Wavelet compression on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
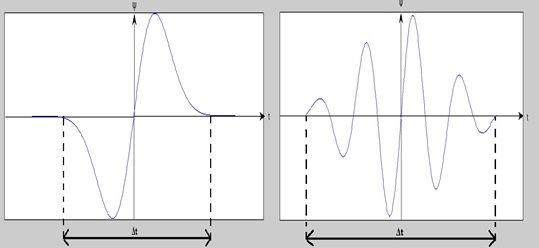 When is large,
# Bad time resolution
# Good frequency resolution
# Low frequency, large scaling factor
When is small
# Good time resolution
# Bad frequency resolution
# High frequency, small scaling factor
In other words, the basis function can be regarded as an impulse response of a system with which the function has been filtered. The transformed signal provides information about the time and the frequency. Therefore, wavelet-transformation contains information similar to the short-time-Fourier-transformation, but with additional special properties of the wavelets, which show up at the resolution in time at higher analysis frequencies of the basis function. The difference in time resolution at ascending frequencies for the
When is large,
# Bad time resolution
# Good frequency resolution
# Low frequency, large scaling factor
When is small
# Good time resolution
# Bad frequency resolution
# High frequency, small scaling factor
In other words, the basis function can be regarded as an impulse response of a system with which the function has been filtered. The transformed signal provides information about the time and the frequency. Therefore, wavelet-transformation contains information similar to the short-time-Fourier-transformation, but with additional special properties of the wavelets, which show up at the resolution in time at higher analysis frequencies of the basis function. The difference in time resolution at ascending frequencies for the  This shows that wavelet transformation is good in time resolution of high frequencies, while for slowly varying functions, the frequency resolution is remarkable.
Another example: The analysis of three superposed sinusoidal signals with STFT and wavelet-transformation.
This shows that wavelet transformation is good in time resolution of high frequencies, while for slowly varying functions, the frequency resolution is remarkable.
Another example: The analysis of three superposed sinusoidal signals with STFT and wavelet-transformation.

Diary Of An x264 Developer: The problems with wavelets
(2010) for discussion of practical issues of current methods using wavelets for video compression.
 The transformation system contains two analysis filters (a low pass filter and a high pass filter ), a decimation process, an interpolation process, and two synthesis filters ( and ). The compression and reconstruction system generally involves low frequency components, which is the analysis filters for image compression and the synthesis filters for reconstruction. To evaluate such system, we can input an impulse and observe its reconstruction ; The optimal wavelet are those who bring minimum shift variance and sidelobe to . Even though wavelet with strict shift variance is not realistic, it is possible to select wavelet with only slight shift variance. For example, we can compare the shift variance of two filters:
By observing the impulse responses of the two filters, we can conclude that the second filter is less sensitive to the input location (i.e. it is less shift variant).
Another important issue for image compression and reconstruction is the system's oscillatory behavior, which might lead to severe undesired artifacts in the reconstructed image. To achieve this, the wavelet filters should have a large peak to sidelobe ratio.
So far we have discussed about one-dimension transformation of the image compression system. This issue can be extended to two dimension, while a more general term - shiftable multiscale transforms - is proposed.
The transformation system contains two analysis filters (a low pass filter and a high pass filter ), a decimation process, an interpolation process, and two synthesis filters ( and ). The compression and reconstruction system generally involves low frequency components, which is the analysis filters for image compression and the synthesis filters for reconstruction. To evaluate such system, we can input an impulse and observe its reconstruction ; The optimal wavelet are those who bring minimum shift variance and sidelobe to . Even though wavelet with strict shift variance is not realistic, it is possible to select wavelet with only slight shift variance. For example, we can compare the shift variance of two filters:
By observing the impulse responses of the two filters, we can conclude that the second filter is less sensitive to the input location (i.e. it is less shift variant).
Another important issue for image compression and reconstruction is the system's oscillatory behavior, which might lead to severe undesired artifacts in the reconstructed image. To achieve this, the wavelet filters should have a large peak to sidelobe ratio.
