Vivian Pinn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vivian Winona Pinn (born 1941) is an American
 In her 20 years as ORWH director, Pinn employed her position as a federal policymaker to raise awareness of women's health issues and underrepresentation in science and medicine worldwide, across educational, political and cultural communities. She became known for her advocacy of women's health issues and concerns, particularly for ensuring that federally funded medical studies include female patients, and well as encouraging women to follow medical and scientific careers.
At NIH in 1998, Pinn briefed
In her 20 years as ORWH director, Pinn employed her position as a federal policymaker to raise awareness of women's health issues and underrepresentation in science and medicine worldwide, across educational, political and cultural communities. She became known for her advocacy of women's health issues and concerns, particularly for ensuring that federally funded medical studies include female patients, and well as encouraging women to follow medical and scientific careers.
At NIH in 1998, Pinn briefed  In a keynote at the Penn-International Council of Women's Health Issues (ICOWHI) conference in Philadelphia in 2010, Pinn addressed the myriad health issues presented for women and children by global urbanization, as an increasing number of people worldwide move to live in city environments. She said as more people migrate to the world's cities, local governments are often outpaced to provide adequate systems for housing, sanitation, electricity, and water for citizens. Persistent health problems result.
In a keynote at the Penn-International Council of Women's Health Issues (ICOWHI) conference in Philadelphia in 2010, Pinn addressed the myriad health issues presented for women and children by global urbanization, as an increasing number of people worldwide move to live in city environments. She said as more people migrate to the world's cities, local governments are often outpaced to provide adequate systems for housing, sanitation, electricity, and water for citizens. Persistent health problems result.
 In 2011, Pinn led a group of NIH staffers in a meeting with actress
In 2011, Pinn led a group of NIH staffers in a meeting with actress
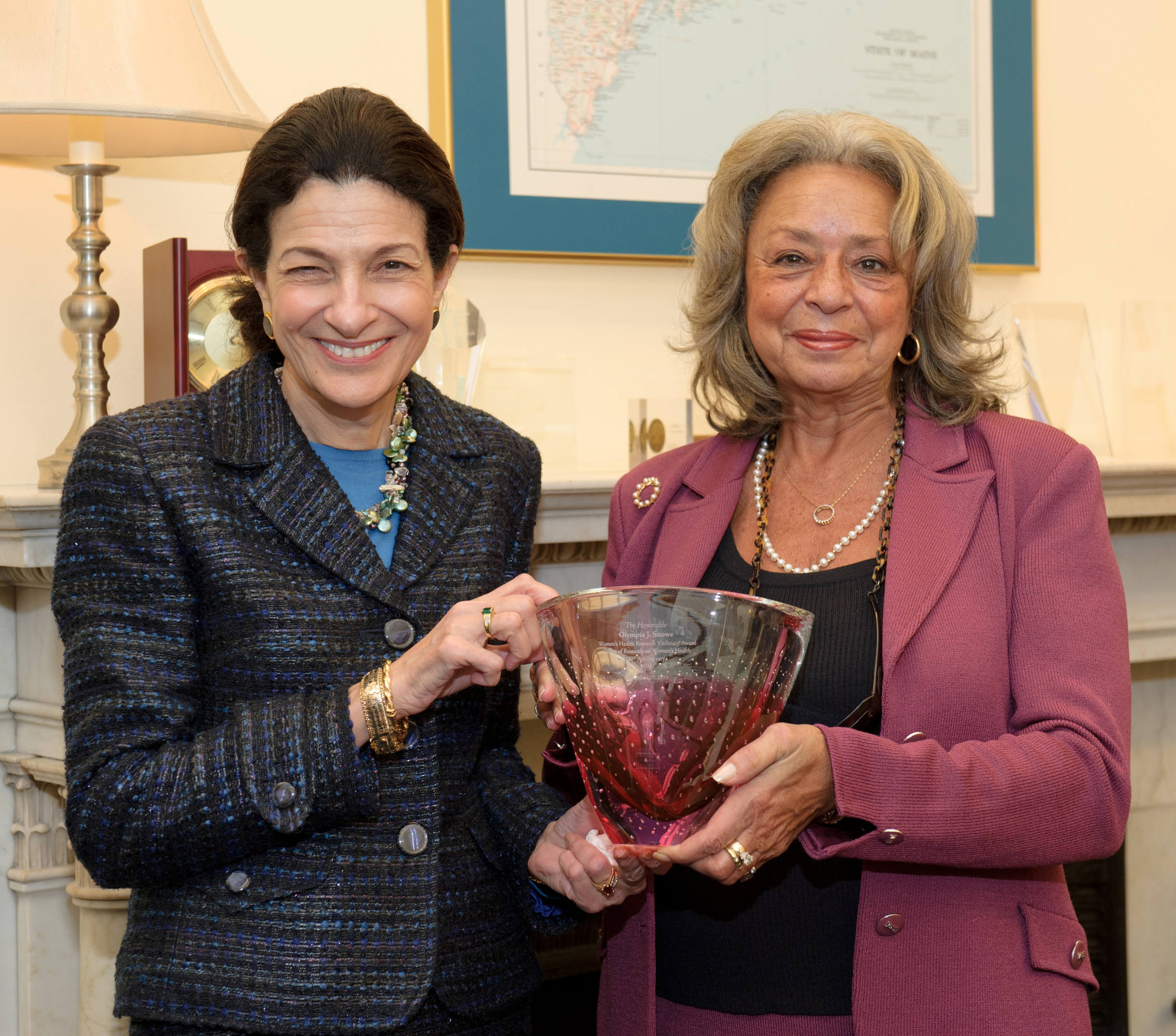 Since retirement from ORWH in 2011, Pinn has been an outspoken advocate for scientific research in general, and specifically for inclusion of women, women scientists, and underserved minorities in every aspect of biomedical research, as conductors of and participants in the full spectrum of scientific inquiry. Pinn has continued working as a senior scientist emerita at the
Since retirement from ORWH in 2011, Pinn has been an outspoken advocate for scientific research in general, and specifically for inclusion of women, women scientists, and underserved minorities in every aspect of biomedical research, as conductors of and participants in the full spectrum of scientific inquiry. Pinn has continued working as a senior scientist emerita at the
physician-scientist A physician-scientist is traditionally a holder of a medical degree and a doctor of philosophy also known as an MD-PhD. Compared to other clinicians, physician-scientists invest significant time and professional effort in scientific research an ...
and pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in t ...
known for her advocacy of women's health
Women's health differs from that of men in many unique ways. Women's health is an example of population health, where health is defined by the World Health Organization as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not mer ...
issues and concerns, particularly for ensuring that federally funded medical studies include female patients, and well as encouraging women to follow medical and scientific careers. She served as associate director for research on women's health at the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
(NIH), concurrently was the inaugural director of NIH's Office of Research on Women's Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. It comprises 27 sep ...
. Pinn previously taught at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
, Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
, and Howard University College of Medicine
The Howard University College of Medicine (HUCM) is an academic division of Howard University that grants the Doctor of Medicine (M.D.), Ph.D., M.S., and the M.PH. HUCM is located at the Howard University Health Sciences Center in Washington, D ...
. Since retiring from NIH in 2011, Pinn has continued working as a senior scientist emerita at the Fogarty International Center
The John E. Fogarty International Center was founded in 1968 by US President Lyndon Johnson at the National Institutes of Health to support international medical and behavioral research and to train international researchers.
History
On July 1, ...
.
Early life and education
Vivian Winona Pinn was born in 1941 on a farm inHalifax, Virginia
Halifax is a town in Halifax County, Virginia, United States, along the Banister River. The population was 1,309 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Halifax County.
History
Carlbrook, Halifax County Courthouse, Mountain Road Historic ...
. She attended segregated schools in Lynchburg. From the age of 4, Pinn was interested in a medical career, especially since she assisted both sets of her grandparents with their health concerns (including some insulin injections) and observed the relief they experienced after a doctor visit. The daughter and granddaughter of teachers, Pinn's family encouraged her to study hard so that she could reach her goals. Pinn graduated from high school as valedictorian of her class. Considering her education beyond high school, Pinn explored a wide variety of options, including DePauw and Wellesley, and decided on Wellesley College, the last acceptance letter she received.
Pinn won a scholarship to Wellesley College, earning a Bachelor of Arts in zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ...
in 1962. She took a leave of absence from college during sophomore year to care for her mother, who was ailing from a metastatic bone tumor
A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroi ...
; the cancer had been erroneously diagnosed as arthritis. In the wake of her mother's diagnosis, treatment, and eventual death from the disease, Pinn's desire to become a doctor was cemented. Based upon her mother's experience, she resolved to listen to her patients, pay attention to their complaints, and be open-minded about practicing medicine.
