Western-pattern diet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Western pattern diet is a modern dietary pattern that is generally characterized by high intakes of pre-packaged foods, refined grains,

 This diet is "rich in
This diet is "rich in
Is Sugar Toxic?
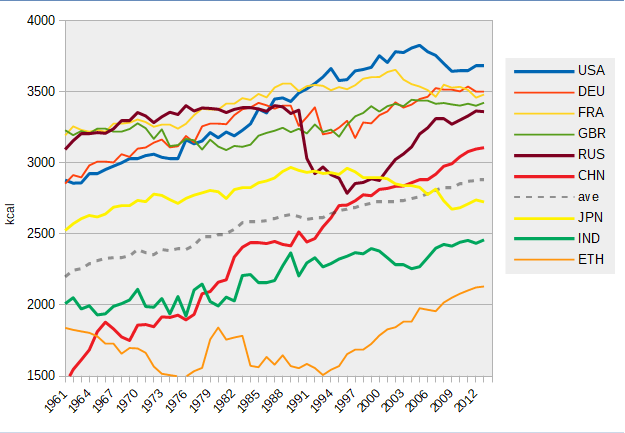
The New York Times, April 13, 2011 The energy-density of a typical WPD has continuously increased over time. USDA research conducted in the mid twenty-tens suggests that the average intake of American adults is at least 2,390 kcal per day. Researchers that used different data collection/analysis methods have predicted that the average was about 3,680 kcal per day. By contrast, a healthy daily intake is much lower. Since American adults usually have
 A Western pattern diet is associated with an increased risk of
A Western pattern diet is associated with an increased risk of
 The Western diet present in today's world is a consequence of the Neolithic revolution and
The Western diet present in today's world is a consequence of the Neolithic revolution and
red meat
In gastronomy, red meat is commonly red when raw and a dark color after it is cooked, in contrast to white meat, which is pale in color before and after cooking. In culinary terms, only flesh from mammals or fowl (not fish) is classified as ...
, processed meat
Processed meat is considered to be any meat which has been modified in order to either improve its taste or to extend its shelf life. Methods of meat processing include salting, curing, fermentation, smoking, and/or the addition of chemical pr ...
, high-sugar drinks, candy and sweets, fried foods
Frying is the cooking of food in oil or another fat. Similar to sautéing, pan-fried foods are generally turned over once or twice during cooking to make sure that the food is well-made, using tongs or a spatula, while sautéed foods are cooked ...
, conventionally-raised animal products, butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread, melted as a condimen ...
and other high-fat dairy products, eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
, potatoes, corn (and high-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
), and low intakes of fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
s, vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
s, whole grain
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.
As part of a general healthy diet, consumption of whole grains is associated ...
s, pasture-raised animal products, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
, nut
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Co ...
s, and seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
s.
Dietary pattern analysis focuses on overall diets (such as the Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is a diet inspired by the eating habits of people who live near the Mediterranean Sea. When initially formulated in the 1960s, it drew on the cuisines of Greece, Italy, France and Spain. In decades since, it has also incor ...
) rather than individual foods or nutrients. Compared to the "prudent pattern diet", which has higher proportions of "fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and poultry", the Western pattern diet is associated with higher risks of cardiovascular disease and obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
.
Elements
red meat
In gastronomy, red meat is commonly red when raw and a dark color after it is cooked, in contrast to white meat, which is pale in color before and after cooking. In culinary terms, only flesh from mammals or fowl (not fish) is classified as ...
, dairy products, processed and artificially sweetened foods, and salt, with minimal intake of fruits, vegetables, fish, legumes, and whole grains." Various foods and food processing procedures that had been introduced during the Neolithic and Industrial Periods had fundamentally altered 7 nutritional characteristics of ancestral hominin diets: glycemic load
The glycemic load (GL) of food is a number that estimates how much the food will raise a person's blood glucose level after eating it. One unit of glycemic load approximates the effect of eating one gram of glucose. Glycemic load accounts for how ...
, fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
composition, macronutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
composition, micronutrient density, acid-base balance, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
-potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
ratio, and fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorpora ...
content.
In 2006 the typical American diet was about 2,200 calories per day, with 50% of calories from carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
s, 15% protein, and 35% fat
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple est ...
. These macronutrient intakes fall within the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDR) for adults identified by the Food and Nutrition Board of the United States Institute of Medicine as "associated with reduced risk of chronic diseases while providing adequate intakes of essential nutrients," which are 45–65% carbohydrate, 10–35% protein, and 20–35% fat as a percentage of total energy. However, the nutritional quality of the specific foods comprising those macronutrients is often poor, as with the "Western" pattern discussed above. Complex carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may ...
such as starch are believed to be more healthy than sugar, which is frequently consumed in the Standard American Diet.Gary TaubesIs Sugar Toxic?
The New York Times, April 13, 2011 The energy-density of a typical WPD has continuously increased over time. USDA research conducted in the mid twenty-tens suggests that the average intake of American adults is at least 2,390 kcal per day. Researchers that used different data collection/analysis methods have predicted that the average was about 3,680 kcal per day. By contrast, a healthy daily intake is much lower. Since American adults usually have
sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
s guidelines suggest 1,600–2,000 kcal is appropriate for most women and 2,000–2,600 kcal is appropriate for men with the same PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
.
A review of eating habits in the United States in 2004 found that about 75% of restaurant meals were from fast-food restaurants
A fast-food restaurant, also known as a quick-service restaurant (QSR) within the industry, is a specific type of restaurant that serves fast-food cuisine and has minimal table service. The food served in fast-food restaurants is typicall ...
. Nearly half of the meals ordered from a menu were hamburger
A hamburger, or simply burger, is a food consisting of fillings—usually a patty of ground meat, typically beef—placed inside a sliced bun or bread roll. Hamburgers are often served with cheese, lettuce, tomato, onion, pickles, bacon, ...
, French fries, or poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, ...
— and about one third of orders included a carbonated beverage drink. From 1970 to 2008, the per capita consumption of calories increased by nearly one-quarter in the United States and about 10% of all calories were from high-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
.
Americans consume more than 13% of their daily calories in the form of added sugars. Beverages such as flavored water, soft drinks, and sweetened caffeinated beverages make up 47% of these added sugars.
Americans ages 1 and above consume significantly more added sugars, oils, saturated fats, and sodium than recommended in the Dietary Guidelines outlined by the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 89% of Americans consume more sodium than recommended. Additionally, excessive consumption of oils, saturated fats, and added sugars is seen in 72%, 71%, and 70% of the American population, respectively.
Consumers began turning to margarine due to concerns over the high levels of saturated fats found in butter. By 1958, margarine had become more commonly consumed than butter, with the average American consuming 8.9 pounds of margarine per year. Margarine is produced by refining vegetable oils, a process that introduces trans elaidic acid not found naturally in food. The consumption of trans fatty acids such as trans elaidic acid has been linked to cardiovascular disease. By 2005, margarine consumption had fallen below butter consumption due to the risks associated with trans fat intake.
Vegetable consumption is low among Americans, with only 13% of the population consuming the recommended amounts. Boys ages 9 to 13 and girls ages 14 to 18 consume the lowest amounts of vegetables relative to the general population. Potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es and tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
es, which are key components of many meals, account for 39% of the vegetables consumed by Americans. 60% of vegetables are consumed individually, 30% are included as part of a dish, and 10% are found in sauces.
Whole grains should consist of over half of total grain consumption, and refined grains should not exceed half of total grain consumption. However, 85.3% of the cereals eaten by Americans are produced with refined grains
Refined grains have been significantly modified from their natural composition, in contrast to whole grains. The modification process generally involves the mechanical removal of bran and germ, either through grinding or selective sifting.
Overv ...
, where the germ and bran are removed. Grain refining increases shelf life and softens breads and pastries; however, the process of refining decreases its nutritional quality.
Health concerns
Based on preliminary epidemiological studies, compared to a healthy diet, the Western pattern diet is positively correlated with an elevated incidence ofobesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, death from heart disease, cancer (especially colon cancer), and other "Western pattern diet"-related diseases. It increases the risk of the metabolic syndrome and may have a negative impact on cardio-metabolic health.
Crohn's disease
A Western pattern diet has been associated with Crohn's disease. Crohn's disease has its effects on the symbiotic bacteria within the human gut that show a positive correlation with a Western pattern diet. Symptoms can range from abdominal pain to diarrhea and fever.Obesity
obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
. There is a positive correlation between a Western pattern diet and several plasma biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, p ...
s that may be mediators of obesity, such as HDL cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are t ...
, high levels of fasting insulin, and leptin. Meta-analyses have also shown that, compared to a healthy diet, a Western pattern diet is linked to increased weight gain among females and adolescents.
Diabetes
Several studies have shown that there is a positive correlation between adoption of a Western pattern diet and incidence oftype 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
among both men and women.
Cancer
The Western pattern diet has been generally linked to increased risk for colorectalcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
. Meta-analyses have found that diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
patterns consistent with those of the Western pattern diet are positively correlated with risk for prostate cancer. Greater adherence to a Western pattern diet was also found to increase the overall risk of mortality due to cancer.
No significant relation has been established between the Western pattern diet and breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
.
Prevalence
The western-versus-eastern dichotomy has become less relevant as such a diet is no longer "foreign" to any global region (just as traditional East Asian cuisine is no longer "foreign" to the west), but the term is still a well-understood shorthand in medical literature, regardless of where the diet is found. Other dietary patterns described in the medical research include "drinker" and "meat-eater" patterns. Because of the variability in diets, individuals are usually classified not as simply "following" or "not following" a given diet, but instead by ranking them according to how closely their diets line up with each pattern in turn. The researchers then compare the outcomes between the group that most closely follows a given pattern to the group that least closely follows a given pattern.History
 The Western diet present in today's world is a consequence of the Neolithic revolution and
The Western diet present in today's world is a consequence of the Neolithic revolution and Industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
s. The Neolithic revolution introduced the staple foods of the western diet, including domesticated meats, sugar, alcohol, salt, cereal grains, and dairy products. The modern Western diet emerged after the Industrial Revolution, which introduced new methods of food processing including the addition of cereals, refined sugars, and refined vegetable oils to the Western diet, and also increased the fat content of domesticated meats. More recently, food processors began replacing sugar with high-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
.
See also
* European cuisine * Fast food * Healthy diet *Junk food
"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from sugar and/or fat, and possibly also sodium, but with little dietary fiber, protein, vitamins, minerals, or other important forms of nutritional value. It is also known as ...
* List of diets
An individual's diet is the sum of food and drink that one habitually consumes. Dieting is the practice of attempting to achieve or maintain a certain weight through diet. People's dietary choices are often affected by a variety of factors, incl ...
* Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is a diet inspired by the eating habits of people who live near the Mediterranean Sea. When initially formulated in the 1960s, it drew on the cuisines of Greece, Italy, France and Spain. In decades since, it has also incor ...
* Metabolic syndrome
* Nutritional gatekeeper
Nutritional gatekeeper has been used to refer to the person in a household who typically makes the purchasing and preparation decisions related to food. Nutritional gatekeepers can be a parent, grandparent, sibling, or caregiver.
History
The con ...
References
Further reading
* . About the changes in dietary advice and eating patterns between 1880 and 1930. {{Authority control Diets Western cuisine