So far we have discussed about one-dimension transformation of the image compression system. This issue can be extended to two dimension, while a more general term - shiftable multiscale transforms - is proposed.
Concise Introduction to Wavelets
by René Puschinger {{Authority control Wavelets Functional analysis Signal processing Image compression
 In
In mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, a wavelet series is a representation of a square-integrable
In mathematics, a square-integrable function, also called a quadratically integrable function or L^2 function or square-summable function, is a real- or complex-valued measurable function for which the integral of the square of the absolute value ...
(real
Real may refer to:
Currencies
* Brazilian real (R$)
* Central American Republic real
* Mexican real
* Portuguese real
* Spanish real
* Spanish colonial real
Music Albums
* ''Real'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album) (2000)
* ''Real'' (Bright album) (2010) ...
- or complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
-valued) function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
by a certain orthonormal
In linear algebra, two vectors in an inner product space are orthonormal if they are orthogonal (or perpendicular along a line) unit vectors. A set of vectors form an orthonormal set if all vectors in the set are mutually orthogonal and all of ...
series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used in ...
generated by a wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the num ...
. This article provides a formal, mathematical definition of an orthonormal wavelet and of the integral wavelet transform.
Definition
A function is called an orthonormal wavelet if it can be used to define aHilbert basis Hilbert basis may refer to
* In Invariant theory, a finite set of invariant polynomials, such that every invariant polynomial may be written as a polynomial function of these basis elements
* Orthonormal basis of a Hilbert space
* Hilbert basis ...
, that is a complete orthonormal system, for the Hilbert space
In mathematics, Hilbert spaces (named after David Hilbert) allow generalizing the methods of linear algebra and calculus from (finite-dimensional) Euclidean vector spaces to spaces that may be infinite-dimensional. Hilbert spaces arise natural ...
of square integrable
In mathematics, a square-integrable function, also called a quadratically integrable function or L^2 function or square-summable function, is a real- or complex-valued measurable function for which the integral of the square of the absolute value i ...
functions.
The Hilbert basis is constructed as the family of functions by means of dyadic translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
s and dilation
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to:
Physiology or medicine
* Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc.
* Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex
* Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgi ...
s of ,
:
for integers .
If under the standard inner product
In mathematics, an inner product space (or, rarely, a Hausdorff pre-Hilbert space) is a real vector space or a complex vector space with an operation called an inner product. The inner product of two vectors in the space is a scalar, often ...
on ,
:
this family is orthonormal, it is an orthonormal system:
:
where is the Kronecker delta
In mathematics, the Kronecker delta (named after Leopold Kronecker) is a function of two variables, usually just non-negative integers. The function is 1 if the variables are equal, and 0 otherwise:
\delta_ = \begin
0 &\text i \neq j, \\
1 & ...
.
Completeness is satisfied if every function may be expanded in the basis as
:
with convergence of the series understood to be convergence in norm. Such a representation of ''f'' is known as a wavelet series. This implies that an orthonormal wavelet is self-dual
In mathematics, a duality translates concepts, theorems or mathematical structures into other concepts, theorems or structures, in a one-to-one fashion, often (but not always) by means of an involution operation: if the dual of is , then the ...
.
The integral wavelet transform is the integral transform
In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integration, where some of the properties of the original function might be more easily characterized and manipulated than in ...
defined as
:
The wavelet coefficients are then given by
:
Here, is called the binary dilation or dyadic dilation, and is the binary or dyadic position.
Principle
The fundamental idea of wavelet transforms is that the transformation should allow only changes in time extension, but not shape. This is affected by choosing suitable basis functions that allow for this. Changes in the time extension are expected to conform to the corresponding analysis frequency of the basis function. Based on theuncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physic ...
of signal processing,
:
where represents time and angular frequency
In physics, angular frequency "''ω''" (also referred to by the terms angular speed, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit ti ...
(, where is ordinary frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
).
The higher the required resolution in time, the lower the resolution in frequency has to be. The larger the extension of the analysis windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
is chosen, the larger is the value of .
