Visvesvaraya on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya (15 September 1861 – 12/14 April 1962), also referred to by his initials, MV, was an
 Visvesvaraya was appointed a Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (CIE) in 1911 by
Visvesvaraya was appointed a Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (CIE) in 1911 by
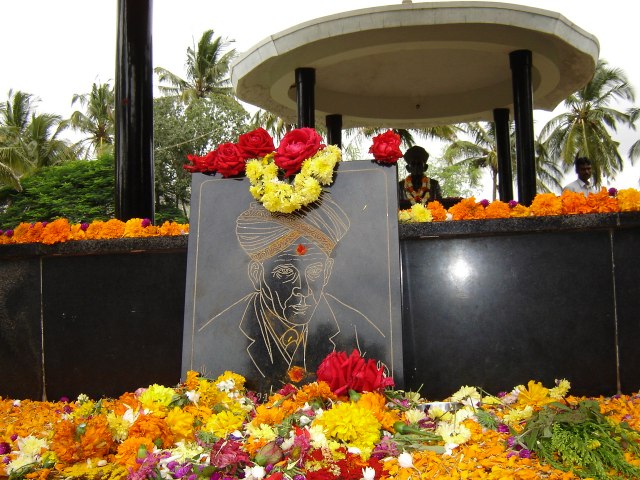 Visvesvaraya died on 12/14 April 1962, aged 100.
Visvesvaraya was known for his sincerity, time management and dedication to his cause.
A very important part of Visvesvaraya's nature was his love for
Visvesvaraya died on 12/14 April 1962, aged 100.
Visvesvaraya was known for his sincerity, time management and dedication to his cause.
A very important part of Visvesvaraya's nature was his love for
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
civil engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing ...
, administrator, and statesman, who served as the 19th Diwan of Mysore
The diwan of Mysore, also spelled dewan of Mysore, synonymously the prime minister of Mysore, was the ''de-facto'' chief executive officer of the government of the Kingdom of Mysore and the prime minister and royal adviser to the Maharaja of ...
from 1912 to 1918.
Visvesvaraya is regarded in India as one of the foremost civil engineers whose birthday, 15 September, is celebrated every year as Engineer’s Day in India, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
. He is also often regarded as “the maker of modern Mysore ingdom��. According to '' Prajavani'', a Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
language newspaper, he is also the most popular figure in the southern Indian
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territo ...
state of Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
.
Visvesvaraya worked as a civil engineer for the government of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and later as Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
. For his services to British India, he was appointed CIE and later knighted KCIE. For his services to the Kingdom of Mysore and the Republic of India, he was awarded the Bharata Ratna by Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
in 1955.
Early life
M. Visvesvaraya was born on 15 September 1861 atMuddenahalli
Muddenahalli is a village situated 7 km from Chikballapur in Chikballapur District of Karnataka State. It is the birthplace of M. Vishweshwarayya, one of the India's most accomplished engineers.
Transportation
A railway station and ra ...
, Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
(in present-day Chikkaballapur district, Karnataka) in a Telugu Brahmin family to Mokshagundam Srinivasa Shastry and Venkatalakshmi. His ancestors hail from Mokshagundam, a village in present-day Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, and had migrated to the kingdom around three hundred years prior to Visvesvaraya's birth.
Visvesvaraya received his primary education in Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
and earned a Bachelor of Science (BSc) degree from the University of Madras. He later studied at the College of Engineering, Pune
COEP Technological University, is A Unitary Public University of Government of Maharashtra, situated in Pune, Maharashtra, India. Established in 1854, it is the 2nd oldest engineering college in India, after IIT Roorkee (1847). The students and ...
(then College of Science at the University of Bombay) and graduated as an engineer, receiving Diploma in Civil Engineering (DCE). It was here that he became a member of the Deccan Club and was its first secretary; he would therefore have been well-acquainted with the progressives in Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
, including Sir R. G. Bhandarkar, Gopal Krishna Gokhale, and Justice Mahadev Govind Ranade, who were all members of the club.
Career
Engineering career
Visvesvaraya became an assistant engineer in 1885 at the Public Works Department,Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' fin ...
, in Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency or Bombay Province, also called Bombay and Sind (1843–1936), was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India, with its capital in the city that came up over the seven islands of Bombay. The first mainl ...
.
In 1899, Visvesvaraya was invited to join the Indian Irrigation Commission where he implemented an intricate system of irrigation in the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
and designed and patented a system of automatic weir water floodgates that were first installed in 1903 at Khadakvasla Dam near Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
. These gates raised the storage level in the reservoir to the highest level likely to be attained without causing any damage to the dam. Based on the success of these gates, the same system was installed at Tigra Dam
Tigra Dam (also spelled "Tig Dam") creates a freshwater reservoir on the Sank River, about 23 km from Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India It plays a crucial role in supplying water to the city and is an important tourism spot of Gwalior.
...
in Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
and later at the KRS Dam at Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude o ...
, Karnataka. He later became the chief engineer of the Laxmi Talav Dam near Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is ...
.
In around 1906/1907, the Government of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
sent Visvesvaraya to the British Colony of Aden (present-day Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
), to study water supply and drainage systems. The project prepared by him was successfully implemented in Aden.
