bob Good, U.S. congressman
* Kevin Gryboski
Kevin John Gryboski (born November 15, 1973) is an American former Major League Baseball pitcher and current head coach of Wilkes University's baseball team.
Career
High school career
At Bishop Hoban High School in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvani ...
, Retired Major League Baseball pitcher
* William Harmatz, jockey, winner of 1959 Preakness Stakes
The Preakness Stakes is an American thoroughbred horse race held on Armed Forces Day which is also the third Saturday in May each year at Pimlico Race Course in Baltimore, Maryland. It is a Graded stakes race, Grade I race run over a distance of ...
* Laning Harvey, Pennsylvania state senator
* Mickey Haslin
Michael Joseph "Mickey" Haslin (October 25, 1909 – March 7, 2002), born Michael Joseph Hazlinsky, was a Jewish-Austrian American professional baseball player whose career spanned 13 seasons, six of which were spent in Major League Baseball (MLB) ...
, Major League Baseball infielder
* George Washington Helme, businessman and founder of Helmetta, New Jersey
Helmetta is a borough in Middlesex County, New Jersey, United States. The borough is nestled within the heart of the Raritan Valley region, with Manalapan Brook (a Raritan River tributary) flowing through the center of the community. As of th ...
* Joe Hergert, former professional football player
* William Henry Hines, U.S. Representative for Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district from 1893 to 1895
* Raye Hollitt
Raye Hollitt (born April 17, 1964) is an American actress and bodybuilder, also known by her stage name Zap, one of the original cast members of '' American Gladiators''.
Biography
Hollitt graduated from Lake-Lehman High School in 1982, then ...
, bodybuilder and actress
* Qadry Ismail
Qadry Rahmadan Ismail (born November 8, 1970), nicknamed "the Missile", is a former American football wide receiver. He was drafted by the Minnesota Vikings in the second round (52nd overall) of the 1993 NFL draft. He played college football at ...
, former NFL wide receiver on the Baltimore Ravens
The Baltimore Ravens are a professional American football team based in Baltimore, Maryland. The Ravens compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the American Football Conference (AFC) North division. The team plays its ...
* Raghib Ismail, former NFL player and Heisman Trophy
The Heisman Memorial Trophy (usually known colloquially as the Heisman Trophy or The Heisman) is awarded annually to the most outstanding player in college football. Winners epitomize great ability combined with diligence, perseverance, and har ...
runner-up
* Florence Foster Jenkins, unconventional operatic soprano, subject of film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
starring Meryl Streep
* Candy Jones, fashion model, writer, radio personality
* Dorothy Andrews Elston Kabis, Treasurer of the United States
The treasurer of the United States is an officer in the United States Department of the Treasury who serves as custodian and trustee of the federal government's collateral assets and the supervisor of the department's currency and coinage produc ...
* James Karen
James Karen (born Jacob Karnofsky; November 28, 1923 – October 23, 2018) was an American character actor of Broadway, film and television. Karen is known for his roles in ''Poltergeist'', ''The China Syndrome'', ''Wall Street'', ''The Return ...
, actor
* Mary Holland Kinkaid, journalist
* Michael J. Kirwan, represented Youngstown, Ohio in Congress, 1938–1970
* Al Klawitter, Major League Baseball pitcher
* Franz Kline, abstract expressionist
Abstract expressionism is a post–World War II art movement in American painting, developed in New York City in the 1940s. It was the first specifically American movement to achieve international influence and put New York at the center of th ...
painter
* Mike Konnick, former MLB player
* Mary Jo Kopechne
Mary Jo Kopechne (; July 26, 1940 – July 18 or 19, 1969) was an American secretary, and one of the campaign workers for U.S. Senator Robert F. Kennedy's 1968 presidential campaign, a close team known as the "Boiler Room Girls". In 1969, she d ...
, passenger killed in car driven by Ted Kennedy
Edward Moore Kennedy (February 22, 1932 – August 25, 2009) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Massachusetts for almost 47 years, from 1962 until his death in 2009. A member of the Democratic ...
at Chappaquiddick
* Harley Jane Kozak, actress and author
* Matthew Lesko, infomercial personality
* Edward B. Lewis
Edward Butts Lewis (May 20, 1918 – July 21, 2004) was an American geneticist, a corecipient of the 1995 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. He helped to found the field of evolutionary developmental biology.
Early life
Lewis was born in Wi ...
, winner of the 1995 Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine
* Santo Loquasto, production designer
* Garrick Mallery, ethnologist
* Herman Mankiewicz, screenwriter of ''Citizen Kane
''Citizen Kane'' is a 1941 American drama film produced by, directed by, and starring Orson Welles. He also co-wrote the screenplay with Herman J. Mankiewicz. The picture was Welles' first feature film. ''Citizen Kane'' is frequently cited ...
''
* Joseph L. Mankiewicz, Academy Award-winning director and producer
* Al Markim, actor ( ''Tom Corbett, Space Cadet'')
* Mary McDonnell, actress twice nominated for Academy Award
* Edward Peter McManaman
Edward Peter McManaman (May 3, 1900 – July 18, 1964) was a bishop of the Catholic Church in the United States. He served as an auxiliary bishop of the Diocese of Erie from 1948 to 1964.
