Wallace Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Wallace Line or Wallace's Line is a
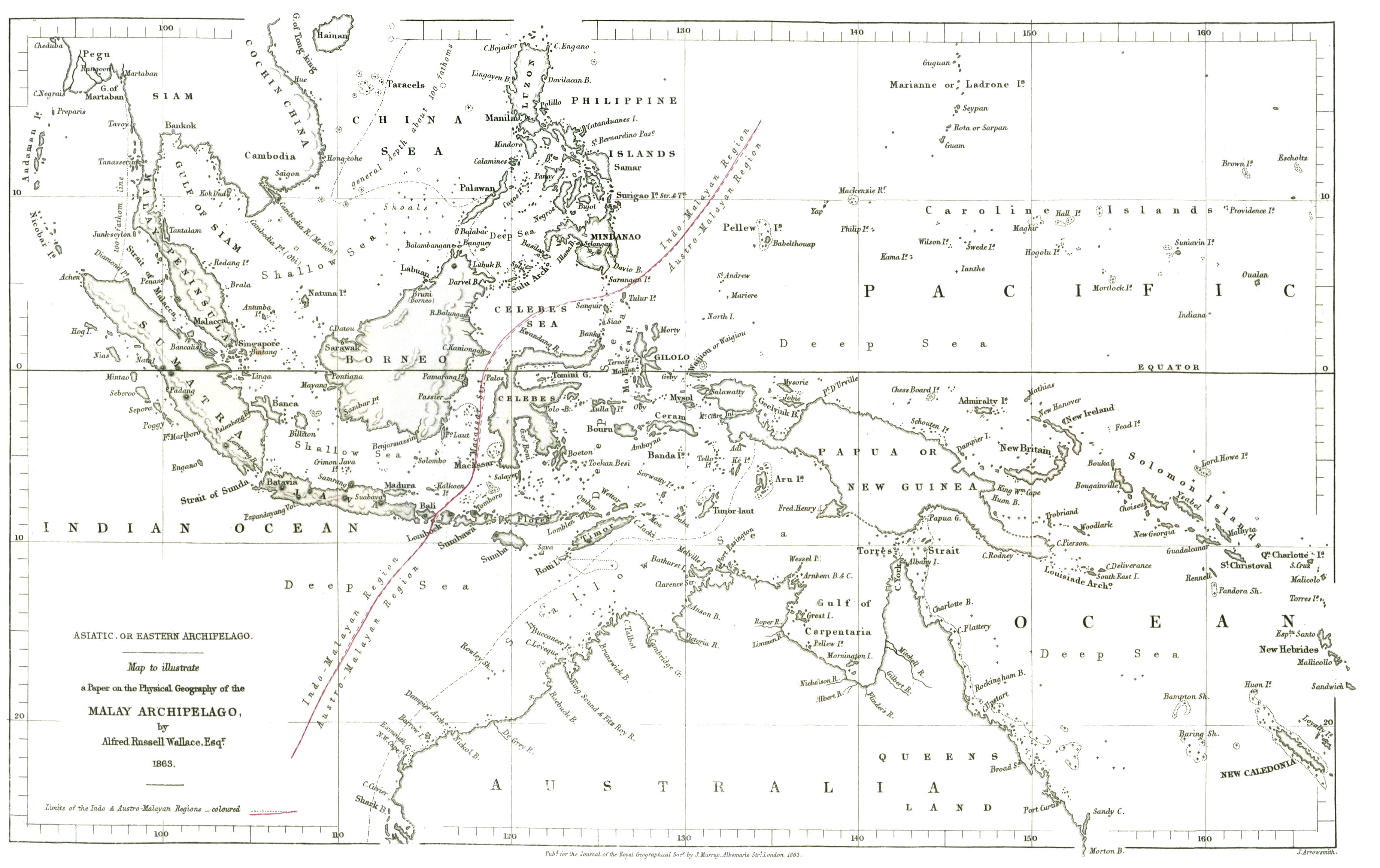 The Venetian explorer Antonio Pigafetta had recorded the biological contrasts between the Philippines and the
The Venetian explorer Antonio Pigafetta had recorded the biological contrasts between the Philippines and the
 Understanding of the
Understanding of the
the original paper
Regions of Southeast Asia
Too Many Lines; The Limits of the Oriental and Australian Zoogeographic Regions
George Gaylord Simpson, Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society, Vol. 121, No. 2 (Apr. 29, 1977), pp. 107–120
Wallacea Research Group
Pleistocene Sea Level Maps
Australasian realm biota Biogeography Celebes Sea Ecoregions of Indonesia Indomalayan realm biota Natural history of Indonesia Wallacea
faunal
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zool ...
boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British natural history, naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution thro ...
and named by English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stori ...
that separates the biogeographical realms
A biogeographic realm or ecozone is the broadest biogeographic division of Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms. They are subdivided into bioregions, which are further subdivided into ecoregions.
De ...
of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as ...
, a transitional zone between Asia and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. West of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origin is present. Wallace noticed this clear division during his travels through the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
in the 19th century.
The line runs through Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, between Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
and Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
(Celebes), and through the Lombok Strait between Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
and Lombok. The distance between Bali and Lombok is small, about . The distributions of many bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
species observe the line, since many birds do not cross even the shortest stretches of open ocean water. Some bats have distributions that cross the line, but larger terrestrial mammals are generally limited to one side or the other; exceptions include macaques, pigs and tarsiers on Sulawesi. Other groups of plants and animals show differing patterns, but the overall pattern is striking and reasonably consistent. Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
...
do not follow the Wallace Line to the same extent as fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is '' flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. ...