After opting for voluntary retirement in 1908, Visvesvaraya took a foreign tour to study industrialised nations. Then, for a short period, he worked for Nizam Osman Ali Khan. He was one of the chief engineers of the flood protection system for the city of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
who suggested flood relief measures for the city, which was under constant threat by the Musi river Musi may refer to:
* Musi River (Indonesia)
* Musi River (India), Telangana
* Moosy River, Andhra Pradesh, India
* Musi language, a Malay language spoken in Indonesia
* Angelo Musi (1918–2009), American basketball player
* Agostino de' Musi, rea ...
. He achieved celebrity status when he designed a flood protection system for the city. He was instrumental in developing a system to protect Visakhapatnam
, image_alt =
, image_caption = From top, left to right: Visakhapatnam aerial view, Vizag seaport, Simhachalam Temple, Aerial view of Rushikonda Beach, Beach road, Novotel Visakhapatnam, INS Kursura submarine museu ...
port from sea erosion. This dam created the biggest reservoir in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
at the time of its construction.
In November 1909, Visvesvaraya was appointed Chief Engineer of Mysore State. He was the chief engineer of the KRS Dam near Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude o ...
. He was also later the chairman of the board of engineers for the Tungabhadra Dam in Hospet, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
.
Premiership
In 1912, Visvesvaraya was appointedDiwan of Mysore
The diwan of Mysore, also spelled dewan of Mysore, synonymously the prime minister of Mysore, was the ''de-facto'' chief executive officer of the government of the Kingdom of Mysore and the prime minister and royal adviser to the Maharaja of ...
by Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV
Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV (Nalwadi Krishnaraja Wadiyar; 4 June 1884 – 3 August 1940) was the twenty-fourth maharaja of the Kingdom of Mysore, from 1902 until his death in 1940. He is popularly called '' Rajarshi'' ( sa, rājarṣi, li ...
. He served for nearly seven years until 1918. With support from the maharaja, Visvesvaraya contributed to the general development of the Kingdom of Mysore.
During his premiership as Diwan, Visvesvaraya was responsible for the founding of factories and institutions funded for by the maharaja, including Mysore Soap Factory, Parasitoid Laboratory, Mysore Iron & Steel Works in Bhadravathi, Bangalore Polytechnic (now Sri Jayachamarajendra Polytechnic Bangalore), Bangalore Agricultural University, State Bank of Mysore, Century Club, Mysore Chamber of Commerce (now Federation of Karnataka Chambers of Commerce & Industry), Mysore Apex Chamber of Commerce (now Apex Chamber of Karnataka), and numerous other industrial places. The Bangalore Press was also established during his tenure as Diwan. He was also instrumental in the founding of Government Engineering College (now University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering) at Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
in 1917, one of the first engineering institutes in India. He commissioned several new railway lines in Mysore Railways (now part of Southwestern Indian Railways).
Visvesvaraya encouraged private investment in industry during his tenure as Diwan. He was instrumental in charting out a plan for road construction between Tirumala
Tirumala is a spiritual town in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the suburbs of the Tirupati urban agglomeration. The town is a part of Tirupati Urban Development Authority and located in Tirupati (rura ...
and Tirupati
Tirupati () is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Tirupati district. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple and other historic temples and is re ...
.
Visvesvaraya gave his technical advice for the location of Mokama Bridge over the Ganga
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
in Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
. At the time, he was over 90 years old.
Career timeline
* Assistant Engineer in Bombay, 1885; served in Nasik, Khandesh (mainly in Dhule) and Pune * Services lent to Municipality of Sukkur, Sind, 1894; designed and carried out waterworks for the municipality * Executive Engineer, Surat, 1896 * Assistant Superintending Engineer, Pune, 1897–1899; visitedChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
, 1898
* Executive Engineer for Irrigation, Pune, 1899
* Sanitary Engineer, Bombay, and member, Sanitary Board, 1901; gave evidence before Indian Irrigation Commission
* Designed and constructed automatic gates patented by him at Lake Fife Storage Reservoir; introduced a new system of irrigation known as "Block System", 1903; represented the Bombay Government at Simla Irrigation Commission, 1904; on special duty, 1905
* Superintending Engineer, 1907; visited Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, 1908
* Consulting Engineer to Hyderabad/Nizam State supervised and carried out engineering works on Musi river; Hyderabad floods of 1909
* Retired from British Service, 1909
* Chief Engineer and Secretary to Government of Mysore, 1909
* Diwan of Mysore, Public Works Department and Railway, 1913
* Board of Directors of Tata Steel, 1927–1955
Awards and honours
 Visvesvaraya was appointed a Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (CIE) in 1911 by
Visvesvaraya was appointed a Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (CIE) in 1911 by King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
. In 1915, while he was Diwan of Mysore
The diwan of Mysore, also spelled dewan of Mysore, synonymously the prime minister of Mysore, was the ''de-facto'' chief executive officer of the government of the Kingdom of Mysore and the prime minister and royal adviser to the Maharaja of ...
, Visvesvaraya was knighted as a Knight Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire (KCIE) by King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Qu ...
for his contributions to the public good.
After India attained independence, Visvesvaraya received the Bharat Ratna
The Bharat Ratna (; ''Jewel of India'') is the highest Indian honours system, civilian award of the Republic of India. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is conferred in recognition of "exceptional service/performance of the highest orde ...
, India's highest civilian honour, in 1955. He received an honorary membership from the Institution of Civil Engineers, London, a fellowship from the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, and several honorary degrees including D.Sc.
Doctor of Science ( la, links=no, Scientiae Doctor), usually abbreviated Sc.D., D.Sc., S.D., or D.S., is an academic research degree awarded in a number of countries throughout the world. In some countries, "Doctor of Science" is the degree used f ...
, LL.D., D.Litt. from eight universities in India. He was the president of the 1923 session of the Indian Science Congress.
Recognition
Visvesvaraya received recognition in many fields, most notably education and engineering.Visvesvaraya Technological University
Visvesvaraya Technological University (VTU), previously spelled Visveswaraiah Technological University, is a collegiate public state university in Belagavi, Karnataka established by the Government of Karnataka. All colleges in the State of ...
in Belagavi (to which most engineering colleges in Karnataka are affiliated) was named in his honour, as well as prominent colleges like University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering
University of Visvesvaraya College of Engineering (UVCE) was established in 1917, under the name Government Engineering College, by Bharat Ratna Sir M. Visvesvaraya. It is the fifth engineering college to be established in the country and first ...
, Bangalore; Sir M. Visvesvaraya Institute of Technology
Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya Institute of Technology (commonly referred to as Sir MVIT) is an Indian educational institution located in Bengaluru, Karnataka. The institute is affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University and approved b ...
, Bangalore; and Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nagpur is projected to ...
; Visvesvaraya Hostel, IIT (BHU) Varanasi
Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi (IIT BHU) is a Public university, public technical university located in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Founded in 1919 as the Banaras Engineering college, Engineering College, it became the Institu ...
; Visvesvaraya Industrial and Technological Museum, Bangalore.
The College of Engineering, Pune
COEP Technological University, is A Unitary Public University of Government of Maharashtra, situated in Pune, Maharashtra, India. Established in 1854, it is the 2nd oldest engineering college in India, after IIT Roorkee (1847). The students and ...
, his alma mater, erected a statue in Visvesvaraya's honour. Two metro stations in India, one in Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
on the Purple Line ( Sir M. Visveshwaraya Station, Central College), and another one in Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
on the Pink Line ( Sir Vishweshwaraiah Moti Bagh), are named after him.
On 15 September 2018, to celebrate his 158th birthday, Visvesvaraya was honored with a Google Doodle.
Death
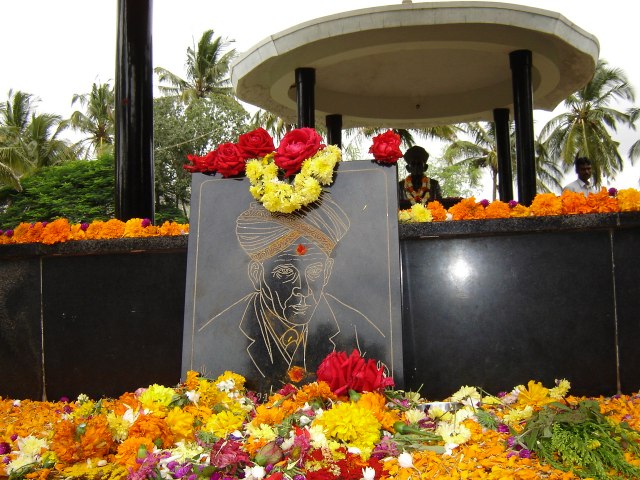 Visvesvaraya died on 12/14 April 1962, aged 100.
Visvesvaraya was known for his sincerity, time management and dedication to his cause.
A very important part of Visvesvaraya's nature was his love for
Visvesvaraya died on 12/14 April 1962, aged 100.
Visvesvaraya was known for his sincerity, time management and dedication to his cause.
A very important part of Visvesvaraya's nature was his love for Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
language. He set up Kannada Parishat for the improvement of Kannada. He wanted seminars for Kannada supporters to be instituted and conducted right in Kannada.
Memorial at Muddenahalli
Visvesvaraya National Memorial Trust manages a memorial for Visvesvaraya at his birthplace of Muddenahalli. The memorial exhibits his awards, titles and personal belongings, including his living room, spectacles, cups, books and block with which his visiting cards were printed. Models of the Krishna Raja Sagar Dam, which Visvesvaraya designed and supervised the construction of, are exhibited. The memorial is adjacent to his house, which was refurbished and is regarded as a shrine by locals.Works
* * * * *References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Visvesvaraya, Mokshagundam 1962 deaths Telugu people Recipients of the Bharat Ratna Indian centenarians Diwans of Mysore Engineers from Karnataka Engineers from Andhra Pradesh University of Madras alumni Indian irrigation engineers 19th-century Indian engineers 20th-century Indian engineers Indian knights People from Chikkaballapur district Knights Commander of the Order of the Indian Empire 1860s births