 When is large,
# Bad time resolution
# Good frequency resolution
# Low frequency, large scaling factor
When is small
# Good time resolution
# Bad frequency resolution
# High frequency, small scaling factor
In other words, the basis function can be regarded as an impulse response of a system with which the function has been filtered. The transformed signal provides information about the time and the frequency. Therefore, wavelet-transformation contains information similar to the short-time-Fourier-transformation, but with additional special properties of the wavelets, which show up at the resolution in time at higher analysis frequencies of the basis function. The difference in time resolution at ascending frequencies for the
When is large,
# Bad time resolution
# Good frequency resolution
# Low frequency, large scaling factor
When is small
# Good time resolution
# Bad frequency resolution
# High frequency, small scaling factor
In other words, the basis function can be regarded as an impulse response of a system with which the function has been filtered. The transformed signal provides information about the time and the frequency. Therefore, wavelet-transformation contains information similar to the short-time-Fourier-transformation, but with additional special properties of the wavelets, which show up at the resolution in time at higher analysis frequencies of the basis function. The difference in time resolution at ascending frequencies for the Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed ...
and the wavelet transform is shown below. Note however, that the frequency resolution is decreasing for increasing frequencies while the temporal resolution increases. This consequence of the Fourier uncertainty principle
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
is not correctly displayed in the Figure.
 This shows that wavelet transformation is good in time resolution of high frequencies, while for slowly varying functions, the frequency resolution is remarkable.
Another example: The analysis of three superposed sinusoidal signals with STFT and wavelet-transformation.
This shows that wavelet transformation is good in time resolution of high frequencies, while for slowly varying functions, the frequency resolution is remarkable.
Another example: The analysis of three superposed sinusoidal signals with STFT and wavelet-transformation.

Wavelet compression
Wavelet compression is a form ofdata compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressio ...
well suited for image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior re ...
(sometimes also video compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressio ...
and audio compression). Notable implementations are JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding th ...
, DjVu
DjVu ( , like French " déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as im ...
and ECW for still images, JPEG XS
JPEG XS (ISO/IEC 21122) is an interoperable, visually lossless, low-latency and lightweight image and video coding system used in professional applications. Applications of the standard include streaming high quality content for virtual reality ...
, CineForm
CineForm Intermediate is an open source (from October 2017) video codec developed for CineForm Inc by David Taylor, David Newman and Brian Schunck. On March 30, 2011, the company was acquired by GoPro which in particular wanted to use the 3D film c ...
, and the BBC's Dirac. The goal is to store image data in as little space as possible in a file. Wavelet compression can be either lossless
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistic ...
or lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data si ...
.
Using a wavelet transform, the wavelet compression methods are adequate for representing transient
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program (signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:Given the 5 dialects that us ...
s, such as percussion sounds in audio, or high-frequency components in two-dimensional images, for example an image of stars on a night sky. This means that the transient elements of a data signal can be represented by a smaller amount of information than would be the case if some other transform, such as the more widespread discrete cosine transform, had been used.
Discrete wavelet transform
In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal ...
has been successfully applied for the compression of electrocardiograph (ECG) signals In this work, the high correlation between the corresponding wavelet coefficients of signals of successive cardiac cycles is utilized employing linear prediction.
Wavelet compression is not effective for all kinds of data. Wavelet compression handles transient signals well. But smooth, periodic signals are better compressed using other methods, particularly traditional harmonic analysis
Harmonic analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with the representation of functions or signals as the superposition of basic waves, and the study of and generalization of the notions of Fourier series and Fourier transforms (i.e. an ex ...
in the frequency domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a s ...
with Fourier-related transforms. Compressing data that has both transient and periodic characteristics may be done with hybrid techniques that use wavelets along with traditional harmonic analysis. For example, the Vorbis
Vorbis is a free and open-source software project headed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The project produces an audio coding format and software reference encoder/decoder ( codec) for lossy audio compression. Vorbis is most commonly used in con ...