In 1967, Pinn earned a medical degree from the University of Virginia School of Medicine
The University of Virginia School of Medicine (UVA SoM) is the graduate medical school of the University of Virginia. The school's facilities are on the University of Virginia grounds adjacent to Academical Village in Charlottesville, Virginia ...
, where she was the only woman and only African-American student in her class. Pinn planned to become a pediatrician until she took a summer internship position as a research assistant at Massachusetts General Hospital. She worked there throughout medical school, with Benjamin Barnes and Martin Flax, in the areas of experimental transplant surgery and immunopathology. That training spurred her lifelong interests in research and academic medicine, forming the basis for Pinn's eventual career in renal and transplant pathology. She completed a residency in pathology at Mass General while serving as a teaching fellow at Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the graduate medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is one of the oldest medical schools in the United States and is consi ...
.
Pathology career
In 1970, Pinn joined the pathology department atTufts University School of Medicine
The Tufts University School of Medicine is the medical school of Tufts University, a private research university in Massachusetts. It was established in 1893 and is located on the university's health sciences campus in downtown Boston.
The '' ...
, where she served as assistant professor and assistant dean of student affairs. Her 12 years there were recognized by Tufts over the subsequent decades with numerous honors and awards.
Pinn joined the staff and faculty of Howard University
Howard University (Howard) is a Private university, private, University charter#Federal, federally chartered historically black research university in Washington, D.C. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classifie ...
Hospital in 1982, serving as professor and chair of the pathology department. At the time of her appointment, Pinn became the third woman and the first African-American woman to lead a U.S. pathology department.
In 1989, Pinn was installed as president of the National Medical Association
The National Medical Association (NMA) is the largest and oldest national organization representing African American physicians and their patients in the United States. The NMA is a 501(c)(3) national professional and scientific organization repr ...
(NMA). NMA is the nation's oldest and largest organization representing African-American physicians and health professionals in the United States. Established in 1895, the NMA is the collective voice of more than 30,000 African-American physicians and the patients they serve.
Women's health at the NIH
In 1991, Pinn was appointed as first director of the newOffice of Research on Women's Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. It comprises 27 sep ...
(ORWH) at the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
(NIH) and first permanent NIH associate director of research on women's health. The ORWH was established in September 1990 to strengthen and enhance NIH's efforts to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of illnesses in women, and to enhance research related to diseases and conditions that affect women. The office helps establish NIH goals and policies for women's health issues and assures that all appropriate clinical trials include the participation of women.
 In her 20 years as ORWH director, Pinn employed her position as a federal policymaker to raise awareness of women's health issues and underrepresentation in science and medicine worldwide, across educational, political and cultural communities. She became known for her advocacy of women's health issues and concerns, particularly for ensuring that federally funded medical studies include female patients, and well as encouraging women to follow medical and scientific careers.
At NIH in 1998, Pinn briefed
In her 20 years as ORWH director, Pinn employed her position as a federal policymaker to raise awareness of women's health issues and underrepresentation in science and medicine worldwide, across educational, political and cultural communities. She became known for her advocacy of women's health issues and concerns, particularly for ensuring that federally funded medical studies include female patients, and well as encouraging women to follow medical and scientific careers.
At NIH in 1998, Pinn briefed Sarah, Duchess of York
Sarah, Duchess of York (born Sarah Margaret Ferguson; 15 October 1959), also known by the nickname Fergie, is a member of the British royal family. She is the former wife of Prince Andrew, Duke of York, the younger brother of King Charles III ...
, on medical research topics and major health messages regarding women. Information was shared on the Women's Health Initiative, obesity, breast cancer, and osteoporosis.
 In a keynote at the Penn-International Council of Women's Health Issues (ICOWHI) conference in Philadelphia in 2010, Pinn addressed the myriad health issues presented for women and children by global urbanization, as an increasing number of people worldwide move to live in city environments. She said as more people migrate to the world's cities, local governments are often outpaced to provide adequate systems for housing, sanitation, electricity, and water for citizens. Persistent health problems result.
In a keynote at the Penn-International Council of Women's Health Issues (ICOWHI) conference in Philadelphia in 2010, Pinn addressed the myriad health issues presented for women and children by global urbanization, as an increasing number of people worldwide move to live in city environments. She said as more people migrate to the world's cities, local governments are often outpaced to provide adequate systems for housing, sanitation, electricity, and water for citizens. Persistent health problems result.