. One genus of plants that does not cross the Line is the Australasian genus ''Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as ...
'', except for one species, '' Eucalyptus deglupta'', which naturally occurs on the island of Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
Historical context
 The Venetian explorer Antonio Pigafetta had recorded the biological contrasts between the Philippines and the
The Venetian explorer Antonio Pigafetta had recorded the biological contrasts between the Philippines and the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
(Spice Islands) (on opposite sides of the line) in 1521 during the continuation of the voyage of Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
, after Magellan had been killed on Mactan
Mactan is a densely populated island located a few kilometers (~1 mile) east of Cebu Island in the Philippines. The island is part of Cebu province and it is divided into the city of Lapu-Lapu and the municipality of Cordova. The island is se ...
. Moreover, as noted by Wallace himself, the observations in faunal differences between the two regions had already been made earlier by English navigator George Windsor Earl published in 1845. In Wallace's 1863 paper ''On the Physical Geography of South-Eastern Asia and Australia'', he described how shallow seas connected islands on the west (Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, etc.) with the Asian continent and with similar wildlife, and islands on the east such as New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
were connected to Australia and were characterised by the presence of marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in ...
s. Wallace used his extensive travel in the region to propose a line to the east of Bali since "all the islands eastward of Borneo and Java formed part of an Australian or Pacific Continent, from which they were separated." The name 'Wallace's Line' was first used by Thomas Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stori ...
in an 1868 paper to the Zoological Society of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity devoted to the worldwide conservation of animals and their habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained the London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Park.
History
On 29 ...
, but showed the line to the west of the Philippines. Wallace's studies in Indonesia demonstrated the emerging theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
, at about the same time as Joseph Dalton Hooker
Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker (30 June 1817 – 10 December 1911) was a British botanist and explorer in the 19th century. He was a founder of geographical botany and Charles Darwin's closest friend. For twenty years he served as director of ...
and Asa Gray
Asa Gray (November 18, 1810 – January 30, 1888) is considered the most important American botanist of the 19th century. His ''Darwiniana'' was considered an important explanation of how religion and science were not necessarily mutually excl ...
published essays also supporting Darwin's hypothesis.
Biogeography
 Understanding of the
Understanding of the biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
of the region centers on the relationship of ancient sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardis ...
s to the continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
. Wallace's Line is visible geographically when the continental shelf contours are examined; it can be seen as a deep-water channel that marks the southeastern edge of the Sunda Shelf which links Borneo, Bali, Java, and Sumatra underwater to the mainland of southeastern Asia. Australia is likewise connected by the Sahul Shelf to New Guinea. The biogeographic boundary known as Lydekker's Line
Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 – 16 April 1915) was an English naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history.
Biography
Richard Lydekker was born at Tavistock Square in London. His father was Gerard Wolfe Lydekker, ...
, which separates the eastern edge of Wallacea from the Australian region, has a similar origin to the Wallace line.
During ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
glacial advances, when the ocean levels were up to lower, both Asia and Australia were united with what are now islands on their respective continental shelves as continuous land masses, but the deep water between those two large continental shelf areas was, for over 50 million years, a barrier that kept the flora and fauna of Australia separated from those of Asia. Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as ...
consists of islands that were not recently connected by dry land to either of the continental land masses, and thus were populated by organisms capable of crossing the straits between islands. "Weber's Line
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber van Bosse or Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (5 December 1852, in Bonn – 7 February 1937, in Eerbeek) was a German-Dutch zoologist and biogeographer.
Weber studied at the University of Bonn, then at the Humboldt University in B ...
" runs through this transitional area (to the east of centre), at the tipping point between dominance by species of Asian against those of Australian origin.
It can reasonably be concluded it was an ocean barrier preventing species migration because the physical aspects of the separated islands are very similar. Species found only on the Asian side include tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living Felidae, cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily pr ...
s and rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct specie ...
es, while marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in ...
s and monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals ( Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brai ...
s are only found on the eastern side of the Line.
See also
* * *Citation and notes
References
* witthe original paper
Regions of Southeast Asia
Further reading
*van Oosterzee, Penny (1997). ''Where Worlds Collide: the Wallace Line''. * Dawkins, Richard (2004). ''The Ancestor's Tale
''The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of Life'' is a science book by Richard Dawkins and Yan Wong on the subject of evolution, which follows the path of humans backwards through evolutionary history, describing some of humanity's cou ...
''. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. . Chapter 14 - Marsupials.
*Abdullah, M. T. (2003). Biogeography and variation of ''Cynopterus brachyotis'' in Southeast Asia. PhD thesis. The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Australia.
*Hall, L. S., Gordon G. Grigg, Craig Moritz, Besar Ketol, Isa Sait, Wahab Marni and M. T. Abdullah (2004). "Biogeography of fruit bats in Southeast Asia". ''Sarawak Museum Journal'' LX(81):191-284.
*Wilson D. E., D. M. Reeder (2005). ''Mammal species of the world''. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution Press.
External links
{{Commons categoryToo Many Lines; The Limits of the Oriental and Australian Zoogeographic Regions
George Gaylord Simpson, Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society, Vol. 121, No. 2 (Apr. 29, 1977), pp. 107–120
Wallacea Research Group
Australasian realm biota Biogeography Celebes Sea Ecoregions of Indonesia Indomalayan realm biota Natural history of Indonesia Wallacea