audio codec
An audio codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream (a codec) that encodes or decodes audio. In software, an audio codec is a computer program implementing an algorithm that compresses and decompres ...
primarily uses the modified discrete cosine transform
The modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) is a transform based on the type-IV discrete cosine transform (DCT-IV), with the additional property of being lapped: it is designed to be performed on consecutive blocks of a larger dataset, where ...
to compress audio (which is generally smooth and periodic), however allows the addition of a hybrid wavelet filter bank
In signal processing, a filter bank (or filterbank) is an array of bandpass filters that separates the input signal into multiple components, each one carrying a single frequency sub-band of the original signal. One application of a filter bank is ...
for improved reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual or ...
of transients.
SeDiary Of An x264 Developer: The problems with wavelets
(2010) for discussion of practical issues of current methods using wavelets for video compression.
Method
First a wavelet transform is applied. This produces as manycoefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
s as there are pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s in the image (i.e., there is no compression yet since it is only a transform). These coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
s can then be compressed more easily because the information is statistically concentrated in just a few coefficients. This principle is called transform coding
Transform coding is a type of data compression for "natural" data like audio signals or photographic images. The transformation is typically lossless (perfectly reversible) on its own but is used to enable better (more targeted) quantization, ...
. After that, the coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves ...
s are quantized and the quantized values are entropy encoded and/or run length encoded.
A few 1D and 2D applications of wavelet compression use a technique called "wavelet footprints".
Evaluation
Requirement for image compression
For most natural images, the spectrum density of lower frequency is higher. As a result, information of the low frequency signal (reference signal) is generally preserved, while the information in the detail signal is discarded. From the perspective of image compression and reconstruction, a wavelet should meet the following criteria while performing image compression: * Being able to transform more original image into the reference signal. * Highest fidelity reconstruction based on the reference signal. * Should not lead to artifacts in the image reconstructed from the reference signal alone.Requirement for shift variance and ringing behavior
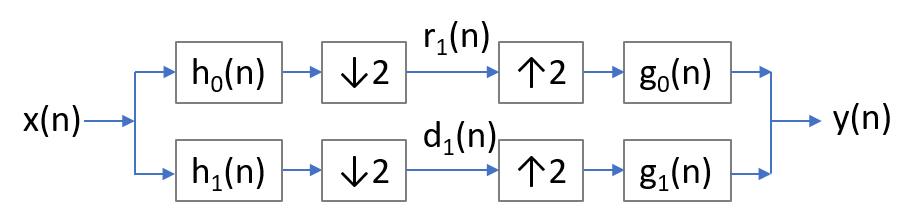
Wavelet image compression system involves filters and decimation, so it can be described as a linear shift-variant system. A typical wavelet transformation diagram is displayed below: The transformation system contains two analysis filters (a low pass filter and a high pass filter ), a decimation process, an interpolation process, and two synthesis filters ( and ). The compression and reconstruction system generally involves low frequency components, which is the analysis filters for image compression and the synthesis filters for reconstruction. To evaluate such system, we can input an impulse and observe its reconstruction ; The optimal wavelet are those who bring minimum shift variance and sidelobe to . Even though wavelet with strict shift variance is not realistic, it is possible to select wavelet with only slight shift variance. For example, we can compare the shift variance of two filters:
By observing the impulse responses of the two filters, we can conclude that the second filter is less sensitive to the input location (i.e. it is less shift variant).
Another important issue for image compression and reconstruction is the system's oscillatory behavior, which might lead to severe undesired artifacts in the reconstructed image. To achieve this, the wavelet filters should have a large peak to sidelobe ratio.
So far we have discussed about one-dimension transformation of the image compression system. This issue can be extended to two dimension, while a more general term - shiftable multiscale transforms - is proposed.
The transformation system contains two analysis filters (a low pass filter and a high pass filter ), a decimation process, an interpolation process, and two synthesis filters ( and ). The compression and reconstruction system generally involves low frequency components, which is the analysis filters for image compression and the synthesis filters for reconstruction. To evaluate such system, we can input an impulse and observe its reconstruction ; The optimal wavelet are those who bring minimum shift variance and sidelobe to . Even though wavelet with strict shift variance is not realistic, it is possible to select wavelet with only slight shift variance. For example, we can compare the shift variance of two filters:
By observing the impulse responses of the two filters, we can conclude that the second filter is less sensitive to the input location (i.e. it is less shift variant).
Another important issue for image compression and reconstruction is the system's oscillatory behavior, which might lead to severe undesired artifacts in the reconstructed image. To achieve this, the wavelet filters should have a large peak to sidelobe ratio.
So far we have discussed about one-dimension transformation of the image compression system. This issue can be extended to two dimension, while a more general term - shiftable multiscale transforms - is proposed.
Derivation of impulse response
As mentioned earlier, impulse response can be used to evaluate the image compression/reconstruction system. For the input sequence , the reference signal after one level of decomposition is goes through decimation by a factor of two, while is a low pass filter. Similarly, the next reference signal is obtained by goes through decimation by a factor of two. After L levels of decomposition (and decimation), the analysis response is obtained by retaining one out of every samples: . On the other hand, to reconstruct the signal x(n), we can consider a reference signal . If the detail signals are equal to zero for , then the reference signal at the previous stage ( stage) is , which is obtained by interpolating and convoluting with . Similarly, the procedure is iterated to obtain the reference signal at stage . After L iterations, the synthesis impulse response is calculated: , which relates the reference signal and the reconstructed signal. To obtain the overall L level analysis/synthesis system, the analysis and synthesis responses are combined as below: . Finally, the peak to first sidelobe ratio and the average second sidelobe of the overall impulse response can be used to evaluate the wavelet image compression performance.Comparison with Fourier transform and time-frequency analysis
Wavelets have some slight benefits over Fourier transforms in reducing computations when examining specific frequencies. However, they are rarely more sensitive, and indeed, the commonMorlet wavelet
In mathematics, the Morlet wavelet (or Gabor wavelet)0).
The parameter \sigma in the Morlet wavelet allows trade between time and frequency resolutions. Conventionally, the restriction \sigma>5 is used to avoid problems with the Morlet wavelet a ...
is mathematically identical to a short-time Fourier transform
The short-time Fourier transform (STFT), is a Fourier-related transform used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. In practice, the procedure for computing STFTs is to divi ...
using a Gaussian window function. The exception is when searching for signals of a known, non-sinusoidal shape (e.g., heartbeats); in that case, using matched wavelets can outperform standard STFT/Morlet analyses.
Other practical applications
The wavelet transform can provide us with the frequency of the signals and the time associated to those frequencies, making it very convenient for its application in numerous fields. For instance, signal processing of accelerations for gait analysis, for fault detection, for design of low power pacemakers and also in ultra-wideband (UWB) wireless communications.Synchro-squeezed transform
Synchro-squeezed transform can significantly enhance temporal and frequency resolution of time-frequency representation obtained using conventional wavelet transform.See also
*Continuous wavelet transform
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...
* Discrete wavelet transform
In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal ...
* Complex wavelet transform The complex wavelet transform (CWT) is a complex-valued extension to the standard discrete wavelet transform (DWT). It is a two-dimensional wavelet transform which provides multiresolution, sparse representation, and useful characterization of the ...
* Constant-Q transform
In mathematics and signal processing, the constant-Q transform and variable-Q transform, simply known as CQT and VQT, transforms a data series to the frequency domain. It is related to the Fourier transform Judith C. BrownCalculation of a constant ...
* Stationary wavelet transform
The Stationary wavelet transform (SWT) is a wavelet transform algorithm designed to overcome the lack of translation-invariance of the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). Translation-invariance is achieved by removing the downsamplers and upsample ...
* Dual wavelet
In mathematics, a dual wavelet is the dual to a wavelet. In general, the wavelet series generated by a square-integrable function will have a dual series, in the sense of the Riesz representation theorem. However, the dual series is not itself in ...