 In 2011, Pinn led a group of NIH staffers in a meeting with actress
In 2011, Pinn led a group of NIH staffers in a meeting with actress Geena Davis
Virginia Elizabeth "Geena" Davis (born January 21, 1956) is an American actor
to discuss how girls and women are perceived based on their roles in children's films, television shows, and video games. During the hour-long session, participants talked about strategies for balancing gender portrayals and how everyone's overall health might be improved as a result.
Awards and honors
Pinn received aCandace Award
The Candace Award is an award that was given from 1982 to 1992 by the National Coalition of 100 Black Women (NCBW) to "Black role models of uncommon distinction who have set a standard of excellence for young people of all races". Candace (pronou ...
from the National Coalition of 100 Black Women
The National Coalition of 100 Black Women, Inc. (NCBW) is a non-profit volunteer organization for African American women. Its members address common issues in their communities, families and personal lives, promoting gender and racial equity.
Hi ...
in 1990.
The Commonwealth Fund
The Commonwealth Fund is a private foundation (United States), private U.S. foundation whose stated purpose is to "promote a high-performing health care system that achieves better access, improved quality, and greater efficiency, particularly fo ...
named Pinn the recipient of its 2000 Margaret E. Mahoney Award for Outstanding Service, citing Pinn's work to advance the quality of healthcare for women. The award was established in 1994 to honor "an individual whose contributions have fostered the field of health policy and health services and contributed to a better understanding of the complex issues involved."
In 2005, Pinn delivered the keynote address at the University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United States, with highly selective ad ...
's 176th commencement exercises, becoming the first African-American female ever to do so. She recalled "the many challenges to my own sanity and passion for my medical studies during the sociopolitical era of the 1960s." She told the nearly 5,000 graduates, accompanied by some 25,000 family members and guests, I learned then, and have confirmed as years go by, that we can either dwell in the smallness of slights or difficulties, or rejoice in the larger meanings of life's experiences, and build a positive, constructive, and worldly view of barriers we have faced, and the satisfaction of having overcome them. Don't let difficulties make you small, a complaining spectator of life—but rather let a vision for your own life make you great, a vital participant of life.In 2011, Tufts University School of Medicine honored Pinn for her commitment to the school and its students by dedicating the Office of Student Affairs in the Sackler Building in her honor and by launching a scholarship fund in her name. Pinn was also awarded the Dean's Medal of Honor, TUSM's highest honor, from Dean Harris Berman. The medal, rarely conferred, is given to people whose service to the school and medical careers have enhanced TUSM's national standing. Pinn served as associate professor of pathology, as well as assistant dean for student affairs, in the 1970s and early 1980s. During her 12-year tenure at Tufts, she was a role model of mentorship. She also played a pivotal part in recruiting students of color and in expanding financial aid. In 2013, Pinn received the Foremother Award from the
National Center for Health Research
The National Center for Health Research (formerly known as the National Research Center for Women & Families) is a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit organization founded in 1999, providing health-related services such as providing free informatio ...
for her remarkable contributions to the lives of women in our country. In 2021, she was elected a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science
Fellowship of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (FAAAS) is an honor accorded by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) to distinguished persons who are members of the Association. Fellows are elected ...
.