Biography
Born in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, McM ...
, Roman Catholic bishop
* Edward Meneeley, painter
* Asher Miner, U.S. Army brigadier general and prominent businessman
* Albert Mudrian, author and magazine editor
* Leo C. Mundy, Pennsylvania state senator and physician
* Jozef Murgas, radio pioneer
* Joe Murray, left-handed pitcher for the Philadelphia A's
The Philadelphia Athletics were a Major League Baseball team that played in Philadelphia from 1901 to 1954, when they moved to Kansas City, Missouri, and became the Kansas City Athletics. Following another move in 1967, the team became the Oakla ...
* Claudette Nevins, actress
* Amedeo Obici, founder of Planters Peanuts
* Kid O'Hara, baseball player
* Rose O'Neill, cartoonist, illustrator, artist, and writer.
* Jerry Orbach, Tony award
The Antoinette Perry Award for Excellence in Broadway Theatre, more commonly known as the Tony Award, recognizes excellence in live Broadway theatre. The awards are presented by the American Theatre Wing and The Broadway League at an annual c ...
-winning actor
* Phil Ostrowski, NFL player
* John Paluck, football player for Washington Redskins
The Washington Commanders are a professional American football team based in the Washington metropolitan area. The Commanders compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) ...
and Pro Bowl
The National Football League All-Star Game (1939–1942), Pro Bowl (1951–2022), or Pro Bowl Games (starting in 2023) is an annual event held by the National Football League (NFL) featuring the league's star players.
The format has changed thro ...
selection
* William Daniel Phillips, co-recipient of the 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
* Mendy Rudolph
Marvin "Mendy" Rudolph (March 8, 1926July 4, 1979) was an American professional basketball referee in the National Basketball Association (NBA) for 22 years, from 1953 to 1975. One of the few basketball game officials to be inducted into the Bas ...
, NBA referee from 1953 to 1975
* Sam Savitt, equestrian artist, author
* Michael Schoeffling
Michael Earl Schoeffling (born December 10, 1960) is an American former actor and model. He is known for playing the role of Jake Ryan in ''Sixteen Candles'', Al Carver in ''Wild Hearts Can't Be Broken'', Kuch in ''Vision Quest'', and Joe in '' ...
, actor, played Jake Ryan in film '' Sixteen Candles''
* Don Schwall, MLB pitcher
* M. Gerald Schwartzbach, California criminal defense attorney
* Greg Skrepenak
Gregory Andrew Skrepenak (born January 31, 1970) is an American former county commissioner in Pennsylvania and retired professional football player. He was an offensive lineman in the National Football League (NFL) for the Los Angeles/Oaklan ...
, former NFL player, convicted felon
* Jonathan Slavin
Jonathan Slavin (born November 8, 1969) is an American actor and activist.
Early life
Slavin was born in Camp Lejeune, North Carolina and raised in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
Career
Slavin portrayed illustrator Byron Togler on the Fox netw ...
, character actor
A character actor is a supporting actor who plays unusual, interesting, or eccentric characters.28 April 2013, The New York Acting SchoolTen Best Character Actors of All Time Retrieved 7 August 2014, "..a breed of actor who has the ability to b ...
* Ron Solt
Ronald Matthew Solt (born May 19, 1962) is a former American football guard in the National Football League. He played professionally for the Indianapolis Colts and the Philadelphia Eagles.
Biography
Solt was born in Bainbridge, Maryland and g ...
, former NFL player
* Jacob Sullum, journalist and author, featured in Academy Award
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
-nominated documentary '' Super Size Me''
* Bob Sura, basketball player, Houston Rockets
The Houston Rockets are an American professional basketball team based in Houston. The Rockets compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member team of the league's Western Conference Southwest Division. The team plays its ho ...
* Louis Teicher, pianist; member of the duo Ferrante & Teicher
* Alexis Toth (St. Alexis of Wilkes-Barre), saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
* Ty Tyson
Edwin Lloyd "Ty" Tyson (May 11, 1888 – December 12, 1968) was an American sports broadcaster and radio play-by-play announcer.
Early life
Tyson was born in Phillipsburg, Pennsylvania and he attended Penn State University. As a young man, he ...
* John Walsh, MLB third baseman
* Helen L. Webster (1853–1928), philologist and educator
* Michael Whalen, actor
* Ira W. Wood
Ira Wells Wood (June 19, 1856 in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania – October 5, 1931 in Trenton, New Jersey) was an American Republican Party politician who represented from 1904 to 1913.
Walsh was born in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania on June 19 ...
, represented from 1904 to 1913
* Hal Woodeshick, professional baseball player
* Tom Woodeshick, professional football player
* Frank Zane, bodybuilder, three-time Mr. Olympia, won Mr. America, Mr. Universe, Mr. World; donated gym at Wilkes University
See also
* Giants Despair HillclimbNotes
References
External links
*Greater Wilkes-Barre Chamber of Commerce
* {{Authority control 1769 establishments in Pennsylvania Cities in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania Cities in Pennsylvania County seats in Pennsylvania Municipalities of the Anthracite Coal Region of Pennsylvania Populated places established in 1769 Pennsylvania populated places on the Susquehanna River