* Least-squares spectral analysis
Least-squares spectral analysis (LSSA) is a method of estimating a frequency spectrum, based on a least squares fit of sinusoids to data samples, similar to Fourier analysis. Fourier analysis, the most used spectral method in science, generally ...
* Multiresolution analysis
A multiresolution analysis (MRA) or multiscale approximation (MSA) is the design method of most of the practically relevant discrete wavelet transforms (DWT) and the justification for the algorithm of the fast wavelet transform (FWT). It was introd ...
* MrSID
MrSID (pronounced Mister Sid) is an acronym that stands for ''multiresolution seamless image database''. It is a file format (filename extension ''.sid'') developed and patented by LizardTech (in October 2018 absorbed into Extensis) for encoding o ...
, the image format developed from original wavelet compression research at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
(LANL)
* ECW, a wavelet-based geospatial
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position).
It is also ca ...
image format designed for speed and processing efficiency
* JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding th ...
, a wavelet-based image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior re ...
standard
* DjVu
DjVu ( , like French " déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as im ...
format uses wavelet-based IW44 algorithm for image compression
* scaleograms, a type of spectrogram
A spectrogram is a visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time.
When applied to an audio signal, spectrograms are sometimes called sonographs, voiceprints, or voicegrams. When the data are represen ...
generated using wavelets instead of a short-time Fourier transform
The short-time Fourier transform (STFT), is a Fourier-related transform used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. In practice, the procedure for computing STFTs is to divi ...
* Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the num ...
* Haar wavelet
In mathematics, the Haar wavelet is a sequence of rescaled "square-shaped" functions which together form a wavelet family or basis. Wavelet analysis is similar to Fourier analysis in that it allows a target function over an interval to be repre ...
* Daubechies wavelet
The Daubechies wavelets, based on the work of Ingrid Daubechies, are a family of orthogonal wavelets defining a discrete wavelet transform and characterized by a maximal number of vanishing moments for some given support. With each wavelet type ...
* Binomial QMF A binomial QMF – properly an orthonormal binomial quadrature mirror filter – is an orthogonal wavelet developed in 1990.
The binomial QMF bank with perfect reconstruction (PR) was designed by Ali Akansu, and published in 1990, using the family ...
(also known as Daubechies wavelet
The Daubechies wavelets, based on the work of Ingrid Daubechies, are a family of orthogonal wavelets defining a discrete wavelet transform and characterized by a maximal number of vanishing moments for some given support. With each wavelet type ...
)
* Morlet wavelet
In mathematics, the Morlet wavelet (or Gabor wavelet)0).
The parameter \sigma in the Morlet wavelet allows trade between time and frequency resolutions. Conventionally, the restriction \sigma>5 is used to avoid problems with the Morlet wavelet a ...
* Gabor wavelet
* Chirplet transform
* Time–frequency representation
A time–frequency representation (TFR) is a view of a signal (taken to be a function of time) represented over both time and frequency. Time–frequency analysis means analysis into the time–frequency domain provided by a TFR. This is achieved b ...
* S transform
* Set partitioning in hierarchical trees Set partitioning in hierarchical trees (SPIHT) is an image compression algorithm that exploits the inherent similarities across the subbands in a wavelet decomposition of an image. The algorithm was developed by Brazilian engineer Amir Said with ...
* Short-time Fourier transform
The short-time Fourier transform (STFT), is a Fourier-related transform used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. In practice, the procedure for computing STFTs is to divi ...
*Biorthogonal nearly coiflet basis In applied mathematics, biorthogonal nearly coiflet bases are wavelet bases proposed by Lowell L. Winger. The wavelet is based on biorthogonal coiflet wavelet bases, but sacrifices its regularity to increase the filter's bandwidth, which might lea ...
, which shows that wavelet for image compression can also be nearly coiflet (nearly orthogonal).
References
External links
* *Concise Introduction to Wavelets
by René Puschinger {{Authority control Wavelets Functional analysis Signal processing Image compression