Retirement years
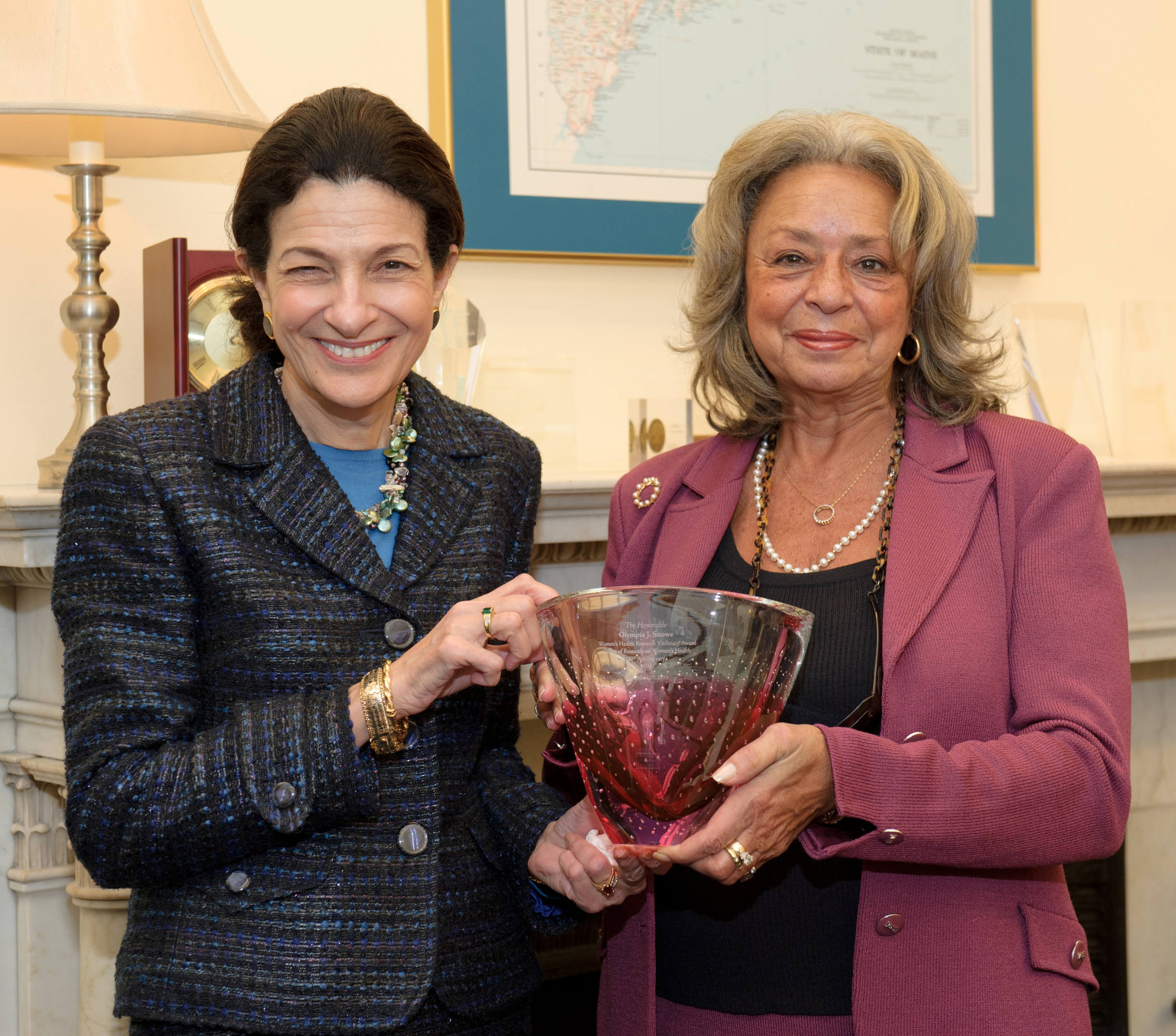 Since retirement from ORWH in 2011, Pinn has been an outspoken advocate for scientific research in general, and specifically for inclusion of women, women scientists, and underserved minorities in every aspect of biomedical research, as conductors of and participants in the full spectrum of scientific inquiry. Pinn has continued working as a senior scientist emerita at the
Since retirement from ORWH in 2011, Pinn has been an outspoken advocate for scientific research in general, and specifically for inclusion of women, women scientists, and underserved minorities in every aspect of biomedical research, as conductors of and participants in the full spectrum of scientific inquiry. Pinn has continued working as a senior scientist emerita at the Fogarty International Center
The John E. Fogarty International Center was founded in 1968 by US President Lyndon Johnson at the National Institutes of Health to support international medical and behavioral research and to train international researchers.
History
On July 1, ...
.
She was honored by a statement read into the Congressional Record by Senator Olympia Snowe (R-Maine), upon Pinn's retirement which acknowledged her public service and dedication to women's health and leadership roles in research and academia.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pinn, Vivian Howard University faculty Living people 1941 births National Institutes of Health people American pathologists University of Virginia School of Medicine alumni Wellesley College alumni Tufts University faculty People from Halifax, Virginia NIH Women Scientists Project Scientists from Virginia 20th-century American women scientists 21st-century American women scientists 20th-century American physicians 21st-century American physicians Women pathologists 20th-century American women physicians 21st-century American women physicians Physicians from Virginia African-American women physicians American women academics 20th-century African-American women 20th-century African-American physicians 21st-century African-American women 21st-century African-American physicians Members of the National Academy of Medicine Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences